Page 28 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINEEG-31
System
Outline
Engine
Immobilizer*
2
Prohibits fuel delivery and ignition if an attempt is made to start the engine with
an invalid ignition key.
Diagnosis
(See page EG-67)When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM diagnoses and memorizes the
failed section.
Fail-safe
(See page EG-67)When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM stops or controls the engine
according to the data already stored in memory.
*2: Models with Engine Immobilizer System
Page 46 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
185EG48
185EG49
185EG50
287EG34
185EG48
185EG48
TDCLatest Timing
EX IN
BDC
To Advance Side
EX IN
EX IN
To Advance Side
EX IN
To Retard Side
Latest Timing
EX IN
Latest Timing
EX INEG-49
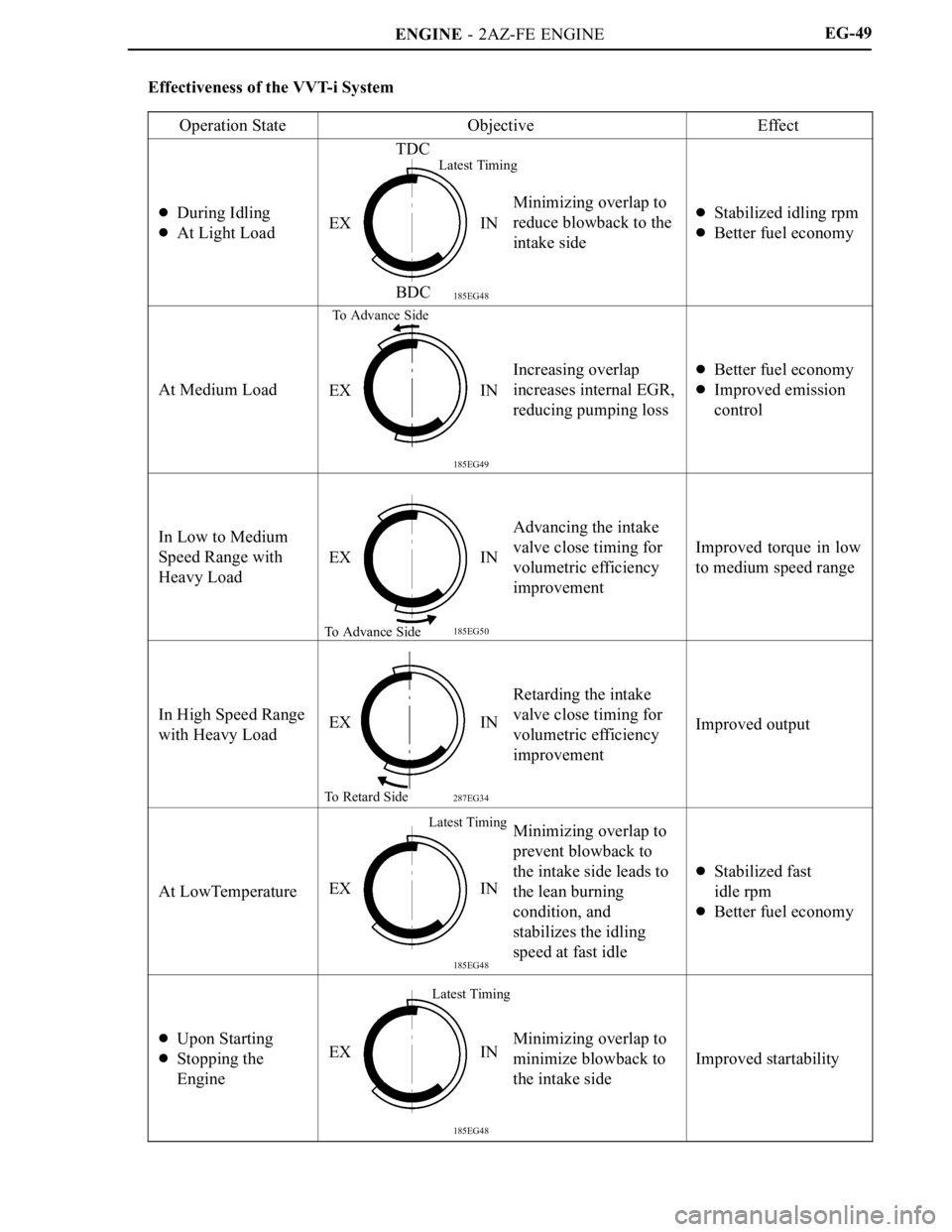
Effectiveness of the VVT-i System
Operation State
ObjectiveEffect
During Idling
At Light Load
Minimizing overlap to
reduce blowback to the
intake sideStabilized idling rpm
Better fuel economy
At Medium Load
Increasing overlap
increases internal EGR,
reducing pumping lossBetter fuel economy
Improved emission
control
In Low to Medium
Speed Range with
Heavy LoadAdvancing the intake
valve close timing for
volumetric efficiency
improvement
Improved torque in low
to medium speed range
In High Speed Range
with Heavy Load
Retarding the intake
valve close timing for
volumetric efficiency
improvement
Improved output
At LowTemperature
Minimizing overlap to
prevent blowback to
the intake side leads to
the lean burning
condition, and
stabilizes the idling
speed at fast idle
Stabilized fast
idle rpm
Better fuel economy
Upon Starting
Stopping the
Engine
