2008 GREAT WALL FLORID engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 92 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 85Suspension System
Drive shaft installation
1. Insert the drive shaft.
First, align the inner end of the drive shaft and differential
spline. Keep the drive shaft axes and the differential axes
bases uniform, then hammer towards the direction of the
differential drive shaft's outer end until a clear and sharp
clicking sound is heard. Here, the drive shaft and the
transmission should have a clearance of about 1 mm.
2. According to the front suspension and wheel assembly
installation specifications, properly install the front
shock absorber with coil spring assembly LH and
wheel.
3. Use an M32 sleeve, ratchet wrench, and extension bar
to tighten front drive shaft nut LH.
Tightening torque: 225±20 N·m
F
F
Page 93 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual86
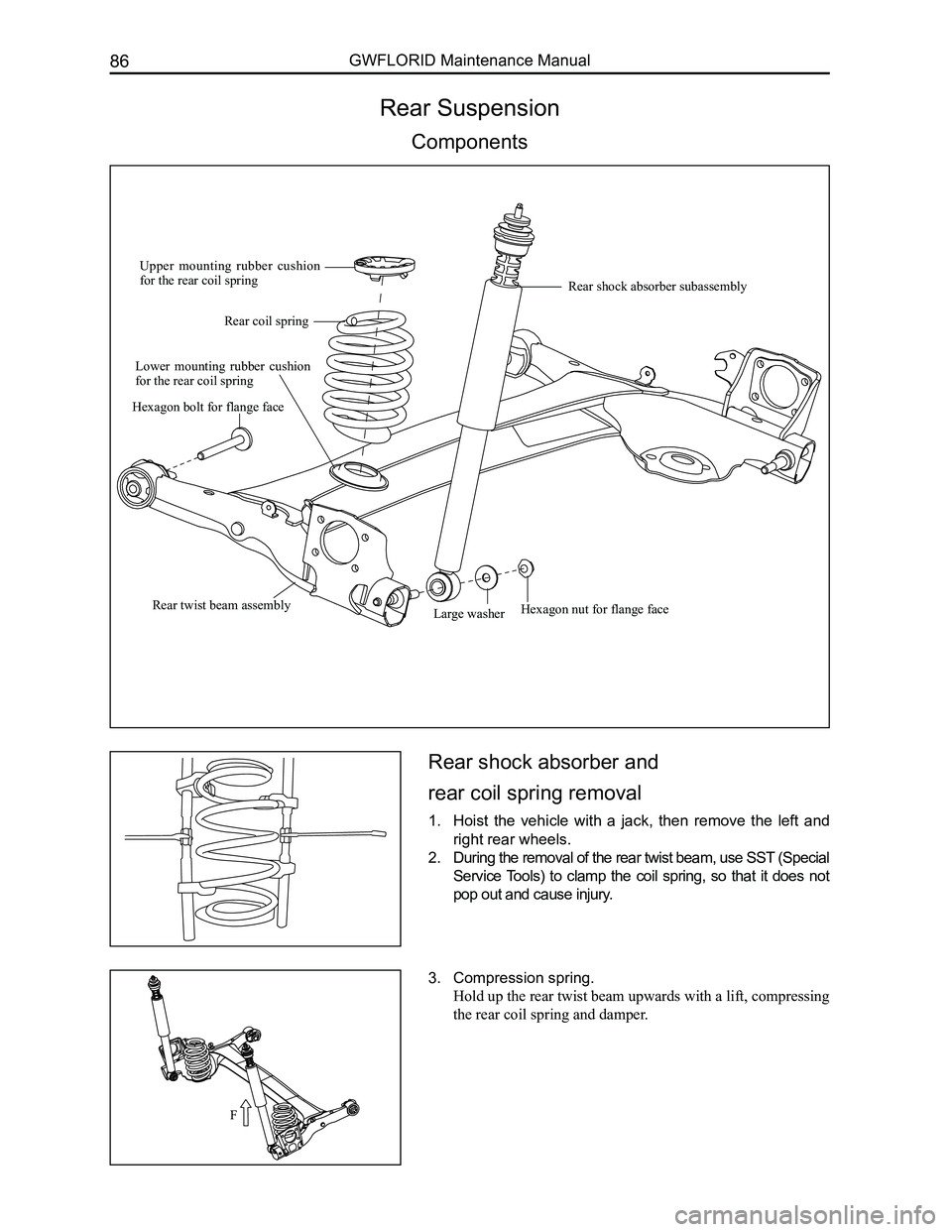
Rear Suspension
Components
Rear shock absorber and
rear coil spring removal
1. Hoist the vehicle with a jack, then remove the left and
right rear wheels.
