2007 ISUZU KB P190 Wiring
[x] Cancel search: WiringPage 3365 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–87
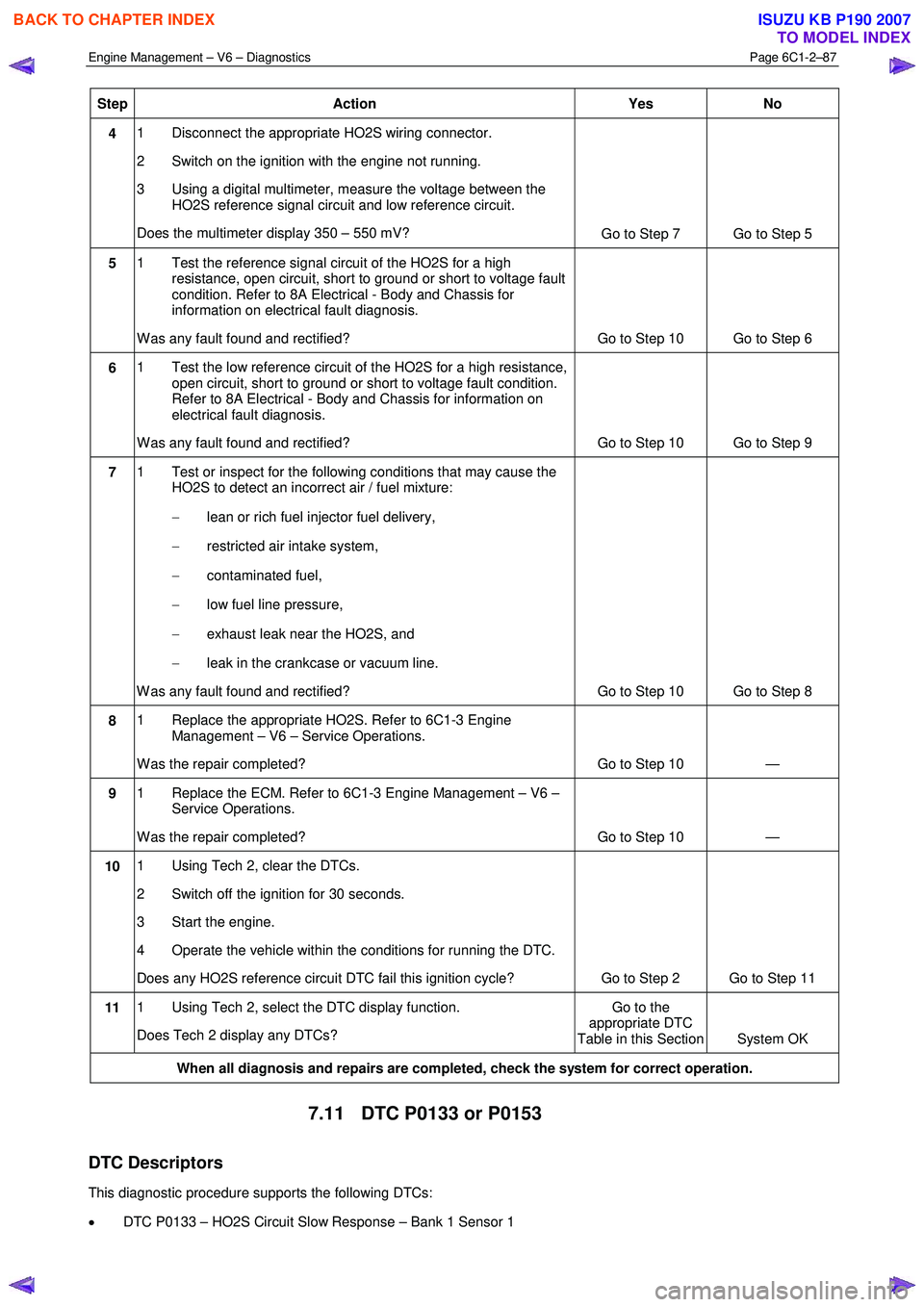
Step Action Yes No
4 1 Disconnect the appropriate HO2S wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the HO2S reference signal circuit and low reference circuit.
