2008 GREAT WALL FLORID air suspension
[x] Cancel search: air suspensionPage 96 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 89Suspension System
Wheel and Tire
Tire
Remark
This vehicle's tire is of the tubeless type. The optimal design condition is met when the inflation pressure is at
the recommended value, and the tire is under full load. Maintaining suitable tire pressure and proper driving
habits greatly influence the tire's use life. For the vehicle, it improves riding comfort, stability, and handling. For
the tire, it reduces tread wear, damage to the tire and extends tire life. Overloading, speeding, and unnecessary
emergency braking will all add to the tire's wear and tear.
Tire pressure measurements should be taken under normal temperature. If the tire pressure rises due to motion
generated heat when driving, cooling it will return to the normal temperature. Therefore, do not deflate the tire
when the air pressure has risen to this point. The tire's air pressure will naturally and slowly decrease when used
under normal conditions. Hence please inspect the air pressure regularly (suggested once a month). The spare
tire should be kept in a useable condition at all times.
Inspect the tire pressure when it is cool monthly or before a long drive. Adjust the tire pressure to the recom-
mended level. The air pressure will normally rise because the tire warms up due to movement. Therefore, after
driving, you absolutely must not deflate or reduce the tire's air pressure, as deflating could reduce the cool tire's
air pressure.
Tire inflation
During a new tire's initial stage of use, warning due to bending motions will cause the tire to swell, and thus
reduce the corresponding air pressure. After 24 hours or 2000-3000 km worth of drive, charge the air pressure.
After inflating, check if the air nozzle core is leaking air with soapy \
water, then lock on the cap.
Possible problems caused by tire pressure
Exceeding the recommended air
pressure
Below the recommended air pressureSame vehicle axle, different
air pressure
Possible problems it
can create
1. Bumpy ride
2. The tear or rupturing of the tire
3. Rapid wear of the tire tread's center
1. Noisy turns
2. Uneasy turns
3. Tread edge wear is accelerated and uneven
4. The tire's rim is damaged or ruptured
5. The tire cord ruptures
6. High tire temperature
7. Steering failure
8. Large oil consumption
1. Uneven braking
2. Over steering
3. Steering failure
4. Deviation while accelerating
Tire and wheel (steel wheel) installation instructions
When installing the tire and wheel, the tire's radial hardware components, also called "high spot", should be at
the same level of the wheel's minimum radius or so called "low spot".
The "high spot" of the tire is initially marked by the paint spot on the side of the tire's surface. This paint will
eventually be washed away.
The "low spot" of the wheel is initially marked by a paint spot on the wheel flange. Whenever the tire is
removed from the wheel, the tire and wheel need re-balancing to make sure the vehicle runs smoothly. If no
paint spot is found on the tire, draw a line on the tire and the wheel before they are removed, in order to make
sure that the tire and the wheel will be re-assembled at the same place.\
Tire replacement
When a tire needs to be replaced, make sure to use a tire with the same specification as the original one. A new
tire used for replacement must be of the same dimension, load area, and structure as the original one. Using tires
that are different in dimension or type will influence the vehicle's riding comfort, handling, speedometer and
odometer calibration, vehicle ground clearance, and the clearance between the tire or the tire's snow chain and
the vehicle body or chassis.
It is suggested to use a new pair of tires on the same axle. If only one tire is needed to be replaced, make sure to
use a tire with a tread most similar to the original, so as to keep brak\
e power and traction balanced.
Warning: Do not mix radial tires, bias tires, bias belted tires, etc., which are of different structure on the
same vehicle unless it is an emergency. Mixing different tires would seriously influence the vehicle's
handling and stability, and even possibly lead to losing control of the vehicle.
Page 100 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 93Suspension System
Dynamic balance and static balance
There are two types of wheel balance: static and dynamic.
Picture 1 shows static balance. Picture 2 shows dynamic
balance.
Static balance means that the weight distribution around the
wheel is equal. If the wheel is static and unbalanced, violent
vibrations may be created, called jump vibration.This kind
of situation can ultimately lead to the uneven wear and tear
of the tires. Shown in diagram 1.
Dynamic balance means that the weight distribution on the
two sides of the medium plane of the wheel is equal, so
during the rotation process, the tire assembly cannot create a
tendency for the medium plane of the wheel to shift from one
side to the other. If the wheel is dynamic and unbalanced, it
can create a shimmying effect. Shown in diagram 2.
