Page 1053 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -On-vehicle Service35A-11
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR CHECK
The brake fluid level sensor is in good condition if there is
no continuity when the float surface is above “MIN” and if
there is continuity when the float surface is below “MIN”.
DISC BRAKE PAD CHECK AND REPLACEMENT
NOTE
The wear indicator contacts the brake disc when the brake
pad thickness reaches approximately 2 mm and emit a
squealing sound to warn the driver.
1. Check the brake pad thickness through the caliper body
check port.
Standard value: 10.0 mm
Limit: 2.0 mm
2. When the thickness is less than the limit, always replace
the pads at an axle set.
3. Remove the pin bolt. Pivot the caliper assembly and hold
it with wires.
Caution
Do not wipe off the special grease that is on the pin
or allow it to contaminate the pin.
4. Remove the following parts from the caliper support.
1. Pad and wear indicator assembly
2. Pad assembly
3. Clip
4. Outer shim
5. In order to measure the brake drag force after pad
installation, measure the rotary-sliding resistance of the
hub with the pads removed. (Refer to P.35A-21.)
6. Install the pads and caliper assembly, and then check
the brake drag force. (Refer to P.35A-21.)
14Z0017
Front Rear
Front Rear
Front Rear
12 34
3
1
2 3
4
3
Page 1054 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -On-vehicle Service35A-12
Caution
Take care not to contact the parts or tools to the caliper
because the paint of caliper will be scratched. And if
there is brake fluid on the caliper, wipe out quickly.
NOTE
The wear indicator contacts the brake disc when the brake
pad thickness reaches approximately 2 mm and emit a
squealing sound to warn the driver.
1. Check the brake pad thickness through the caliper body
check port.
Standard value: 10.0 mm , 9.0 mm
Limit: 2.0 mm
2. When the thickness is less than the limit, always replace
the pads at an axle set.
(1) Holding the cross spring with one hand, pull the pin
out of the caliper.
(2) Remove the pad from the caliper.
(3) To measure brake drag force after new pads have
been installed, use a spring balance to measure the
turning sliding resistance of the hub with the pads
removed. (Refer to P.35A-21.)
(4) Clean the piston and, using the special tool, push
the piston into the cylinder.
Pads
Front Rear
Pads
MB990520
Page 1055 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -On-vehicle Service35A-13
(5) Apply repair kit grease to the portions of the pads
indicated on the left. At this time, make sure that
the grease will not be applied to any other surfaces.
(6) Mount the pads to the caliper so that its side with
the wear indicator is on the outside of the vehicle.
With the rear pads, ensure that the arrow on the
pad faces in the same direction as the brake disc
turns when the vehicle moves forward.
(7) Holding the cross spring with one hand, fit pins in
the caliper.
(8) Using a spring balance, measure the turning sliding
resistance of the hub in the forward direction.
(9) Find the brake disc drag force [the difference in
measurements taken in step(3) and in step(8)].
Standard value: 69 N or less
DISC BRAKE ROTOR CHECK
Caution
When servicing disc brakes, it is necessary to exercise caution to keep the disc brakes within
the allowable service values in order to maintain normal brake operation.
Before re-finishing or re-processing the brake disc surface, the following conditions should be checked.
Inspection itemsRemarks
Scratches, rust, saturated lining materials
and wearDIf the vehicle is not driven for a certain period, the sections of
the discs that are not in contact with lining will become rusty, causing
noise and shuddering.
DIf grooves resulting from excessive disc wear and scratches are
not removed prior to installing a new pad assembly, there will
momentarily be inappropriate contact between the disc and the
lining (pad).
Run-out or driftExcessive run-out or drift of the discs will increase the pedal depression
resistance due to piston knock-back.
Change in thickness (parallelism)If the thickness of the disc changes, this will cause pedal pulsation,
shuddering and surging.
Inset or warping (flatness)Overheating and improper handling while servicing will cause inset or
warping.
