Page 3938 of 4264
7A4–130 UNIT REPAIR (AW30–40LE)
Torque Specifications (Cont'd)
N·m (Ibft)
RT W37 A LF00 1001
Page 3939 of 4264
UNIT REPAIR (AW30–40LE) 7A4–131
Torque Specifications (Cont'd)
N·m (Ibft)
RT W37 A LF00 0901
Page 3940 of 4264
7A4–132 UNIT REPAIR (AW30–40LE)
Special Tools
ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
J–37227
Holding fixture
J–3289–20
Holding fixture base
J–37228
Oil pan seal cutter
J–23327–1
Spring compressor
J–9617
Oil seal installer; oil
pump
J–37233
Spring compressor; OD
brake piston
J–29770–A
Oil pressure gauge
J–25048
Spring compressor
J–37236
Reaction sleeve puller;
first and reverse brake
J–37237
Piston puller; first and
reverse brake
J–37232–2
Oil seal installer;
manual valve shaft seal
installer & remover
J–35467
Onennway clutch
testing tool; torque
converter ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
Page 3947 of 4264

CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-1
SECTION 7A1
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
DESCRIPTION ..............................................................................................................................7A1- 3
CONSTRUCTION ....................................................................................................................7A1- 3
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION .....................................................................................7A1- 4
NUMBER PLATE LOCATION ...............................................................................................7A1- 5
ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS LOCATION ..................................................7A1- 6
TRANSMISSION CONTROL UNIT (TCM) PERIPHERAL CIRCUIT ..............................7A1- 7
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF COMPONENT ...........................................................7A1- 8
TORQUE CONVERTER (WITH LOCK-UP FUNCTION) ..................................................7A1- 8
OIL PUMP .................................................................................................................................7A1- 9
INPUT SHAFT ..........................................................................................................................7A1- 10
OUTPUT SHAFT ......................................................................................................................7A1- 10
GEAR SHIFTING MECHANISM ............................................................................................7A1- 10
CONTROL VALVE ...................................................................................................................7A1- 14
OIL PASSAGE .........................................................................................................................7A1- 19
PARKING FUNCTION .............................................................................................................7A1- 20
