2002 DODGE RAM warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 1294 of 2255

FRAME SERVICE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE EYE PROTECTION WHEN GRIND-
ING OR WELDING METAL, SERIOUS EYE INJURY
CAN RESULT. BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FRAME
REPAIR INVOLVING GRINDING OR WELDING, VER-
IFY THAT VEHICLE FUEL SYSTEM IS NOT LEAKING
OR IN CONTACT WITH REPAIR AREA, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT ALLOW OPEN
FLAME TO CONTACT PLASTIC BODY PANELS.
FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAN RESULT. WHEN
WELDED FRAME COMPONENTS ARE REPLACED,
100% PENETRATION WELD MUST BE ACHIEVED
DURING INSTALLATION. IF NOT, DANGEROUS
OPERATING CONDITIONS CAN RESULT. STAND
CLEAR OF CABLES OR CHAINS ON PULLING
EQUIPMENT DURING FRAME STRAIGHTENING
OPERATIONS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT SUPPORTED ON SAFETY STANDS,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Do not reuse damaged fasteners, quality
of repair would be suspect. Do not drill holes in top
or bottom frame rail flanges, frame rail failure can
result. Do Not use softer than Grade 5 bolts to
replace production fasteners, loosening or failure
can result. When using heat to straighten frame
components do not exceed 566ÉC (1050ÉF), metal
fatigue can result. Welding the joints around riveted
cross members and frame side rails can weaken
frame.
FRAME STRAIGHTENING
When necessary, a conventional frame that is bent
or twisted can be straightened by application of heat.
The temperature must not exceed 566ÉC (1050ÉF).
The metal will have a dull red glow at the desired
temperature. Excessive heat will decrease the
strength of the metal and result in a weakened
frame.
Welding the joints around riveted cross members
and frame side rails is not recommended.
A straightening repair process should be limited to
frame members that are not severely damaged. The
replacement bolts, nuts and rivets that are used to
join the frame members should conform to the same
specifications as the original bolts, nuts and rivets.
FRAME REPAIRS
DRILLING HOLES
Do not drill holes in frame side rail top and bottom
flanges, metal fatigue can result causing frame fail-
ure. Holes drilled in the side of the frame rail must
be at least 38 mm (1.5 in.) from the top and bottom
flanges.
Additional drill holes should be located away from
existing holes.
WELDING
Use MIG, TIG or arc welding equipment to repair
welded frame components.
Frame components that have been damaged should
be inspected for cracks before returning the vehicle
to use. If cracks are found in accessible frame com-
ponents perform the following procedures.
(1) Drill a hole at each end of the crack with a 3
mm (O.125 in.) diameter drill bit.
(2) Using a suitable die grinder with 3 inch cut off
wheel, V-groove the crack to allow 100% weld pene-
tration.
(3) Weld the crack.
(4) If necessary when a side rail is repaired, grind
the weld smooth and install a reinforcement channel
(Fig. 9) over the repaired area.
NOTE: If a reinforcement channel is required, the
top and bottom flanges should be 0.250 inches nar-
rower than the side rail flanges. Weld only in the
areas indicated (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9 Frame Reinforcement
1 - .250 IN FROM EDGE
2 - TOP FLANGE
3 - BOTTOM FLANGE
4 - FRAME RAIL
5 - FRAME REPAIR REINFORCEMENT
BR/BEFRAME & BUMPERS 13 - 7
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1304 of 2255

FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
A combination fuel filter and fuel pressure regula-
tor (Fig. 2) is used on all engines. It is located on the
top of the fuel pump module. A separate frame
mounted fuel filter is not used with any engine.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the powertrain control
module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at the fuel injectors. It contains
a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a fuel return
valve. The internal fuel filter (Fig. 2) is also part of
the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator (Fig. 2) .
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain
some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second checkvalve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel
pump.Refer to Fuel PumpÐDescription and
Operation for more information. Also refer to
the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and the Fuel
Pump Pressure Tests.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 49.2 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE, EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRES-
SURE REGULATOR, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED.
Refer to Fuel System Pressure Release in Fuel
Delivery System section of this group.
The fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 3) is
located at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 4) or (Fig.
5).
Fuel pump module removal is not necessary.
