2009 CHERY TIGGO steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 1341 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3. Check the tires on the vehicle. The tires are to beinflated to the recommended air pressure. All tires
must be the same size and in good condition with
approximately the same tread wear.
4. Check the front tire and wheel assemblies for excessive radial runout.
5. Inspect all suspension component fasteners for looseness and proper torque.
6. Inspect all ball joints and all steering linkage for looseness and any sign of wear or damage.
7. Inspect the rubber bushings on all the suspension components for signs of wear or deterioration. If any bushings show signs of wear or deterioration, they should be replaced prior to aligning the vehicle.
8. Check vehicle curb height.
Wheel Alignment Setup
1. Position the vehicle on an alignment rack.
2. Install all required alignment equipment on the vehicle, per the alignment equipment manufacturer’s instructions. On this vehicle, a four-wheel alignment is recommended.
3. Read the vehicle’s current front and rear alignment settings. Compare the vehicle’s current alignment settings to the vehicle specifications for camber, caster and toe-in.
NOTE :
Prior to reading the vehicle’s alignment readouts, the front and rear of vehicle should be jounced. Induce jounce (rear
first, then front) by grasping the center of the bumper and jouncing each end of the vehicle an equal number of
times. The bumper should always be released when vehicle is at the bottom of the jounce cycle.
Specifications
Torque Specifications
DESCRIPTION TORQUE (N·m)
Camber Adjustment Bolts 100
Inner Tie Rod Adjuster Jam Nut 30
Rear Lower Control Arm Eccentric Cam Bolt 80 - 100
Rear Upper Control Arm Eccentric Cam Bolt 80 - 100
Wheel Mounting Nuts 110
GENERAL INFORMATION
LTSM100027
LTSM110026
10–40Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1344 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Alignment Troubleshooting Chart
CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
Early Tire Wearing · Incorrect tire pressure.
· Incorrect wheel alignment.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
Tire Noise · Incorrect tire pressure.
· Tire wearing.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
Road Noise Or Vehicle Body
Vibration · Incorrect tire pressure.
· Unbalanced tire.
· Deformation of rim or tire.
· Tire wearing.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
Up-Down Vibration Of The Steering
Wheel · Loose wheel nut or axle.
· Unbalanced tire.
· Crack or wearing of engine
mounting rubber.
· Crack or wearing of transmission
bracket rubber.· Fasten wheel nut.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
· Repair or install new engine or
transmission mounting rubber as
necessary.
Circular Vibration Of The Steering
Wheel · Loose wheel nut or axle.
· Unbalanced tire.
· Deficient tire pressure.
· Damage or wearing of front wheel
bearing.
· Failure of steering system.· Fasten wheel nut.
· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
Steering Wheel Deflecting To Single
Side · Incorrect tire pressure.
· Excessive tire wearing.
· Failure of steering system.
· Failure of suspension system.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check steering system.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
Unstable Driving · Loose wheel nut.
· Failure of steering system.
· Failure of suspension system.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check steering system.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
Heavy Steering Wheel · Incorrect tire pressure.
· Failure of steering system.
· Failure of suspension system.
· Incorrect wheel alignment.· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check steering system.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
Bad Alignment Return Of Steering
Wheel · Incorrect tire pressure
· Failure of steering system
· Failure of suspension system· Adjust the tire pressure.
· Check steering system.
· Check the wheel alignment and
then adjust.
· Repair or install new suspension
component as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
10
10–43Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1345 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Front Wheel Alignment
Front Wheel Alignment Specifications
NOTE :
If the vehicle has been in an accident causing the front axle components to be damaged, the damaged components
must be replaced before performing a front wheel alignment.
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT PREFERRED SETTINGACCEPTABLE RANGE
Camber -51’+9’ to -1°51’
Caster +2°50’+3°30’ to +2°5’
Inclination +11°30’+12°15’ to +10°45’
Toe-Individual 0’+5’ to -5’
Front Axle Toe-In Adjustment
CAUTION:
Do not twist the inner tie rod steering gear boot (bellows) while turning the inner tie rod during
front toe-in adjustment. It may be necessary to remove the clamp where the boot meets the inner
tie rod.