INHIBITOR SWITCH ...............................................................................................................7A1- 21
TURBINE SENSOR .................................................................................................................7A1- 22
SPEED SENSOR .....................................................................................................................7A1- 22
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) .............................................................................7A1- 23
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR (=TDC SENSOR) ....................................................................7A1- 23
BRAKE SWITCH ......................................................................................................................7A1- 24
MODE SELECT SWITCH .......................................................................................................7A1- 24
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM) ..................................................................7A1- 25
CONTROL MECHANISM ............................................................................................................7A1- 26
CONTENT OF FUNCTION AND CONTROL ......................................................................7A1- 26
CONTROL ITEM, INPUT AND OUTPUT .................................................................... 7A1- 29
LINE PRESSURE CONTROL ..................................................................................... 7A1- 30
Page 3949 of 4264
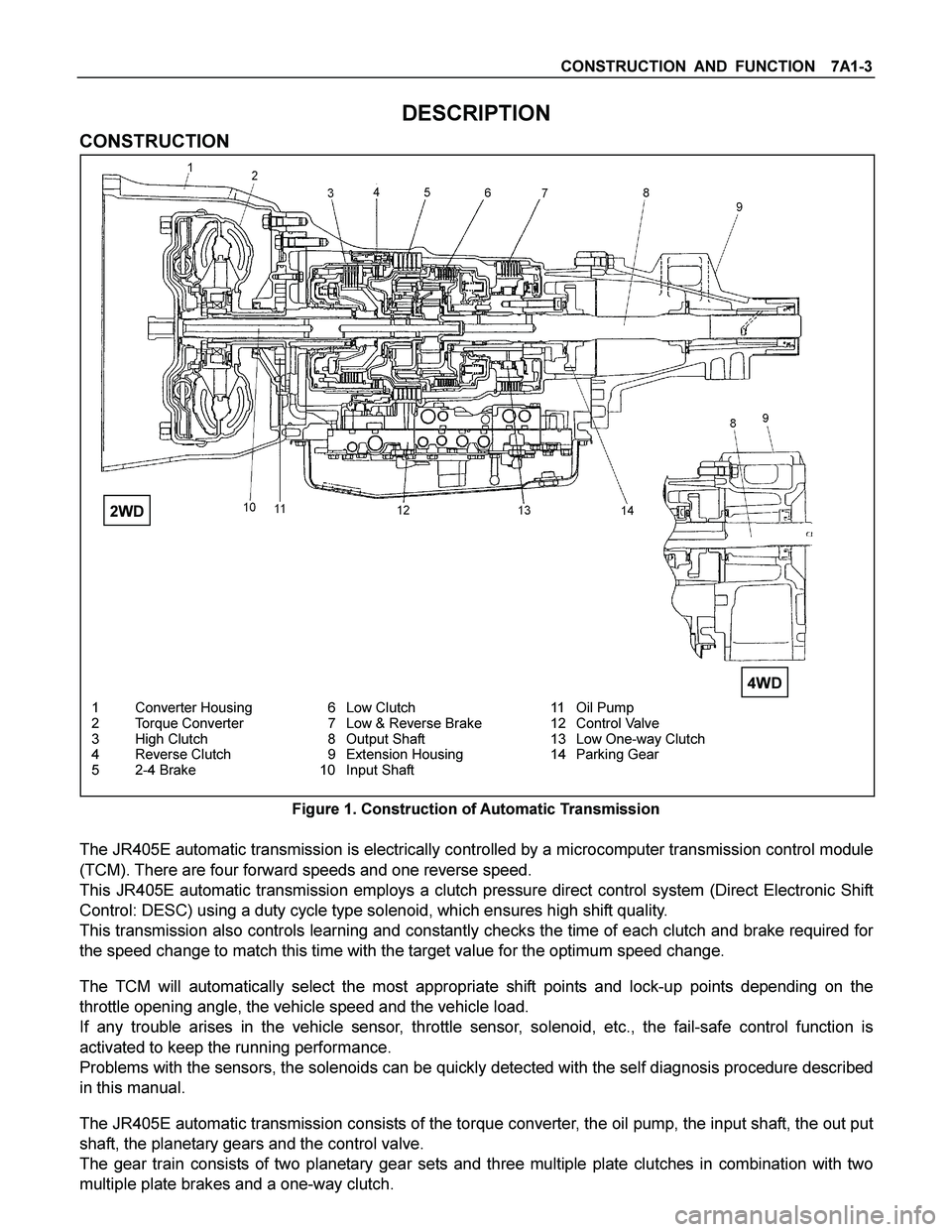
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-3
DESCRIPTION
CONSTRUCTION
1 Converter Housing 6 Low Clutch 11 Oil Pump
2 Torque Converter 7 Low & Reverse Brake 12 Control Valve
3 High Clutch 8 Output Shaft 13 Low One-way Clutch
4 Reverse Clutch 9 Extension Housing 14 Parking Gear
5 2-4 Brake 10 Input Shaft
Figure 1. Construction of Automatic Transmission
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically controlled by a microcomputer transmission control module
(TCM). There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using a duty cycle type solenoid, which ensures high shift quality.
This transmission also controls learning and constantly checks the time of each clutch and brake required for
the speed change to match this time with the target value for the optimum speed change.
The TCM will automatically select the most appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending on the
throttle opening angle, the vehicle speed and the vehicle load.
If any trouble arises in the vehicle sensor, throttle sensor, solenoid, etc., the fail-safe control function is
activated to keep the running performance.
Problems with the sensors, the solenoids can be quickly detected with the self diagnosis procedure described
in this manual.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the torque converter, the oil pump, the input shaft, the out put
shaft, the planetary gears and the control valve.
