2005 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 850 of 1232

Injector opens fully
The control plunger reaches its upper stop where it
remains supported by a cushion of fuel which is gen-
erated by the flow of fuel between the bleed and feed
orifices. The injector nozzle has now opened fully,
and the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber
at a pressure almost equal to that in the fuel rail
(Fig. 8).
Injector closes (end of injection)
As soon as the solenoid valve is no longer trig-
gered, the valve spring forces the armature down-
wards and the ball closes the bleed orifice. The
armature is a 2±piece design. Here, although the
armature plate is guided by a driver shoulder in its
downward movement, it can ªoverspringº with the
return spring so that it exerts no downwards-acting
forces on the armature and the ball. The closing of
the bleed orifice lead to pressure build up in the con-
trol chamber via the input from the feed orifice. This
pressure is the same as that in the rail and exerts an
increased force on the control plunger through its
end face. This force, together with that of the spring,
now exceeds the force exerted by the chamber volume
and the nozzle needle closes. Injection ceases as soon
as the nozzle needle comes up against its bottom stop
again (Fig. 8).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INJECTOR
CLASSIFICATION
The classification of injectors into 3 classes
describes the quantity characteristic of the injector.
This will make it possible in the future to match the
engine software to the tolerances of the injector
within a more narrowly graduated range. Classifica-
tion can be clearly recognized, and assigned only by
means of a DRBIIIt.
Classified injectors can be recognized by the part
number and identification on the magnetic head (cir-
cle with a number between 1 and 3 inside) (Fig. 9).
The number corresponds to the classification stage.
These general conditions equally apply if, as a
result of replacing an engine, carrying out repairs to
the cylinder head etc., the cylinder selective assign-
ment of the injectors or the engine control module
assignment may have changed. If proper attention is
not paid to the classification on these vehicles drive-
ability and smoking concerns could result.
If an injector is replaced, it is then necessary to
assign the classification number to the corresponding
cylinder with theDRBIIItin the control module.
INJECTOR CLASSIFICATION PROCEDURE
(1) Turn ignition switch ªONº.
(2) Using a DRB IIItand select ENGINE then
MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select LEARN INJECTORS.
(4) Using the up and down arrows, scroll to the
appropriate injector.
(5) Using the right and left arrows, set injector to
proper classification.
(6) Once injectors are classified, cycle ignition to
complete.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLEANING FUEL
INJECTORS
NOTE: Before cleaning the injector recesses, seal
the injector holes in the injector recesses with the
appropriate pin to prevent debris from falling into
the recesses and entering the motor.
(1) Seal the injector holes inside the cylinder head
recesses.
(2) Wipe out injector recesses with a non-woven
cloth, then clean with a cylinder brush.
(3) Clean the bottom of the cylinder recess with a
round brush.
(4) Blow out the recess and clean again with a
non-woven cloth and cover over.
(5) Perform these steps for each injector recess.
NOTE: DO NOT clean the tip of the injector with a
wire brush. Use a non - woven cloth.
(6) Clean injector body with a wire brush.
(7) Clean injector tips with a non-woven cloth.
NOTE: Do Not apply antiseize lubricant to the injec-
tor nozzle area.
(8) Grease injector body with anti seize lubricant.
Fig. 9 INJECTOR CLASSIFICATION MARKINGS
14 - 22 FUEL INJECTIONVA
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 851 of 1232

