2008 GREAT WALL FLORID maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 103 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual96
Brake System Maintenance
Brake fluid inspection and replacement
Brake fluid directly influences the brake performance and the operating conditions and use life of the brake
system components. Brake fluid has very strong hygroscopic properties, and thus absorbs water easily,
which will then deteriorate the metal and rubber pieces. Polluted and deteriorated brake fluid or its mixture
would cause the brake fluid to boil and gasify, hence reduces braking efficiency. Therefore, pay attention to
the items below when filling or changing the brake fluid:
1. Containers used to hold brake fluid must be tightly closed and sealed
2. Brake fluid is poisonous and damaging to the paint. Hence if it gets on the vehicle surface, rub it
off at once
3. If water or other contaminates found in the brake fluid, and the brake master cylinder's piston seal
has been broken, then the brake fluid and all the rubber pieces inside the brake system including
the brake hose must be replaced
4. The correct brake fluid level in the reservoir must be between MAX and MIN. After the vehicle has
been driven for over 1000 km, check the brake fluid level in the reservoir. If the brake fluid level is
not up to regulation, more brake fluid should be added to the reservoir \
until it reaches MAX.
Hydraulic component inspection and system flushing
1. If the oil-based solvent gets into the hydraulic system, flush the whole system and change all of
the rubber pieces
2. Clean your hands before installing new rubber pieces or other components
3. Do not use regular solvents (kerosene, gas, etc.) when inspecting or cleaning hydraulic
components, instead use absorbing alcohol or brake fluid
4. After inspecting the components, drain the brake fluid from the system. Use new brake fluid to
flush the system. Afterwards, add new brake fluid to perform hydraulic system exhaust
5. Flushing completion sign: When the brake fluid flowing out of the dump valve is clear from any
contaminate.
Hydraulic pressure system drainage
If the brake fluid inside the whole hydraulic pressure system needs to be emptied, open all the bleed screws
with each connected to a hose, as to allow the brake fluid to flow into a container. Step on the pedal slowly
until only air flows out. During the whole procedure, make sure all the \
valves are open.
Hydraulic pressure system air bleeding
The hydraulic brake system must work under a vacuum environment. The air will cause spongy brake or
overall brake failure when it flows into the hydraulic system. It is extremely necessary to bleed system air
when performing any operation on the brake system or if any air inside t\
he brake system is suspected.
1. Air bleeding sequence
If air inside the brake master cylinder is suspected, first perform air bleeding.
(a) If numerous valves are equipped, air bleed each valve
(b) Another sequence principle is: Air bleed from the wheel brake furthest away from the master cylinder.
The air bleeding sequence for the LHD modules is: rear right wheel - left rear wheel - front right wheel
- front left wheel, Right rudder vehicles: rear right wheel - left rear wheel - front left wheel - front right
wheel.
2. Air bleeding method
(1) Manual air bleeding
Use the brake pedal or pump as the air bleeding power source. When the air bleed screws are open, vent the
brake fluid containing the bubbles from the system. Usually this is simultaneously done by two people. One
steps on the brake pedal and the other operates the air bleed screws. Important points to take note of when
performing the operation:
(a) Place the ignition switch to the off position and step on the pedal repeatedly to remove the
vacuum pressure or hydraulic pressure.
(b) Before and after air bleeding, add clean brake fluid into the master cylinder until it reaches
the correct (stated) level.
(c) Check the fluid level frequently to make sure that more than half of the reservoir's capacity is
available.
(d) Bleed screws should only be opened when the pedal is pressed down, and closed before the
pedal is loosened. Meanwhile, check if the vented brake fluid has bubble\
s inside.
Page 104 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 97Brake System
(e) Make sure not to let the system valves block the air bleeding.
(f) When the brake fluid that flows out of the hose or connector has no bubbles, it means that the air
in the system has been exhausted. There is still air inside the system if the hose inserted into the
brake fluid is still bubbling when pressing down the pedal.
(g) Keep the free end of the hose immerged in the brake fluid to avoid air from flowing into the
system while opening the screw.
(h) While air bleeding, hammer the casting part of the vibrating brake device with a rubber hammer.
This is helpful for removing bubbles deep in the brake fluid.
(i) If air in the master cylinder is suspected, then perform air bleeding on the master cylinder first,
then the wheel cylinder or brake caliper.
(j) When releasing air from the tires, generally make sure to release air out of all the tires.
