Page 4243 of 6020
7A1-4 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
Model JR405E
Torque Converter Type Three-Elements, One-Stage & Two-Phases
Type W ith Lock-up Function
Torque Converter Stall Torque Ratio 1.8
Name ATF DEXRON III
Quantity L (US gal/Imp gal) 9.2-9.6 (2.43-2.54/2.02-2.11) AT F
Cooling System Water Cooled Type (Radiator)
1st 2.785
2nd 1.545
3rd 1.000
4th (Over Drive) 0.694
Gear Ratio
Reverse 2.272
Low Clutch L/C 7
High Clutch H/C 5
Reverse Clutch R/C 2Number of Discs Clutch
Low One-way Clutch L/O.C 1 Set
Low & Reverse
Brake L&R/B 6
Brake
2-4 Brake 2-4/B 5 Number of Discs
Sun Gear
33
Pinion
Gear 21Front Planetary
Ring Gear 75
Sun Gear 42
Pinion
Gear 17
Planetary Gear Unit
Rear Planetary Ring Gear 75 Number of Teeth
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4247 of 6020
7A1-8 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
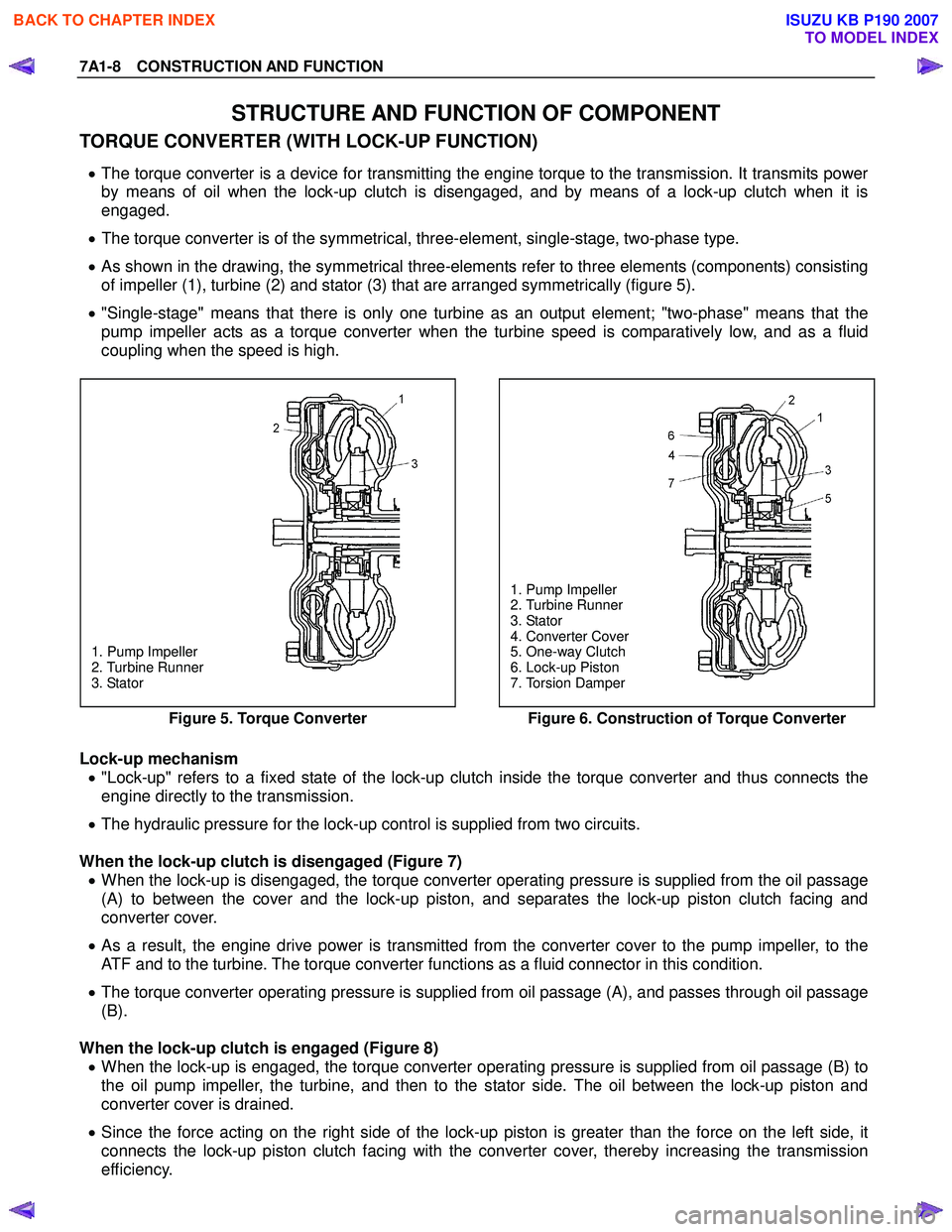
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF COMPONENT
TORQUE CONVERTER (WITH LOCK-UP FUNCTION)
• The torque converter is a device for transmitting the engine torque to the transmission. It transmits power
by means of oil when the lock-up clutch is disengaged, and by means of a lock-up clutch when it is
engaged.
