Page 2743 of 2870
5MT-31
MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND DIFFERENTIAL
Transmission Gear Oil
2. Transmission Gear Oil
A: INSPECTION
1) Park the vehicle on a level surface.
2) Turn the ignition switch to OFF, and wait until the
engine cools.
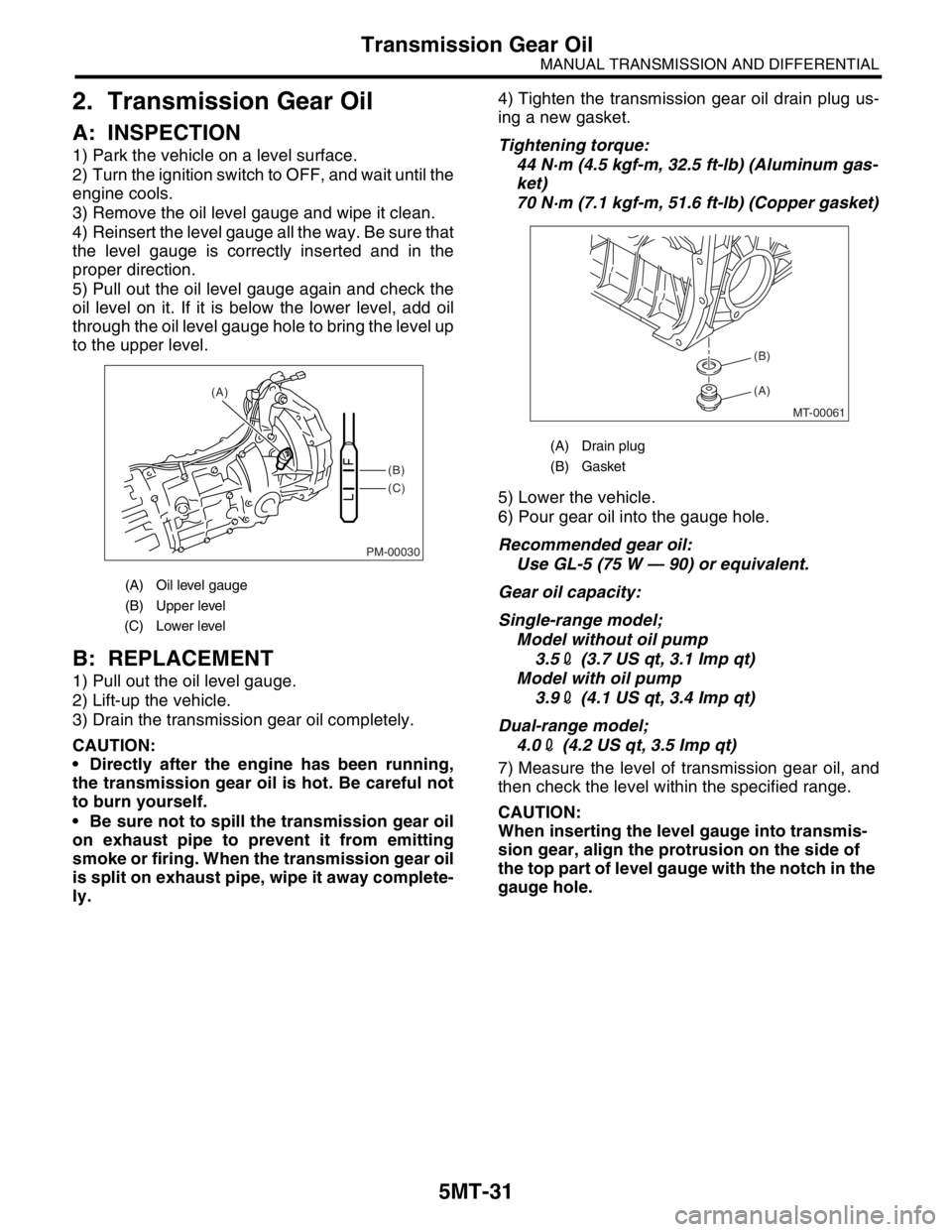
3) Remove the oil level gauge and wipe it clean.
4) Reinsert the level gauge all the way. Be sure that
the level gauge is correctly inserted and in the
proper direction.
5) Pull out the oil level gauge again and check the
oil level on it. If it is below the lower level, add oil
through the oil level gauge hole to bring the level up
to the upper level.
