2007 KIA CARNIVAL clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 354 of 1575

Objective
* Energy (hydraulic pressure) storage
* Impact and pulsation damping when solenoid valves operating
* Operation as spring element
* Smooth shifting by preventing sudden operation of clutches and brakes
TRANSFER DRIVE GEAR
With the transfer drive gear, increased tooth height and a higher contact ratio have reduced gear noise.
Also, the bearing that supports the drive gear is a preloaded type that eliminates rattle, and the rigidity of the gear
mounting has been increased by bolting the bearing directly onto the case.
OUTPUT SHAFT/TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR
As shown in the illustration below, the transfer driven gear is press- fitted onto the output shaft, and the output shaft is
secured by a locking nut and supported by bearings.
The locking nut has a left- handed thread, and a hexagonal hole in the other end of the shaft enables the shaft to be
held in position for locking nut removal.
Page 355 of 1575

MANUAL CONTROL SYSTEM
MANUAL CONTROL LEVER
The manual control lever is fitted to the top of the valve body and is linked to the parking roller rod and manual control
valve pin.
A detent mechanism is provided to improve the gear shift feeling during manual selection.
PARKING MECHANISM
When the manual control lever is moved to the parking position, the parking roller rod moves along the parking roller
support and pushes up the parking sprag.
As a result, the parking sprag meshes with the transfer driven gear (parking gear), thereby locking the output shaft. To
minimize the operating force required, a roller is fitted to the end of the rod.
POWER TRAIN
P POSITION
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the LR brake and the RED brake, so power is not transmitted from the input shaft to
the UD clutch or OD clutch, and the output shaft is locked by the park brake pawl interlocking the park gear.
N POSITION
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the LR brake(A) and the RED brake, so power is not transmitted from the input shaft
to the UD clutch or OD clutch.
Page 356 of 1575

1st GEAR POWER FLOW
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the UD clutch(B) the LR brake(A) and the one way clutch(OWC), then the UD clutch
transmits driving force from the input shaft to the UD sun gear, and the LR brake locks the LR annulus gear to the
case.The UD sun gear of the planetary gear drives the output pinion gear, and the LR brake locks the annulus gear,
and the output pinion drives the output carriers, and the output carrier drives the transfer drive gear, and the transfer
drive gear drives the transfer driven gear of the output shaft, and power is transmitted to the differential gear through
the differential drive gear.
2nd GEAR POWER FLOW
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the UD clutch(A) the 2nd brake(B) and the one way clutch(OWC), then the UD clutch
transmits driving force from the input shaft to the UD sun gear, and the 2nd brake locks the reverse sun gear to the
case.The UD sun gear of the planetary gear drives the output pinion gear and the LR annulus gear, and the LR
annulus gear drives the OD planetary carriers, and OD planetary carriers drives OD pinion gear, and the OD pinion
gear drives the output carriers, and the output carrier drives the transfer drive gear, and the transfer drive gear drives
the transfer driven gear of the output shaft, and power is transmitted to the differential gear through the differential
drive gear.
Page 357 of 1575

3rd GEAR POWER FLOW
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the UD clutch(A) and the OD clutch(B), then the UD clutch transmits driving force from
the input shaft to the UD sun gear, and the OD clutch transmits driving force from the input shaft to the overdrive
planetary carrier and low&reverse annulus gear.The UD sun gear of the planetary gear drives the output pinion gear
and the LR annulus gear, and the LR annulus gear drives the OD pinion gear through the OD planetary carrier, and
the OD pinion gear drives the reverse sun gear and the output carrier.The OD clutch drives the OD carrier, and the
OD carrier drives the OD pinion gear, and the OD pinion gear drives the reverse sun gear and the output carrier, and
the output carrier drives the transfer drive gear, and the transfer drive gear drives the transfer driven gear of the
output shaft, and power is transmitted to the differential gear through the differential drive gear.
4th GEAR POWER FLOW
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the OD clutch(A) and the 2nd brake(B), then the OD clutch transmits driving force
from the input shaft to the OD planetary carrier and LR annulus gear, and the 2nd brake locks the reverse sun gear to
the case.The OD clutch drives the OD carrier, and the OD carrier drives the OD pinion gear and the LR annulus gear,
and the OD pinion gear drives the output carrier, and the output carrier drives the transfer drive gear, and the transfer
drive gear drives the transfer driven gear of the output shaft, and power is transmitted to the differential gear through
the differential drive gear.
Page 358 of 1575