• The torque converter is of the symmetrical, three-element, single-stage, two-phase type.
• As shown in the drawing, the symmetrical three-elements refer to three elements (components) consisting
of impeller (1), turbine (2) and stator (3) that are arranged symmetrically (figure 5).
• "Single-stage" means that there is only one turbine as an output element; "two-phase" means that the
pump impeller acts as a torque converter when the turbine speed is comparatively low, and as a fluid
coupling when the speed is high.
1. Pump Impeller
2. Turbine Runner
3. Stator
1. Pump Impeller
2. Turbine Runner
3. Stator
4. Converter Cover
5. One-way Clutch
6. Lock-up Piston
7. Torsion Damper
Figure 5. Torque Converter
Figure 6. Construction of Torque Converter
Lock-up mechanism
• "Lock-up" refers to a fixed state of the lock-up clutch inside the torque converter and thus connects the
engine directly to the transmission.
• The hydraulic pressure for the lock-up control is supplied from two circuits.
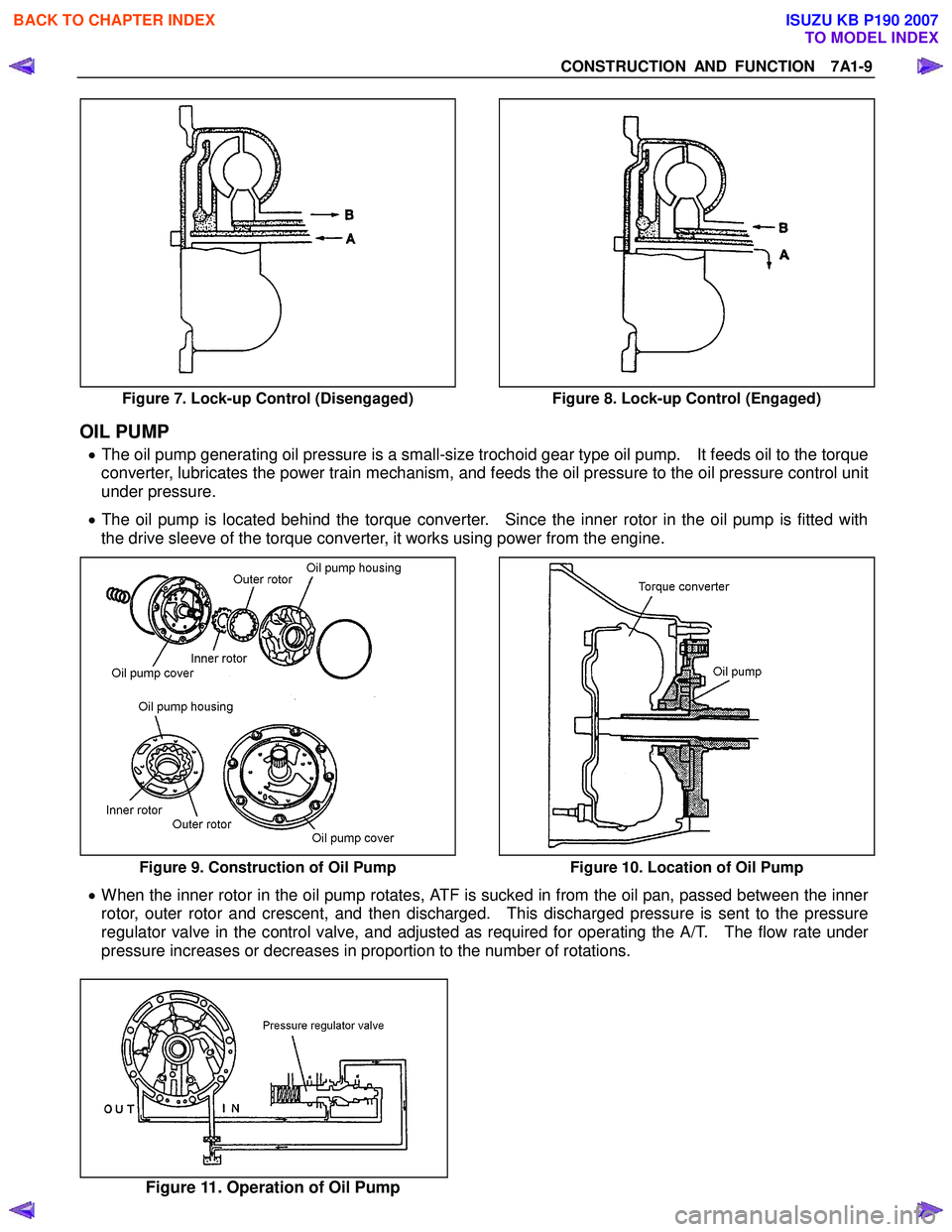
When the lock-up clutch is disengaged (Figure 7) • When the lock-up is disengaged, the torque converter operating pressure is supplied from the oil pass age
(A) to between the cover and the lock-up piston, and separates the lock-up piston clutch facing and
converter cover.
• As a result, the engine drive power is transmitted from the converter cover to the pump impeller, to the
ATF and to the turbine. The torque converter functions as a fluid connector in this condition.
• The torque converter operating pressure is supplied from oil passage (A), and passes through oil passage
(B).
When the lock-up clutch is engaged (Figure 8) • When the lock-up is engaged, the torque converter operating pressure is supplied from oil passage (B) to
the oil pump impeller, the turbine, and then to the stator side. The oil between the lock-up piston and
converter cover is drained.
• Since the force acting on the right side of the lock-up piston is greater than the force on the left side, it