Minimizing overlap to
minimize blowback to
the intake side
Improved startability
Page 47 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
169EG36
HousingLock Pin
Intake Camshaft
Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Oil Pressure
At a Stop In Operation
Lock Pin
221EG17
To VVT-i Controller
(Advance Side)To V V T- i C o n t r o l l e r
(Retard Side)
Sleeve
Spring
Drain
Oil PressureDrain
Spool ValveCoil
Plunger EG-50
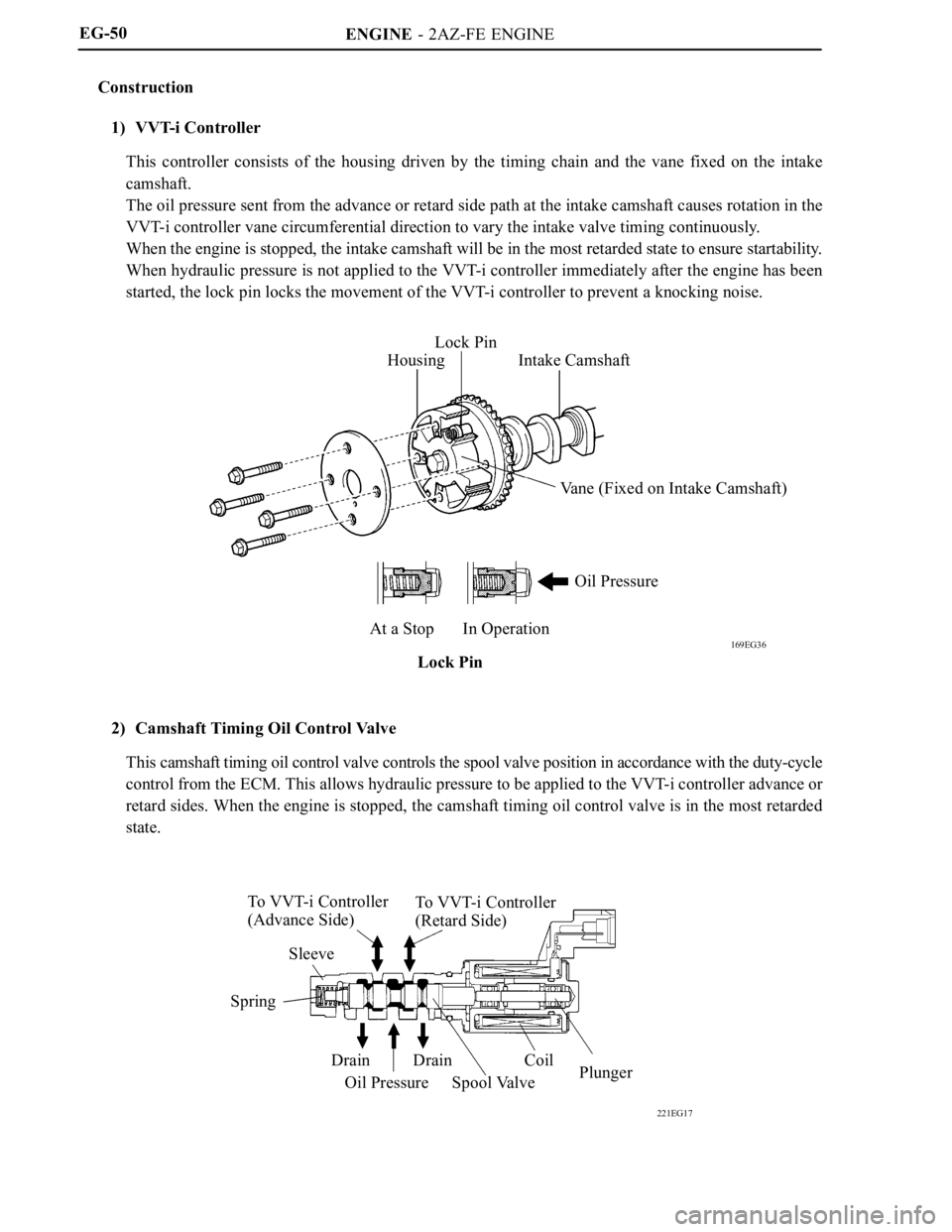
Construction
1) VVT-i Controller
This controller consists of the housing driven by the timing chain and the vane fixed on the intake
camshaft.
The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake camshaft causes rotation in the
VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing continuously.
When the engine is stopped, the intake camshaft will be in the most retarded state to ensure startability.
When hydraulic pressure is not applied to the VVT-i controller immediately after the engine has been
started, the lock pin locks the movement of the VVT-i controller to prevent a knocking noise.
2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
This camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve position in accordance with the duty-cycle
control from the ECM. This allows hydraulic pressure to be applied to the VVT-i controller advance or
retard sides. When the engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retarded
state.
Page 50 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
00REG18Y
Front Airbag
Sensor
(RH and LH)
Curtain Shield
Airbag Sensor*
(RH and LH)Airbag
Sensor
Side Airbag
Sensor*
(RH or LH)ECMCircuit
Opening
Relay
Fuel
Pump
Motor
: CANEG-53
9. Fuel Pump Control