The gear train consists of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate clutches in combination with two
multiple plate brakes and a one-way clutch.
2WD
4WD
Page 3950 of 4264
7A1-4 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
Model JR405E
Torque Converter Type Three Elements, One Stage & Two Phase Type
With Lock-up Function
Torque Converter Stall Torque Ratio 1.8
Name ATF DEXRON����
Quantity 9.2L-9.6L AT F
Cooling System Water Cooled Type (Radiator)
1st 2.786
2nd 1.546
3rd 1.000
4th (Over Drive) 0.694
Gear Ratio
Reverse 2.273
Low Clutch L/C 7
High Clutch H/C 5
Reverse Clutch R/C 2Number of Disc Clutch
Low One-way Clutch L/O.C 1 Set
Low & Reverse
Brake L&R/B 6
Brake
2-4 Brake 2-4/B 5Number of Disc
Sun Gear 33
Pinion
Gear 21Front Planetary
Ring Gear 75
Sun Gear 42
Pinion
Gear 17
Planetary Gear Unit
Rear Planetary
Ring Gear 75Number of Teeth
Page 3954 of 4264
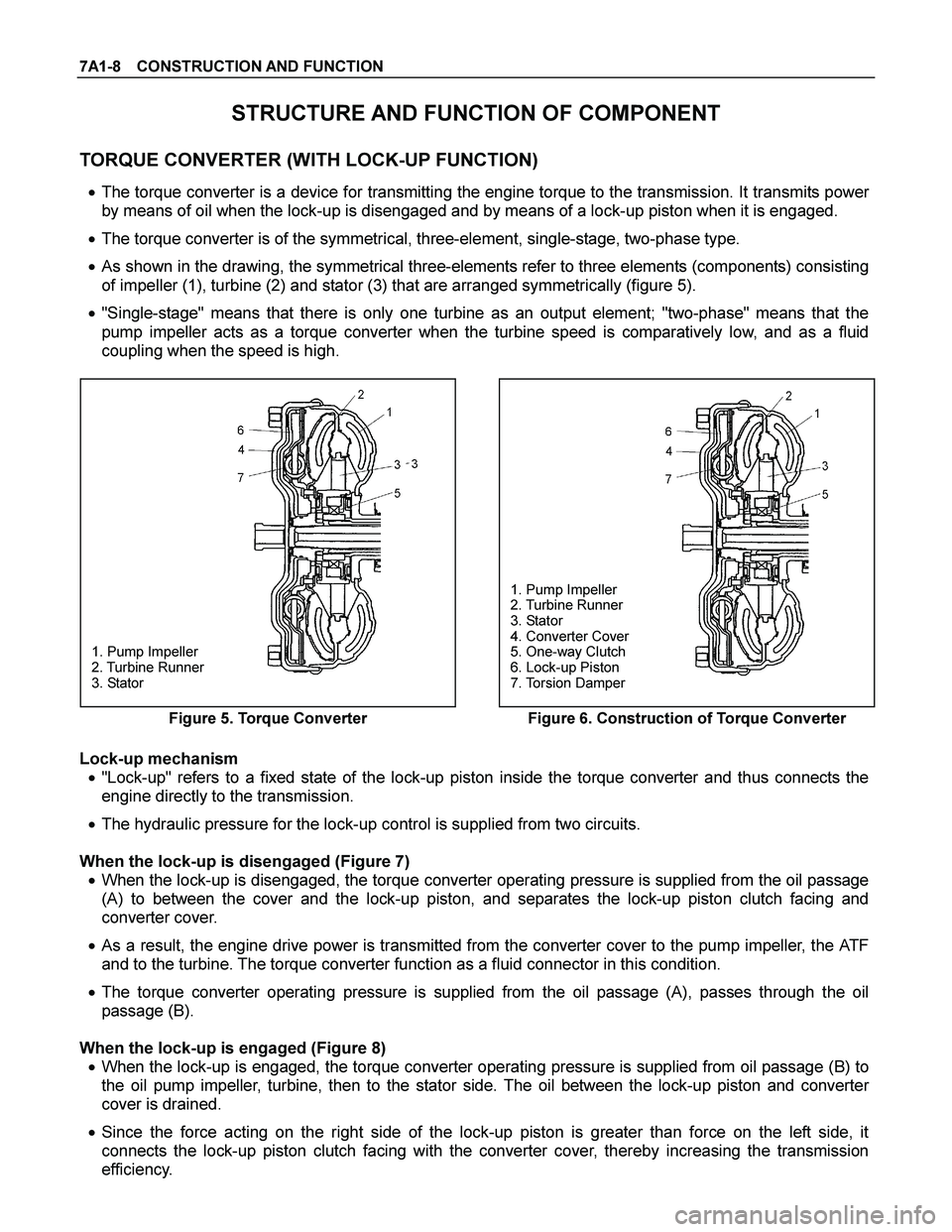
7A1-8 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF COMPONENT
TORQUE CONVERTER (WITH LOCK-UP FUNCTION)
� The torque converter is a device for transmitting the engine torque to the transmission. It transmits power
by means of oil when the lock-up is disengaged and by means of a lock-up piston when it is engaged.
� The torque converter is of the symmetrical, three-element, single-stage, two-phase type.
� As shown in the drawing, the symmetrical three-elements refer to three elements (components) consisting
of impeller (1), turbine (2) and stator (3) that are arranged symmetrically (figure 5).
� "Single-stage" means that there is only one turbine as an output element; "two-phase" means that the