connects the lock-up piston clutch facing with the converter cover, thereby increasing the transmission
efficiency.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4248 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-9
Figure 7. Lock-up Control (Disengaged) Figure 8. Lock-up Control (Engaged)
OIL PUMP
• The oil pump generating oil pressure is a small-size trochoid gear type oil pump. It feeds oil to the torque
converter, lubricates the power train mechanism, and feeds the oil pressure to the oil pressure control unit
under pressure.
• The oil pump is located behind the torque converter. Since the inner rotor in the oil pump is fitted with
the drive sleeve of the torque converter, it works using power from the engine.
Figure 9. Construction of Oil Pump Figure 10. Location of Oil Pump
• When the inner rotor in the oil pump rotates, ATF is sucked in from the oil pan, passed between the inner
rotor, outer rotor and crescent, and then discharged. This discharged pressure is sent to the pressure
regulator valve in the control valve, and adjusted as required for operating the A/T. The flow rate under
pressure increases or decreases in proportion to the number of rotations.
Figure 11. Operation of Oil Pump
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4249 of 6020

7A1-10 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
INPUT SHAFT
• The input shaft has some oil holes, through which lubricating ATF is supplied to the torque converter, the
bearings, etc.
• The input shaft is fitted to the turbine runner in the torque converter, the reverse & high clutch drum and
the rear sun gear by means of the spline. Therefore, the engine driving force received by the torque
converter is transmitted to the reverse & high clutch drum and rear sun gear.
OUTPUT SHAFT
• The output shaft has some oil holes, through which the lubricating ATF is supplied to the bearings, the
planetary gear unit, etc.
• The output shaft transmits the engine driving force from the planetary gear to the propeller shaft.