(1) Drain fuel tank and remove tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
Fig. 3 Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 5
Page 1307 of 2255
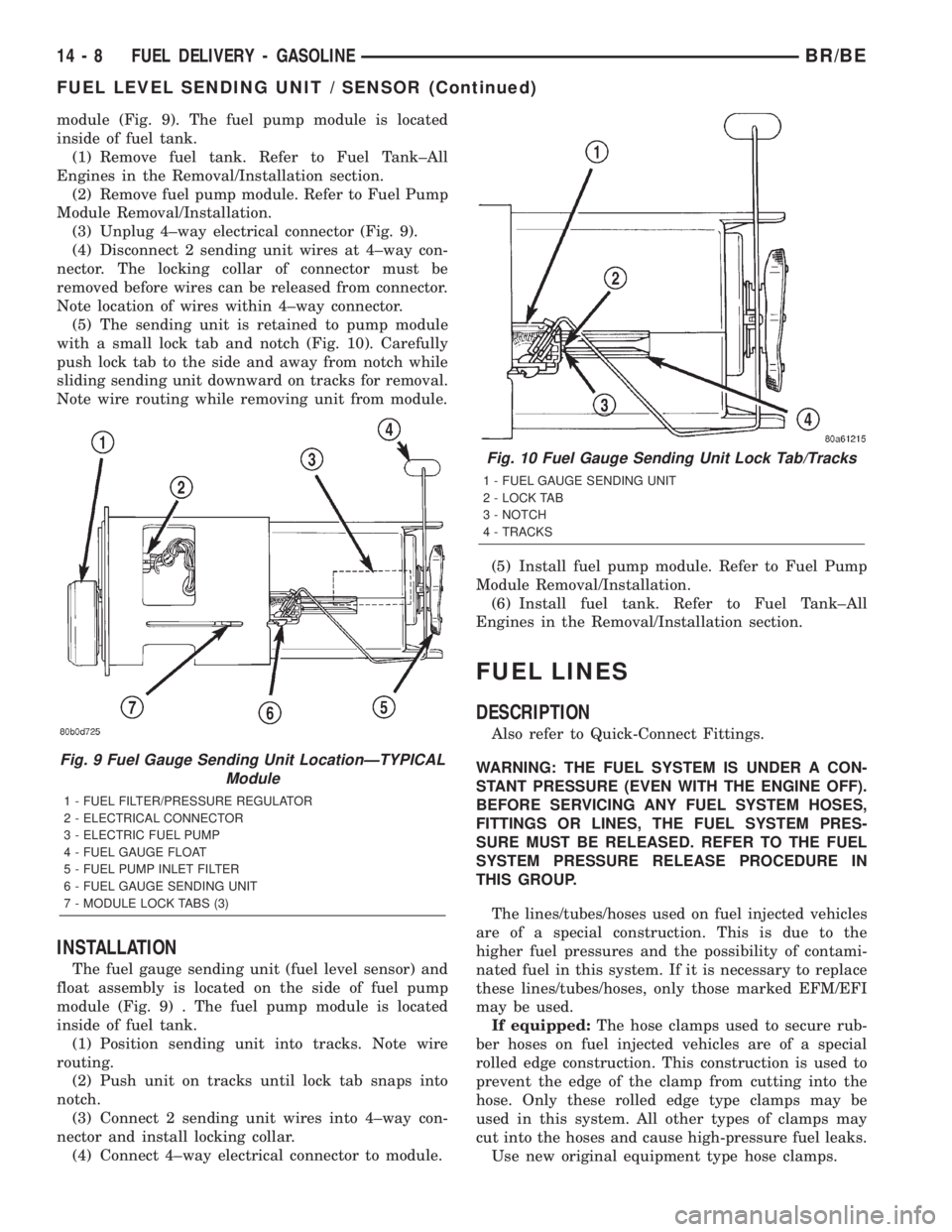
module (Fig. 9). The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
(2) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Unplug 4±way electrical connector (Fig. 9).
(4) Disconnect 2 sending unit wires at 4±way con-
nector. The locking collar of connector must be
removed before wires can be released from connector.
Note location of wires within 4±way connector.
(5) The sending unit is retained to pump module
with a small lock tab and notch (Fig. 10). Carefully
push lock tab to the side and away from notch while
sliding sending unit downward on tracks for removal.
Note wire routing while removing unit from module.
INSTALLATION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 9) . The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Position sending unit into tracks. Note wire
routing.
(2) Push unit on tracks until lock tab snaps into
notch.
(3) Connect 2 sending unit wires into 4±way con-
nector and install locking collar.