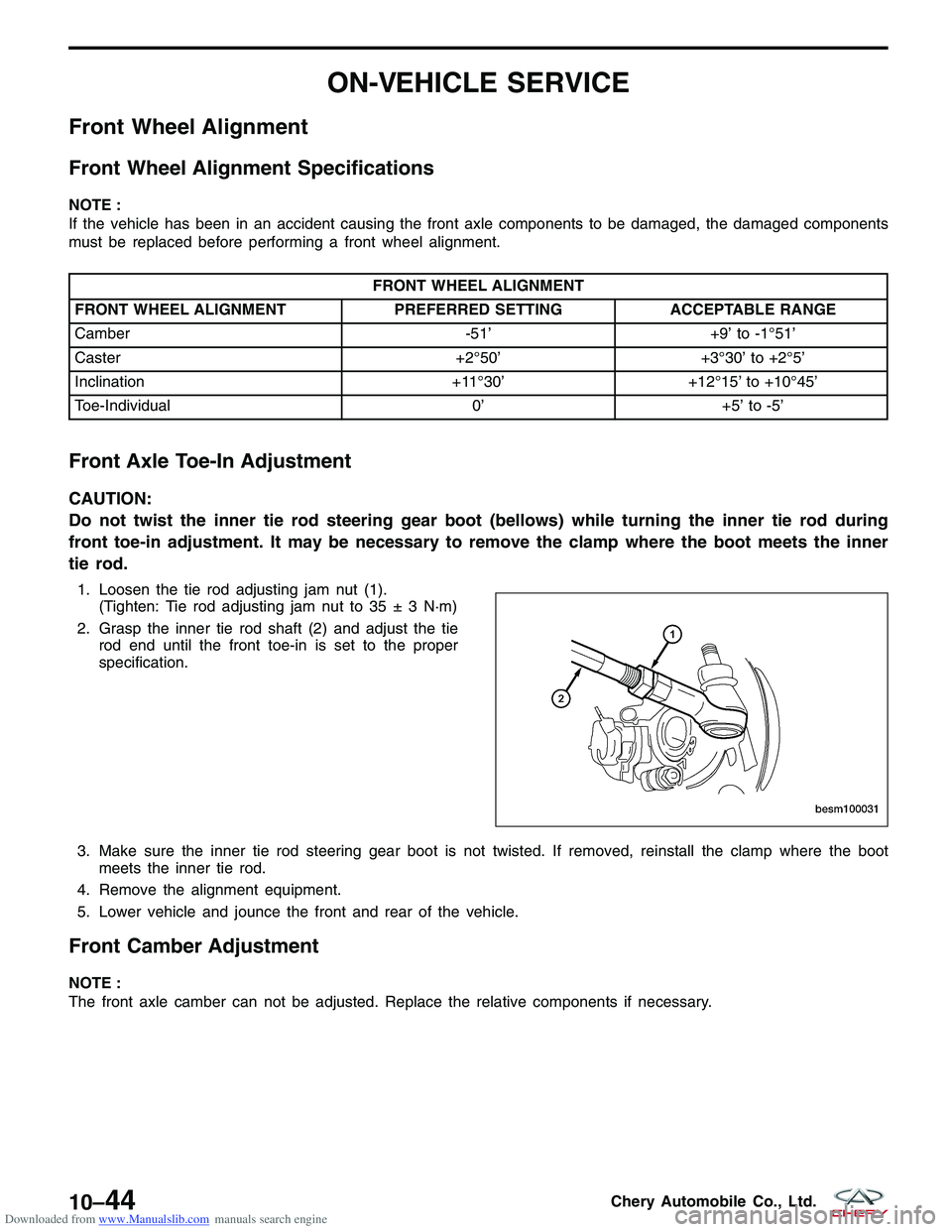
1. Loosen the tie rod adjusting jam nut (1).
(Tighten: Tie rod adjusting jam nut to 35 ± 3 N·m)
2. Grasp the inner tie rod shaft (2) and adjust the tie rod end until the front toe-in is set to the proper
specification.
3. Make sure the inner tie rod steering gear boot is not twisted. If removed, reinstall the clamp where the boot meets the inner tie rod.
4. Remove the alignment equipment.
5. Lower vehicle and jounce the front and rear of the vehicle.
Front Camber Adjustment
NOTE :
The front axle camber can not be adjusted. Replace the relative components if necessary.
BESM100031
10–44Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1351 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
Vehicle Inspection
Visual inspection of the vehicle is recommended prior to road testing or performing any other procedure. Raise the
vehicle on a suitable hoist.
Inspect the following:
•Inspect tires and wheels for damage, mud packing and unusual wear; correct as necessary.
• Check and adjust tire pressure to the pressure listed on the label attached to the driver’s door opening.