• The front internal gear is fitted with the rear carrier assembly by spline. The parking gear is also fitted by
spline. By fixing this gear mechanically, the output shaft is fixed as required when parking the vehicle.
GEAR SHIFTING MECHANISM
• The JR405E consists of two sets of planetary gears, three multiple plate clutches, two multiple plate
brakes and a one-way clutch. They are activated in different combinations in any of four forward and one
reverse gear positions.
Principle of gear shifting (Figure 12) • Planetary gears have the advantage of a compact configuration because of the way they are constructed
with a single central shaft.
• Also, unlike the manual transmission gears that require changing of the gear mesh, the gear ratio of the
planetary gears can be changed more easily by locking, releasing or rotating only some of their parts.
• A planetary gear is made up of a sun gear (1) at its center, and pinion gears (2) each of which rotates
about its own center and around the sun gear, as shown. They are all contained within the internal gear
(3).
• Also, since the pinion gears are further supported by the planetary carrier (4), they rotate as a unit in the
same direction, and at the same rate.
• As shown below, each planetary gear is constructed of three elements; a sun gear, pinion gears, an
internal gear and a planetary carrier. Gear shifting is achieved by conditioning two of the three elements,
namely the sun gear, the internal gear and planetary carrier.
• The planetary gears are locked by the clutch, brake and one-way clutch according to the gear shifting.
1. Sun Gear
2. Pinion Gear
3. Internal Gear
4. Planetary Carrier
Figure 12. Planetary Gear
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4280 of 6020
