2002 DODGE RAM warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 1125 of 2255

(2) Position the oil pump cover onto the pump
body. Tighten cover bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install the relief valve and spring. Insert the
cotter pin.
(4) Tap on a new retainer cap.
(5) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pump. During installation slowly
rotate pump body to ensure driveshaft-to-pump rotor
shaft engagement.
(2) Hold the oil pump base flush against mating
surface on No.5 main bearing cap. Finger tighten
pump attaching bolts. Tighten attaching bolts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The aluminum intake manifold (Fig. 64) is a single
plane design with equal length runners and uses a
separate plenum, therefore the manifold does have a
plenum gasket. It also uses separate flange gaskets
and front and rear cross-over gaskets. Extreme care
must be used when sealing the gaskets to ensure
that excess sealant does not enter the intake runners
causing a restriction. Whenever the intake manifold
is removed inspect the plenum pan for evidence of
excess oil buildup, this condition indicates that the
plenum pan gasket is leaking.
OPERATION
The intake manifold, meters and delivers air to the
combustion chambers allowing the fuel delivered by
the fuel injectors to ignite, thus producing power.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS, OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.(3) If a change in RPMs occur, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the accessory drive bracket.
(6) Remove the air cleaner.
(7) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect the accelerator linkage (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE
CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL) and if so equipped,
the speed control and transmission kickdown cables.
(9) Remove the return spring.
(10) Remove the distributor cap and wires.
(11) Disconnect the coil wires.
(12) Disconnect the heat indicator sending unit
wire.
Fig. 64 Intake Manifold and Throttle BodyÐV-8 Gas
Engines Typical
1 - FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
2 - FUEL RAIL MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSES
9 - 50 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1139 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings.
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings.
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves.
5. Leaking intake gasket. 5. Replace intake gaskets.
6. Leaking valve guide seals. 6. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART.
9 - 64 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1151 of 2255

CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The alloy cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 7) are held
in place by 12 bolts. The spark plugs are located in
the peak of the wedge between the valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the heat shields (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Remove the air cleaner.
(8) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
Fig. 7 Cylinder Head Assembly
1 - SPARK PLUG
2 - INTAKE VALVES
3 - SPARK PLUG
4 - INTAKE VALVES
5 - SPARK PLUG
6 - SPARK PLUG
7 - INTAKE VALVE
8 - SPARK PLUG
9 - EXHAUST VALVE
10 - EXHAUST VALVES
11 - EXHAUST VALVES
9 - 76 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
Page 1181 of 2255

when compressed to 34 mm (1-11/32 inches). Replace
spring that fails to meet these specifications.
If oil pressure was low and pump is within specifi-
cations, inspect for worn engine bearings or other
reasons for oil pressure loss.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate both oil pump rotors using petroleum
jelly or lubriplate and install in the timing chain
cover. Use new parts as required (Fig. 67).
(2) Position the oil pump cover onto the timing
chain cover. Tighten cover screws to 14 N´m (125 in.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Make sure that inner ring moves freely after
cover is installed.
(4) Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(5) Squirt oil into relief valve hole until oil runs
out.
(6) Install the relief valve and spring.
(7) Using a new pressure relief valve gasket,
install the relief valve plug. Tighten the plug to 20
N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install oil filter that has been filled with oil.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The aluminum intake manifold (Fig. 68) has two
plenum chambers an upper and lower which supply
air to five runners each. Passages across the longitu-
dinal center of the manifold feed air from the throttle
body to the plenum chambers.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS, OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.
(3) If a change in RPMs occur, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
Fig. 67 Priming Oil Pump.
1 - FILL WITH PETROLEUM JELLY OR LUBER PLATE
Fig. 68 Upper and Lower Intake ManifoldÐ8.0L
Engine
1 - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - THROTTLE BODY (MPI)
3 - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD
9 - 106 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1211 of 2255
INSTALLATION
WARNING: THE OUTSIDE EDGE OF THE HEAD
GASKET IS VERY SHARP. WHEN HANDLING THE
NEW HEAD GASKET, USE CARE NOT TO INJURE
YOURSELF.
(1) Install a new gasket with the part number side
up, and locate the gasket over the dowel sleeves.
(2) Using an engine lifting crane, lower the cylin-
der head onto the engine.