NOTE: Always replace the seals that seal off the
injectors at the cylinder head to the combustion
chamber and replace the retaining screws.
REMOVAL
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 1600BAR (23,200 PSI).
USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. FUEL UNDER THIS
AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENETRATE SKIN
CAUSING PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH. INSPECT
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARD BOARD. WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND
ADEQUATE PROTECTIVE CLOTHING WHEN SER-
VICING FUEL SYSTEM.
WARNING: NO SPARKS, OPEN FLAMES OR SMOK-
ING. RISK OF POISONING FROM INHALING AND
SWALLOWING FUEL. RISK OF INJURY TO EYES
AND SKIN FROM CONTACT WITH FUEL. POUR
FUELS ONLY INTO SUITABLE AND APPROPRI-
ATELY MARKED CONTAINERS. WEAR PROTECTIVE
CLOTHING.
NOTE: The engine must be lowered in the vehicle to
remove the fourth and fifth cylinders fuel injectors.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
(4) Remove lower radiator deflector plate.
(5) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(6) Remove turbocharger down pipe assembly.
(7) Remove oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and pull
tube from oil pan.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Remove upper radiator hose.
(10) Remove air cleaner box assembly and hoses.
(11) Remove charge air cooler inlet hose.
(12) Remove charge air cooler to turbocharger inlet
adaptor.
(13) Remove turbocharger to right engine mount
bracket.
(14) Disconnect steering coupler at gear box (RHD
Only).
(15) Remove battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(16) Unclip PDC from battery tray and set aside.(17) Remove battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(18) Remove power steering reservoir (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP/RESERVOIR - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove charger air cooler outlet hose.
(20) Remove intake manifold to left engine mount
bracket.
(21) Evacuate air conditioning system (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(22) Disconnect air conditioning suction / discharge
lines at A/C compressor.
(23) Disconnect pedal position sensor electrical
connector.
(24) Unplug injector electrical connectors.
(25) Remove fuel / water separator to intake man-
ifold retaining bolts.
(26) Support engine with hoist.
(27) Remove engine mount through bolts.
(28) Remove right engine mount sill plate.
NOTE: Counterhold injection lines with wrench
socket at threaded connections of injectors.
(29) Disconnect fuel injector high pressure line.
(30) Remove fuel injector retaining bolt and ten-
sion claw.
(31) Suitably lower engine to gain fuel injector
access and remove injector.
NOTE: If injectors are tight, remove with extraction
claw in place of tensioning claw. If extraction claw
contacts cylinder head cover, remove cylinder head
cover. If necessary, remove injectors with threaded
adaptor and discard injector.
(32) Remove injectors (Fig. 10).
(33) Clean injectors and recesses (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJEC-
TOR - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 1600BAR (23,200 PSI).
USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. FUEL UNDER THIS
AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENETRATE SKIN
CAUSING PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH. INSPECT
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARD BOARD. WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND
ADEQUATE PROTECTIVE CLOTHING WHEN SER-
VICING FUEL SYSTEM.
VAFUEL INJECTION 14 - 23
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 852 of 1232

WARNING: NO SPARKS, OPEN FLAMES OR SMOK-
ING. RISK OF POISONING FROM INHALING AND
SWALLOWING FUEL. RISK OF INJURY TO EYES
AND SKIN FROM CONTACT WITH FUEL. POUR
FUELS ONLY INTO SUITABLE AND APPROPRI-
ATELY MARKED CONTAINERS. WEAR PROTECTIVE
CLOTHING.
(1) Clean injectors and recesses (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJEC-
TOR - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Coat injector body with anti seize lubricant
then install injectors with new seals.
(3) Install tensioning claws with new screws at
injectors. Tighten screws in two stages, 7 N´m (62
lbs. in.) then 90É.
NOTE: If locking clamp has been pulled off at injec-
tor, the locking clamp must be replaced.
(4) Position fuel return line at injectors and secure
locking clamps.NOTE: Counterhold injection lines with wrench
socket at threaded connections of injectors.
(5) Install high pressure injection lines (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES
- INSTALLATION).
(6) Reconnect injector electrical connectors.
(7) Raise engine and install right sill plate.
(8) Install engine mount through bolts and tighten
to 40N´m (30 lbs. ft.).
(9) Install fuel / water separator to intake mani-
fold retaining bolts.
(10) Connect pedal position sensor electrical con-
nector.
(11) Connect air conditioning lines to A/C compres-
sor.
(12) Install intake manifold to left engine mount
bracket.
(13) Install charge air cooler outlet hose.
(14) Install power steering reservoir(Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP/RESERVOIR - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 10 FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL / INSTALLATION
1 - FUEL INJECTOR RETURN LINE
2 - RETAINING CLIP
3 - INJECTOR HIGH PRESSURE LINE
4 - INJECTOR SEAL5 - FUEL INJECTOR
6 - TENSIONING CLAW
7 - SPECIAL TOOLS #8938 AND # 8937
14 - 24 FUEL INJECTIONVA
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 853 of 1232