2. During the removal of the rear twist beam, use SST (Special
Service Tools) to clamp the coil spring, so that it does not
pop out and cause injury.
3. Compression spring.
Hold up the rear twist beam upwards with a lift, compressing
the rear coil spring and damper.
Upper mounting rubber cushion for the rear coil spring
Rear coil spring
Lower mounting rubber cushion for the rear coil spring
Large washerRear twist beam assembly
Rear shock absorber subassembly
Hexagon bolt for flange face
Hexagon nut for flange face
F
Page 94 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 87Suspension System
Inspection, installation, and removal of the
trailing arm spindle sleeve assembly
1. Trailing arm spindle sleeve inspection.
(a) Inspect the trailing arm spindle sleeve for deformities,
shifting, partial or serious cracks, or loosening.
(b) If any existing damage of the trailing arm spindle
sleeve is not clearly seen, take the following steps:
Wash the trailing arm spindle sleeve's rubber areas with
clean water. Rub it clean with cotton meanwhile (shown
on the left). Check and make sure the rubber surface has
none of the previously mentioned flaws. If it does, re-
place with a new trailing arm spindle sleeve assembly.
2. Trailing arm spindle sleeve removal.
(a) Use a white paint pen to mark, and remember the trail-
ing arm spindle sleeve assembly direction.
(b) T h e t r a i l i n g a r m s p i n d l e s l e e v e i s d i s p o s a b l e . I f
damaged, first use a pry bar to lift up the edge of the
trailing arm spindle sleeve's outer tube in order to
install the SST (Special Service Tools).
Rear twist beam assembly removal
1. Hold up the rear twist beam assembly with a lift, and
remove the rear shock absorber and rear coil spring.
For detailed steps, refer to the rear shock absorber and
coil spring removal.
2. Remove the hexagon bolt for flange face
Q151B12110TF2 + Q402 (d2=35 t=5) FD, and slowly
set down the twist beam (as shown on the left).
Tightening torque: 77-87 N·m
When removing bolts, check and ensure that the rear
twist beam is reliably supported, to avoid injury from it
falling.
4. Remove the rear shock absorber.
Screw down the hexagon nut for flange face Q32012T13F2
(M12×1.25) FD linking the rear shock absorber and rear
twist beam, and remove the rear shock absorber. Make sure
the rear twist beam is firmly supported meanwhile.
Tightening torque: 44-54 N·m
5. Remove the coil spring.
Slowly release the firmly supported rear twist beam, at
the same time support the coil spring, until the coil spring
loosens, then take it down.
Rear shock absorber
Large washer
Hexagon nut for flange face
Page 96 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 89Suspension System
Wheel and Tire
Tire
Remark
This vehicle's tire is of the tubeless type. The optimal design condition is met when the inflation pressure is at
the recommended value, and the tire is under full load. Maintaining suitable tire pressure and proper driving
habits greatly influence the tire's use life. For the vehicle, it improves riding comfort, stability, and handling. For
the tire, it reduces tread wear, damage to the tire and extends tire life. Overloading, speeding, and unnecessary
emergency braking will all add to the tire's wear and tear.
Tire pressure measurements should be taken under normal temperature. If the tire pressure rises due to motion
generated heat when driving, cooling it will return to the normal temperature. Therefore, do not deflate the tire
when the air pressure has risen to this point. The tire's air pressure will naturally and slowly decrease when used
under normal conditions. Hence please inspect the air pressure regularly (suggested once a month). The spare
tire should be kept in a useable condition at all times.
Inspect the tire pressure when it is cool monthly or before a long drive. Adjust the tire pressure to the recom-
mended level. The air pressure will normally rise because the tire warms up due to movement. Therefore, after
driving, you absolutely must not deflate or reduce the tire's air pressure, as deflating could reduce the cool tire's
air pressure.
Tire inflation
During a new tire's initial stage of use, warning due to bending motions will cause the tire to swell, and thus
reduce the corresponding air pressure. After 24 hours or 2000-3000 km worth of drive, charge the air pressure.
After inflating, check if the air nozzle core is leaking air with soapy \
water, then lock on the cap.
Possible problems caused by tire pressure
Exceeding the recommended air
pressure
Below the recommended air pressureSame vehicle axle, different
air pressure
Possible problems it
can create
1. Bumpy ride
2. The tear or rupturing of the tire
3. Rapid wear of the tire tread's center
1. Noisy turns
2. Uneasy turns
3. Tread edge wear is accelerated and uneven
4. The tire's rim is damaged or ruptured
5. The tire cord ruptures
6. High tire temperature
7. Steering failure
8. Large oil consumption
1. Uneven braking
2. Over steering
3. Steering failure
4. Deviation while accelerating
Tire and wheel (steel wheel) installation instructions
When installing the tire and wheel, the tire's radial hardware components, also called "high spot", should be at
the same level of the wheel's minimum radius or so called "low spot".