(k) To avoid the possibility of air reversely entering into the system, a bleeder hose that has a check
valve could be used.
(2) Pressure blow-off
Under the proper conditions, a pressure blow-off device can be used to release the air inside the brake system.
3. Air releasing sequence
(1) Master cylinder air bleeding
If the master cylinder does not have air bleed screws, perform the follo\
wing steps:
(a) Check the brake fluid level inside the master cylinder’s reservoir and add to it if necessary.
(b) Slowly take off the front brake pipe connector until the brake fluid flows out from the end.
(c) Reconnect the brake pipe, but do not tighten it.
(d) Slowly step down and press on the brake pedal, check if the brake fluid flowing out of the connector
contains bubbles.
(e) Tighten the pipe fitting.
(f) Have the assistant loosen the pedal, wait for 15 s.
(g) Repeat the above steps until all the air is released.
(h) Take off the rear brake pipe connector, repeat the above steps.
(2) Wheel brake air releasing
(a) Check the brake fluid level inside the master cylinder’s reservoir and add to it if necessary. During the
entire air releasing period, check repeatedly and add promptly.
(b) Connect one end of the bleeder hose with the bleed screw and the other end immerged in the brake fluid.
(c) Have the assistant step on the pedal several times, raise the pedal gradually until it cannot be stepped on
any more, then forcibly press on the pedal once more.
(d) Loosen the bleed screw, check if there are any bubbles in the brake fluid flowing out. Meanwhile, slowly
lower the pedal.
(e) When the brake pedal is close to the stroke end or the out flowing brake fluid does not have any bubbles,
tighten the bleed screw.
(f) Have the assistant release the pedal and wait for 15 s.
(g) Repeat the above steps until there are no bubbles in the flowing brake fluid when the screw is loosened.
(h) Release the air for all the wheels in turn using the same method.
(i) After releasing the air from the entire system, switch the ignition to the on position.
(j) Inspect the stroke of the brake pedal and its reaction.
(k) Inspect the lighting condition of the brake warning lamp, and repeatedly perform maintenance or air
bleeding if necessary.
( l ) Add brake fluid to the reservoir until the specified fluid level, air bleeding is complete.
Page 105 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual98
Brake Pedal
Components
Areas of Importance
1. During removal, all components should be gently handled to avoid knocking, especially the junction
surface. All components should be placed in order to avoid losing or taking the w\
rong parts.
2. Keep all parts clean and free of dust, scuffs, rust, corrosion, oil build-up, or any other contaminants.
3. All rubbing surfaces in a relative motion must be coated with lubricant\
.
4. During installation, strictly adhere to the standard torque for installi\
ng nuts.
5. While installing the return spring, be careful to avoid operator injury \
from it bouncing back.
Troubleshooting
SymptomsPossible causesEliminating methods
Brake pedal cannot return
to the original position
Return spring is brokenReplace the spring
Return spring's fixed end comes offCheck, secure in place
Feels slippery when
stepping on the pedal
Pedal pad is worn outReplace
Pedal pad comes offReinstall
Stepping on the pedal
produces abnormal noise
The plastic bushing is seriously worn outReplace
Spring brokenReplace
Spring's fixed end comes offCheck, re-fix
Pedal pad
Cotter pin
Return spring
Pedal shaft
Brake pedal bracket
welding assembly
Brake pedal lever welding assembly
Bushing
Nut
Limiting stopper
Center pin
Page 107 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual100
2. Install the pedal pad and limiting stopper to the pedal
lever.
3. Apply lubricant on the inner bushing and the outer
pedal shaft. Install the pedal lever assembly, pedal
shaft, and brake pedal bracket welding assembly.
4. Put on a nut, and tighten the nut and spring washer
using a 30 N·m torque.
Brake pedal examination and adjustment
1. Check if the pedal height is correct.
Height between pedal and the lower cowl panel: 109 mm
Pedal push rod's working empty stroke: 2 mm
2. Adjust pedal height if necessary.
(a) Disconnect the brake lamp's switch wire connector,
loosen the lock nuts, rotate the brake switch and
unscrew it until no contact with the brake pedal's
limiting stopper.
(b) Loosen the control rod lock nut and use combination
pliers to rotate the control rod and adjust the brake
pedal height to its standard value. After arriving at the
standard value, tighten the lock nut, and make sure the
working empty stroke of the pedal push rod is 2 mm.