Tire and Wheel Vibration
Tire and wheel imbalance, runout and force variation can cause vehicles to exhibit steering wheel vibration.
NOTE :
Balance equipment must be calibrated and maintained per equipment manufacturer’s specifications.
Tire Wear Patterns
Tire wear patterns can be traced to the following tire conditions:
•Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of tire.
• Over inflation will cause wear at the center of tire.
• Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn more than the
other.
• Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread.
NOTE :
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm, the tread wear
indicators will appear as a band. Tire replacement is necessary when indicators appear in two or more grooves, or
if localized balding occurs.
Wheel Out-Of-Round Inspection
• Raise vehicle and securely support it.
• Attach a dial indicator on the edge of the rim and measure its unevenness.
• Replace the rim if necessary.10
10–50Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1352 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Tire Repair
Description
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific vehicle. They provide the best overall performance for normal
operation. The ride and handling characteristics match the vehicle’s requirements. With proper care they will give
excellent reliability, traction, skid resistance, and tread life.
WARNING!
Failure to equip the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capability can result in sudden tire failure.
In order to maintain the speed capability of the vehicle, replacement tires must have speed ratings equal to or
higher than those fitted to the vehicle as original equipment. If tires with lower speed ratings are fitted, the vehi-
cle’s handling may be affected and the speed capability of the vehicle may be lowered to the maximum speed
capability of the replacement tires. To avoid an accident resulting in severe or fatal injury, consult the tire man-
ufacturer in regards to maximum speed ratings.
Replacement Procedure
Note the following guidelines when replacing a tire:
•It is recommended that tires equivalent to the original equipment tires be used when replacement is needed.
• Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehicle.
• The use of tires smaller than the minimum tire size approved for the vehicle can result in tire overloading and
failure.
• Use tires that have the approved load rating for the vehicle and never overload them.
• Failure to equip the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capability can result in sudden tire failure and
loss of vehicle control.
• The use of oversize tires may cause interference with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspension and