(4) Connect 4±way electrical connector to module.(5) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(6) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Fig. 9 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit LocationÐTYPICAL
Module
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
5 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
6 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - MODULE LOCK TABS (3)
Fig. 10 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Lock Tab/Tracks
1 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
2 - LOCK TAB
3 - NOTCH
4 - TRACKS
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1308 of 2255

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
All fuel systems are equipped with a fuel tank
module mounted, combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0±414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 11).The DRBtIII Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 9
Page 1310 of 2255

WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING TO NEXT STEP,
NOTE THE FUEL PUMP WILL BE ACTIVATED AND
SYSTEM PRESSURE WILL BE PRESENT. THIS WILL
OCCUR AFTER CONNECTING TEST LEADS FROM
LCS ADAPTER INTO FUEL PUMP RELAY CAVITIES.
THE FUEL PUMP WILL OPERATE EVEN WITH IGNI-
TION KEY IN OFF POSITION. BEFORE ATTACHING
TEST LEADS, BE SURE ALL FUEL LINES AND
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS ARE CONNECTED.
CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the vehi-
cle electrical system and LCS adapter, the test
leads must be connected into relay cavities exactly
as shown in following steps.
Depending upon vehicle model, year or engine con-
figuration, three different types of relays may be
used: Type-1, type-2 and type±3.
(14) If equipped withtype±1 relay(Fig. 13),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 13).
(15) If equipped withtype±2 relay(Fig. 14),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 14).
(16) If equipped withtype±3 relay(Fig. 15),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 3 and 5. For location of these cavi-
ties, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 15).
(17) When LCS adapter test leads are attached
into relay cavities, fuel pumpwill be activated.
Determine fuel pump amperage on DRB screen.
Amperage should be below 10.0 amps. If amperage is
below 10.0 amps, and specifications for the Fuel
Pump Pressure, Fuel Pump Capacity and Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down tests were met, the fuel pump mod-
ule is OK.
(18) If amperage is more than 10.0 amps, replace
fuel pump module assembly. The electric fuel pump
is not serviced separately.
(19) Disconnect test leads from relay cavities
immediately after testing.
Fig. 13 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 1
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 14 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 11
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1312 of 2255
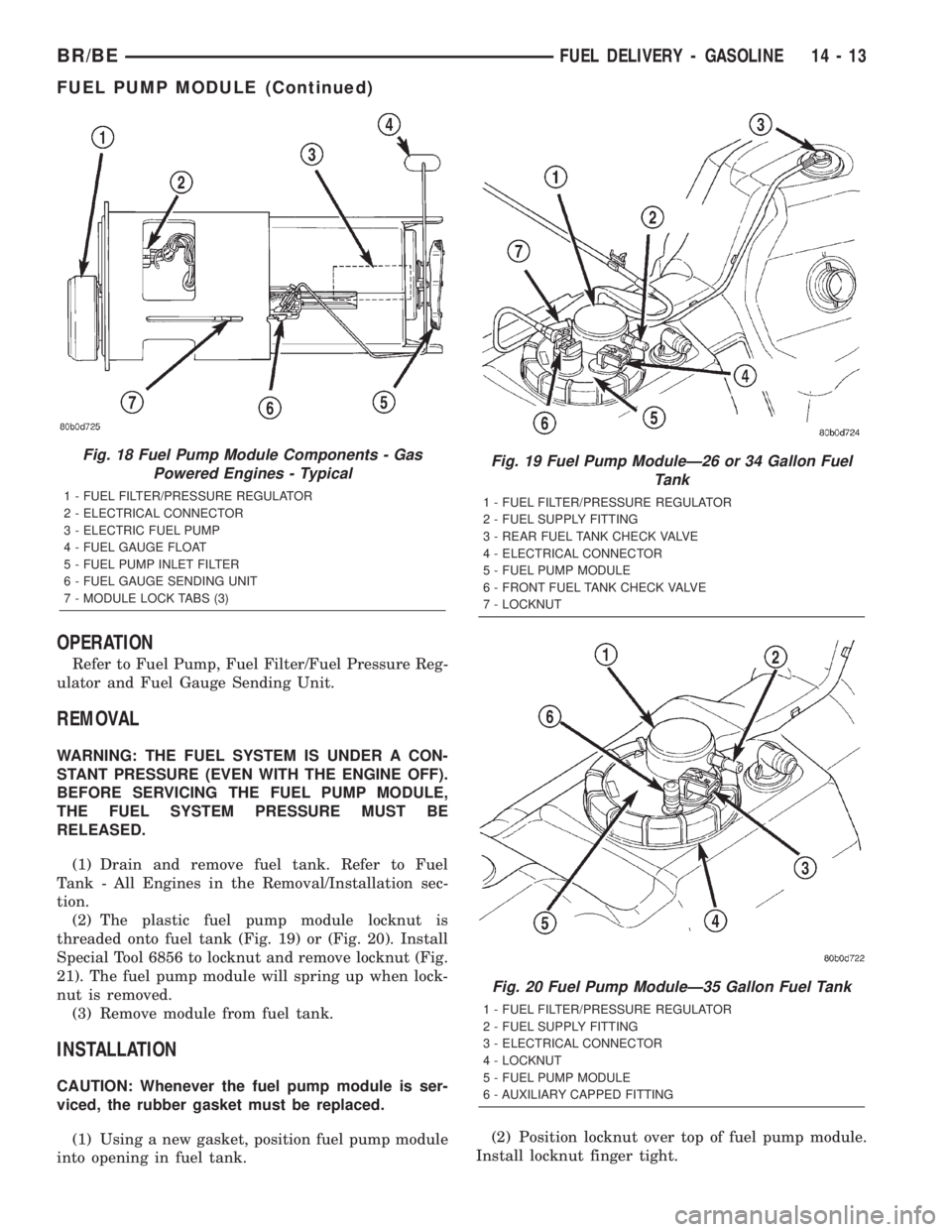
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Pump, Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Reg-
ulator and Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED.