The "high spot" of the tire is initially marked by the paint spot on the side of the tire's surface. This paint will
eventually be washed away.
The "low spot" of the wheel is initially marked by a paint spot on the wheel flange. Whenever the tire is
removed from the wheel, the tire and wheel need re-balancing to make sure the vehicle runs smoothly. If no
paint spot is found on the tire, draw a line on the tire and the wheel before they are removed, in order to make
sure that the tire and the wheel will be re-assembled at the same place.\
Tire replacement
When a tire needs to be replaced, make sure to use a tire with the same specification as the original one. A new
tire used for replacement must be of the same dimension, load area, and structure as the original one. Using tires
that are different in dimension or type will influence the vehicle's riding comfort, handling, speedometer and
odometer calibration, vehicle ground clearance, and the clearance between the tire or the tire's snow chain and
the vehicle body or chassis.
It is suggested to use a new pair of tires on the same axle. If only one tire is needed to be replaced, make sure to
use a tire with a tread most similar to the original, so as to keep brak\
e power and traction balanced.
Warning: Do not mix radial tires, bias tires, bias belted tires, etc., which are of different structure on the
same vehicle unless it is an emergency. Mixing different tires would seriously influence the vehicle's
handling and stability, and even possibly lead to losing control of the vehicle.
Page 103 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual96
Brake System Maintenance
Brake fluid inspection and replacement
Brake fluid directly influences the brake performance and the operating conditions and use life of the brake
system components. Brake fluid has very strong hygroscopic properties, and thus absorbs water easily,
which will then deteriorate the metal and rubber pieces. Polluted and deteriorated brake fluid or its mixture
would cause the brake fluid to boil and gasify, hence reduces braking efficiency. Therefore, pay attention to
the items below when filling or changing the brake fluid:
1. Containers used to hold brake fluid must be tightly closed and sealed
2. Brake fluid is poisonous and damaging to the paint. Hence if it gets on the vehicle surface, rub it
off at once
3. If water or other contaminates found in the brake fluid, and the brake master cylinder's piston seal
has been broken, then the brake fluid and all the rubber pieces inside the brake system including
the brake hose must be replaced
4. The correct brake fluid level in the reservoir must be between MAX and MIN. After the vehicle has
been driven for over 1000 km, check the brake fluid level in the reservoir. If the brake fluid level is
not up to regulation, more brake fluid should be added to the reservoir \
until it reaches MAX.
Hydraulic component inspection and system flushing
1. If the oil-based solvent gets into the hydraulic system, flush the whole system and change all of
the rubber pieces
2. Clean your hands before installing new rubber pieces or other components
3. Do not use regular solvents (kerosene, gas, etc.) when inspecting or cleaning hydraulic
components, instead use absorbing alcohol or brake fluid
4. After inspecting the components, drain the brake fluid from the system. Use new brake fluid to
flush the system. Afterwards, add new brake fluid to perform hydraulic system exhaust
5. Flushing completion sign: When the brake fluid flowing out of the dump valve is clear from any
contaminate.
Hydraulic pressure system drainage
If the brake fluid inside the whole hydraulic pressure system needs to be emptied, open all the bleed screws
with each connected to a hose, as to allow the brake fluid to flow into a container. Step on the pedal slowly
until only air flows out. During the whole procedure, make sure all the \
valves are open.
Hydraulic pressure system air bleeding
The hydraulic brake system must work under a vacuum environment. The air will cause spongy brake or
overall brake failure when it flows into the hydraulic system. It is extremely necessary to bleed system air
when performing any operation on the brake system or if any air inside t\
he brake system is suspected.
1. Air bleeding sequence
If air inside the brake master cylinder is suspected, first perform air bleeding.
(a) If numerous valves are equipped, air bleed each valve
(b) Another sequence principle is: Air bleed from the wheel brake furthest away from the master cylinder.
The air bleeding sequence for the LHD modules is: rear right wheel - left rear wheel - front right wheel
- front left wheel, Right rudder vehicles: rear right wheel - left rear wheel - front left wheel - front right
wheel.
2. Air bleeding method
(1) Manual air bleeding
Use the brake pedal or pump as the air bleeding power source. When the air bleed screws are open, vent the
brake fluid containing the bubbles from the system. Usually this is simultaneously done by two people. One
steps on the brake pedal and the other operates the air bleed screws. Important points to take note of when
performing the operation:
(a) Place the ignition switch to the off position and step on the pedal repeatedly to remove the
vacuum pressure or hydraulic pressure.