steering travel, interference with vehicle components may cause tire damage.
Perform the following when replacing a tire: 1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheel mounting nuts and the wheel assembly.
3. Deflate the tire completely before removing the tire from the wheel.
4. Use lubrication such as a mild soap solution when dismounting or mounting tire.
5. Replace the tire with a tire approved for the vehicle.
6. Use tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
7. Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust is removed from the rim bead and repaint if necessary.
8. Balance the wheel assembly.
9. Install the wheel assembly and install the wheel mounting nuts. (Tighten: Wheel mounting nuts to 110 N·m)
Repair Procedure
Note the following guidelines when performing a tire repair:
•For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed from the wheel.
• Repairs should only be made if the defect, or puncture, is in the tread area.
• The tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in the sidewall.
Perform the following when repairing a tire: 1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheel mounting nuts and the wheel assembly.
3. Deflate the tire completely before removing the tire from the wheel.
4. Use lubrication such as a mild soap solution when dismounting or mounting tire.
5. Repair the tire only if the defect, or puncture, is in the tread area.
6. Use tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
7. Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust is removed from the rim bead and repaint if necessary.
10–51Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1354 of 1903
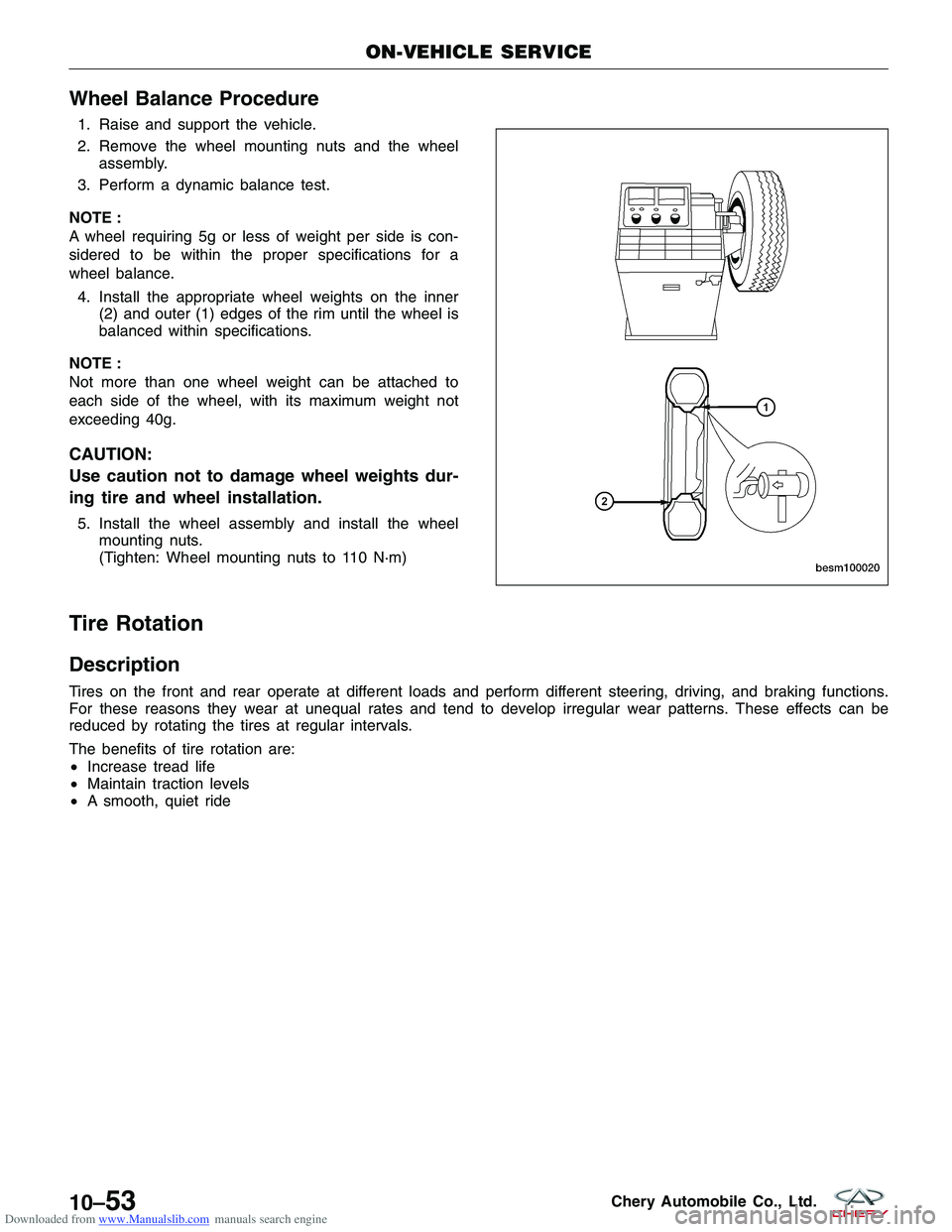
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheel Balance Procedure
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheel mounting nuts and the wheelassembly.
3. Perform a dynamic balance test.
NOTE :
A wheel requiring 5g or less of weight per side is con-
sidered to be within the proper specifications for a
wheel balance. 4. Install the appropriate wheel weights on the inner (2) and outer (1) edges of the rim until the wheel is
balanced within specifications.
NOTE :
Not more than one wheel weight can be attached to
each side of the wheel, with its maximum weight not
exceeding 40g.
CAUTION:
Use caution not to damage wheel weights dur-
ing tire and wheel installation.
5. Install the wheel assembly and install the wheel mounting nuts.
(Tighten: Wheel mounting nuts to 110 N·m)
Tire Rotation
Description
Tires on the front and rear operate at different loads and perform different steering, driving, and braking functions.
For these reasons they wear at unequal rates and tend to develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be
reduced by rotating the tires at regular intervals.
