2007 ISUZU KB P190 torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 4394 of 6020

7A2-110 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
C12: Large Shock When Gearshift from 1st to 2nd or 2nd to 1st
C13: Large Shock When Gearshift from 2nd to 3rd or 3rd to 2nd
C14: Large Shock When Gearshift from 3rd to 4th or 4th to 3rd
C15: Large Shock When Kick-down
C16: Large Shock When Accelerator Pedal is Stepped ON or OFF without Gearshift
C17: Large Shock When Gearshift from 2nd to 1st in L Range
C18: Large Shock Others
C19: Large Shock When Vehicle Speed is Reduced by No Accelerator Pedal or Vehicle is Stopped
C20: Large Shock at Lock Up
C21: Shift Down or Engine Overrun When Accelerator Pedal is Stepped ON in 4th Gear
D1: Faulty Gearshift Schedule (Different from Shift Speed Chart)
Checks Action
Definition: • A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is stepped on for acceleration and the gear is shifted up or down.
• A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is stepped on for kick-down.
• A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is not stepped on.
• A large shock is felt when the selector lever is selected in L range.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)” are
suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
A large shock is felt at lock up.
Diagnosis Hints Incorrect input signals or faulty operation of torque converter clutch is suspected.
Refer to category No. “I1: No Lock Up.”
Checks Action
Definition:
Shift down or engine overrun occurs above than kick-down area.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)” are
suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Faulty gearshift schedule, it is differ from the shift speed chart.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4398 of 6020
7A2-114 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
F1: Low Maximum Speed or Poor Acceleration
F2: Engine Race Up (Slipping) During Acceleration
Control Valve Body ChecksInspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking shift solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Checks
Action
ChecksAction
Definition: • Starting acceleration is poor.
• Acceleration is slow, even though the accelerator pedal is stepped on during the running.
Diagnosis Hints In addition to the low engine output, faulty gearshift of the transmission or
fixing at the 3rd gear in the fail-safe operation may also be possible.
Therefore, if “maximum speed is low, and acceleration is poor”, it should be
cleared up whether the trouble originates from the engine system or
transmission control system by a running test, inspection of stall speed, etc.
Transmission Range Switch & Selector Lever
Cable Checks Inspect the transmission range switch and selector lever cable for
misadjusting or disordering. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
• Smell
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in forward ranges for a possible dropped pressure.
Refer to Line Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
Stall Speed Checks Inspect the stall speed in forward ranges. Refer to Stall Test in Test Instruction
section.
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking shift solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Torque Converter Checks Inspect the torque converter for faulty operation.
Clutch and Brake Checks Inspect the low clutch and high clutch for slipping.
Additional Checks • Inspect the engine for proper outputs. Refer to appropriate inspection
chart in engine section.
• Inspect the TCM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from 0 to 99 or 100% according to the accelerator pedal
operation.
Checks Action
Definition: • Engine speed increases but the vehicle speed does not increase when the accelerator pedal is being stepped on.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4400 of 6020
7A2-116 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
G2: Large Creeping Force
G3: Small Creeping Force
G4: Large Noise During Idle with Vehicle Stop
Transmission Range Switch & Selector Lever
Cable Checks Inspect the transmission range switch and selector lever cable for
misadjusting or disordering. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
Additional Checks Inspect the parking mechanism for faulty operation. Checks Action
Checks
Action
Definition:
Vehicle accelerates in R, D, 3, 2 or L range, even though the accelerator pedal is not being stepped on.
Diagnosis Hints Too high idle speed is suspected. Inspect the engine for proper idle speed.
Checks Action
Definition:
Vehicle does not move, even though a run position is selected on a flat road during idling.
Diagnosis Hints When the creep force is small in all positions, low engine output is suspected.
If the creep is normal only in the R position, operation of the fail-safe function
due to trouble in the electrical system is suspected.
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
•Smell
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in forward ranges for a possible dropped pressure.
Refer to Line Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
Stall Speed Checks Inspect the stall speed in forward ranges. Refer to Stall Test in Test
Instruction section.