Does the multimeter display 350 – 550 mV? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Test the reference signal circuit of the HO2S for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
6 1 Test the low reference circuit of the HO2S for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition.
Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
7 1 Test or inspect for the following conditions that may cause the
HO2S to detect an incorrect air / fuel mixture:
− lean or rich fuel injector fuel delivery,
− restricted air intake system,
− contaminated fuel,
− low fuel line pressure,
− exhaust leak near the HO2S, and
− leak in the crankcase or vacuum line.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 1 Replace the appropriate HO2S. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 1 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any HO2S reference circuit DTC fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 1 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.11 DTC P0133 or P0153
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0133 – HO2S Circuit Slow Response – Bank 1 Sensor 1
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3367 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–89
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL/DTC.
Additional Information
• Use the J 35616 Connector Test Adapter Kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a
component harness connector.
• The lower connector of the ECM is connector A43-X1 and the upper connector of the ECM is connector A43-X2.
Refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section.
• The front wide band sensors do not toggle or switch like a switching HO2S. The front HO2S signals will be
relatively stable for an idling engine.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical-
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
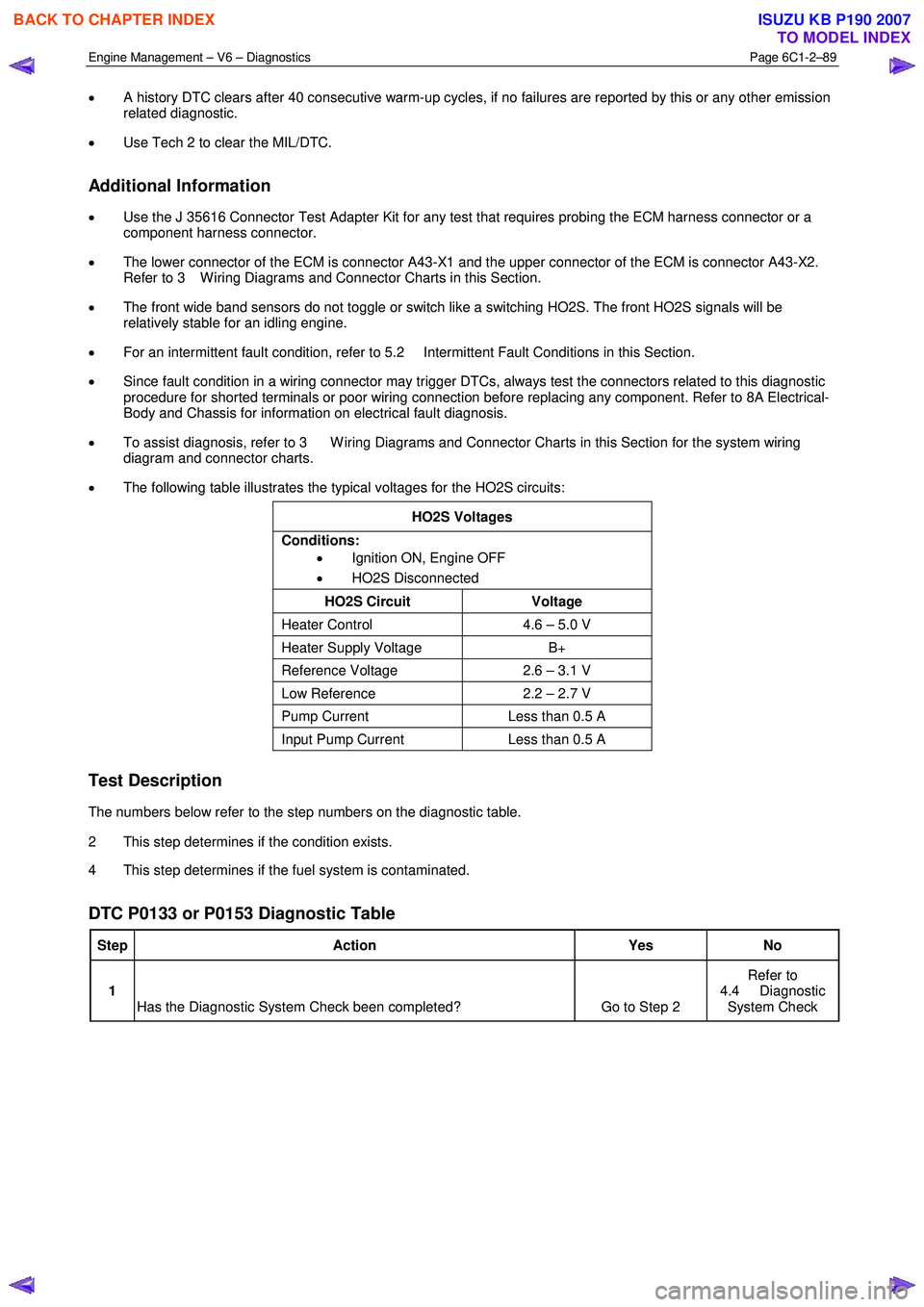
• The following table illustrates the typical voltages for the HO2S circuits:
HO2S Voltages
Conditions: • Ignition ON, Engine OFF
• HO2S Disconnected
HO2S Circuit Voltage
Heater Control 4.6 – 5.0 V
Heater Supply Voltage B+
Reference Voltage 2.6 – 3.1 V
Low Reference 2.2 – 2.7 V
Pump Current Less than 0.5 A
Input Pump Current Less than 0.5 A
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines if the condition exists.