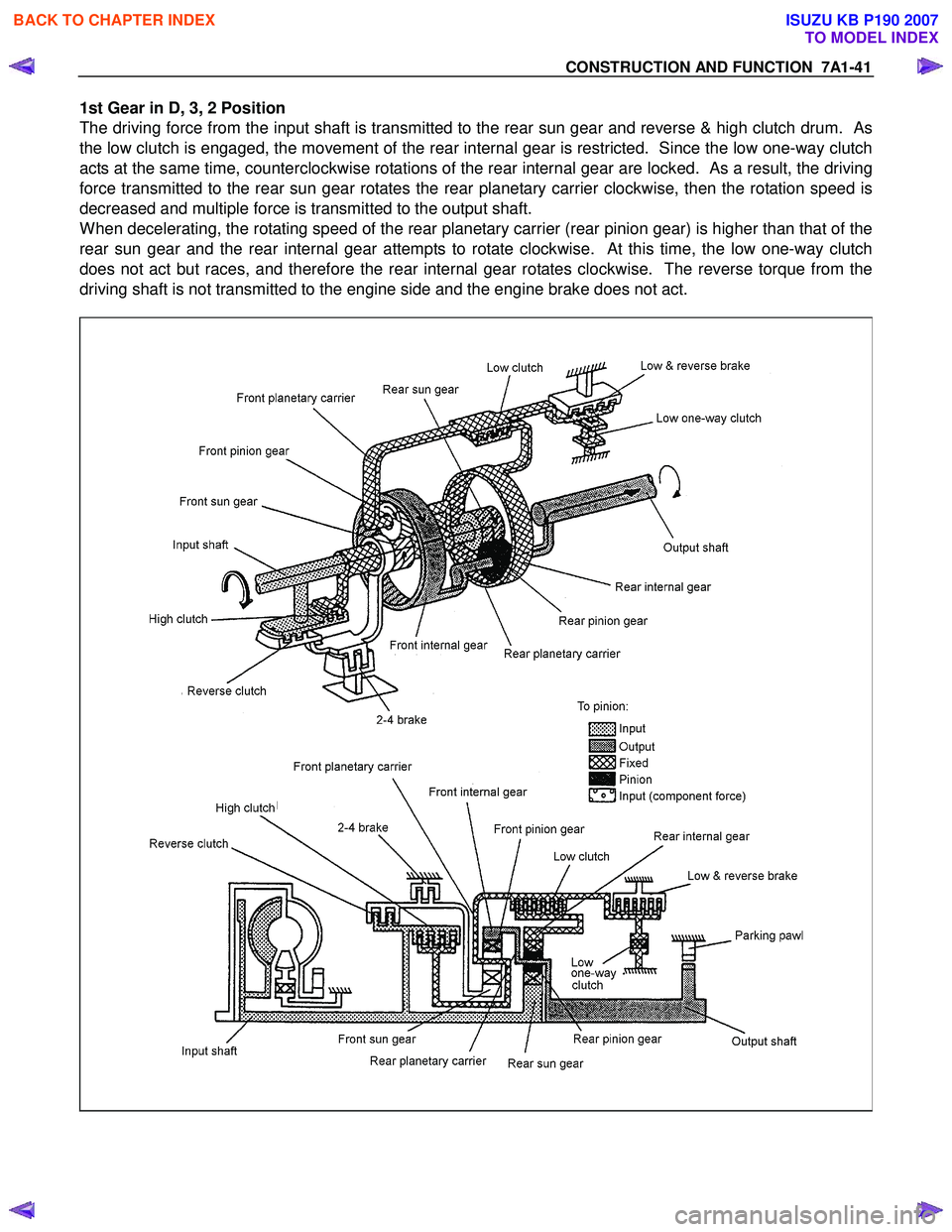
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-41
1st Gear in D, 3, 2 Position
The driving force from the input shaft is transmitted to the rear sun gear and reverse & high clutch drum. As
the low clutch is engaged, the movement of the rear internal gear is restricted. Since the low one-way clutch
acts at the same time, counterclockwise rotations of the rear internal gear are locked. As a result, the driving
force transmitted to the rear sun gear rotates the rear planetary carrier clockwise, then the rotation speed is
decreased and multiple force is transmitted to the output shaft.
When decelerating, the rotating speed of the rear planetary carrier (rear pinion gear) is higher than that of the
rear sun gear and the rear internal gear attempts to rotate clockwise. At this time, the low one-way clutch
does not act but races, and therefore the rear internal gear rotates clockwise. The reverse torque from the
driving shaft is not transmitted to the engine side and the engine brake does not act.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4281 of 6020
7A1-42 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
1st Gear in L Position
The basic mechanism is the same as in the D, 3, and 2 positions. To apply the engine brake, the low &
reverse brake is engaged to restrict the movement of the low one-way clutch.
When decelerating, as the rear internal gear is fixed, reverse torque from the drive shaft is transmitted to the
engine side so that the engine brake is applied.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4286 of 6020
7A2-2 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
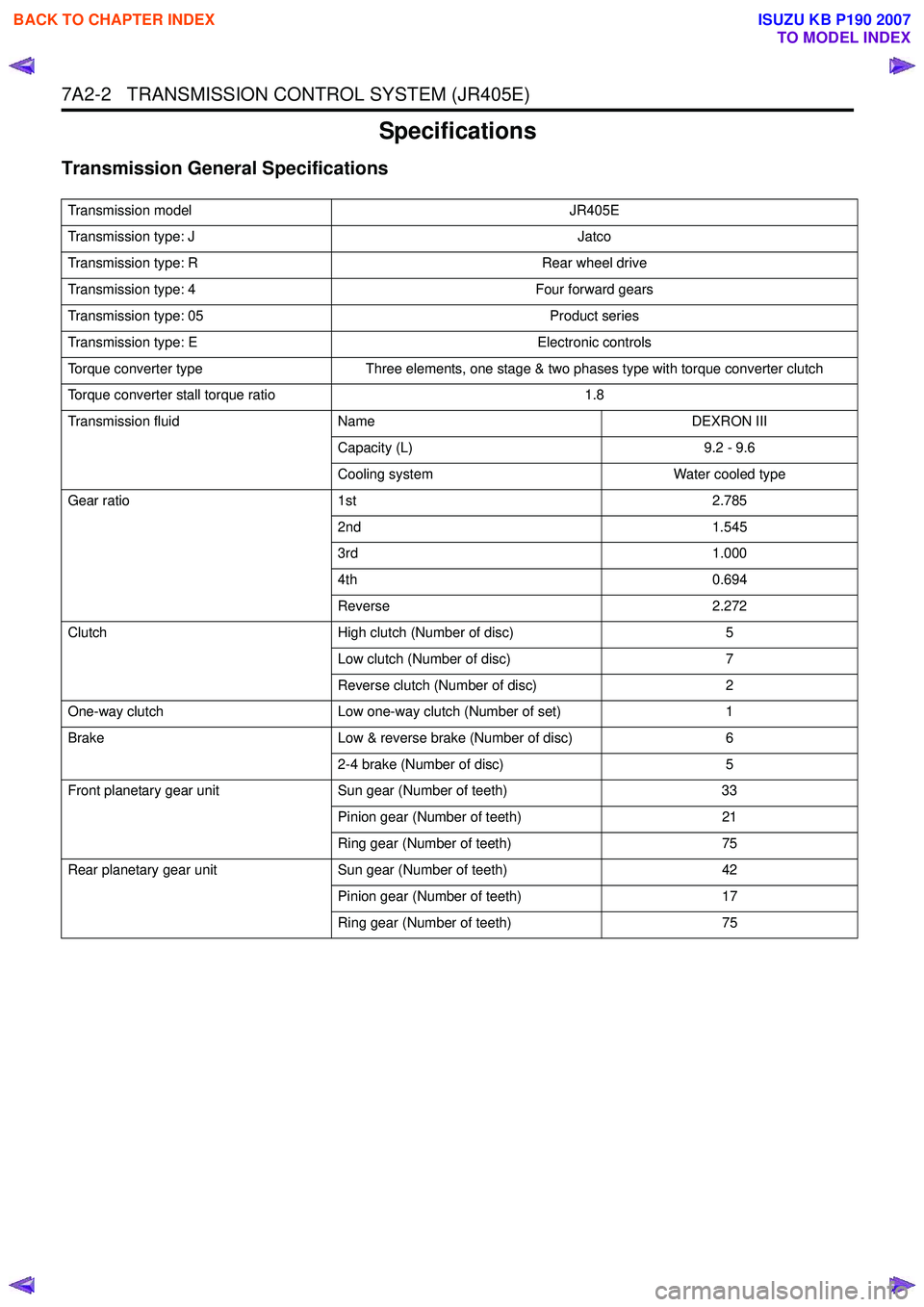
Specifications
Transmission General Specifications