A fuel cut control is used to stop the fuel pump when the SRS airbag is deployed at the front collision. In this
system, the airbag deployment signal from the airbag sensor is detected by the ECM, which turns OFF the
circuit opening relay.
After the fuel cut control has been activated, turning the ignition switch from OFF to ON cancels the fuel cut
control, and the engine can be restarted.
*: Models with SRS Driver, Front Passenger, Side and Curtain Shield Airbags
Page 98 of 2000

ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE EG-102
System
Outline
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor and
Oxygen Sensor Heater
ControlMaintains the temperature of the air-fuel ratio sensor or oxygen sensor at an
appropriate level to increase accuracy of detection of the oxygen
concentration in the exhaust gas.
Evaporative Emission
Control
[See page EG-131]
The ECM controls the purge flow of evaporative emission (HC) in the
canister in accordance with engine conditions.
Approximately five hours after the ignition switch has been turned OFF,
the ECM operates the canister pump module to detect any evaporative
emission leakage occurring in the EVAP (evaporative emission) control
system through changes in the EVAP control system pressure.
Engine ImmobilizerProhibits fuel delivery and ignition if an attempt is made to start the engine
with an invalid ignition key.
Diagnosis
[See page EG-132]When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM diagnoses and memorizes
the failed section.
Fail-safe
[See page EG-133]When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM stops or controls the engine
according to the data already stored in the memory.