(b) Before and after air bleeding, add clean brake fluid into the master cylinder until it reaches
the correct (stated) level.
(c) Check the fluid level frequently to make sure that more than half of the reservoir's capacity is
available.
(d) Bleed screws should only be opened when the pedal is pressed down, and closed before the
pedal is loosened. Meanwhile, check if the vented brake fluid has bubble\
s inside.
Page 105 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual98
Brake Pedal
Components
Areas of Importance
1. During removal, all components should be gently handled to avoid knocking, especially the junction
surface. All components should be placed in order to avoid losing or taking the w\
rong parts.
2. Keep all parts clean and free of dust, scuffs, rust, corrosion, oil build-up, or any other contaminants.
3. All rubbing surfaces in a relative motion must be coated with lubricant\
.
4. During installation, strictly adhere to the standard torque for installi\
ng nuts.
5. While installing the return spring, be careful to avoid operator injury \
from it bouncing back.
Troubleshooting
SymptomsPossible causesEliminating methods
Brake pedal cannot return
to the original position
Return spring is brokenReplace the spring
Return spring's fixed end comes offCheck, secure in place
Feels slippery when
stepping on the pedal
Pedal pad is worn outReplace
Pedal pad comes offReinstall
Stepping on the pedal
produces abnormal noise
The plastic bushing is seriously worn outReplace
Spring brokenReplace
Spring's fixed end comes offCheck, re-fix
Pedal pad
Cotter pin
Return spring
Pedal shaft
Brake pedal bracket
welding assembly
Brake pedal lever welding assembly
Bushing
Nut
Limiting stopper
Center pin
Page 110 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 103Brake System
Vacuum Booster with Brake Cylinder Assembly
Components
Areas of Importance
1. The vacuum booster with brake cylinder assembly is tightly connected with the brake pedal assembly on
the cowl panel using four nuts. It is also connected with the brake pedal push rod via an center pin and
lock pin. Thus before removal of the assembly, first loosen the rigid pipe fitting with an open-end wrench,
disconnect the lock pin and center pin using pliers, loosen the four nuts, and then proceed with the booster.
2. Tighten the lock nuts on brake master cylinder and vacuum booster according to the specified torque,
and coat with signal paint.
3. Dimensions between the rear housing head face and the adjusting fork hole center is adjusted to
standard before it leaves factory. Please do not adjust it again.
4. The vacuum booster valve rod on the vehicle must be in a free state.
5. The brake master cylinder's working agent is DOT4 brake fluid. It must not be mixed with any other
brake fluid.
Problems and symptomsCausesEliminating methods
M a s t e r c y l i n d e r ' s o i l r e s e r v o i r i s severely leakingThe master cylinder, slave cylinder, or hydraulic line is leaking.Eliminate the areas with leaks (in general, it may be that the pipe fitting's tightening torque is not enough, check one by one and tighten as necessary)
1. Vacuum booster not sufficient2. No boost when the engine is off3. May lead to unsteady engine idling when severe
1. Under non-operating conditions, the vacuum booster leaks air.2. Front and rear housing connection are not sealed.3. Booster's front and rear gas seal sealing failure.4. Vacuum check valve leaks.
1. Replace the front and back gas seal and control valve assembly.2. Replace the vacuum booster.3. Replace the vacuum check valve assembly.
Brake pedal is heavy with no boost effect1. Under non-operating conditions, the vacuum booster leaks air.2. Booster diaphragm worn and damaged.3. Control valve ring cup worn and damaged.
1. Replace the front, back gas seal and booster diaphragm.2. Replace the vacuum booster.3. Replace the control valve assembly.
Spongy pedal when braking1. There is air in the brake fluid.2. Cylinder or slave cylinder leaks oil.3. There is brake line seepage.
1. Eliminate the air in the system.2. Inspect the cylinder and sub-pump cup and replace with new parts.3. Inspect the pipeline and eliminate the seepage.
When continuously step on the brake pedal, the pedal will gradually change and expand till the highest extend.
Pump valve opening blockage.Brake fluid cleanliness is insufficient, please replace the brake fluid.