Transmission modelJR405E
Transmission type: J Jatco
Transmission type: R Rear wheel drive
Transmission type: 4 Four forward gears
Transmission type: 05 Product series
Transmission type: E Electronic controls
Torque converter type Three elements, one stage & two phases type with torque converter clutch
Torque converter stall torque ratio 1.8
Transmission fluid Name DEXRON III
Capacity (L) 9.2 - 9.6
Cooling system Water cooled type
Gear ratio 1st 2.785
2nd 1.545
3rd 1.000
4th 0.694
Reverse 2.272
Clutch High clutch (Number of disc) 5
Low clutch (Number of disc) 7
Reverse clutch (Number of disc) 2
One-way clutch Low one-way clutch (Number of set) 1
Brake Low & reverse brake (Number of disc) 6
2-4 brake (Number of disc) 5
Front planetary gear unit Sun gear (Number of teeth) 33
Pinion gear (Number of teeth) 21
Ring gear (Number of teeth) 75
Rear planetary gear unit Sun gear (Number of teeth) 42
Pinion gear (Number of teeth) 17
Ring gear (Number of teeth) 75
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4298 of 6020
7A2-14 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Legend1. Torque converter housing
2. Torque converter
3. High clutch
4. Reverse clutch
5. 2-4 brake
6. Low clutch
7. Low & reverse brake 8. Output shaft
9. Extension housing
10. Input shaft 11 . O i l p u m p
12. Valve body
13. Low one-way clutch
14. Parking gear
High Clutch
Legend 1. Dish plate
2. High clutch piston
3. Centrifugal cancel cover
4. Centrifugal balance chamber
5. Driven plate
6. Drive plate
7. Retaining plate
8. Snap ring
Low Clutch
Legend
1. Drive plate
2. Driven plate
3. Retaining plate
4. Snap ring
5. Centrifugal cancel cover
6. Centrifugal balance chamber
7. Dish plate
8. Low clutch piston
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007