(c) Rotate the brake lamp's switch and push it in until it
barely contacts with the brake pedal limiting stopper,
continue rotating 1/2-1 circle, then tighten the lock nut.
(d) Connect the brake lamp's switch wire connector.
(e) When the brake pedal is loose, the brake lamp should
be off.
Pedal height
Pedal padLimiting stopper
Page 109 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual102
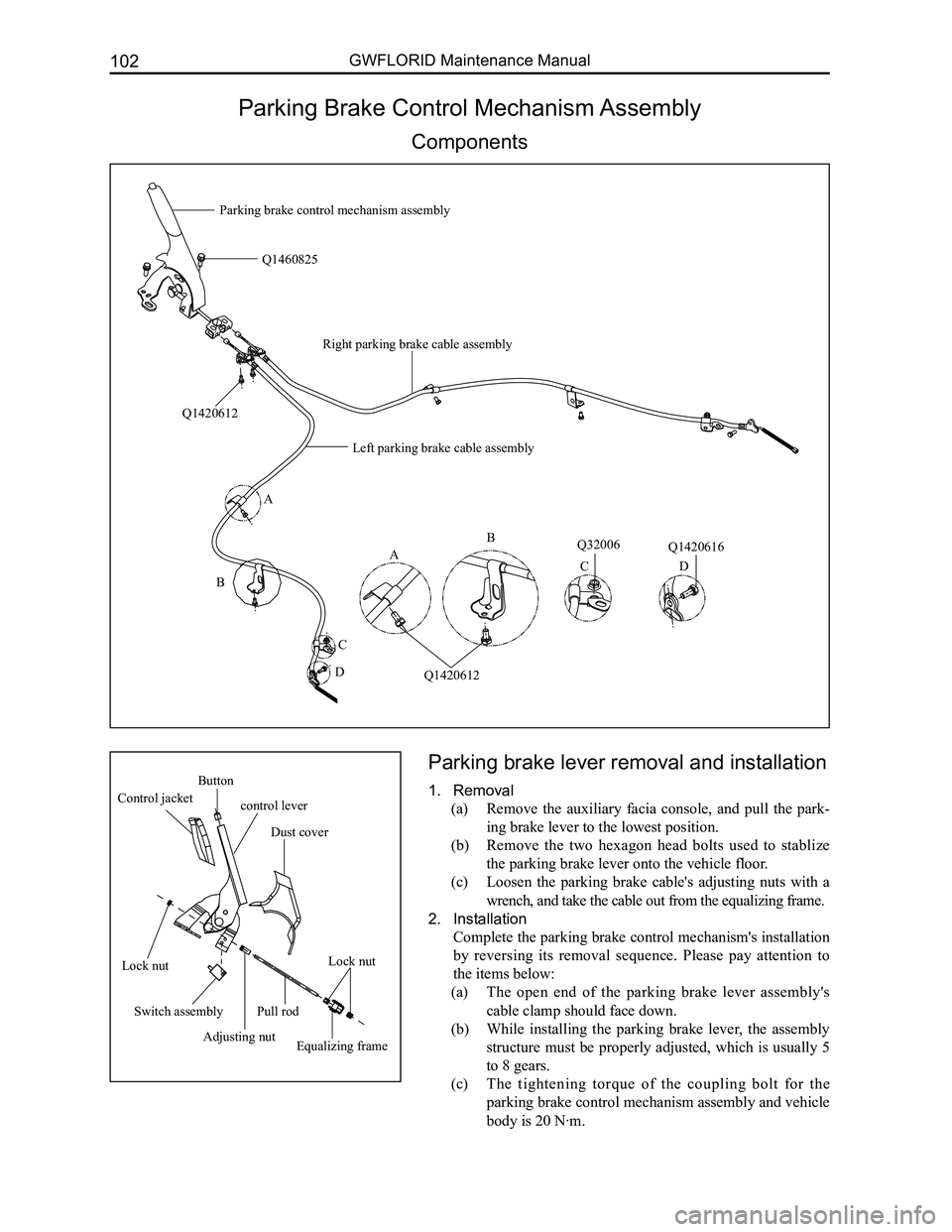
Parking Brake Control Mechanism Assembly
Components
Parking brake lever removal and installation
1. Removal
(a) Remove the auxiliary facia console, and pull the park-
ing brake lever to the lowest position.
(b) Remove the two hexagon head bolts used to stablize
the parking brake lever onto the vehicle floor.