Troubleshooting
Oil cup cover
Oil cup body
Check valve
Check valve seat
Vacuum booster
Pad
Lock nut
Rod clevisCoupling nut
Rectangular sealing ringCylinder body
Fluid supply sealing ring
Page 111 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual104
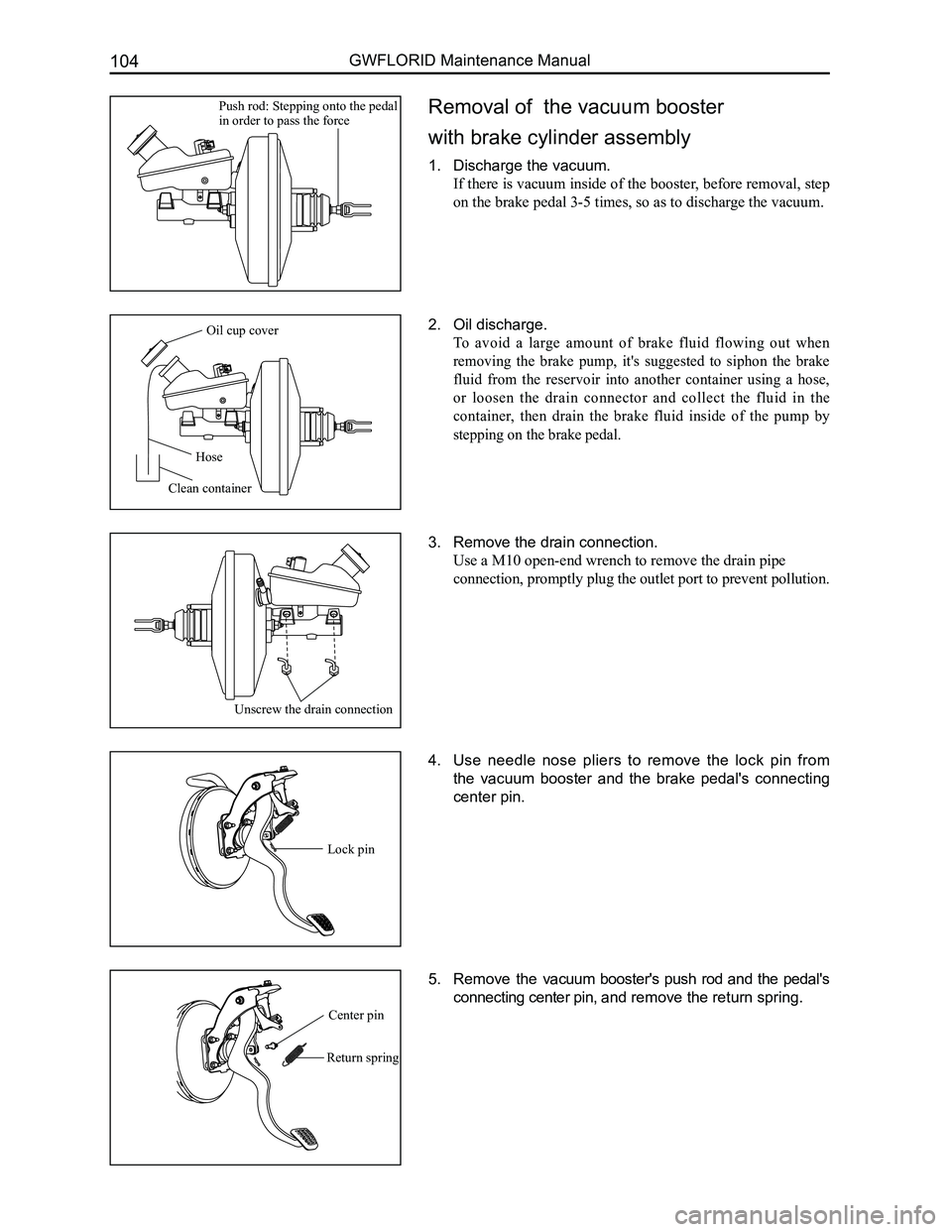
Removal of the vacuum booster
with brake cylinder assembly
1. Discharge the vacuum.
If there is vacuum inside of the booster, before removal, step
on the brake pedal 3-5 times, so as to discharge the vacuum.
2. Oil discharge.
To avoid a large amount of brake fluid flowing out when
removing the brake pump, it's suggested to siphon the brake
fluid from the reservoir into another container using a hose,
or loosen the drain connector and collect the fluid in the
container, then drain the brake fluid inside of the pump by
stepping on the brake pedal.
3. Remove the drain connection.
Use a M10 open-end wrench to remove the drain pipe
connection, promptly plug the outlet port to prevent pollution.
4. Use needle nose pliers to remove the lock pin from
the vacuum booster and the brake pedal's connecting
center pin.
5. Remove the vacuum booster's push rod and the pedal's
connecting center pin, and remove the return spring.
Push rod: Stepping onto the pedal in order to pass the force
Oil cup cover
Hose
Clean container
Unscrew the drain connection
Lock pin
Return spring
Center pin