2007 INFINITI QX56 ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 1983 of 3061

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GI-17
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
Harness Indication
14 Wire color• This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light GreenBR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description • This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch• This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts • Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code• This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow• Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
• A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on circuit
operation.
20 System branch• This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing• This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
• The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preceding
pages.
22 Shielded line • The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23Component box in
wave line• This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name • This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number• This shows the connector number.
• The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
•Example: M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in lo-
cating connectors.
26 Ground (GND)• The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the ground-
ed connector.
27 Ground (GND)• This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views • This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component• Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color• This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31Fusible link and fuse
box• This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of "POW-
ER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area• This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details. Num-
berItem Description
Page 2024 of 3061
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
GW-5
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
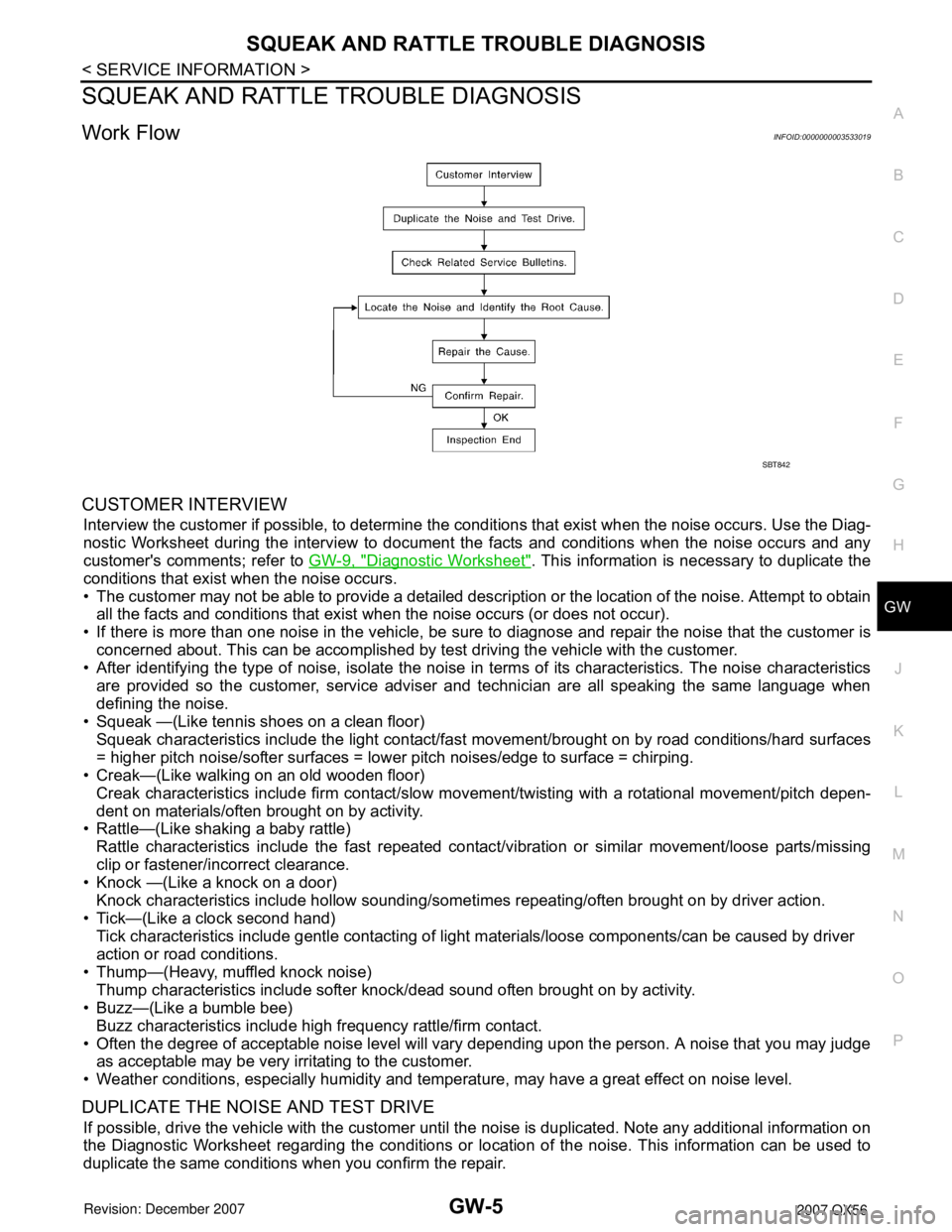
Work FlowINFOID:0000000003533019
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to GW-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842
Page 2116 of 3061
IP-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
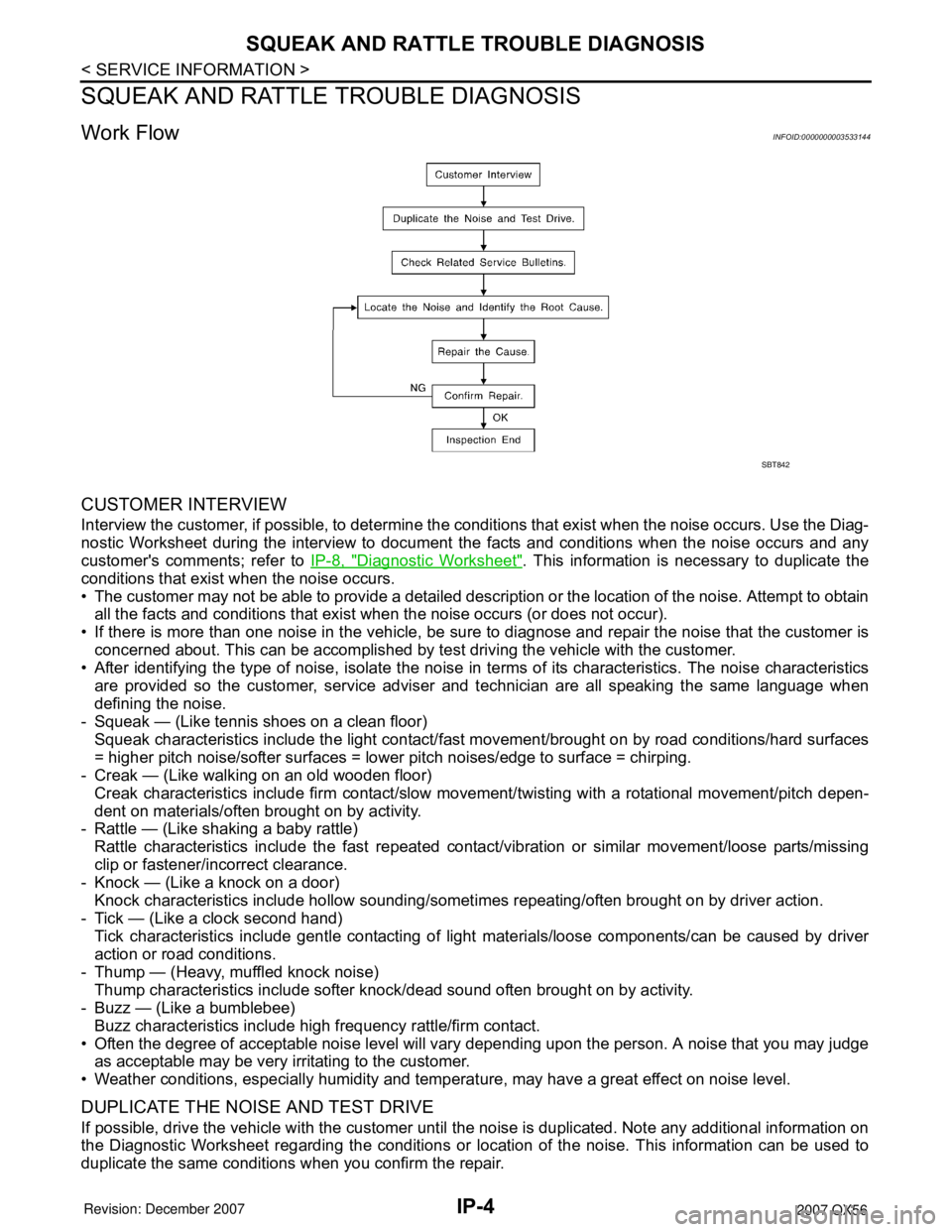
Work FlowINFOID:0000000003533144
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer, if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
- Squeak — (Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