Reverse GEAR POWER FLOW
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the reverse clutch(A) and the LR brake(B), then the reverse clutch transmits driving
force from the input shaft to the reverse sun gear, and the LR brake locks the LR annulus gear and OD planetary
carrier to the case.The reverse clutch drives the reverse sun gear, and the reverse sun gear drives the output carrier
through the OD pinion gear, and the output carrier drives the transfer drive gear, and the transfer drive gear drives the
transfer driven gear of the output shaft, and power is transmitted to the differential gear through the differential drive
gear.
Page 360 of 1575
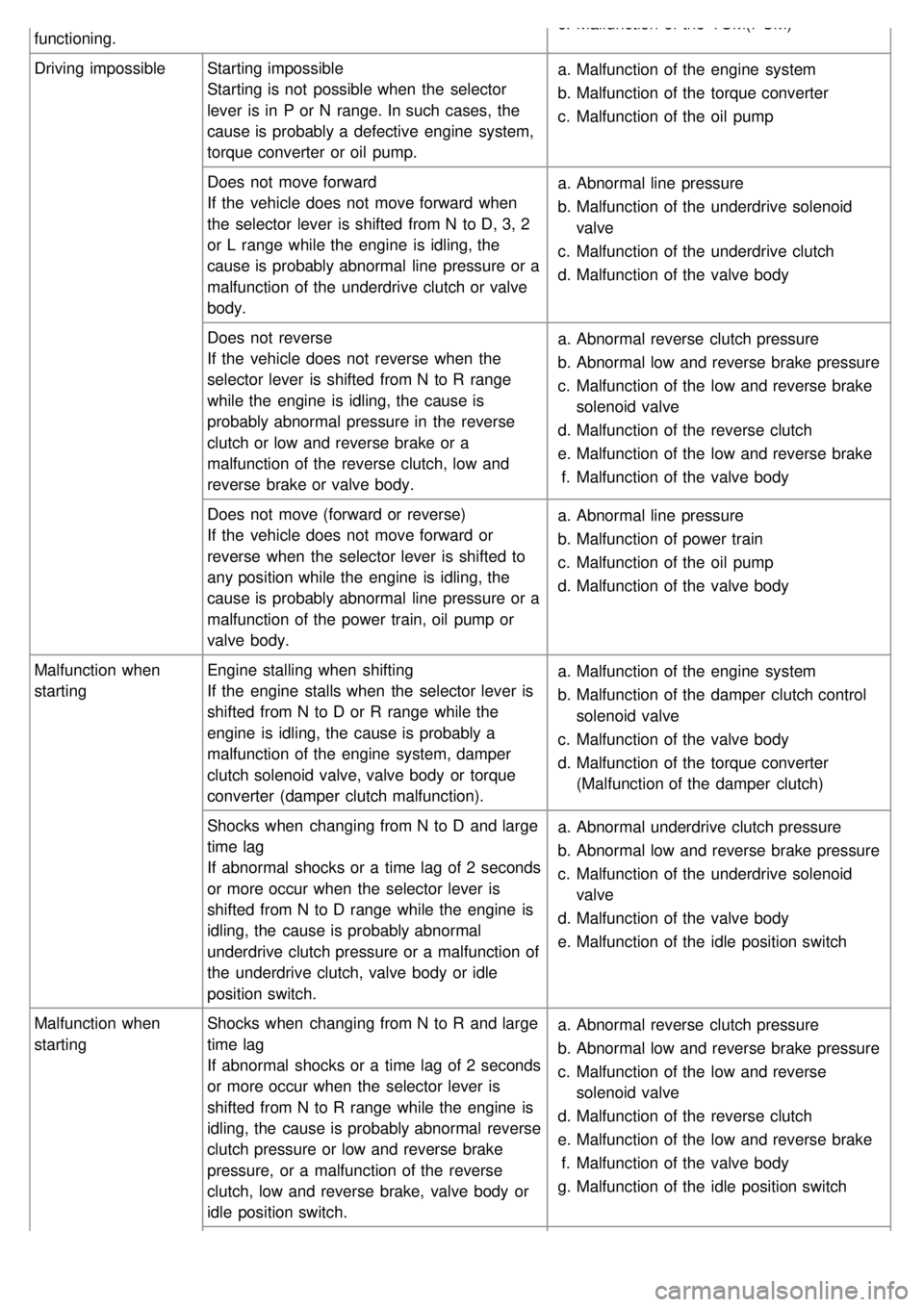
functioning.c.
Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Driving impossible Starting impossible
Starting is not possible when the selector
lever is in P or N range. In such cases, the
cause is probably a defective engine system,
torque converter or oil pump. a.
Malfunction of the engine system
b. Malfunction of the torque converter
c. Malfunction of the oil pump
Does not move forward
If the vehicle does not move forward when
the selector lever is shifted from N to D, 3, 2
or L range while the engine is idling, the
cause is probably abnormal line pressure or a
malfunction of the underdrive clutch or valve
body. a.
Abnormal line pressure
b. Malfunction of the underdrive solenoid
valve
c. Malfunction of the underdrive clutch
d. Malfunction of the valve body
Does not reverse
If the vehicle does not reverse when the
selector lever is shifted from N to R range
while the engine is idling, the cause is
probably abnormal pressure in the reverse
clutch or low and reverse brake or a
malfunction of the reverse clutch, low and
reverse brake or valve body. a.
Abnormal reverse clutch pressure
b. Abnormal low and reverse brake pressure
c. Malfunction of the low and reverse brake
solenoid valve
d. Malfunction of the reverse clutch
e. Malfunction of the low and reverse brake
f. Malfunction of the valve body
Does not move (forward or reverse)
If the vehicle does not move forward or
reverse when the selector lever is shifted to
any position while the engine is idling, the
cause is probably abnormal line pressure or a
malfunction of the power train, oil pump or
valve body. a.
Abnormal line pressure
b. Malfunction of power train
c. Malfunction of the oil pump
d. Malfunction of the valve body
Malfunction when
starting Engine stalling when shifting
If the engine stalls when the selector lever is
shifted from N to D or R range while the
engine is idling, the cause is probably a
malfunction of the engine system, damper
clutch solenoid valve, valve body or torque
converter (damper clutch malfunction). a.
Malfunction of the engine system
b. Malfunction of the damper clutch control
solenoid valve
c. Malfunction of the valve body
d. Malfunction of the torque converter
(Malfunction of the damper clutch)
Shocks when changing from N to D and large
time lag
If abnormal shocks or a time lag of 2 seconds
or more occur when the selector lever is
shifted from N to D range while the engine is
idling, the cause is probably abnormal
underdrive clutch pressure or a malfunction of
the underdrive clutch, valve body or idle
position switch. a.
Abnormal underdrive clutch pressure
b. Abnormal low and reverse brake pressure
c. Malfunction of the underdrive solenoid
valve
d. Malfunction of the valve body
e. Malfunction of the idle position switch
Malfunction when
starting Shocks when changing from N to R and large
time lag
If abnormal shocks or a time lag of 2 seconds
or more occur when the selector lever is
shifted from N to R range while the engine is
idling, the cause is probably abnormal reverse
clutch pressure or low and reverse brake
pressure, or a malfunction of the reverse
clutch, low and reverse brake, valve body or
idle position switch. a.
Abnormal reverse clutch pressure
b. Abnormal low and reverse brake pressure
c. Malfunction of the low and reverse
solenoid valve
d. Malfunction of the reverse clutch
e. Malfunction of the low and reverse brake
f. Malfunction of the valve body
g. Malfunction of the idle position switch
Page 361 of 1575