4 This step determines if the fuel system is contaminated.
DTC P0133 or P0153 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3368 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–90
Step Action Yes No
2 NOTE
• DTC P0133 is for bank 1 sensor 1 and DTC P0153 is
for bank 2 sensor 1.
• DTC P0132 causes DTC P0153 to set. If DTC P0132
is set with DTC P0153, refer to 7.10 DTC
P0130, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140,
P0141, P0150 P0151, P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247, P2270, P2271, P2272,
P2273, P2297 or P2298 in this Section.
• Inspect the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) for being
secure before proceeding with this DTC. A sensor that
is loose could cause this DTC to set.
1 Start engine and allow to reach operating temperature.
2 Observe the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) information with Tech 2.
Did DTC P0133 and / or DTC P0153 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 1 Observe the Freeze Frame / Failure Records for this DTC.
2 Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the vehicle within the conditions that you
observed from the Freeze Frame / Failure Records.
Did the DTC fail this ignition? Go to Step 4 Go to Additional
Information in this DTC
4 Did DTC P0133 and DTC P0153 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Inspect for an exhaust leak near the HO2S. Refer to 6F Exhaust
System – V6. After you inspect the exhaust system, return to
this diagnostic.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 6
6 1 Inspect or test for the following conditions:
• Inspect that the HO2S is securely installed.
• Inspect for corrosion on the HO2S terminals.
• Inspect the terminal tension at the HO2S and at the
engine control module (ECM). Refer to 8A Electrical-Body
and Chassis.
• Inspect the HO2S wiring for damage.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3374 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–96
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
5 Test signal circuit of the EOT sensor. This circuit should display a voltage within the specified range.
6 Measures the integrity of the EOT sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the Fuse 29 enables the ECM to power down completely prior to the test procedure.