- Creak — (Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
- Rattle — (Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
- Knock — (Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
- Tick — (Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
- Thump — (Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
- Buzz — (Like a bumblebee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842
Page 2212 of 3061
HEADLAMP (FOR USA)
LT-5
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
N
O
P
HEADLAMP (FOR USA)
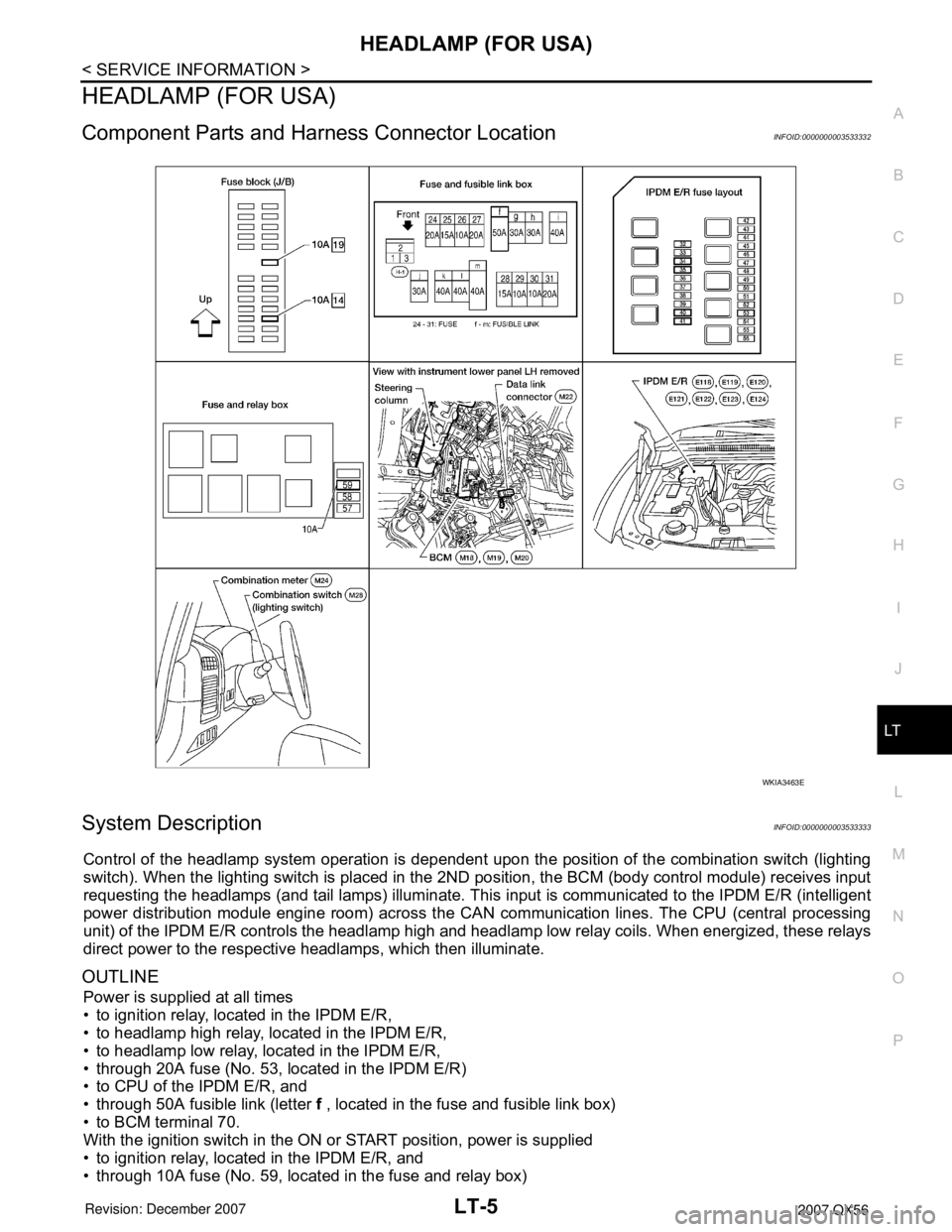
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationINFOID:0000000003533332
System DescriptionINFOID:0000000003533333
Control of the headlamp system operation is dependent upon the position of the combination switch (lighting
switch). When the lighting switch is placed in the 2ND position, the BCM (body control module) receives input
requesting the headlamps (and tail lamps) illuminate. This input is communicated to the IPDM E/R (intelligent
power distribution module engine room) across the CAN communication lines. The CPU (central processing
unit) of the IPDM E/R controls the headlamp high and headlamp low relay coils. When energized, these relays
direct power to the respective headlamps, which then illuminate.