Page 117 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
285EG62 285EG61 285EG60
285EG63
285EG59
285EG59 285EG59
Earliest Timing
(EX)Latest Timing
(IN)TDC
EX IN
BDC
To Advance
Side (EX)To R e t a r d
Side (IN)
EX IN
To Advance
Side (IN)To R e t a r d
Side (EX)
EX IN
EX IN
EX IN
To Retard
Side (EX)To Advance
Side (IN)
To R e t a r d
Side (IN)To A d v a n c e
Side (EX)
Earliest Timing
(EX)Latest Timing
(IN)
Earliest Timing
(EX)Latest Timing
(IN)
EX IN
EX IN
EG-121
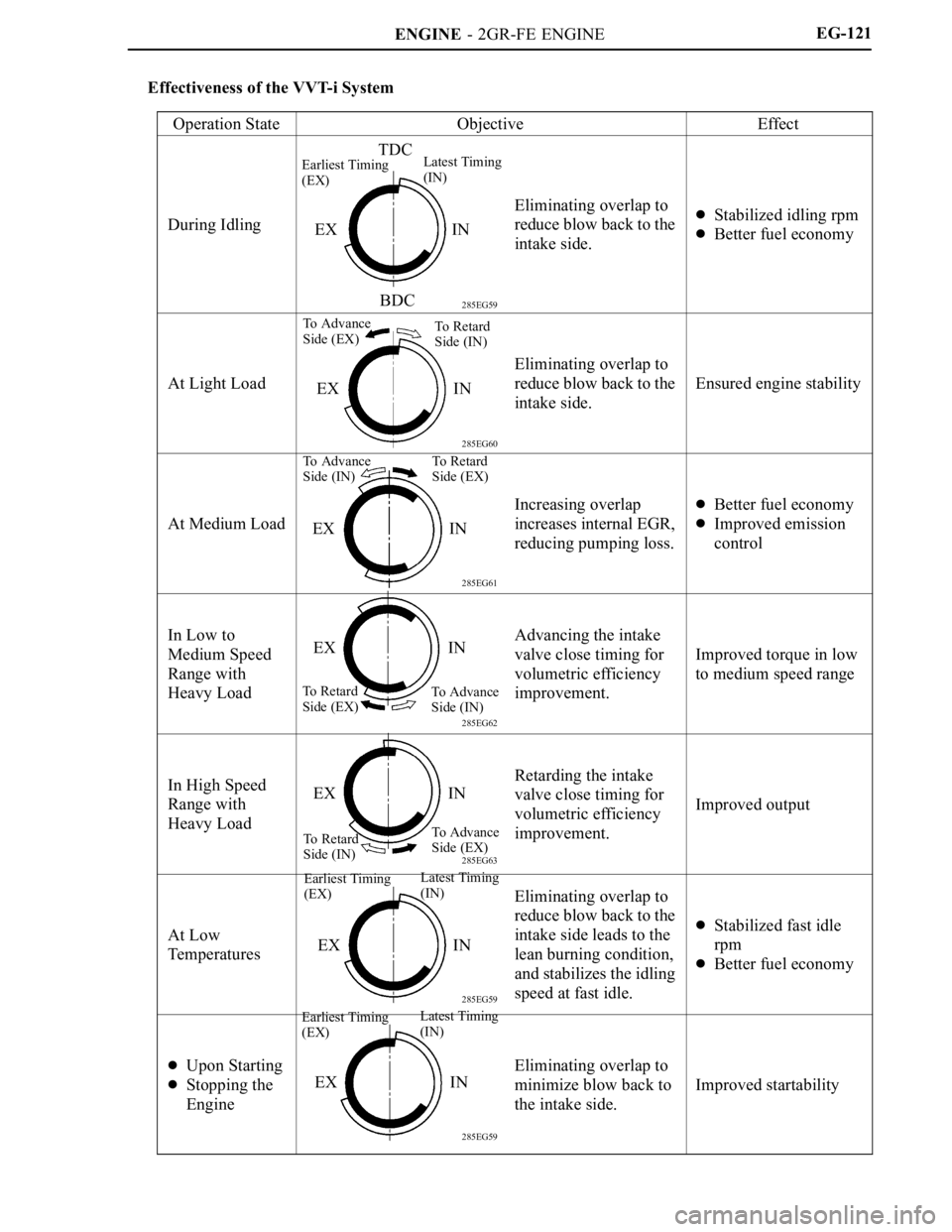
Effectiveness of the VVT-i System
Operation State
ObjectiveEffect
During Idling
Eliminating overlap to
reduce blow back to the
intake side.Stabilized idling rpm
Better fuel economy
At Light Load
Eliminating overlap to
reduce blow back to the
intake side.