(c) Loosen the parking brake cable's adjusting nuts with a
wrench, and take the cable out from the equalizing frame.
2. Installation
Complete the parking brake control mechanism's installation
by reversing its removal sequence. Please pay attention to
the items below:
(a) The open end of the parking brake lever assembly's
cable clamp should face down.
(b) While installing the parking brake lever, the assembly
structure must be properly adjusted, which is usually 5
to 8 gears.
(c) The tightening torque of the coupling bolt for the
parking brake control mechanism assembly and vehicle
body is 20 N·m.
A
B
C
D
Q1420612
Q1460825
Q32006Q1420616
Parking brake control mechanism assembly
Q1420612
A
B
CD
Left parking brake cable assembly
Right parking brake cable assembly
Button
control lever Control jacket
Dust cover
Lock nutLock nut
Switch assembly
Adjusting nutEqualizing frame
Pull rod
Page 111 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual104
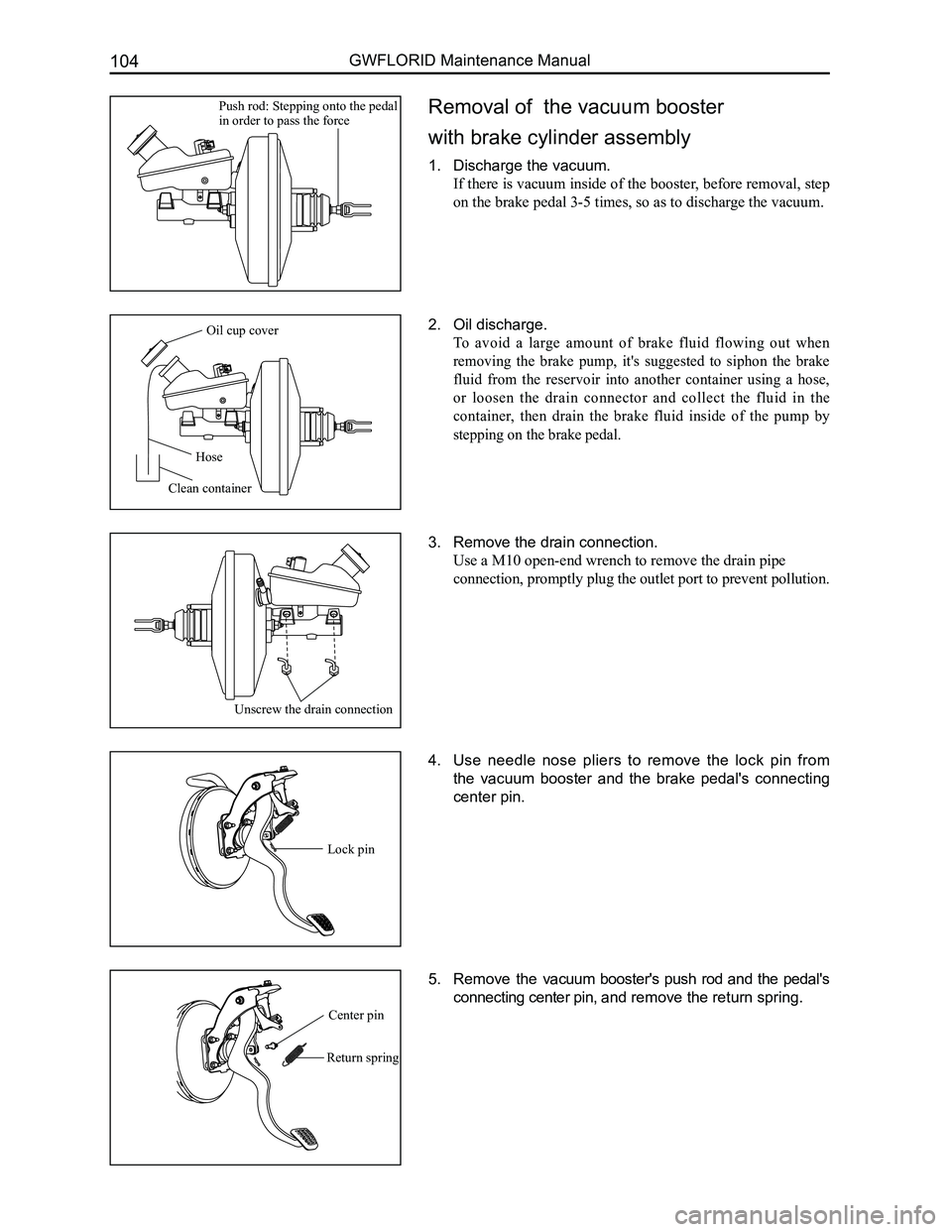
Removal of the vacuum booster
with brake cylinder assembly
1. Discharge the vacuum.
If there is vacuum inside of the booster, before removal, step
on the brake pedal 3-5 times, so as to discharge the vacuum.