(1) Drain and remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank - All Engines in the Removal/Installation sec-
tion.
(2) The plastic fuel pump module locknut is
threaded onto fuel tank (Fig. 19) or (Fig. 20). Install
Special Tool 6856 to locknut and remove locknut (Fig.
21). The fuel pump module will spring up when lock-
nut is removed.
(3) Remove module from fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Whenever the fuel pump module is ser-
viced, the rubber gasket must be replaced.
(1) Using a new gasket, position fuel pump module
into opening in fuel tank.(2) Position locknut over top of fuel pump module.
Install locknut finger tight.
Fig. 18 Fuel Pump Module Components - Gas
Powered Engines - Typical
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
5 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
6 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - MODULE LOCK TABS (3)
Fig. 19 Fuel Pump ModuleÐ26 or 34 Gallon Fuel
Tank
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - REAR FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - FRONT FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
7 - LOCKNUT
Fig. 20 Fuel Pump ModuleÐ35 Gallon Fuel Tank
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
4 - LOCKNUT
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - AUXILIARY CAPPED FITTING
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 13
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
Page 1314 of 2255

The fuel rail is not repairable.
CAUTION: The left and right sections of the fuel rail
are connected with a flexible connecting hose. Do
not attempt to separate the rail halves at this con-
necting hose. Due to the design of this connecting
hose, it does not use any clamps. Never attempt to
install a clamping device of any kind to the hose.
When removing the fuel rail assembly for any rea-
son, be careful not to bend or kink the connecting
hose.
OPERATION - 8.0L
High pressure from the fuel pump is routed to the
fuel rail. The fuel rail then supplies the necessary
fuel to each individual fuel injector.
A fuel pressure test port is located on the fuel rail.
A quick-connect fitting with a safety latch clip is
used to attach the fuel line to the fuel rail.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE TURNED
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY,
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
To release fuel pressure, refer to Fuel System Pres-
sure Release Procedure found in this group.
CAUTION: The left and right fuel rails are replaced
as an assembly. Do not attempt to separate the rail
halves at the connecting hose (Fig. 24). Due to the
design of this connecting hose, it does use any
clamps. Never attempt to install a clamping device
of any kind to the hose. When removing the fuel rail
assembly for any reason, be careful not to bend or
kink the connecting hose.
(1) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Perform fuel pressure release procedure.
(4) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
Refer to Throttle Body removal in this group.
(5) If equipped with air conditioning, remove the
A-shaped A/C compressor-to-intake manifold support
bracket (three bolts) (Fig. 25).
(6) Disconnect electrical connectors at all fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 26). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(7) Disconnect fuel tube (line) at side of fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures,
(8) Remove the remaining fuel rail mounting bolts.
(9) Gently rock and pull theleftfuel rail until the
fuel injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Gently rock and pull therightfuel rail until the fuel
injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all fuel injec-
tors have cleared the intake manifold.