Ensured engine stability
At Medium Load
Increasing overlap
increases internal EGR,
reducing pumping loss.Better fuel economy
Improved emission
control
In Low to
Medium Speed
Range with
Heavy LoadAdvancing the intake
valve close timing for
volumetric efficiency
improvement.
Improved torque in low
to medium speed range
In High Speed
Range with
Heavy LoadRetarding the intake
valve close timing for
volumetric efficiency
improvement.
Improved output
At Low
Temperatures
Eliminating overlap to
reduce blow back to the
intake side leads to the
lean burning condition,
and stabilizes the idling
speed at fast idle.
Stabilized fast idle
rpm
Better fuel economy
Upon Starting
Stopping the
Engine
Eliminating overlap to
minimize blow back to
the intake side.
Improved startability
Page 118 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
271EG93
Timing RotorHousingLock PinSprocket
Intake Camshaft
Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Oil Pressure
In Operation At a Stop
Lock Pin
281EG47
Housing
Advanced Angle Assist SpringVane (Fixed on Exhaust Camshaft)Lock PinExhaust Camshaft Sprocket EG-122
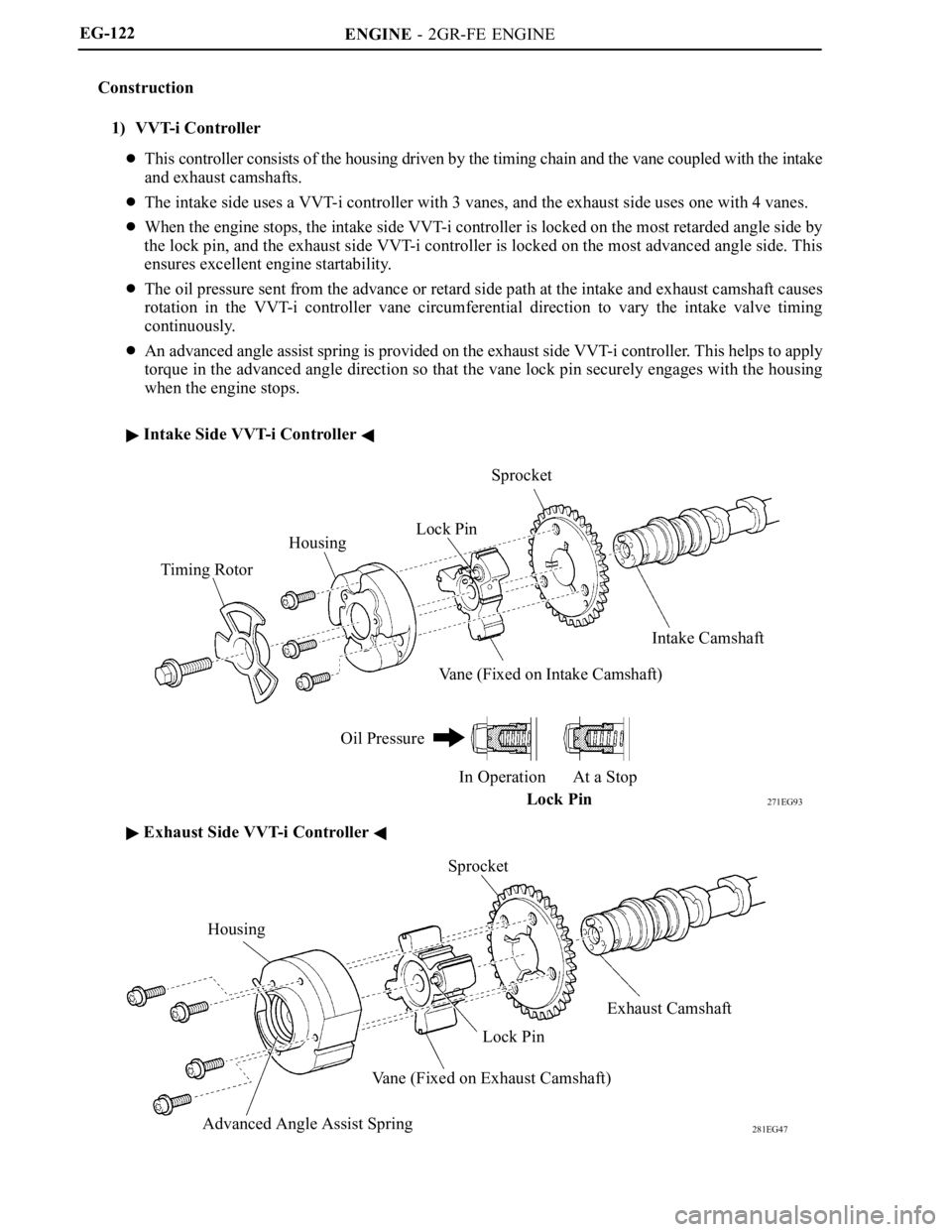
Construction
1) VVT-i Controller
This controller consists of the housing driven by the timing chain and the vane coupled with the intake