2. Oil discharge.
To avoid a large amount of brake fluid flowing out when
removing the brake pump, it's suggested to siphon the brake
fluid from the reservoir into another container using a hose,
or loosen the drain connector and collect the fluid in the
container, then drain the brake fluid inside of the pump by
stepping on the brake pedal.
3. Remove the drain connection.
Use a M10 open-end wrench to remove the drain pipe
connection, promptly plug the outlet port to prevent pollution.
4. Use needle nose pliers to remove the lock pin from
the vacuum booster and the brake pedal's connecting
center pin.
5. Remove the vacuum booster's push rod and the pedal's
connecting center pin, and remove the return spring.
Push rod: Stepping onto the pedal in order to pass the force
Oil cup cover
Hose
Clean container
Unscrew the drain connection
Lock pin
Return spring
Center pin
Page 113 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual106
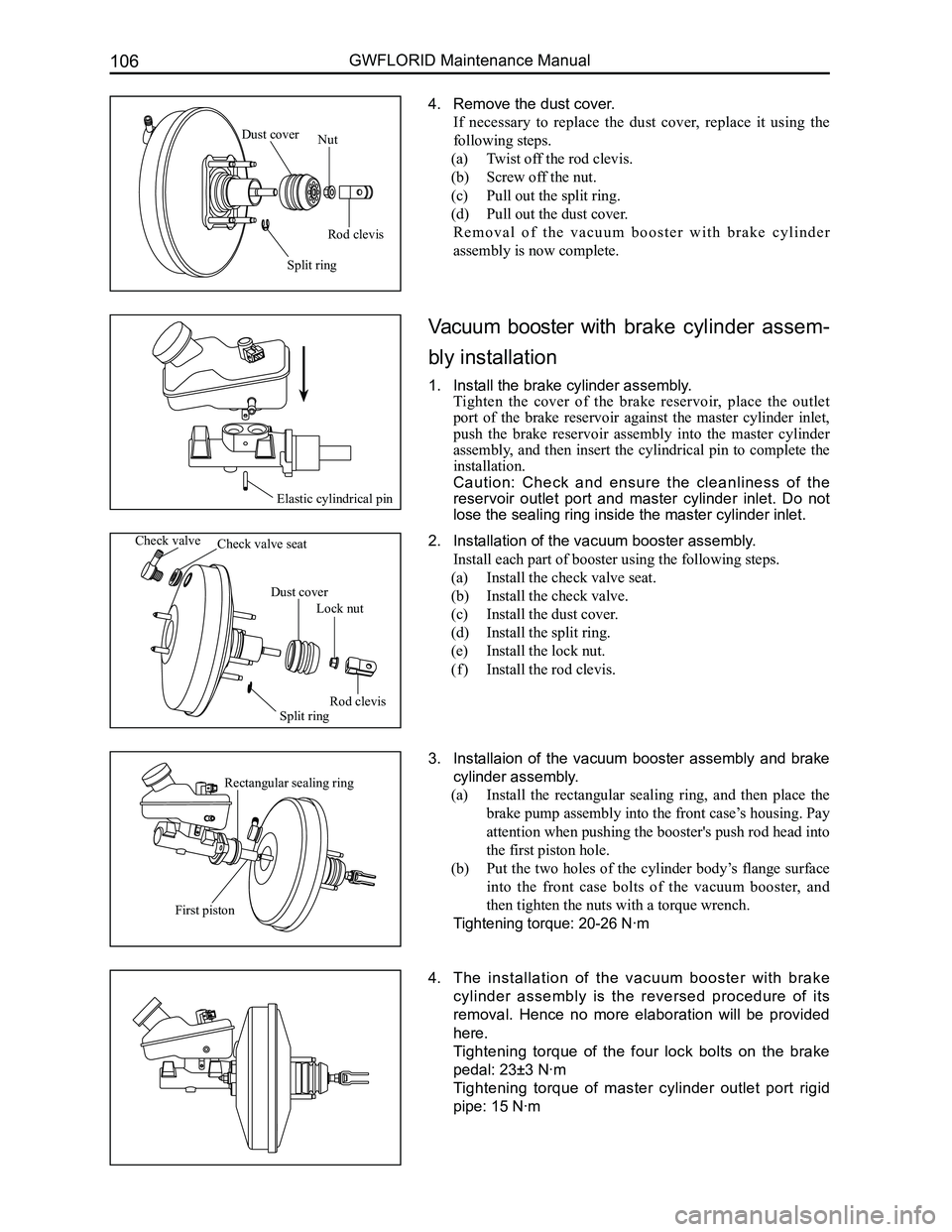
4. Remove the dust cover.
If necessary to replace the dust cover, replace it using the
following steps.
(a) Twist off the rod clevis.
(b) Screw off the nut.
(c) Pull out the split ring.
(d) Pull out the dust cover.
R e m o v a l o f t h e v a c u u m b o o s t e r w i t h b r a k e c y l i n d e r
assembly is now complete.
Vacuum booster with brake cylinder assem-
bly installation
1. Install the brake cylinder assembly.
Tighten the cover of the brake reservoir, place the outlet
port of the brake reservoir against the master cylinder inlet,
push the brake reservoir assembly into the master cylinder
assembly, and then insert the cylindrical pin to complete the
installation.
Caution: Check and ensure the cleanliness of the
reservoir outlet port and master cylinder inlet. Do not
lose the sealing ring inside the master cylinder inlet.
2. Installation of the vacuum booster assembly.
Install each part of booster using the following steps.