Shocks when changing from N to D, N to R
and large time lag
If abnormal shocks or a time lag of 2 seconds
or more occur when the selector lever is
shifted from N to D range and from N to R
range while the engine is idling, the cause is
probably abnormal line pressure or a
malfunction of the oil pump or valve body.a.
Abnormal line pressure
b. Malfunction of the oil pump
c. Malfunction of the valve body
Malfunction when
shifting Shocks and running up
If shocks occur when driving due to up
shifting or down shifting and the transmission
speed becomes higher than the engine
speed, the cause is probably abnormal line
pressure or a malfunction of a solenoid valve,
oil pump, valve body or of a brake or clutch. a.
Abnormal line pressure
b. Malfunction of each solenoid valve
c. Malfunction of the oil pump
d. Malfunction of the valve body
e. Malfunction of each brake or each clutch
Displaced shifting
points All points
If all shift points are displaced while driving,
the cause is probably a malfunction of the
output shaft speed sensor, TPS or of a
solenoid valve. a.
Malfunction of the output shaft speed
sensor
b. Malfunction of the throttle position sensor
c. Malfunction of each solenoid valve
d. Abnormal line pressure
e. Malfunction of the valve body
f. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Some points
If some of the shift points are displaced while
driving, the cause is probably a malfunction of
the valve body, or it is related to control and
is not an abnormality. a.
Malfunction of the valve body
Does not shift No diagnosis codes
If shifting does not occur while driving and no
diagnosis codes are output, the cause is
probably a malfunction of the transaxle range
switch, or TCM(PCM) a.
Malfunction of the transaxle range
b. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Malfunction while
driving Poor acceleration
If acceleration is poor even if down shifting
occurs while driving, the cause is probably a
malfunction of the engine system or of a
brake or clutch. a.
Malfunction of the engine system
b. Malfunction of the brake or clutch
Malfunction while
driving Vibration
If vibration occurs when driving at constant
speed or when accelerating and deceleration
in top range, the cause is probably abnormal
damper clutch pressure or a malfunction of
the engine system, damper clutch control
solenoid valve, torque converter or valve
body. a.
Abnormal damper clutch pressure
b. Malfunction of the engine system
c. Malfunction of the damper clutch control
solenoid valve
d. Malfunction of the torque converter
e. Malfunction of the valve body
Transaxle range switch system
The cause is probably a malfunction of the inhibitor switch circuit,
ignition switch circuit or a defective TCM(PCM). a.
Malfunction of the transaxle range switch
b. Malfunction of the ignition switch
c. Malfunction of connector
d. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Idle position switch system
The cause is probably a defective idle position switch circuit, or a
defective TCM(PCM). a.
Malfunction of the triple pressure switch
b. Malfunction of connector
c. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Page 362 of 1575