OUTLINE
Power is supplied at all times
• to ignition relay, located in the IPDM E/R,
• to headlamp high relay, located in the IPDM E/R,
• to headlamp low relay, located in the IPDM E/R,
• through 20A fuse (No. 53, located in the IPDM E/R)
• to CPU of the IPDM E/R, and
• through 50A fusible link (letter f , located in the fuse and fusible link box)
• to BCM terminal 70.
With the ignition switch in the ON or START position, power is supplied
• to ignition relay, located in the IPDM E/R, and
• through 10A fuse (No. 59, located in the fuse and relay box)
WKIA3463E
Page 2281 of 3061

LT-74
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
COMBINATION SWITCH
If CONSULT-II is used with no connection of CONSULT-II CONVERTER, malfunctions might be
detected in self-diagnosis depending on control unit which carries out CAN communication.
1. Connect CONSULT-II, and select "COMB SW" on "SELECT
TEST ITEM" screen.
2. Select "DATA MONITOR".
3. Select "START", and confirm that other switches in malfunction-
ing system operate normally.
Example: When auto light switch is malfunctioning, confirm that
"FRONT WIPER LOW" and "FRONT WIPER INT" in System 3,
to which the auto light switch belongs, turn ON-OFF normally.
Without CONSULT-II
Operate combination switch, and confirm that other switches in malfunctioning system operate normally.
Example: When auto light switch is malfunctioning, confirm that "FRONT WIPER LOW" and "FRONT WIPER
INT" in System 3, to which the auto light switch belongs, operate normally.
Check results
Other switches in malfunctioning system operate normally.>>Replace lighting switch or wiper switch.
