Page 4403 of 5135
A85355
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector
Injector Spray Supply PumpExhaust Gas
Temperature
Sensor (on up stream)
ECM Exhaust
Gas
Exhaust Gas Temperature
Sensor (on down stream)
Exhaust Fuel Addition InjectorA/F Sensor DPNR Catalytic
Converter
Turbocharger
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−445
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The exhaust fuel addition injector is mounted on the exhaust port of the cylinder head, and low pressure is
provided to the injector by the feed pump in the supply pump. This injector adds fuel by a control signal from
the ECM.
This injector is used for two different controls: DPNR catalyst regeneration and nitrogen oxides (NOx) reduc-
tion.
Under the DPNR catalyst regeneration control, the injector adds fuel to raise a catalyst temperature.
In the other control, the injector helps the air−fuel ratio become RICH. As a result, NOx in the exhaust gas
will be reduced in response to the RICH air−fuel ratio.
Page 4404 of 5135
05−446
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
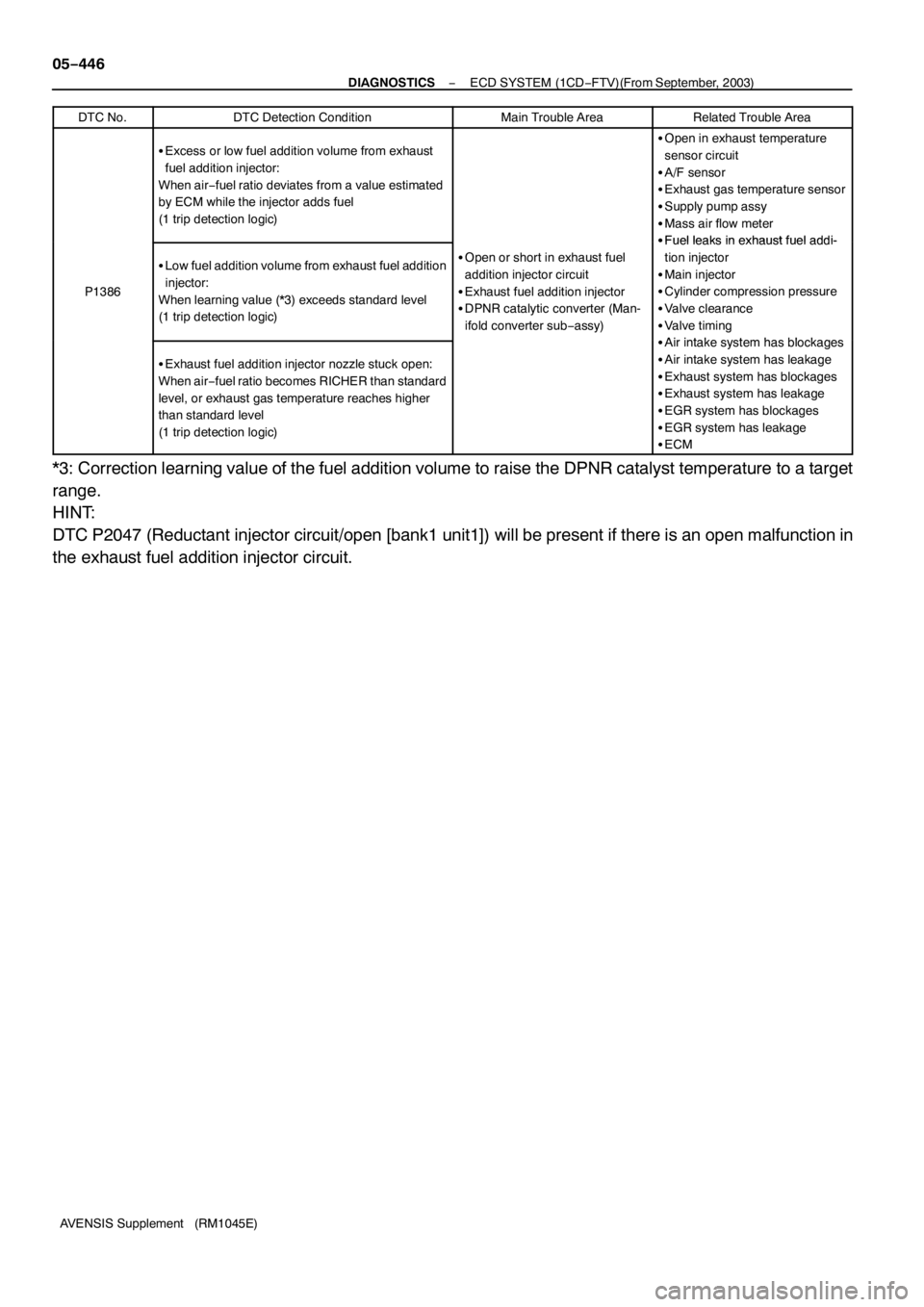
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E) DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionMain Trouble AreaRelated Trouble Area
SExcess or low fuel addition volume from exhaust
fuel addition injector:
When air−fuel ratio deviates from a value estimated
by ECM while the injector adds fuel
(1trip detection logic)SOpen in exhaust temperature
sensor circuit
SA/F sensor
SExhaust gas temperature sensor
SSupply pump assy
SMass air flow meter
SFuelleaksinexhaustfueladdi-
P1386
SLow fuel addition volume from exhaust fuel addition
injector:
When learning value (*3) exceeds standard level
(1trip detection logic)SOpen or short in exhaust fuel
addition injector circuit
SExhaust fuel addition injector
SDPNR catalytic converter (Man-
ifold converter sub−assy)
SFuelleaksinexhaustfueladdi-
tion injector
SMain injector
SCylinder compression pressure
SValve clearance
SValve timing
Airintakesystemhasblockages
SExhaust fuel addition injector nozzle stuck open:
When air−fuel ratio becomes RICHER than standard
level, or exhaust gas temperature reaches higher
than standard level
(1trip detection logic)
SAir intake system has blockages
SAir intake system has leakage
SExhaust system has blockages
SExhaust system has leakage
SEGR system has blockages
SEGR system has leakage
SECM
*3: Correction learning value of the fuel addition volume to raise the DPNR catalyst temperature to a target
range.
HINT:
DTC P2047 (Reductant injector circuit/open [bank1unit1]) will be present if there is an open malfunction in
the exhaust fuel addition injector circuit.
Page 4407 of 5135

−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −449