(a) Install the check valve seat.
(b) Install the check valve.
(c) Install the dust cover.
(d) Install the split ring.
(e) Install the lock nut.
( f ) Install the rod clevis.
3. Installaion of the vacuum booster assembly and brake
cylinder assembly.
(a) Install the rectangular sealing ring, and then place the
brake pump assembly into the front case’s housing. Pay
attention when pushing the booster's push rod head into
the first piston hole.
(b) Put the two holes of the cylinder body’s flange surface
into the front case bolts of the vacuum booster, and
then tighten the nuts with a torque wrench.
Tightening torque: 20-26 N·m
4. The installation of the vacuum booster with brake
cylinder assembly is the reversed procedure of its
removal. Hence no more elaboration will be provided
here.
Tightening torque of the four lock bolts on the brake
pedal: 23±3 N·m
Tightening torque of master cylinder outlet port rigid
pipe: 15 N·m
Rod clevis
Nut
Split ring
Dust cover
Elastic cylindrical pin
Check valveCheck valve seat
Lock nut
Rod clevis
Split ring
Dust cover
Rectangular sealing ring
First piston
Page 115 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual108
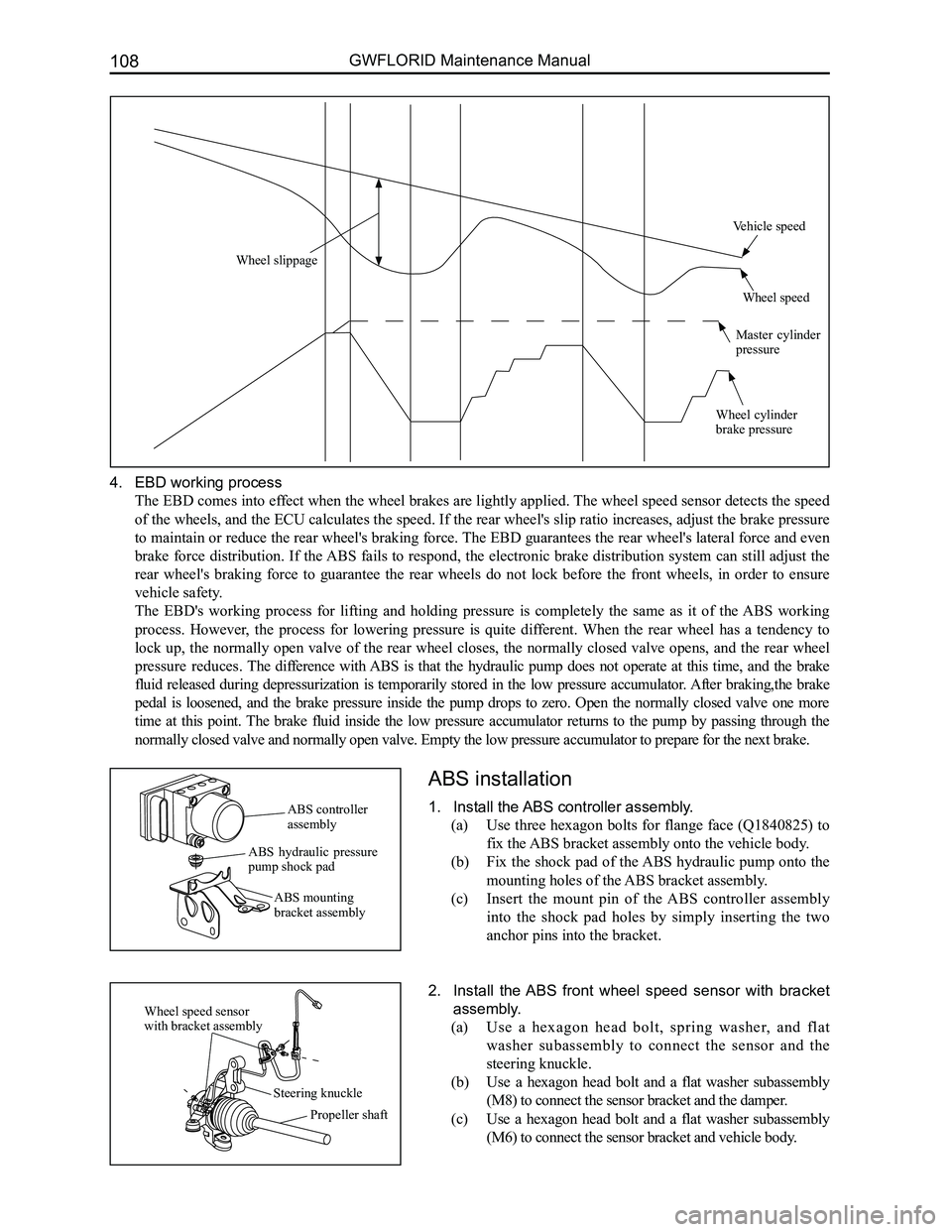
4. EBD working process
The EBD comes into effect when the wheel brakes are lightly applied. The wheel speed sensor detects the speed
of the wheels, and the ECU calculates the speed. If the rear wheel's slip ratio increases, adjust the brake pressure
to maintain or reduce the rear wheel's braking force. The EBD guarantees the rear wheel's lateral force and even
brake force distribution. If the ABS fails to respond, the electronic brake distribution system can still adjust the
rear wheel's braking force to guarantee the rear wheels do not lock before the front wheels, in order to ensure
vehicle safety.
The EBD's working process for lifting and holding pressure is completely the same as it of the ABS working