B: REPLACEMENT
1) Pull out the oil level gauge.
2) Lift-up the vehicle.
3) Drain the transmission gear oil completely.
CAUTION:
Directly after the engine has been running,
the transmission gear oil is hot. Be careful not
to burn yourself.
Be sure not to spill the transmission gear oil
on exhaust pipe to prevent it from emitting
smoke or firing. When the transmission gear oil
is split on exhaust pipe, wipe it away complete-
ly.4) Tighten the transmission gear oil drain plug us-
ing a new gasket.
Tightening torque:
44 N·m (4.5 kgf-m, 32.5 ft-lb) (Aluminum gas-
ket)
70 N·m (7.1 kgf-m, 51.6 ft-lb) (Copper gasket)
5) Lower the vehicle.
6) Pour gear oil into the gauge hole.
Recommended gear oil:
Use GL-5 (75 W — 90) or equivalent.
Gear oil capacity:
Single-range model;
Model without oil pump
3.52 (3.7 US qt, 3.1 Imp qt)
Model with oil pump
3.92 (4.1 US qt, 3.4 Imp qt)
Dual-range model;
4.02 (4.2 US qt, 3.5 Imp qt)
7) Measure the level of transmission gear oil, and
then check the level within the specified range.
CAUTION:
When inserting the level gauge into transmis-
sion gear, align the protrusion on the side of
the top part of level gauge with the notch in the
gauge hole.
(A) Oil level gauge
(B) Upper level
(C) Lower level
PM-00030
(B)
(C) (A)
(A) Drain plug
(B) Gasket
MT-00061
(A) (B)
Page 2824 of 2870
5MT-111
MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND DIFFERENTIAL
General Diagnostic
26.General Diagnostic
A: INSPECTION
1. MANUAL TRANSMISSION
Symptom Possible cause Remedy
1. Gears are difficult to intermesh.
N
OTE:
The cause for difficulty in shifting gears
can be classified into two kinds: one is
malfunction of the gear shift system and
the other is malfunction of the transmis-
sion. However, if the operation is heavy
and engagement of the gears is difficult,
defective clutch disengagement may also
be responsible. Check whether the clutch
is correctly functioning, before checking
the gear shift system and transmission.(a) Worn, damaged or burred chamfer of
internal spline of sleeve and reverse
driven gearReplace.
(b) Worn, damaged or burred chamfer of
spline of gearsReplace.
(c) Worn or scratched bushings Replace.
(d) Incorrect contact between synchro-
nizer ring and gear cone or wear Correct or replace.
2. Gear slips out.
Gear slips out when coasting on rough
road.
Gear slips out during acceleration.(a) Defective pitching stopper adjustment Adjust.
(b) Loose engine mounting bolts Tighten or replace.
(c) Worn fork shifter, broken shifter fork
rail springReplace.
(d) Worn or damaged ball bearing Replace.
(e) Excessive clearance between splines
of synchronizer hub and synchronizer
sleeveReplace.
(f) Worn tooth step of synchronizer hub Replace.
(g) Worn 1st driven gear and driven shaft Replace.
(h) Worn 2nd driven gear and 2nd bush Replace.
(i) Worn reverse idler gear and bushing Replace.
3. Unusual noise comes from transmis-
sion.
N
OTE:
If an unusual noise is heard when the ve-
hicle is parked with its engine idling and if
the noise ceases when the clutch is disen-
gaged, it may be considered that the
noise comes from the transmission.(a) Insufficient or improper lubrication Lubricate or replace with specified oil.
(b) Worn or damaged gears and bearings
NOTE:
If the trouble is only wear of the tooth sur-
faces, merely a high roaring noise will oc-
cur at high speeds, but if any part is
broken, rhythmical knocking sound will be
heard even at low speeds.Replace.
Page 2825 of 2870
5MT-112
MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND DIFFERENTIAL
General Diagnostic
2. DIFFERENTIAL
Symptom Possible cause Remedy
1. Broken differential (case, gear, bear-
ing, etc.)
N
OTE:
Noise will develop and finally it will be-
come impossible to continue to run due to
broken pieces obstructing the gear revo-
lution. (a) Insufficient or improper oil Disassemble the differential and replace
broken components and at the same time
check other components for any trouble,
and replace if necessary.
(b) Use of vehicle under severe condi-
tions such as excessive load and
improper use of clutch Readjust the bearing preload and back-
lash and face contact of gears.