Front Rear
Cross
spring
Pins
Page 1063 of 1449
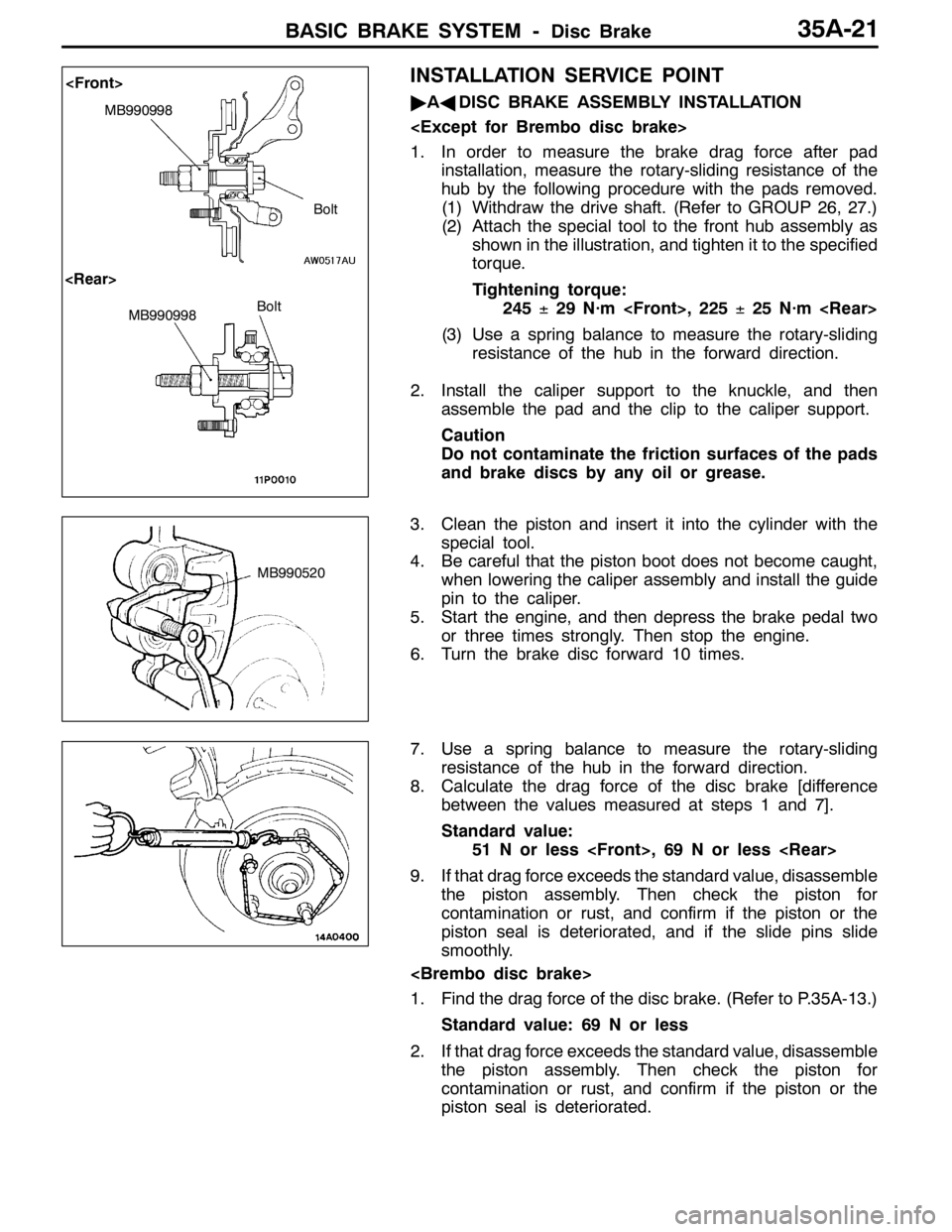
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -Disc Brake35A-21
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
"AADISC BRAKE ASSEMBLY INSTALLATION
1. In order to measure the brake drag force after pad
installation, measure the rotary-sliding resistance of the
hub by the following procedure with the pads removed.
(1) Withdraw the drive shaft. (Refer to GROUP 26, 27.)
(2) Attach the special tool to the front hub assembly as
shown in the illustration, and tighten it to the specified
torque.
Tightening torque:
245±29 N·m , 225±25 N·m
(3) Use a spring balance to measure the rotary-sliding
resistance of the hub in the forward direction.
2. Install the caliper support to the knuckle, and then
assemble the pad and the clip to the caliper support.
Caution
Do not contaminate the friction surfaces of the pads
and brake discs by any oil or grease.
3. Clean the piston and insert it into the cylinder with the
special tool.
4. Be careful that the piston boot does not become caught,
when lowering the caliper assembly and install the guide
pin to the caliper.
5. Start the engine, and then depress the brake pedal two
or three times strongly. Then stop the engine.
6. Turn the brake disc forward 10 times.
7. Use a spring balance to measure the rotary-sliding
resistance of the hub in the forward direction.
8. Calculate the drag force of the disc brake [difference
between the values measured at steps 1 and 7].
Standard value:
51 N or less , 69 N or less
9. If that drag force exceeds the standard value, disassemble
the piston assembly. Then check the piston for
contamination or rust, and confirm if the piston or the
piston seal is deteriorated, and if the slide pins slide
smoothly.
1. Find the drag force of the disc brake. (Refer to P.35A-13.)
Standard value: 69 N or less
2. If that drag force exceeds the standard value, disassemble
the piston assembly. Then check the piston for
contamination or rust, and confirm if the piston or the
piston seal is deteriorated.MB990998
Bolt
MB990998Bolt
MB990520
Page 1070 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -Disc Brake35A-28
"AALOCK PIN/GUIDE PIN INSTALLATION
As shown in the illustration, align the identification mark on
the caliper body and the head mark of the guide pin/lock
pin, then install the guide pin/lock pin.
INSPECTION
DCheck the cylinder for wear, damage or rust.
DCheck the piston surface for wear, damage or rust.
DCheck the caliper body or sleeve for wear.
DCheck pad for damage or adhesion of grease, check
the backing metal for damage.
PAD WEAR CHECK
Measure thickness at the thinnest and worn area of the pad.
Replace the pad assembly if the pad thickness is less than
the limit value.
Standard value:
10.0 mm ,
9.0 mm
Limit: 2.0 mm
Caution
1. Always replace the brake pads as an axle set.
2. If an excessive difference is found in the thickness
between the right and left brake pads, check moving
parts.
Identification
mark ”L”
Front of
vehicle
Rear of
vehicle
Lock pin Lock pin
Guide pin Guide pin
Identification
mark ”G”
Identification
mark ”B”
Identification mark ”A”