process. However, the process for lowering pressure is quite different. When the rear wheel has a tendency to
lock up, the normally open valve of the rear wheel closes, the normally closed valve opens, and the rear wheel
pressure reduces. The difference with ABS is that the hydraulic pump does not operate at this time, and the brake
fluid released during depressurization is temporarily stored in the low pressure accumulator. After braking,the brake
pedal is loosened, and the brake pressure inside the pump drops to zero. Open the normally closed valve one more
time at this point. The brake fluid inside the low pressure accumulator returns to the pump by passing through the
normally closed valve and normally open valve. Empty the low pressure ac\
cumulator to prepare for the next brake.
ABS installation
1. Install the ABS controller assembly.
(a) Use three hexagon bolts for flange face (Q1840825) to
fix the ABS bracket assembly onto the vehicle body.
(b) Fix the shock pad of the ABS hydraulic pump onto the
mounting holes of the ABS bracket assembly.
(c) Insert the mount pin of the ABS controller assembly
into the shock pad holes by simply inserting the two
anchor pins into the bracket.
2. Install the ABS front wheel speed sensor with bracket
assembly.
(a) Use a hexagon head bolt, spring washer, and flat
washer subassembly to connect the sensor and the
steering knuckle.
(b) Use a hexagon head bolt and a flat washer subassembly
(M8) to connect the sensor bracket and the damper.
(c) Use a hexagon head bolt and a flat washer subassembly
(M6) to connect the sensor bracket and vehicle body.
ABS controller assembly
ABS hydraulic pressure pump shock pad
ABS mounting bracket assembly
Wheel speed sensor with bracket assembly
Steering knuckle
Propeller shaft
Wheel slippage
Vehicle speed
Wheel speed
Master cylinder pressure
Wheel cylinder brake pressure