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking shift solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On- Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Torque Converter Checks Inspect the torque converter for faulty operation.
Clutch and Brake Checks Inspect the low clutch for slipping.
Additional Checks • Inspect the engine for proper outputs. Refer to appropriate inspection
chart in engine section.
• Inspect the TCM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the ground return circuit for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission is noisy during idle in all range.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4401 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-117
H1: Judder Occurs at Lock Up
H2: Large Shock at Lock Up
H3: Lock Up Point is High or Low
I1: No Lock Up
Diagnosis Hints • Causes such as the solenoid operating sound or a faulty oil pump are
suspected.
• Distinguishing is possible by stopping the solenoid operation temporarily, checking the correlation for the former case and, changing
the line pressure and confirming the correlation with noise.
• As a matter of course, noise other than the transmission may be generated around the engine, and should be checked carefully.
Notice: When the noise is generated only at the time of a gear shift, it may
be the sound of transmission fluid flowing or gear noise. If the sound varies
depending on the gear speed to be shifted, it may be the gear noise
generated from the planetary gear and its components. If the sound varies
depending on the vehicle speed, it may be the gear noise of the output
system, or the gear noise of the input system or a faulty torque converter.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
Judder occurs when lock up area.
Diagnosis Hints Slip due to burning of the torque converter clutch (TCC) facing or insufficient
engagement due to dropped working pressure are suspected. Refer to
category No. “l1: No Lock Up “.
Notice: When the TCC facing has burnt, foreign material mixed in the oil
cooler is suspected. In such a case, inspect the oil cooler circuit for clogging
of the oil cooler.
Checks Action
Definition: • A large shock is felt at lock up.
• Lock up point is excessively high or low.
Diagnosis Hints Incorrect input signals or faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) is
suspected. Refer to category No. “I1: No Lock Up”.
Checks Action
Definition:
Lock up is not performed even though lock up control conditions being satisfied.
Diagnosis Hints • Monitor the signal to the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
while carrying out a running test.
• When the transmission fluid temperature is lower than 20 °C (68 °F),
lock up control is inhibited.
• When the output signal to the TCC solenoid valve is sent correctly, causing no lock up, clogged hydraulic circuits or malfunction of the TCC
piston may be suspected.
• Even with the lock up area, the output signal to the TCC solenoid valve is not sent, a fault of the transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
controlling the lock up may be suspected.
Notice: When the TCC facing has burnt, foreign material mixed in the oil
cooler is suspected. In such a case, inspect the oil cooler circuit for clogging
of the oil cooler.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4402 of 6020
7A2-118 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
J1: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Breather
J2: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Engine and Converter Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Converter Housing and Transmission Case
J4: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Transmission Case and Extension Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Pan
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Manual Shaft Oil Seal
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Cooler Pipe Joint
Z1: Transmission Overheat
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
• Smell
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking TCC solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On- Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Sensor Checks Inspect the TFT sensor. Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table to test
the TFT sensor at various temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
skewed sensor.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks from breather.
Diagnosis Hints Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks between engine and converter housing.
Transmission fluid leaks between converter housing and transmission case.
Transmission fluid leaks between transmission case and extension housing.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil pan.
Transmission fluid leaks from manual shaft oil seal.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil cooler pipe joint.
Diagnosis Hints Faulty oil seal or contact surface is suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Smells burnt or smoke from transmission.
Diagnosis Hints • Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
• Slipping of the clutch is suspected. Gear ratio error DTC might be set.
• Clogged oil cooler.
• Faulty operation of oil pump.
• Faulty torque converter clutch (TCC) piston.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4406 of 6020

7A2-122 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Standard Value
Diagnosis 1. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in all ranges.
• Abraded oil pump.
• Faulty operation of each solenoid valve.
• Sticking of pressure regulator spool valve or pilot spool valve.
• Fatigued pressure regulator spool valve spring or pilot spool valve spring.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the oil strainer, oil pump, pressure regulator spool valve, torque
converter relief spool valve or pressure relief valve.
2. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in D, 3, 2 and L range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low clutch hydraulic circuit.
3. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in R range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the reverse clutch hydraulic circuit.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low & reverse brake hydraulic circuit.
4. If the line pressure is lower that the standard value at idle in L or R range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low & reverse brake hydraulic circuit.
5. If the line pressure is higher than the standard value at idle in all ranges.
• Faulty accelerator pedal position signal.
• Faulty transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor.
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Sticking pilot spool valve.
• Sticking pressure regulator spool valve or plug.
6. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at stall speed in all ranges.
• Faulty accelerator pedal position signal.
• Faulty operation of pressure control (PC) solenoid valve.
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Sticking pilot spool valve.
• Sticking pressure regulator spool valve or plug.
Selector lever position Engine
speed Line pressure (kPa/ psi)
D, 3, 2 or D Idle 350 - 480 / 51 - 70
R Stall 1050 - 1250 / 152 - 182
Idle 450 - 650 / 65 - 95
Stall 1400 - 1630 / 203 - 237
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4407 of 6020
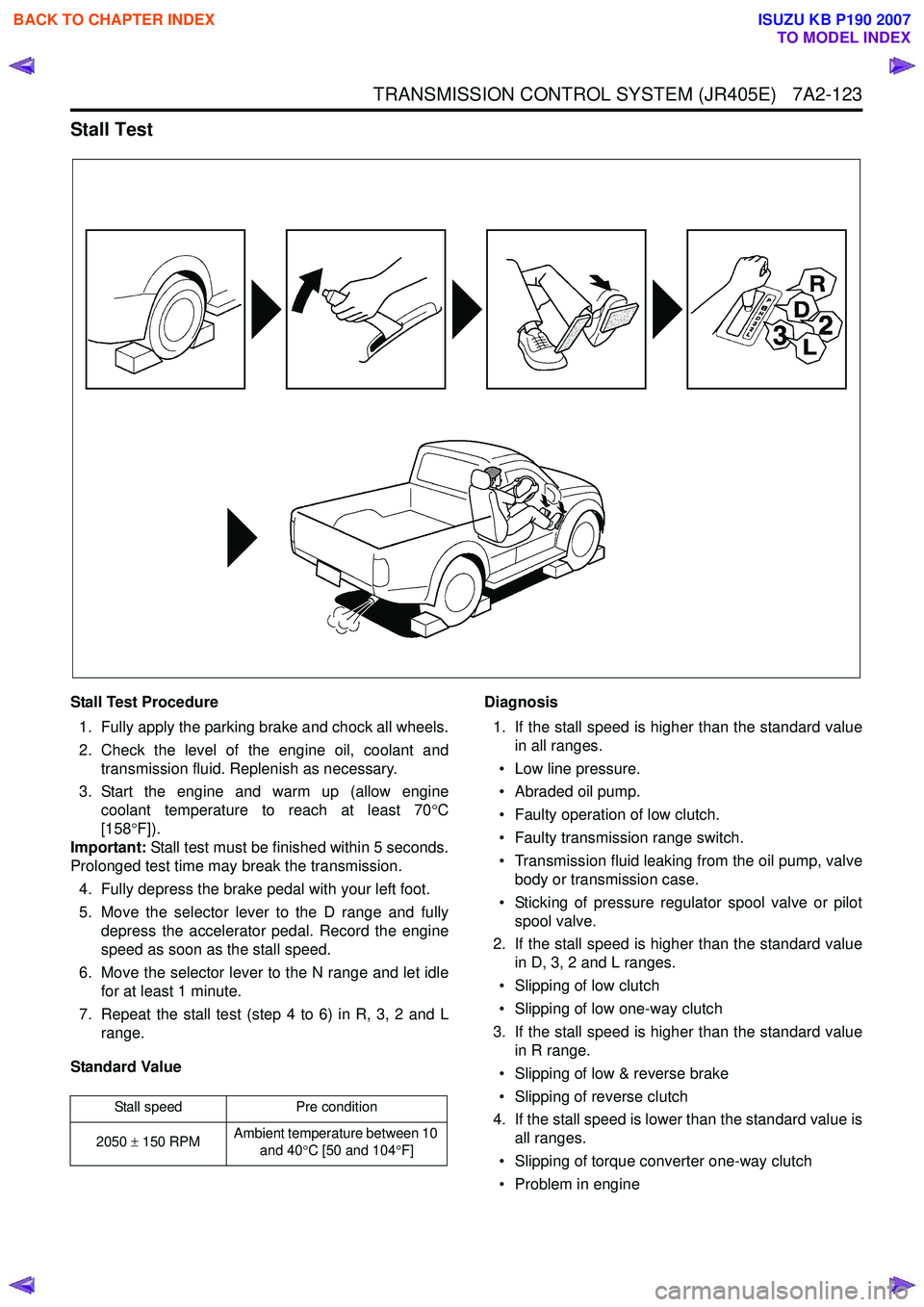
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-123
Stall Test
Stall Test Procedure1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Stall test must be finished within 5 seconds.