1. Wheel shimmy important points[C]: Counterweight not yet added
2. Locations to add counterweight[D]: Counterweight added
3. Axis
Wheel maintenance
Do not use welding, heating, or hammering to repair wheels. All damaged wheels must be replaced.
If the vehicle's wheel is twisted or deformed, sunken or depressed, having too much horizontal or radial hop,
leaking air from the welded parts, stretched out at the bolt holes , having flimsy nut bolt lock, or severely rusty,
the wheel must be replaced. When the wheel is hopping too much, it will lead to undesirable vibratio\
ns.
When replacing the tire, be sure that the load capacity, diameter, rim width, offset distance, and the installation
structure of it, are equal to the settings of original wheel. If the wheel dimensions are not appropriate, this will
influence the wheel and bearing's life, brake cooling effect, speedometer and odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance, as well as the clearance between the tire and the vehi\
cle body, and the tire and vehicle chassis.
Wheel (steel wheel) removal
1. Remove the wheelhouse and loosen the nuts, 1-2 turns is
enough.
2. Hoist the vehicle.
3. Screw off the nuts and remove the wheel.
Nut tightening torque: 110±10 N·m
Caution: Heating methods absolutely must not be used
to loosen tightened wheels, otherwise the heat will
reduce its use life and damage the hub bearing.
Wheel (steel wheel) installation
Installation according to the reversed instructions used for
removal, and pay attention to the following requirements:
Wheel nuts must be tightened in proper order and according to
the specified torque, as to avoid wheel or brake disc deformity.
When installing the wheel house, be sure to line up the wheel
housing notch locations with the inflation nozzle.
Tightening sequence: A – C – B – D
Caution: Before installing the wheel, first clean off the
corrosion on the wheel's mounting surface and drum
brake or brake disc's installation surface with a wire
brush, in order to make the wheel installing easier by
making the space between its metal firmly connect
to the mounting surface, otherwise it may lead to the
wheel nuts loosening to the extent that the vehicle's
wheel may come off while driving some day.
1
3
2[A][B]
1. Wheel hop important points[A]: Counterweight not yet added
2. Locations to add counterweight[B]: Counterweight added
3. Axis
Diagram 1
Diagram 2
[C][D]
1
3
2
AB
CD
Page 142 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 135Steering System
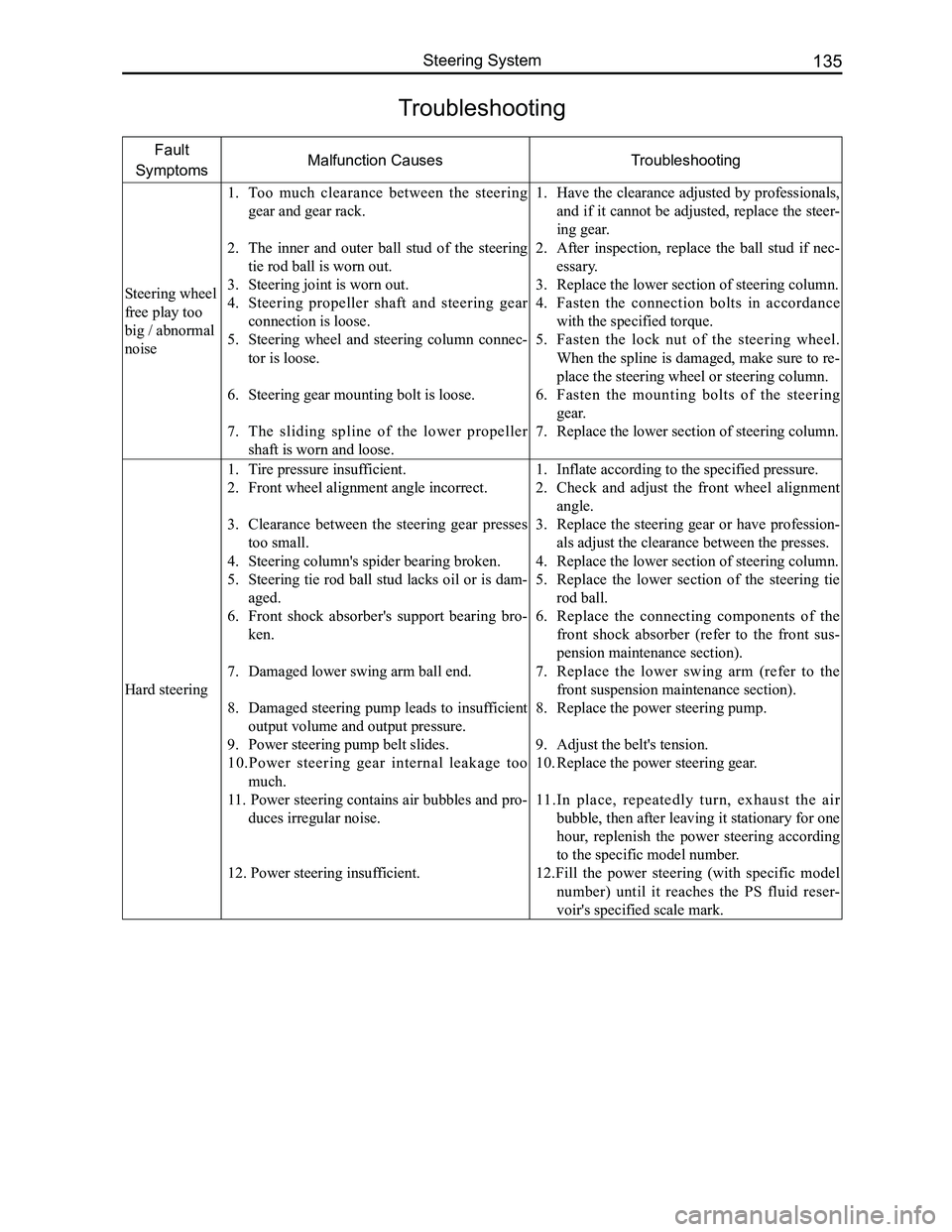