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
1 CHECK OTHER DTC OUTPUT(IN ADDITION TO P 1386)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON.
(c) Select the item ”DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES”.
(d) Read DTCs.
Result:
Display (DTC output)Proceed to
P1386A
P 1386 and other DTCsB
HINT:
If any other codes besides P 1386 are output, perform troubleshooting for those DTCs first.
B GO TO RELEVANT DTC CHART(See page 05 −299)
A
2 CHECK FAIL −SAFE CONDITION
(a) Check the condition of fail −safe operation while the CHK ENG is being illuminated.
Result:
Condition of Fail −Safe OperationProceed to
Permits driving at vehicle speed of approximately 10 km/h (6
mph) at maximumA
Permits driving at vehicle speed of approximately 80 km/h
(50 mph) at maximumB
No fail −safe operationC
B Go to step 7
C Go to step 4
A
3 READ VALUE OF HAND −HELD TESTER(EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON. (Do not start the engine)
(c) Select the item ”DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / EX TEMP (IN)” and ”DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / EX TEMP (OUT)” and read its value displayed on the hand −held tes-
ter.
Result:
Temperature DisplayedProceed to
OK (Same value as actual exhaust gas temperature)A
1 ,000 ˚C( 1,832 ˚F )B
HINT:
If there is a open circuit, the hand −held tester indicates 1,000 ˚C( 1,832 ˚F).
Page 4415 of 5135

A81485
Fuel Pressure
Pressure Discharge Valve Operation by Sudden Deceleration:
Pressure Discharge Valve w/o Pressure Discharge Valve
Close
Accelerator Pedal
Opening Angle
Open
Close
Open
w/ Pressure Discharge Valve
Target Fuel Pressure TimeLong Time
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −435
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
DTC P 127 1 FUEL REGULATOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(EDU DRIVE)
DTC P 1272 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
MALFUNCTION
HINT:
S For more information on the pressure discharge valve and the common rail system, see page 05 −255.
S For more information on the EDU, see page 05 −255.
S If P1271 and/or P1272 is present, refer to the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) table for the fuel system
on page 05 −255.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ECM controls the internal fuel pressure of the common rail by opening and closing the pressure dis-
charge valve. When sudden deceleration is occurred, the internal fuel pressure will temporarily become
higher than usual and combustion noise may result, therefore the ECM will open the valve temporarily to
discharge the pressure inside the common rail. Also, the pressure discharge valve opens when the ignition
switch is turned to OFF, and the internal pressure is then promptly discharged.