Other switches in malfunctioning system do not operate normally.>>GO TO 3.
3.HARNESS INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM and combination switch connectors.
3. Check for continuity between BCM harness connector of the suspect system and the corresponding com-
bination switch connector terminals.
4. Check for continuity between each terminal of BCM harness connector in suspect malfunctioning system
and ground.
SKIA7075E
Sus-
pect
systemTe r m i n a l s
Continuity BCM Combination switch
Connector Terminal Connector Terminal
1
M18Input 1 6
M286
Ye s Output 1 36 1
2Input 2 5 7
Output 2 35 2
3Input 3 4 10
Output 3 34 3
4Input 4 3 9
Output 4 33 4
5Input 5 2 8
Output 5 32 5
LKIA0284E
Page 2468 of 3061
PG-66
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HARNESS CONNECTOR
HARNESS CONNECTOR
DescriptionINFOID:0000000003533849
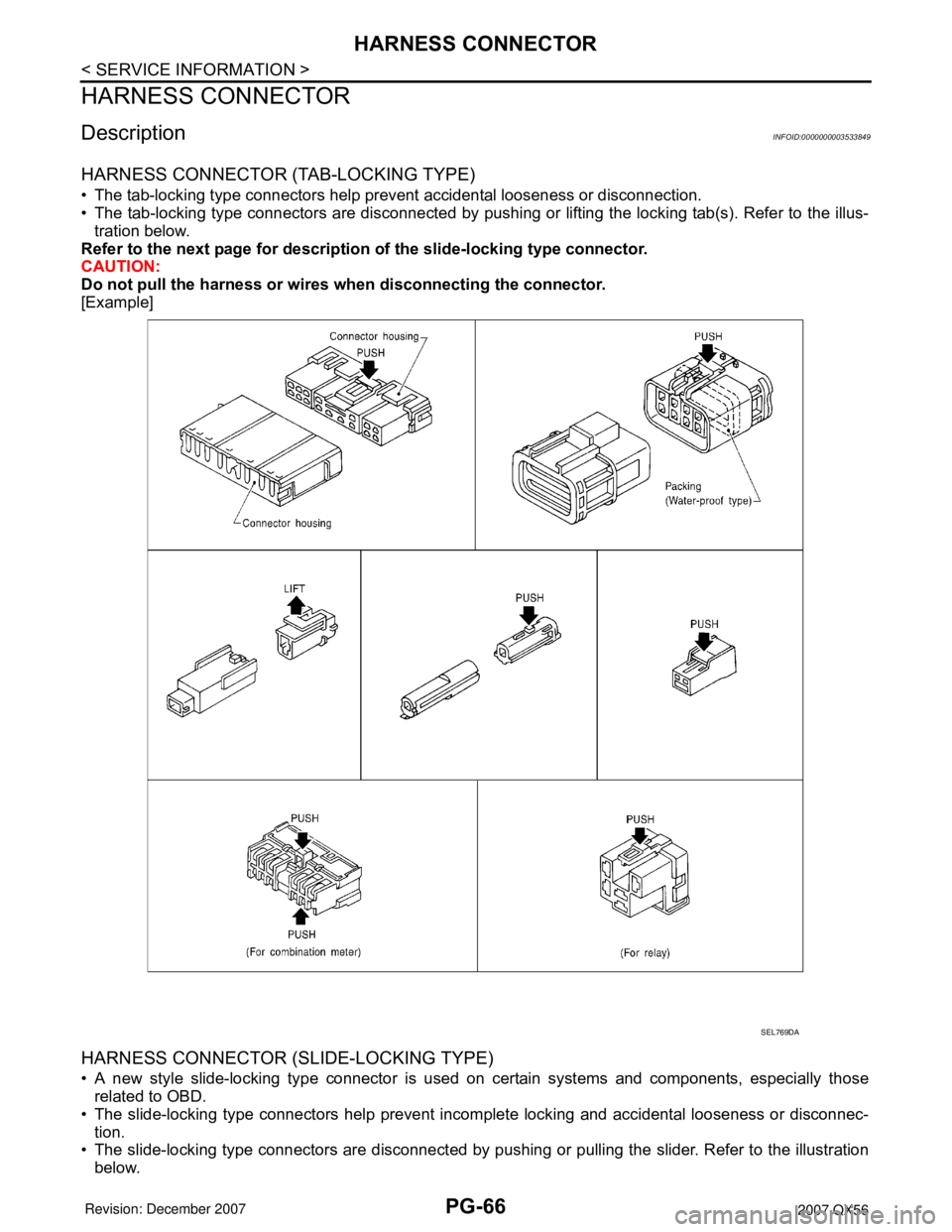
HARNESS CONNECTOR (TAB-LOCKING TYPE)
• The tab-locking type connectors help prevent accidental looseness or disconnection.
• The tab-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or lifting the locking tab(s). Refer to the illus-
tration below.
Refer to the next page for description of the slide-locking type connector.
CAUTION:
Do not pull the harness or wires when disconnecting the connector.
[Example]
HARNESS CONNECTOR (SLIDE-LOCKING TYPE)
• A new style slide-locking type connector is used on certain systems and components, especially those
related to OBD.
• The slide-locking type connectors help prevent incomplete locking and accidental looseness or disconnec-
tion.
• The slide-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or pulling the slider. Refer to the illustration
below.