Prolonged test time may break the transmission.
4. Fully depress the brake pedal with your left foot.
5. Move the selector lever to the D range and fully depress the accelerator pedal. Record the engine
speed as soon as the stall speed.
6. Move the selector lever to the N range and let idle for at least 1 minute.
7. Repeat the stall test (step 4 to 6) in R, 3, 2 and L range.
Standard Value Diagnosis
1. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in all ranges.
• Low line pressure.
• Abraded oil pump.
• Faulty operation of low clutch.
• Faulty transmission range switch.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the oil pump, valve body or transmission case.
• Sticking of pressure regulator spool valve or pilot spool valve.
2. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in D, 3, 2 and L ranges.
• Slipping of low clutch
• Slipping of low one-way clutch
3. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in R range.
• Slipping of low & reverse brake
• Slipping of reverse clutch
4. If the stall speed is lower than the standard value is all ranges.
• Slipping of torque converter one-way clutch
• Problem in engine
Stall speed Pre condition
2050 ± 150 RPM Ambient temperature between 10
and 40 °C [50 and 104 °F]
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4409 of 6020
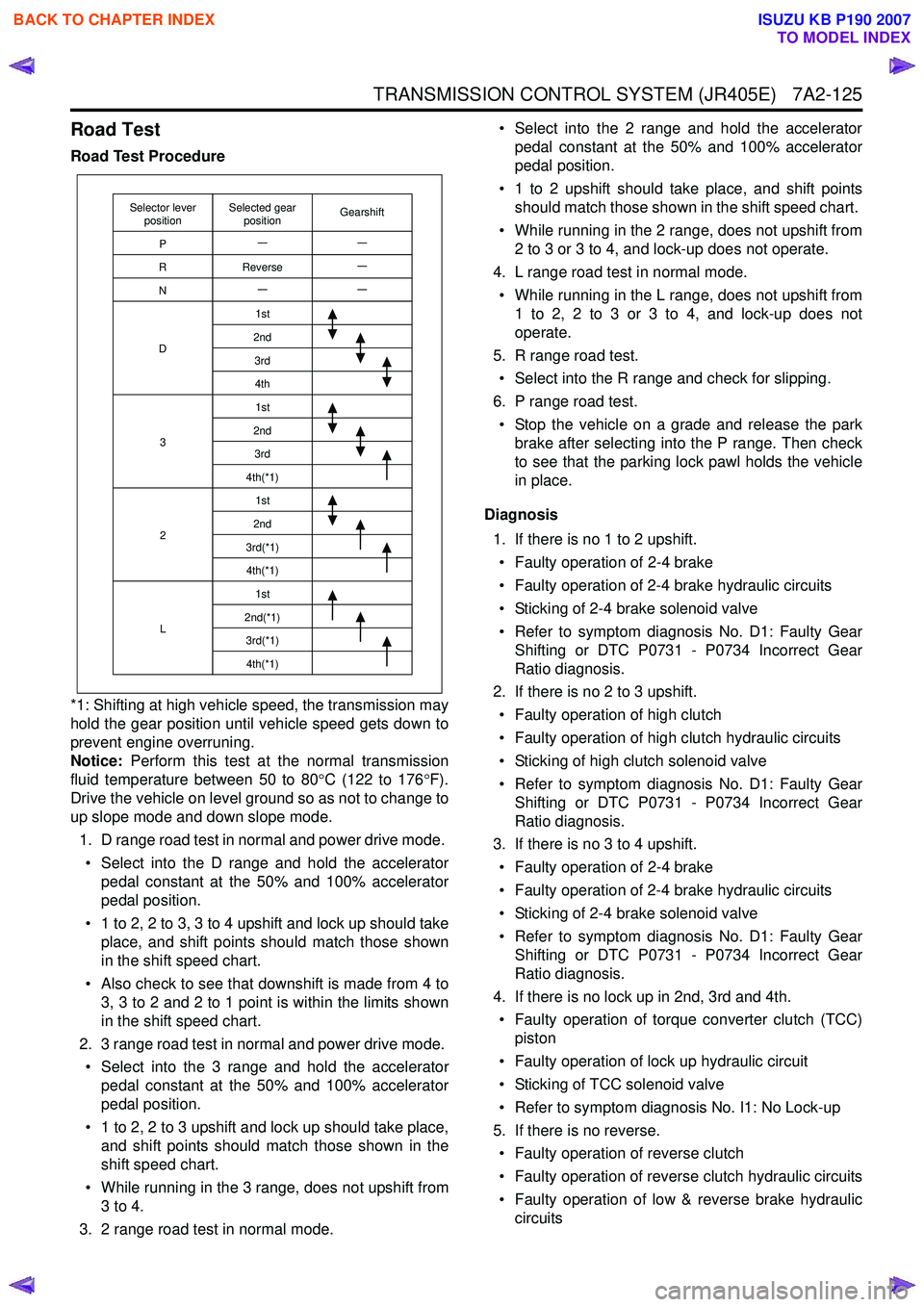
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-125
Road Test
Road Test Procedure
*1: Shifting at high vehicle speed, the transmission may
hold the gear position until vehicle speed gets down to
prevent engine overruning.
Notice: Perform this test at the normal transmission
fluid temperature between 50 to 80 °C (122 to 176 °F).
Drive the vehicle on level ground so as not to change to
up slope mode and down slope mode.
1. D range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the D range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3, 3 to 4 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown
in the shift speed chart.
• Also check to see that downshift is made from 4 to 3, 3 to 2 and 2 to 1 point is within the limits shown