05CQ1 −03
Page 4416 of 5135
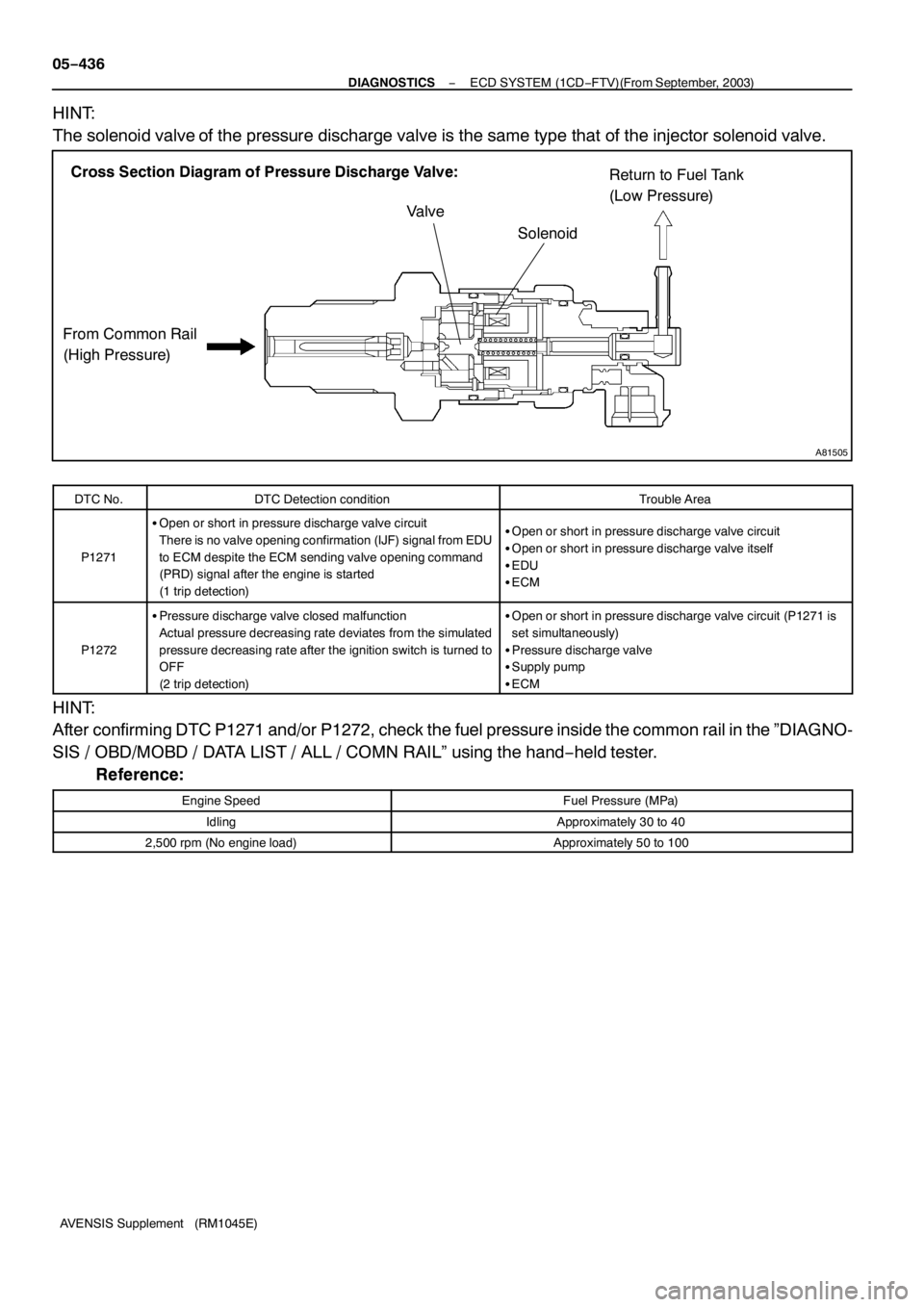
A81505
Cross Section Diagram of Pressure Discharge Valve:
From Common Rail
(High Pressure)Return to Fuel Tank
(Low Pressure)
Valve
Solenoid
05−436
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
HINT:
The solenoid valve of the pressure discharge valve is the same type that of the injector solenoid valve.