(3) Lightly lubricate head bolts with engine oil and
install. Using the sequence shown in (Fig. 30),
tighten bolts in the following steps:
(a) Torque bolts to 80 N´m (59 ft. lbs.)
(b) Torque bolts to 105 N´m (77 ft. lbs.)
(c) Re-check all bolts to 105 N´m (77 ft. lbs.)
(d) Tighten all bolts an additional ò turn (90É)
(4) Connect fuel return line at rear of head (Fig.
24). Install both sealing washers and torque banjo
bolt to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
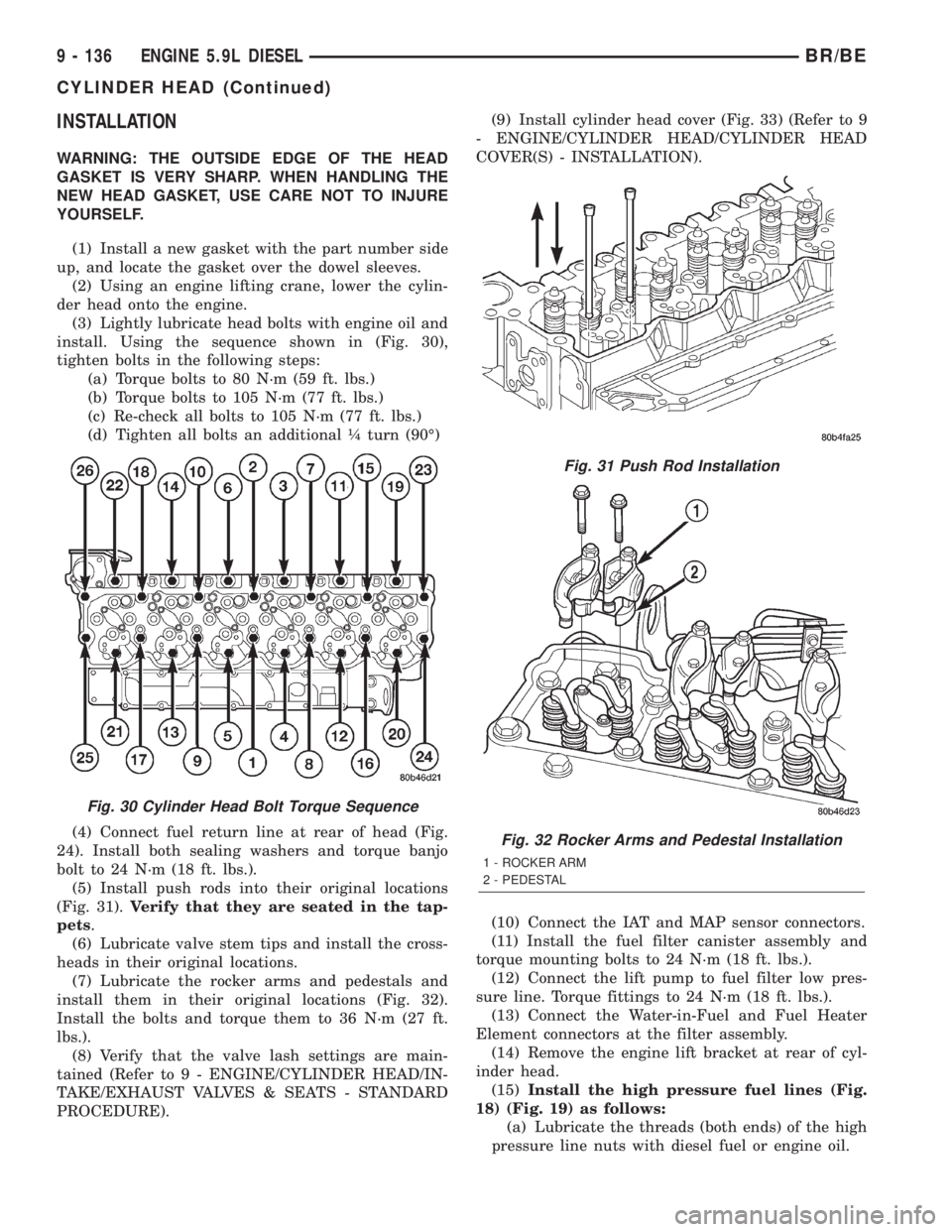
(5) Install push rods into their original locations
(Fig. 31).Verify that they are seated in the tap-
pets.