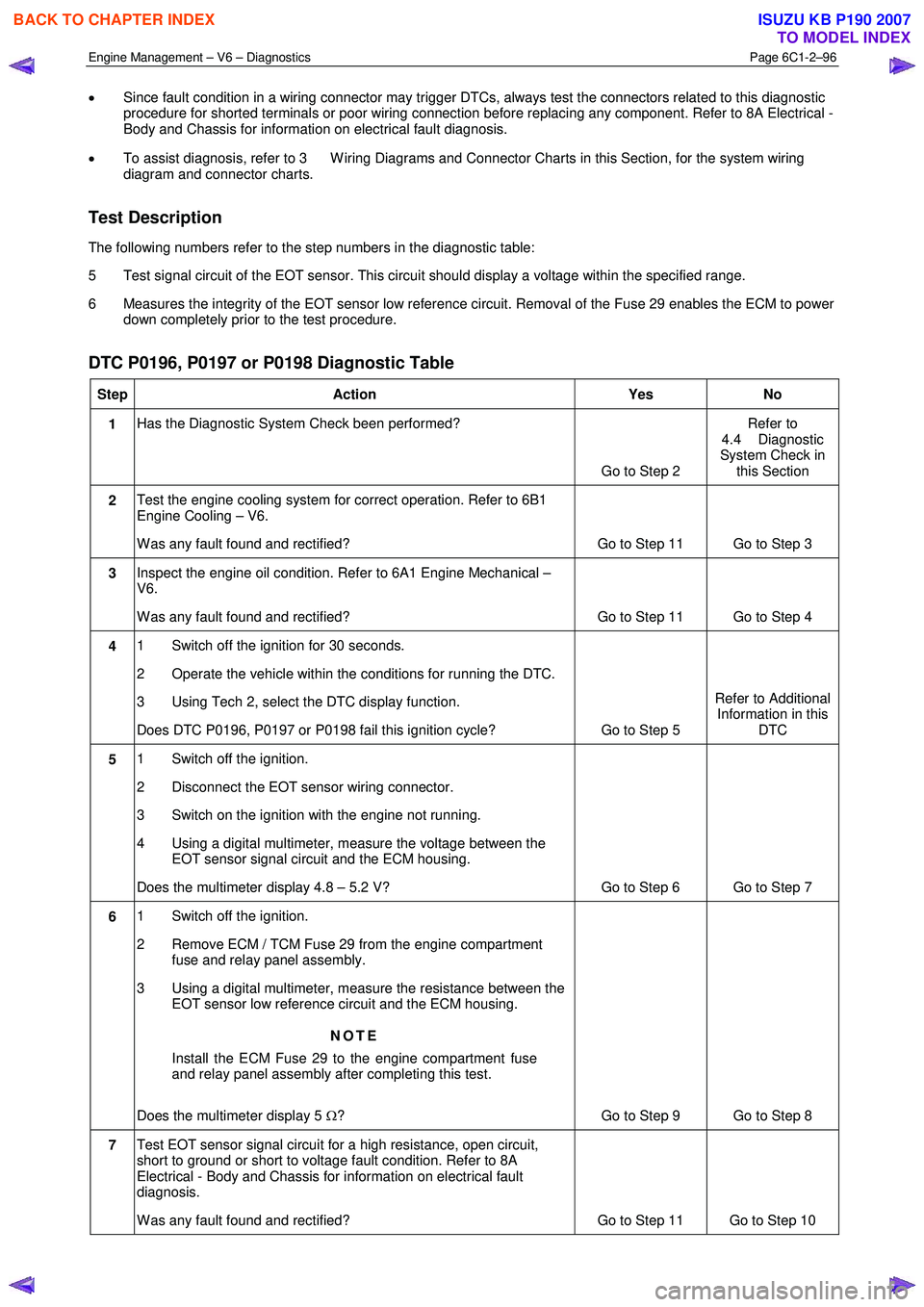
DTC P0196, P0197 or P0198 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 Test the engine cooling system for correct operation. Refer to 6B1
Engine Cooling – V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 3
3 Inspect the engine oil condition. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 4
4 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0196, P0197 or P0198 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 5 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the EOT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the EOT sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM / TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the EOT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Test EOT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3376 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–98
• DTC P0268 – Injector 3 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0270 – Injector 4 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0271 – Injector 4 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0273 – Injector 5 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0274 – Injector 5 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0276 – Injector 6 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0277 – Injector 6 Control Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the fuel injector ignition circuit. The ECM applies a pulse
width modulated (PW M) ground to the injector control circuit through a device within the ECM called a driver to control
each fuel injector on time.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up when the voltage is approximately 3.3 V. The ECM monitors the driver
feedback circuit to determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
A fuel injector control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in a fuel injector control circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• the battery voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V, and
• engine speed is greater than 80 rpm
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0201,P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205 or P0206
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in a fuel injector circuit.