in the shift speed chart.
2. 3 range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the 3 range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the
shift speed chart.
• While running in the 3 range, does not upshift from 3 to 4.
3. 2 range road test in normal mode. • Select into the 2 range and hold the accelerator
pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2 upshift should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the shift speed chart.
• While running in the 2 range, does not upshift from 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not operate.
4. L range road test in normal mode.
• While running in the L range, does not upshift from 1 to 2, 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not
operate.
5. R range road test. • Select into the R range and check for slipping.
6. P range road test. • Stop the vehicle on a grade and release the park brake after selecting into the P range. Then check
to see that the parking lock pawl holds the vehicle
in place.
Diagnosis 1. If there is no 1 to 2 upshift.• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
2. If there is no 2 to 3 upshift.
• Faulty operation of high clutch
• Faulty operation of high clutch hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of high clutch solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
3. If there is no 3 to 4 upshift.
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
4. If there is no lock up in 2nd, 3rd and 4th. • Faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
• Faulty operation of lock up hydraulic circuit
• Sticking of TCC solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. I1: No Lock-up
5. If there is no reverse. • Faulty operation of reverse clutch
• Faulty operation of reverse clutch hydraulic circuits
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake hydraulic circuits
Selector lever
position GearshiftSelected gear
position
P
R
N
D
3
2
L 1st
2nd 3rd4th1st
2nd 3rd
4th(*1) 1st
2nd
3rd(*1) 4th(*1) 1st
2nd(*1) 3rd(*1)4th(*1)
Reverse
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007