(15) Install battery tray(Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect PDC to battery tray.
(17) Install battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLATION).
(18) Connect steering coupler at gear box (RHD
Only).
(19) Install turbocharger to right engine mount
bracket (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBO-
CHARGER SYSTEM - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install charge air cooler to turbocharger inlet
adaptor (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/CHARGE
AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING - INSTALLATION) .
(21) Install charger air cooler inlet hose (Refer to
11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/CHARGE AIR COOLER
AND PLUMBING - INSTALLATION).
(22) Install air cleaner box assembly and hoses.
(23) Install upper radiator hose.
(24) Raise vehicle.
(25) Install dipstick tube into oil pan and tighten
retaining bolt.
(26) Install turbocharger down pipe assembly.
(27) Close cooling system drain.
(28) Install lower radiator deflector plate.
(29) Lower vehicle.
(30) Connect negative battery cable.
(31) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION)..
(32) Fill cooling system with the correct mixture to
the proper level (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO NOT
WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(33) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(34) Recharge air conditioning system.
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure sensor provides the current low
pressure (the pressure that exist at the inlet of the
high pressure injection pump) fuel pressure to the
ECM (Fig. 11).
The fuel pressure when the engine is idling is
approximately 36 psi (2.5 Bar). The fuel pressure
while driving is 50±58 psi (3.5 - 4.0Bar).
DESCRIPTION
The fuel rail pressure sensor provides the current
fuel rail pressure to the ECM.
OPERATION
OPERATION
A diaphragm and an electric resistance meter are
integrated in the fuel pressure sensor. The non-con-
stant fuel system pressure from the low pressure fuel
pump influences the position of the diaphragm which
in turn alters it's electrical resistance. This resis-
tance is analyzed by the ECM. The ECM then actu-
ates the fuel rail pressure control valve until the
desired rail pressure value is obtained (Fig. 11).
OPERATION
The fuel rail pressure sensor measures the current
fuel rail pressure and sends a voltage signal to the
ECM. The ECM then actuates the fuel rail pressure
control valve solenoid until the desired rail pressure
is achieved.
Fig. 11 FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
VAFUEL INJECTION 14 - 25
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 862 of 1232
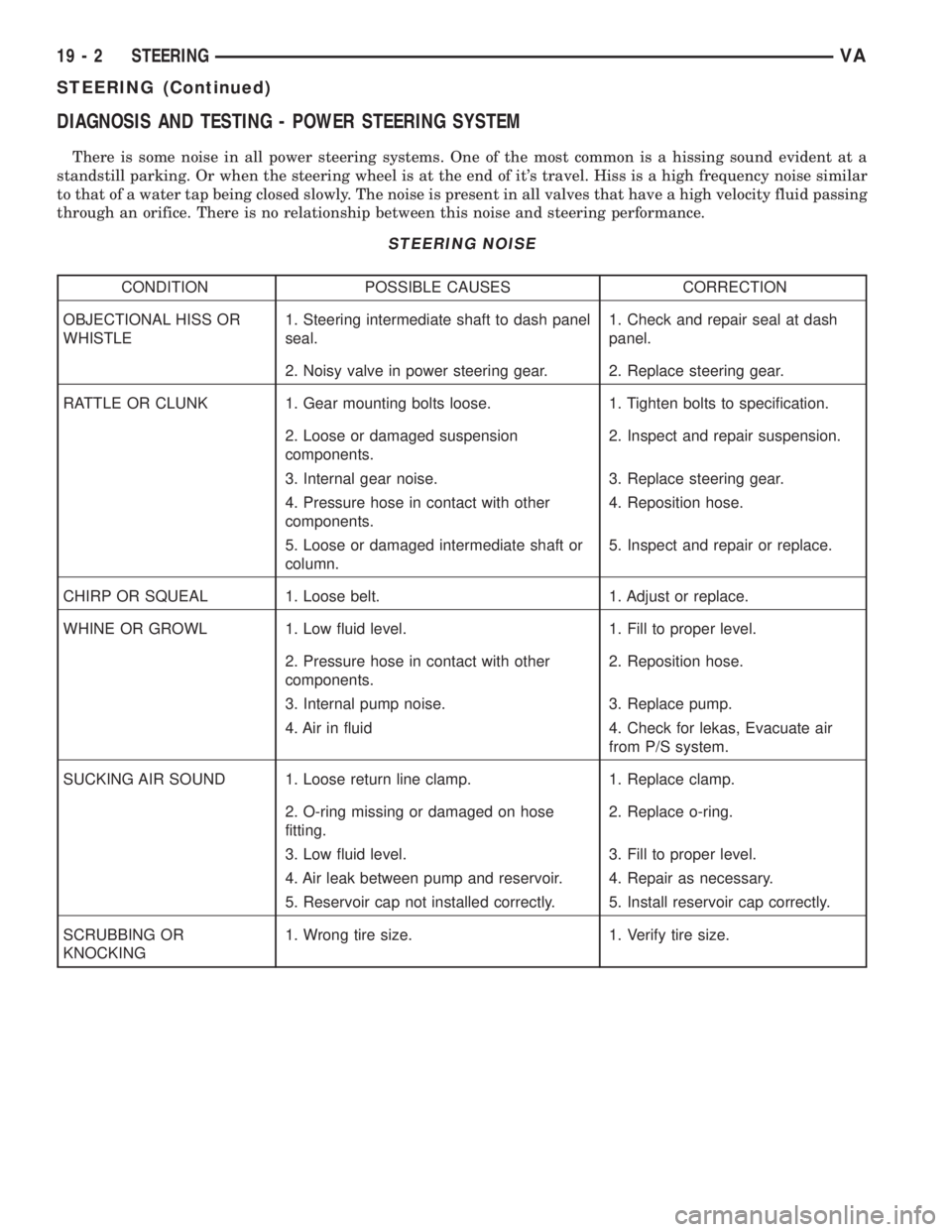
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill parking. Or when the steering wheel is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar
to that of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing
through an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
STEERING NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Replace steering gear.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Internal gear noise. 3. Replace steering gear.
4. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.4. Reposition hose.
5. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.5. Inspect and repair or replace.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
4. Air in fluid 4. Check for lekas, Evacuate air
from P/S system.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
5. Reservoir cap not installed correctly. 5. Install reservoir cap correctly.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
19 - 2 STEERINGVA
STEERING (Continued)
Page 863 of 1232