and exhaust camshafts.
The intake side uses a VVT-i controller with 3 vanes, and the exhaust side uses one with 4 vanes.
When the engine stops, the intake side VVT-i controller is locked on the most retarded angle side by
the lock pin, and the exhaust side VVT-i controller is locked on the most advanced angle side. This
ensures excellent engine startability.
The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake and exhaust camshaft causes
rotation in the VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing
continuously.
An advanced angle assist spring is provided on the exhaust side VVT-i controller. This helps to apply
torque in the advanced angle direction so that the vane lock pin securely engages with the housing
when the engine stops.
Intake Side VVT-i Controller
Exhaust Side VVT-i Controller
Page 208 of 2000
FU–62AZ-FE FUEL – FUEL SYSTEM
FU
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
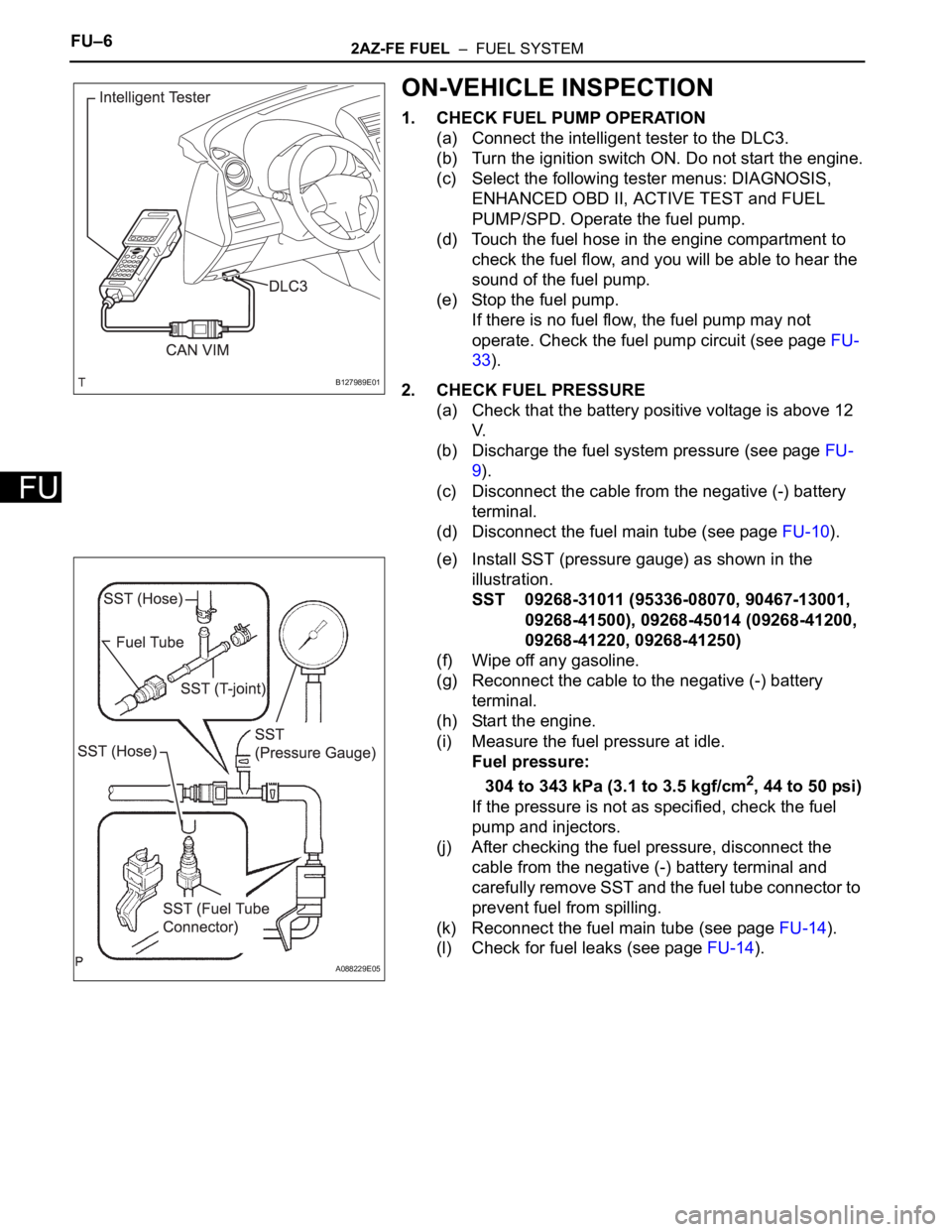
1. CHECK FUEL PUMP OPERATION
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON. Do not start the engine.
(c) Select the following tester menus: DIAGNOSIS,
ENHANCED OBD II, ACTIVE TEST and FUEL
PUMP/SPD. Operate the fuel pump.
(d) Touch the fuel hose in the engine compartment to