DTC No.DTC Detection conditionTrouble Area
P1271
SOpen or short in pressure discharge valve circuit
There is no valve opening confirmation (IJF) signal from EDU
to ECM despite the ECM sending valve opening command
(PRD) signal after the engine is started
(1 trip detection)SOpen or short in pressure discharge valve circuit
SOpen or short in pressure discharge valve itself
SEDU
SECM
P1272
SPressure discharge valve closed malfunction
Actual pressure decreasing rate deviates from the simulated
pressure decreasing rate after the ignition switch is turned to
OFF
(2 trip detection)SOpen or short in pressure discharge valve circuit (P1271 is
set simultaneously)
SPressure discharge valve
SSupply pump
SECM
HINT:
After confirming DTC P1271 and/or P1272, check the fuel pressure inside the common rail in the ”DIAGNO-
SIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / COMN RAIL” using the hand−held tester.
Reference:
Engine SpeedFuel Pressure (MPa)
IdlingApproximately 30 to 40
2,500 rpm (No engine load)Approximately 50 to 100
Page 4417 of 5135
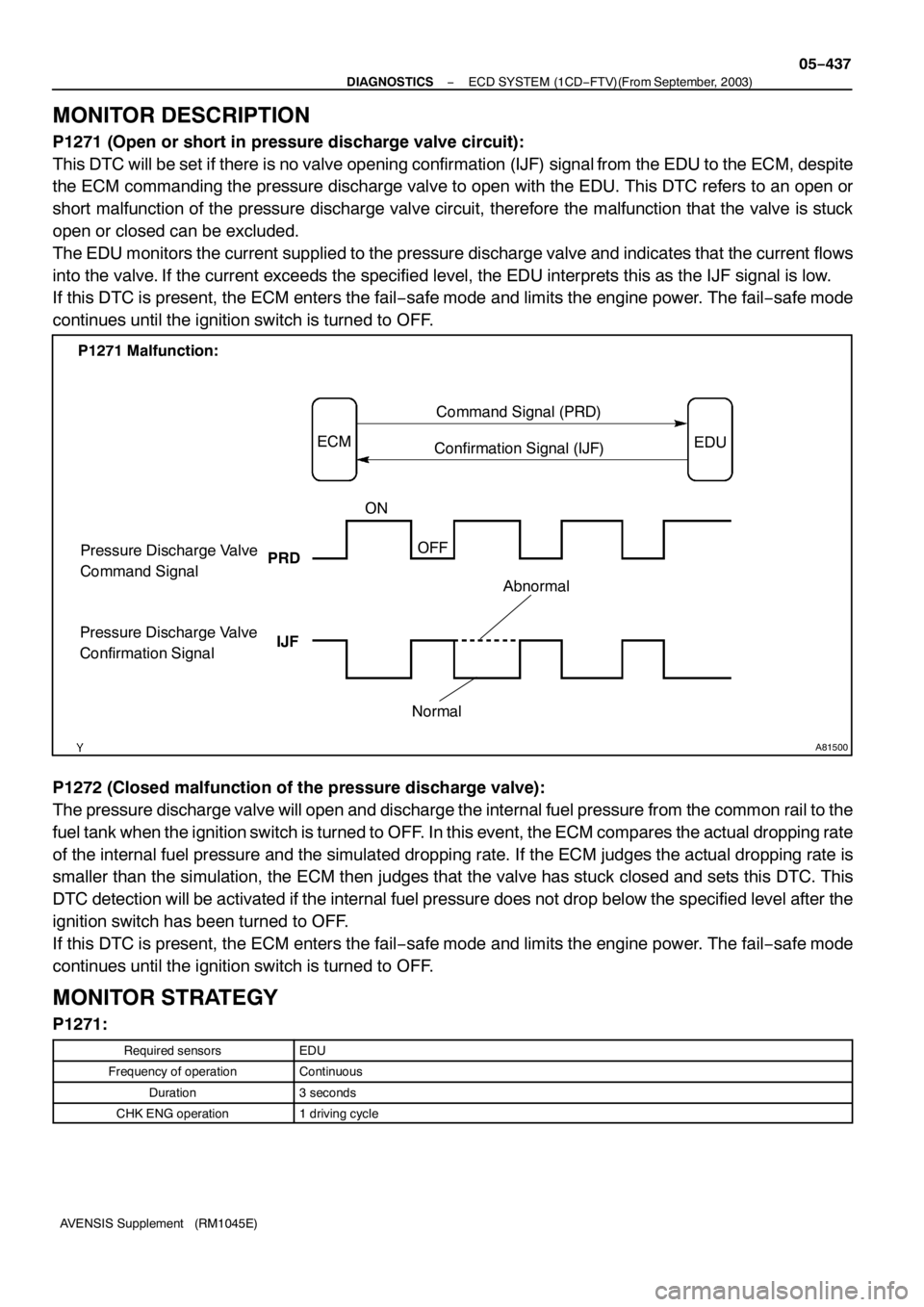
A81500
P1271Malfunction:
ECMCommand Signal (PRD)
EDU
Confirmation Signal (IJF)
Pressure Discharge Valve
Command Signal
Pressure Discharge Valve
Confirmation SignalPRD
IJFON
OFF
Normal
Abnormal
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−437
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
P1271(Open or short in pressure discharge valve circuit):
This DTC will be set if there is no valve opening confirmation (IJF) signal from the EDU to the ECM, despite
the ECM commanding the pressure discharge valve to open with the EDU. This DTC refers to an open or
short malfunction of the pressure discharge valve circuit, therefore the malfunction that the valve is stuck