SEL769DA
Page 2536 of 3061
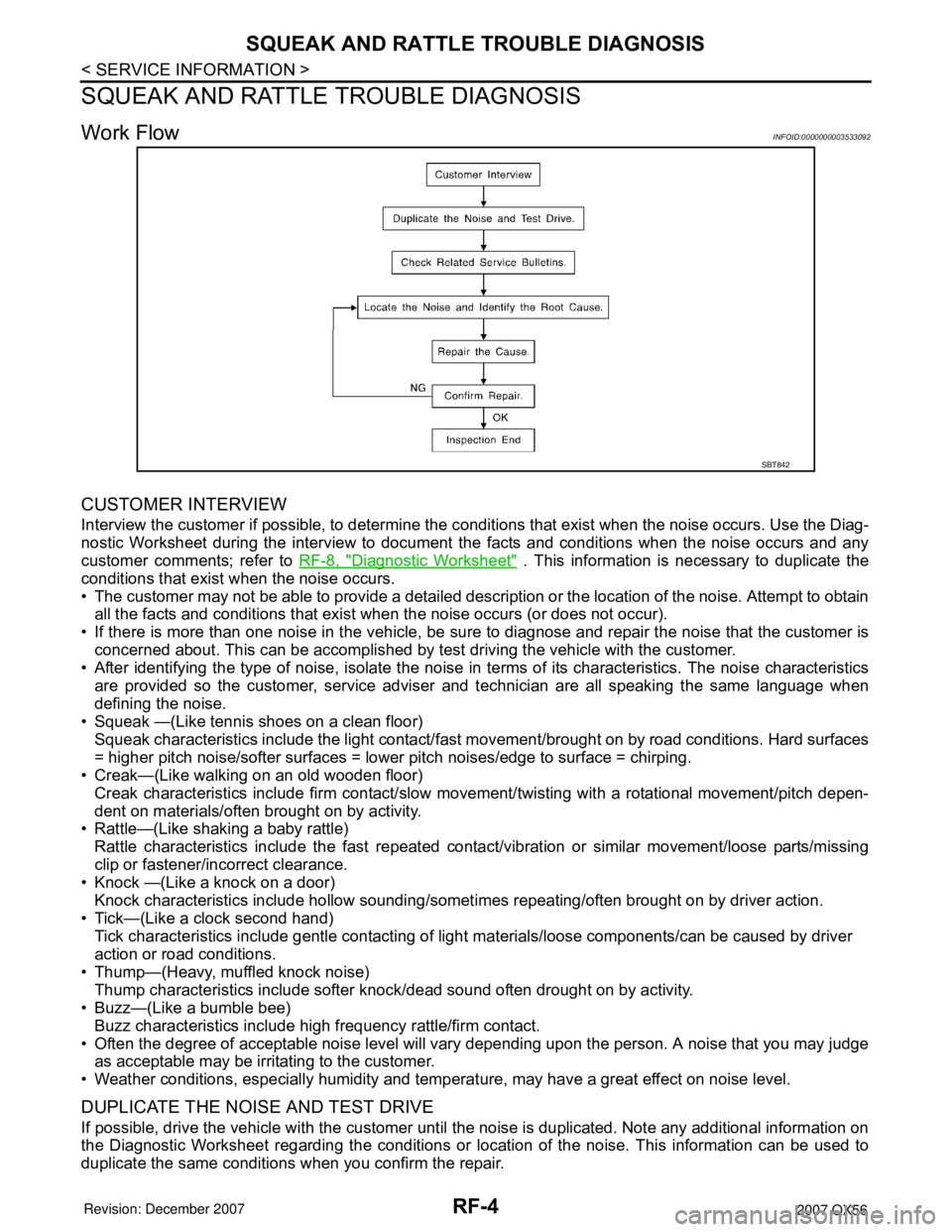
RF-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Work FlowINFOID:0000000003533092
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer comments; refer to RF-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions. Hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often drought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842
Page 2596 of 3061
RSU-6
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate RepairINFOID:0000000003532657
INTRODUCTION
The rear load leveling air suspension system uses an electronic con-
trol unit to control major functions. The control unit accepts input sig-
nals from the height sensor and controls compressor and exhaust
valve operation.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a rear load leveling air suspen-
sion system problem that occurs intermittently rather than continu-
ously. Most intermittent problems are caused by poor electrical
connections or faulty wiring. In this case, careful checking of suspi-
cious circuits may help prevent the replacement of good parts.
Before undertaking actual checks, take just a few minutes to talk with
a customer who approaches with an air suspension system com-
plaint. The customer is a very good source of information on such
problems, especially intermittent ones. Through discussion with the
customer, find out what symptoms are present and under what con-
ditions they occur.
Start your diagnosis by looking for basic mechanical problems first.
This is one of the best ways to troubleshoot concerns on an air sus-
pension system equipped vehicle. Also check related Service Bulle-
tins for information.
CLARIFY CONCERN
• A customer's description of a vehicle concern may vary depending
on the individual. It is important to clarify the customer's concern.
• Ask the customer about what symptoms are present under what
conditions. Use this information to reproduce the symptom.
SEF233G
SEF234G
SBR339B