check the fuel flow, and you will be able to hear the
sound of the fuel pump.
(e) Stop the fuel pump.
If there is no fuel flow, the fuel pump may not
operate. Check the fuel pump circuit (see page FU-
33).
2. CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
(a) Check that the battery positive voltage is above 12
V.
(b) Discharge the fuel system pressure (see page FU-
9).
(c) Disconnect the cable from the negative (-) battery
terminal.
(d) Disconnect the fuel main tube (see page FU-10).
(e) Install SST (pressure gauge) as shown in the
illustration.
SST 09268-31011 (95336-08070, 90467-13001,
09268-41500), 09268-45014 (09268-41200,
09268-41220, 09268-41250)
(f) Wipe off any gasoline.
(g) Reconnect the cable to the negative (-) battery
terminal.
(h) Start the engine.
(i) Measure the fuel pressure at idle.
Fuel pressure:
304 to 343 kPa (3.1 to 3.5 kgf/cm
2, 44 to 50 psi)
If the pressure is not as specified, check the fuel
pump and injectors.
(j) After checking the fuel pressure, disconnect the
cable from the negative (-) battery terminal and
carefully remove SST and the fuel tube connector to
prevent fuel from spilling.
(k) Reconnect the fuel main tube (see page FU-14).
(l) Check for fuel leaks (see page FU-14).
B127989E01
A088229E05