open or closed can be excluded.
The EDU monitors the current supplied to the pressure discharge valve and indicates that the current flows
into the valve. If the current exceeds the specified level, the EDU interprets this as the IJF signal is low.
If this DTC is present, the ECM enters the fail−safe mode and limits the engine power. The fail−safe mode
continues until the ignition switch is turned to OFF.
P1272 (Closed malfunction of the pressure discharge valve):
The pressure discharge valve will open and discharge the internal fuel pressure from the common rail to the
fuel tank when the ignition switch is turned to OFF. In this event, the ECM compares the actual dropping rate
of the internal fuel pressure and the simulated dropping rate. If the ECM judges the actual dropping rate is
smaller than the simulation, the ECM then judges that the valve has stuck closed and sets this DTC. This
DTC detection will be activated if the internal fuel pressure does not drop below the specified level after the
ignition switch has been turned to OFF.
If this DTC is present, the ECM enters the fail−safe mode and limits the engine power. The fail−safe mode
continues until the ignition switch is turned to OFF.
MONITOR STRATEGY
P1271:
Required sensorsEDU
Frequency of operationContinuous
Duration3 seconds
CHK ENG operation1 driving cycle
Page 4418 of 5135
05−438
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
P1272:
Required sensorsFuel pressure sensor
Frequency of operationOnce per driving cycle
Duration1 second
CHK ENG operation2 driving cycles
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
P1271:
Specification
Drive the vehicle at 50 km/h (31 mph) with the 3rd gear and then decelerate it by completely releasing the accelerator pedal