pump impeller acts as a torque converter when the turbine speed is comparatively low, and as a fluid
coupling when the speed is high.
1. Pump Impeller
2. Turbine Runner
3. Stator
1. Pump Impeller
2. Turbine Runner
3. Stator
4. Converter Cover
5. One-way Clutch
6. Lock-up Piston
7. Torsion Damper
Figure 5. Torque Converter
Figure 6. Construction of Torque Converter
Lock-up mechanism
� "Lock-up" refers to a fixed state of the lock-up piston inside the torque converter and thus connects the
engine directly to the transmission.
� The hydraulic pressure for the lock-up control is supplied from two circuits.
When the lock-up is disengaged (Figure 7)
� When the lock-up is disengaged, the torque converter operating pressure is supplied from the oil passage
(A) to between the cover and the lock-up piston, and separates the lock-up piston clutch facing and
converter cover.
� As a result, the engine drive power is transmitted from the converter cover to the pump impeller, the ATF
and to the turbine. The torque converter function as a fluid connector in this condition.
� The torque converter operating pressure is supplied from the oil passage (A), passes through the oil
passage (B).
When the lock-up is engaged (Figure 8)
� When the lock-up is engaged, the torque converter operating pressure is supplied from oil passage (B) to
the oil pump impeller, turbine, then to the stator side. The oil between the lock-up piston and converter
cover is drained.
� Since the force acting on the right side of the lock-up piston is greater than force on the left side, it
connects the lock-up piston clutch facing with the converter cover, thereby increasing the transmission
efficiency.