The benefits of tire rotation are:
•Increase tread life
• Maintain traction levels
• A smooth, quiet ride
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BESM100020
10–53Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1357 of 1903
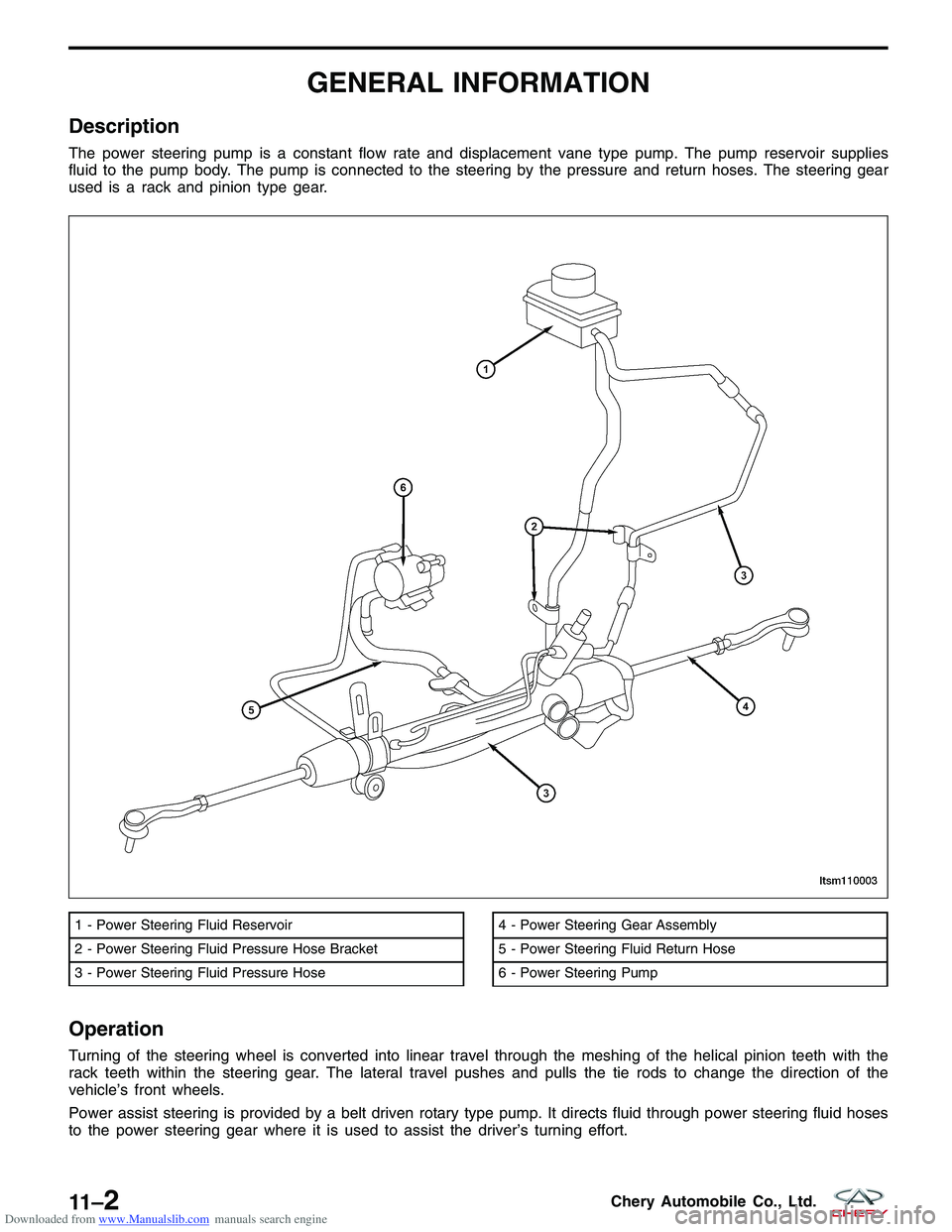
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The power steering pump is a constant flow rate and displacement vane type pump. The pump reservoir supplies
fluid to the pump body. The pump is connected to the steering by the pressure and return hoses. The steering gear
used is a rack and pinion type gear.
Operation
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into linear travel through the meshing of the helical pinion teeth with the
rack teeth within the steering gear. The lateral travel pushes and pulls the tie rods to change the direction of the
vehicle’s front wheels.
Power assist steering is provided by a belt driven rotary type pump. It directs fluid through power steering fluid hoses
to the power steering gear where it is used to assist the driver’s turning effort.
1 - Power Steering Fluid Reservoir
2 - Power Steering Fluid Pressure Hose Bracket
3 - Power Steering Fluid Pressure Hose4 - Power Steering Gear Assembly
5 - Power Steering Fluid Return Hose
6 - Power Steering Pump
LTSM110003
11 –2Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 1358 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Manual steering control of the vehicle can be maintained if power steering assist is lost. However, under this condi-
tion, steering effort is significantly increased.
WARNING!
Power steering fluid, engine parts and exhaust system may be extremely hot if engine has been running. Do not
start engine with any loose or disconnected hoses. Do not allow hoses to touch hot exhaust manifold or cata-
lyst. Fluid level should be checked with the engine off to prevent personal injury from moving parts.
Specifications
Fluid Specifications
DESCRIPTIONCAPACITY (L)
Power Steering Fluid (ATF III) 1.1
Special Tools
Steering Wheel Puller
Ball Joint Separator
CH-10002
GENERAL INFORMATION
11
11 –3Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.