P1272:
ItemSpecificationItemMinimumMaximum
Fuel pressure30 MPa (306 kgf/cm2, 4,351 psi)−
Fuel temperature0_C (32_F)−
Battery voltage11 V−
The monitor will not run if the fuel pressure sensor, pressure discharge valve circuit, or fuel temperature sensor is malfunctioning
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P1271:
Threshold
If the confirmation signals from the EDU is not present, despite the ECM sending the command signals regularly during decelerating
P1272:
Threshold
If the internal pressure stays beyond the specified level after the ignition switch was turned to OFF
Page 4419 of 5135
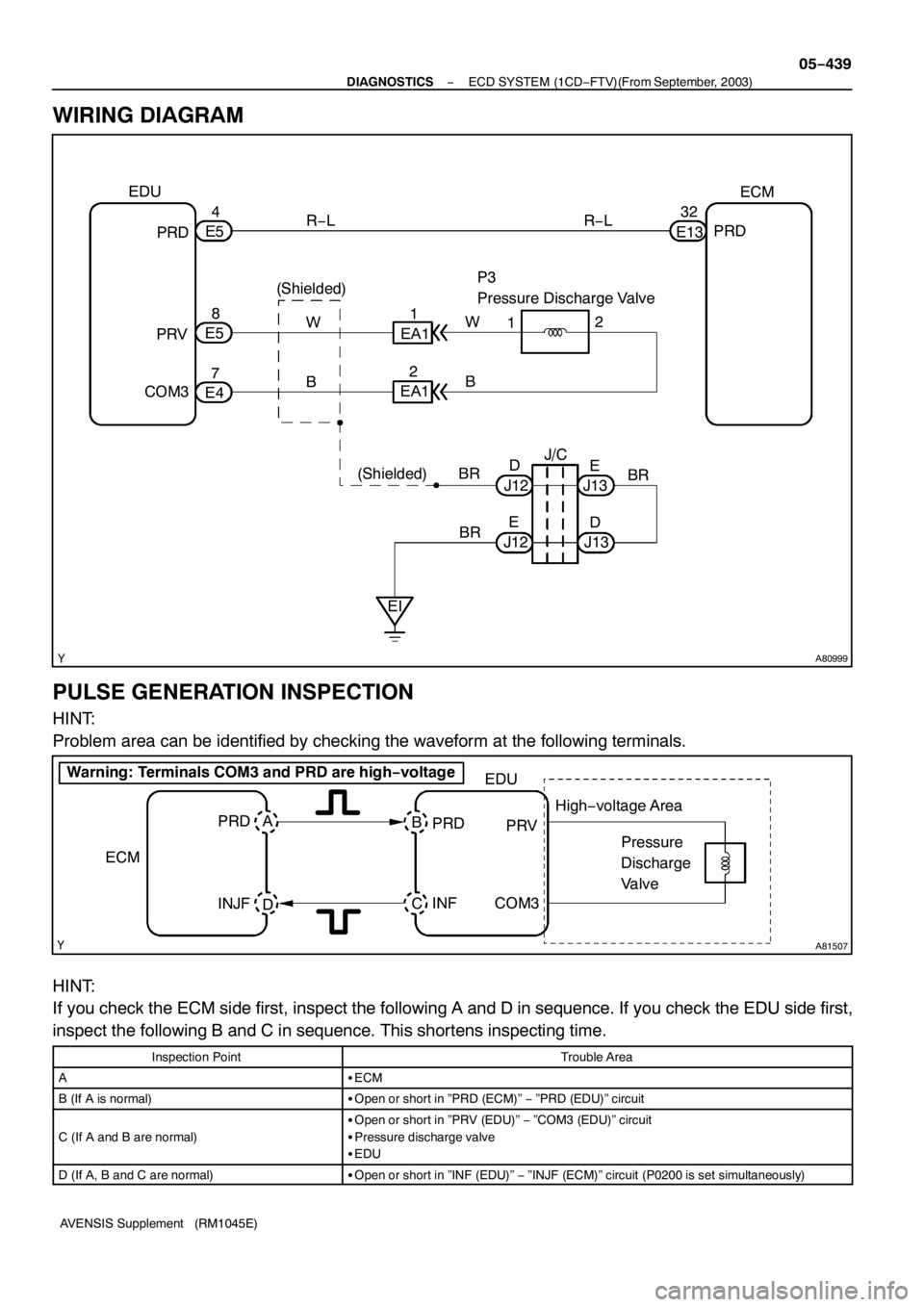
A80999
EDU
1 R−L
PRDECM
E1332
1
EA1 PRDR−L
E54
W
PRVE58
B
COM3
E472 P3
Pressure Discharge Valve
W
B 2
EA1
(Shielded) (Shielded)
BR
BR
BR
EIJ12D
J12E
J13D J13E J/C
A81507
ECMEDU
PRD
Pressure
Discharge
Valve
INJFCOM3 A
PRD
INFPRV B
C
D
Warning: Terminals COM3 and PRD are high−voltage
High−voltage Area
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−439
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
PULSE GENERATION INSPECTION
HINT:
Problem area can be identified by checking the waveform at the following terminals.
HINT:
If you check the ECM side first, inspect the following A and D in sequence. If you check the EDU side first,
inspect the following B and C in sequence. This shortens inspecting time.
Inspection PointTrouble Area
ASECM
B (If A is normal)SOpen or short in ”PRD (ECM)”−”PRD (EDU)” circuit
C (If A and B are normal)
SOpen or short in ”PRV (EDU)”−”COM3 (EDU)” circuit
SPressure discharge valve
SEDU
D (If A, B and C are normal)SOpen or short in ”INF (EDU)”−”INJF (ECM)” circuit (P0200 is set simultaneously)