Page 3955 of 4264
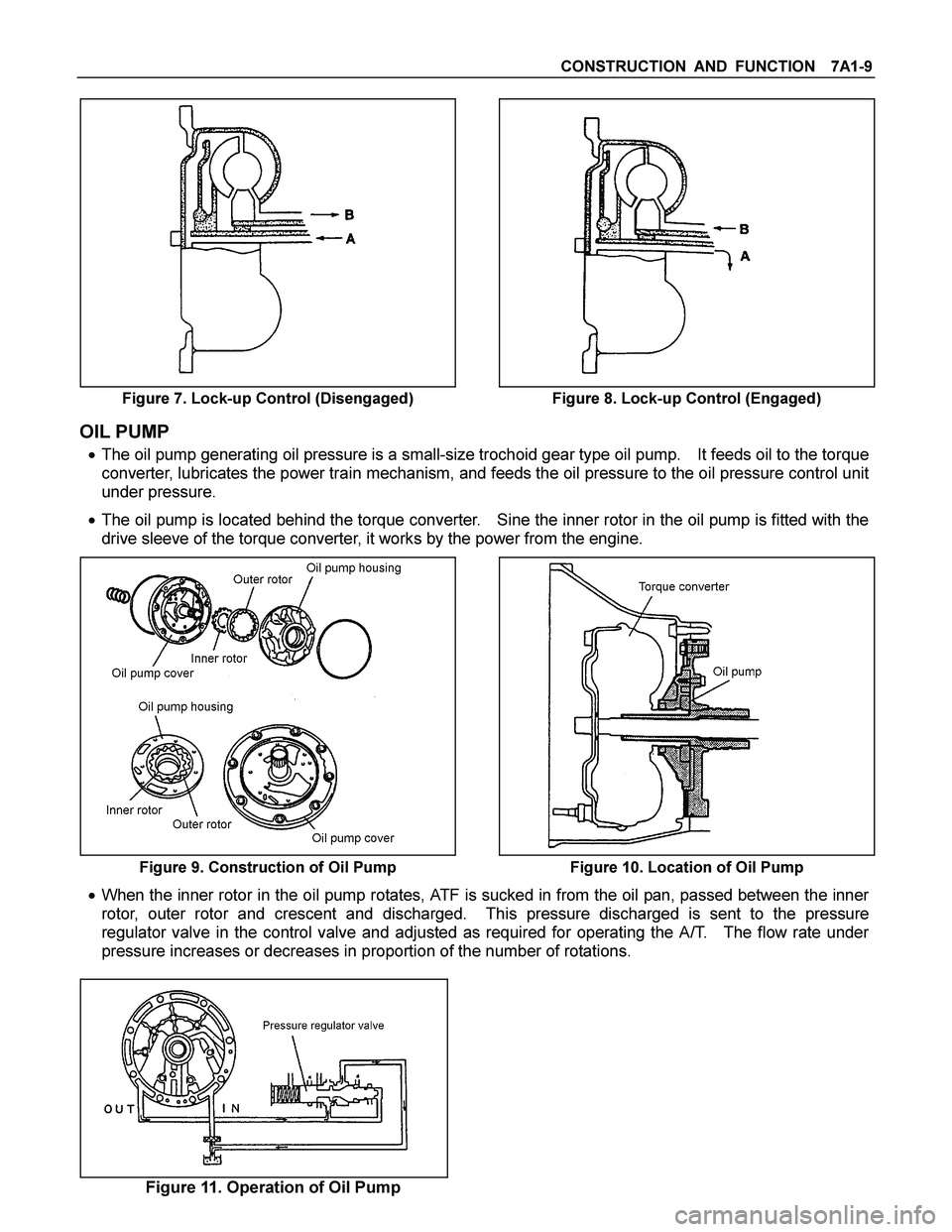
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-9
Figure 7. Lock-up Control (Disengaged) Figure 8. Lock-up Control (Engaged)
OIL PUMP
� The oil pump generating oil pressure is a small-size trochoid gear type oil pump. It feeds oil to the torque
converter, lubricates the power train mechanism, and feeds the oil pressure to the oil pressure control unit
under pressure.
� The oil pump is located behind the torque converter. Sine the inner rotor in the oil pump is fitted with the
drive sleeve of the torque converter, it works by the power from the engine.
Figure 9. Construction of Oil Pump Figure 10. Location of Oil Pump
� When the inner rotor in the oil pump rotates, ATF is sucked in from the oil pan, passed between the inner
rotor, outer rotor and crescent and discharged. This pressure discharged is sent to the pressure
regulator valve in the control valve and adjusted as required for operating the A/T. The flow rate under
pressure increases or decreases in proportion of the number of rotations.
Figure 11. Operation of Oil Pump