BINDING AND STICKING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
DIFFICULT TO TURN WHEEL
STICKS OR BINDS1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Tire pressure. 2. Adjust tire pressure.
3. Steering components (ball
joints/tie rod ends).3 Inspect and repair as necessary.
4. Loose belt. 4. Adjust or replace.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and replace if
necessary.
6. Column shaft coupler binding. 6. Replace coupler.
7. Steering gear worn. 7. Replace gear.
8. Pump seized / Stuck valve 8. Replace pump.
INSUFFICIENT ASST. OR POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HARD TURNING OR MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN TURNING EFFORT1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Low fluid level. 2. Fill to proper level.
3. Loose belt. 3. Adjust or replace.
4. Low pump pressure. 4. Pressure test and repair as
necessary.
5. Internal gear leak. 5. Replace gear.
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
WANT TO RETURN TO CENTER
POSITION1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Wheel alignment. 2. Align front end.
3. Lack of lubrication. 3. Inspect and lubricate suspension
compnents.
4. High friction in steering gear. 4. Replace gear.
VASTEERING 19 - 3
STEERING (Continued)
Page 864 of 1232

LOOSE STEERING AND VEHICLE LEAD
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING
WHEEL1. Worn or loose suspension or
steering components.1. Inspect and repair as necessary.
2. Worn or loose wheel bearings. 2. Inspect and repair or adjust
bearings.
3. Steering gear mounting. 3. Tighten gear mounting bolts to
specification.
4. Gear out of adjustment. 4. Replace gear.
5. Worn or loose steering coupler. 5. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
VEHICLE PULLS OR LEADS TO
ONE SIDE.1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Rotate tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align front end.
19 - 4 STEERINGVA
STEERING (Continued)
Page 899 of 1232

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a NAG1
automatic transmission, check for Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance.
²Improper adjustments.
²Hydraulic malfunctions.
²Mechanical malfunctions.
²Electronic malfunctions.
²Transfer case performance.
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift
cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line pressure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application chart
CLUTCH APPLICATION provides a basis for analyz-
ing road test results.
CLUTCH APPLICATION
GEAR RATIO B1 B2 B3 K1 K2 K3 F1 F2
1 3.59 X* X X* X X
2 2.19 X X X* X
3 1.41 X X X
4 1.00 X X X
5 0.83 X X X X*
NX X
R 3.16 X* X X X
* = The shift components required during coast.
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - NAG1 21 - 23
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - NAG1 (Continued)