Triple pressure switch system
The cause is probably a defective dual pressure switch circuit or a
defective TCM(PCM).a.
Malfunction of the triple pressure switch
b. Malfunction of connector
c. Malfunction of A/C system
d. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
Vehicle speed sensor system
The cause is probably a defective vehicle speed sensor circuit or a
defective TCM(PCM). a.
Malfunction of the vehicle speed sensor
b. Malfunction of connector
c. Malfunction of the TCM(PCM)
DTC TROUBLESHOOTING INDEX
No. Code ItemMILRemark
1 P0707 TRANSAXLE RANGE SWITCH CIRCUIT LOW INPUT ON
2 P0708 TRANSAXLE RANGE SWITCH CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT ON
3 P0711 TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR RATIONALITY ON
4 P0712 TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT ON
5 P0713 TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT ON
6 P0717 A/T INPUT SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
7 P0722 AT OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
8 P0731 GEAR 1 INCORRECT RATIO ON
9 P0732 GEAR 2 INCORRECT RATIO ON
10 P0733 GEAR 3 INCORRECT RATIO ON
11 P0734 GEAR 4 INCORRECT RATIO ON
12 P0741 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH STUCK OFF ON
13 P0742 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH STUCK ON ON
14 P0743 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE - OPEN or
SHORT(GND) ON
15 P0748 VFS SOLENOID OFF
16 P0750 LOW and REVERSE SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
17 P0755 UNDER DRIVE SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
18 P0760 SECOND SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
19 P0765 OVERDRIVE SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
20 P0885 A/T CONTROL RELAY - OPEN or SHORT(GND) ON
21 P0890 TCM power Relay sense circuit low ON
22 P0891 TCM power Relay sense circuit High ON
Failsafe
Activation and deactivation of error failsafe is coordinated Error failsafe Management.
Once Error failsafe is activated, it will be kept until ignition key OFF.
In every new TCM start, TCM start with No Error failsafe and No Error present.
0. Mechanical Limp Home Mode
a. Switch off A/T relay
1. Electrical Limp Home Mode a. Keep 2nd / 3rd gear
2. Prohibit Intelligent Shift a. Fuzzy SAT(Siements Adaptive Transmission) shift pattern (Medium Driver, Sporty Driver) will not be used