Fig. 24 Fuel Rail AssemblyÐTypical
1 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSE
2 - FUEL RAIL
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
Fig. 25 A/C Compressor Support BracketÐTypical
1 - AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR SUPPORT BRACKET
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 15
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1315 of 2255
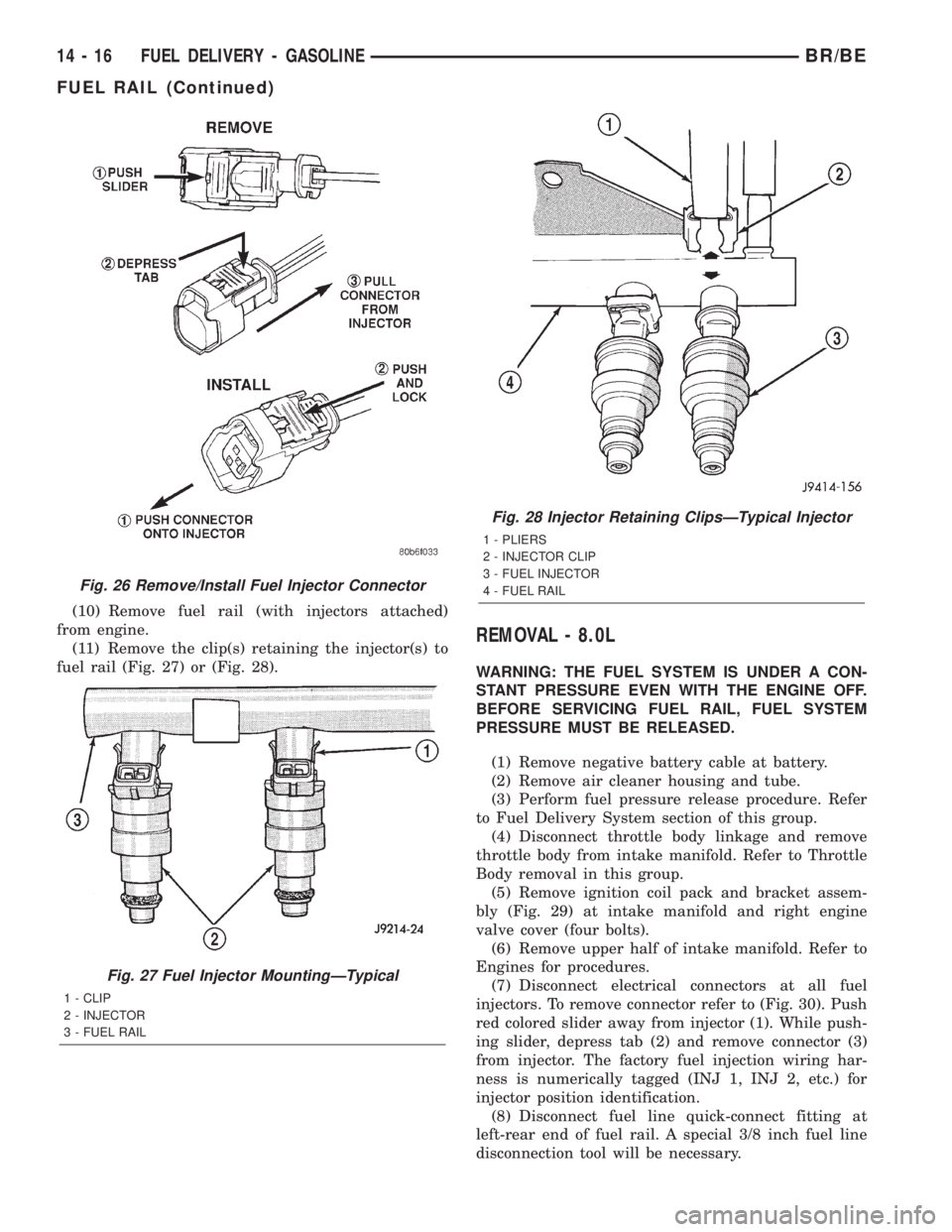
(10) Remove fuel rail (with injectors attached)
from engine.
(11) Remove the clip(s) retaining the injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 27) or (Fig. 28).
REMOVAL - 8.0L
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL RAIL, FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
(1) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing and tube.
(3) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Delivery System section of this group.
(4) Disconnect throttle body linkage and remove
throttle body from intake manifold. Refer to Throttle
Body removal in this group.
(5) Remove ignition coil pack and bracket assem-
bly (Fig. 29) at intake manifold and right engine
valve cover (four bolts).
(6) Remove upper half of intake manifold. Refer to
Engines for procedures.
(7) Disconnect electrical connectors at all fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 30). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification.
(8) Disconnect fuel line quick-connect fitting at
left-rear end of fuel rail. A special 3/8 inch fuel line
disconnection tool will be necessary.
Fig. 26 Remove/Install Fuel Injector Connector
Fig. 27 Fuel Injector MountingÐTypical
1 - CLIP
2 - INJECTOR
3 - FUEL RAIL
Fig. 28 Injector Retaining ClipsÐTypical Injector
1 - PLIERS
2 - INJECTOR CLIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
4 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 16 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL RAIL (Continued)