DTC P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270, P0273 and P0276
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the control circuit a fuel injector.
DTC P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271, P0274 and P0277
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the control circuit of a fuel injector.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The fuel injector control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the fuel injector operation.
• Using Tech 2, observe the appropriate fuel injector status parameter while wriggle testing related harness and
connectors. Tech 2 reading will change from Ok to Fault if there is an intermittent fault condition in the harness or
connector being tested.
• Perform the fuel injector coil test to help isolate an intermittent condition. Refer to 6.2 Fuel Injector Coil
Test in this Section.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3377 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–99
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Determines if there is a fault condition in the ignition voltage supply circuit. The fuel injectors for each bank of the engine are fused separately. If all DTCs for a single bank are set, there may be a fault in one of the ignition supply
circuits.
5 Verifies the ECM is sending control voltage to the fuel injector.
6 Tests if the feed back voltage circuit within the ECM is providing the correct voltage.
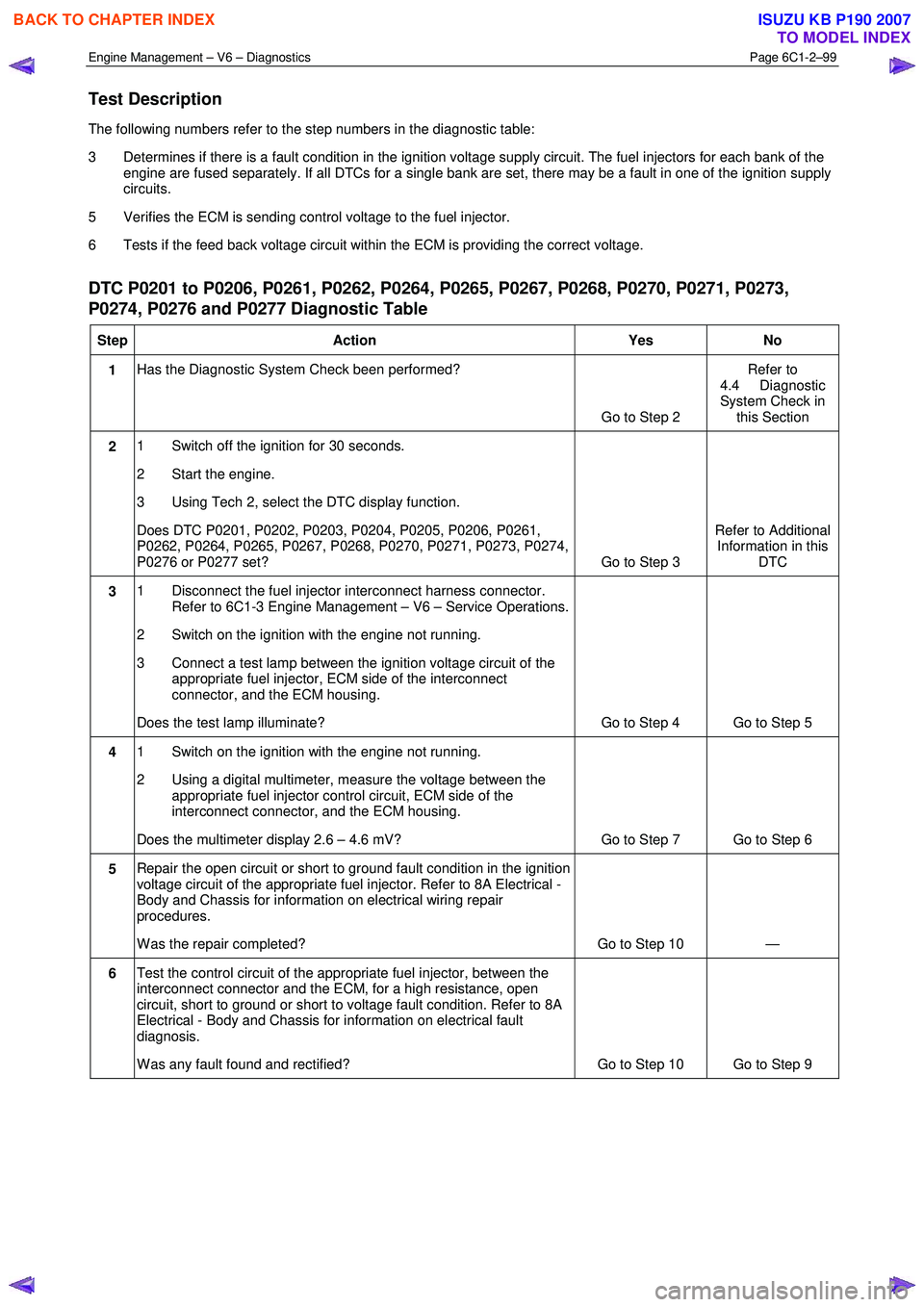
DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273,
P0274, P0276 and P0277 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205, P0206, P0261,
P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273, P0274,
P0276 or P0277 set? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Disconnect the fuel injector interconnect harness connector.
Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the ignition voltage circuit of the appropriate fuel injector, ECM side of the interconnect
connector, and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the appropriate fuel injector control circuit, ECM side of the
interconnect connector, and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2.6 – 4.6 mV? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the open circuit or short to ground fault condition in the ignition
voltage circuit of the appropriate fuel injector. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical wiring repair
procedures.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
6 Test the control circuit of the appropriate fuel injector, between the
interconnect connector and the ECM, for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3379 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–101