Troubleshooting
Fault
SymptomsMalfunction CausesTroubleshooting
Steering wheel
free play too
big / abnormal
noise
1. Too much clearance between the steering
gear and gear rack.
2. The inner and outer ball stud of the steering
tie rod ball is worn out.
3. Steering joint is worn out.
4. Steering propeller shaft and steering gear
connection is loose.
5. Steering wheel and steering column connec-
tor is loose.
6. Steering gear mounting bolt is loose.
7. The sliding spline of the lower propeller
shaft is worn and loose.
1. Have the clearance adjusted by professionals,
and if it cannot be adjusted, replace the steer-
ing gear.
2. After inspection, replace the ball stud if nec-
essary.
3. Replace the lower section of steering column.
4. Fasten the connection bolts in accordance
with the specified torque.
5. Fasten the lock nut of the steering wheel.
When the spline is damaged, make sure to re-
place the steering wheel or steering column.
6. Fasten the mounting bolts of the steering
gear.
7. Replace the lower section of steering column.
Hard steering
1. Tire pressure insufficient.
2. Front wheel alignment angle incorrect.
3. Clearance between the steering gear presses
too small.
4. Steering column's spider bearing broken.
5. Steering tie rod ball stud lacks oil or is dam-
aged.
6. Front shock absorber's support bearing bro-
ken.
7. Damaged lower swing arm ball end.
8. Damaged steering pump leads to insufficient
output volume and output pressure.
9. Power steering pump belt slides.
10.Power steering gear internal leakage too
much.
11. Power steering contains air bubbles and pro-
duces irregular noise.
12. Power steering insufficient.
1. Inflate according to the specified pressure.
2. Check and adjust the front wheel alignment
angle.
3. Replace the steering gear or have profession-
als adjust the clearance between the presses.
4. Replace the lower section of steering column.
5. Replace the lower section of the steering tie
rod ball.
6. Replace the connecting components of the
front shock absorber (refer to the front sus-
pension maintenance section).
7. Replace the lower swing arm (refer to the
front suspension maintenance section).
8. Replace the power steering pump.
9. Adjust the belt's tension.
10. Replace the power steering gear.
11.In place, repeatedly turn, exhaust the air
bubble, then after leaving it stationary for one
hour, replenish the power steering according
to the specific model number.
12.Fill the power steering (with specific model
number) until it reaches the PS fluid reser-
voir's specified scale mark.