(c) Improper adjustment of taper roller
bearingAdjust.
(d) Improper adjustment of drive pinion
and hypoid driven gear Adjust.
(e) Excessive backlash due to worn dif-
ferential side gear, washer or differential
pinion vehicle under severe operating
conditions. Add recommended oil to specified level.
Do not use the vehicle under severe oper-
ating conditions.
(f) Loose hypoid driven gear clamping
boltsTighten.
2. Differential and hypoid gear noises
Troubles of the differential and hypoid
gear always appear as noise problems.
Therefore noise is the first indication of
the trouble. However noises from the
engine, muffler, tire, exhaust gas, bear-
ing, body, etc. are easily mistaken for the
differential noise. Pay special attention to
the hypoid gear noise because it is easily
confused with other gear noises. There
are the following four kinds of noises.
Gear noise when driving: If noise
increases as vehicle speed increases it
may be due to insufficient gear oil, incor-
rect gear engagement, damaged gears,
etc.
Gear noise when coasting: Damaged
gears due to maladjusted bearings and
incorrect shim adjustment
Bearing noise when driving or when
coasting: Cracked, broken or damaged
bearings
Noise which mainly occurs when turn-
ing: Unusual noise from differential side
gear, differential pinion, differential pinion
shaft, etc. (a) Insufficient oil Lubricate.
(b) Improper adjustment of hypoid driven
gear and drive pinionCheck tooth contact.
(c) Worn teeth of hypoid driven gear and
drive pinionReplace as a set.
Readjust the bearing preload.
(d) Loose roller bearing Readjust the hypoid driven gear to drive
pinion backlash and check tooth contact.
(e) Distorted hypoid driven gear or differ-
ential caseReplace.
(f) Worn washer and differential pinion
shaftReplace.
Page 2869 of 2870
CL-43
CLUTCH SYSTEM
General Diagnostic Table
2. CLUTCH PEDAL
3. DIAGNOSTIC DIAGRAM OF CLUTCH DRAG
4. Noisy clutch
Examine whether the noise is generated
when the clutch is disengaged, engaged,
or partially engaged.(a) Broken, worn or unlubricated release
bearingReplace the release bearing.
(b) Insufficient lubrication of pilot bearing Replace.
(c) Loose clutch disc hub Replace the clutch disc.
(d) Loose torsion spring retainer Replace the clutch disc.
(e) Deteriorated or broken torsion spring Replace the clutch disc.
5. Clutch grabs.
When starting the vehicle with the clutch
partially engaged, the clutch engages
suddenly and the vehicle jumps instead
of making a smooth start.(a) Grease or oil on facing Replace the clutch disc.
(b) Deteriorated cushioning spring Replace the clutch disc.
(c) Worn or rusted spline of clutch disc or
main shaftTake off rust, apply grease or replace the
clutch disc or main shaft.
(d) Deteriorated or broken torsion spring Replace the clutch disc.
(e) Loose engine mounting Retighten or replace the mounting.
(f) Deteriorated diaphragm spring Replace.
Trouble Corrective action
Insufficient pedal play Adjust pedal play.
Clutch pedal free play insufficient Adjust pedal free play.
Excessively worn and damaged pedal shaft and/or bushing Replace the bushing and/or shaft with a new one.
Step Check Yes No
1 CHECK GEAR NOISE.
1) Start the engine.
2) Disengage the clutch and shift quickly from
neutral to reverse in idling condition.Is there any abnormal noise
from the transmission gear?Go to step 2.Clutch is normal.
2 CHECK GEAR NOISE.
Disengage the clutch at idle and shift from neu-
tral to reverse within 0.5 — 1.0 seconds.Is there any abnormal noise
from the transmission gear?Go to step 3.Defective trans-
mission or exces-
sive clutch drag
torque. Inspect the
pilot bearing,
clutch disc, trans-
mission and clutch
disc hub spline.
3 CHECK GEAR NOISE.
1) Disengage the clutch at idle and shift from
neutral to reverse within 0.5 — 1.0 seconds.
2) With the clutch disengaged, shift from N to
R, R to N several times.Is there any abnormal noise
from the transmission gear?Defect in clutch
disengaging.
Inspect the clutch
disc, clutch cover,
clutch release, and
clutch pedal free
play.Clutch and fly-
wheel seizure.
Inspect the clutch
disc, spline of
clutch disc hub. Symptom Possible cause Corrective