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an engine speed in excess of 7200 RPM for 1 second or longer.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The engine over-speed DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0219 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the diagnostic system check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.16 DTC P0300
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0300 Engine Misfire Detected.
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses information from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the camshaft position
(CMP) sensors to determine when an engine misfire is occurring. By monitoring variations in the crankshaft rotation
speed for each cylinder, the ECM is able to detect individual misfire events. A misfire rate that is high enough can cause
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3384 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–106
− Damaged accessory drive belt
• For an intermittent condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this
diagnostic procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305 or P0306 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2
W ere you sent here from DTC P0300? Go to Step 3 Go to 7.16
DTC P0300 in this Section
3 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the ignition coil of the misfiring cylinder, but leave the electrical connector connected. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Inspect the ignition coil boot for the following conditions:
− Holes.
− Tears.
− Carbon tracking.
− Oil contamination or water intrusion.
Did you find a condition with the ignition coil boot? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the fuel pump fuse from the under-hood fuse and relay
centre.
2 Install the J 26792 Spark Tester to the ignition coil boot and a good ground.
3 Crank the engine while observing J 26792.
Does the spark tester spark and is the spark consistent? Go to Step 5 Go to Electronic
Ignition System Diagnosis
5 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the spark plug from the cylinder that indicated a misfire.
3 Inspect the spark plug. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Does the spark plug appear to be OK? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6
Is the spark plug oil or coolant fouled? Inspect the spark
plugs. Go to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations Go to Step 7
7 Is the spark plug gas fouled? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Does the spark plug show any signs of being cracked, worn, or
incorrectly gap? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007