(6) Lubricate valve stem tips and install the cross-
heads in their original locations.
(7) Lubricate the rocker arms and pedestals and
install them in their original locations (Fig. 32).
Install the bolts and torque them to 36 N´m (27 ft.
lbs.).
(8) Verify that the valve lash settings are main-
tained (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/IN-
TAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).(9) Install cylinder head cover (Fig. 33) (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(10) Connect the IAT and MAP sensor connectors.
(11) Install the fuel filter canister assembly and
torque mounting bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(12) Connect the lift pump to fuel filter low pres-
sure line. Torque fittings to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(13) Connect the Water-in-Fuel and Fuel Heater
Element connectors at the filter assembly.
(14) Remove the engine lift bracket at rear of cyl-
inder head.
(15)Install the high pressure fuel lines (Fig.
18) (Fig. 19) as follows:
(a) Lubricate the threads (both ends) of the high
pressure line nuts with diesel fuel or engine oil.
Fig. 30 Cylinder Head Bolt Torque Sequence
Fig. 31 Push Rod Installation
Fig. 32 Rocker Arms and Pedestal Installation
1 - ROCKER ARM
2 - PEDESTAL
9 - 136 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1253 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove the engine oil pressure sensor and
install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool C-3292 with
a suitable adapter.
(2) Start engine and warm to operating tempera-
ture.
(3) Record engine oil pressure and compare with
engine oil pressure chart.
CAUTION: If engine oil pressure is zero at idle, DO
NOT RUN THE ENGINE.
Engine Oil Pressure (MIN)
At Idle 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
At 2000 rpm 310.2 kPa (45 psi)
If minimum engine oil pressure is below these
ranges, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(4) Remove oil pressure gauge and install the oil
pressure sensor. Tighten the sensor to 16 N´m (144
in. lbs.) torque.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL LEVEL
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable oil level is in the SAFE RANGE on
the engine oil dipstick (Fig. 150).
Unless the engine has exhibited loss of oil pres-
sure, run the engine for about five minutes before
checking oil level. Checking engine oil level of a cold
engine is not accurate.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Replace dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the SAFE RANGE
area on the dipstick.
(7) Replace dipstick
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE
WARNING: HOT OIL CAN CAUSE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: Change engine oil and filter at intervals
specified in the owner's manual.
(1) Operate the engine until the water tempera-
ture reaches 60ÉC (140ÉF). Shut the engine off.
(2) Use a container that can hold at least 14 liters
(15 quarts) to hold the used oil. Remove the oil drain
plug and drain the used engine oil into the container.
1 - ROCKER ARM
2 - ROCKER SHAFT
3 - PEDESTAL
4 - FROM MAIN OIL RIFLE
5 - TO VALVE TRAIN
6 - MAIN OIL RIFLE
7 - FROM MAIN OIL RIFLE
8 - TO CAMSHAFT9 - TO PISTON COOLING NOZZLE
10 - FROM OIL COOLER
11 - CRANKSHAFT MAIN JOURNAL
12 - ROD JOURNAL
13 - TO ROD BEARING
14 - MAIN OIL RIFLE
Fig. 150 Oil Level Indicator (Dipstick)
1 - ADD OIL MARK
2 - O-RING
3 - SAFE RANGE
9 - 178 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2255

(3) Always check the condition of the used oil. This
can give you an indication of engine problems that
might exist.
²Thin, black oil indicates fuel dilution.
²Milky discoloration indicates coolant dilution.
(4) Clean the area around the oil filter head.
Remove the filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICA-
TION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(5) Install new oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
(6) Clean the drain plug and the sealing surface of
the pan. Check the condition of the threads and seal-
ing surface on the oil pan and drain plug.
(7) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Use only High-Quality Multi-Viscosity lubricat-
ing oil in the Cummins Turbo Diesel engine. Choose
the correct oil for the operating conditions (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(9) Fill the engine with the correct grade of new oil
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID
CAPACITIES - SPECIFICATIONS).
(10) Start the engine and operate it at idle for sev-
eral minutes. Check for leaks at the filter and drain
plug.
(11) Stop engine. Wait several minutes to allow the
oil to drain back to the pan and check the level
again.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL Care should be
exercised when disposing of used engine oil after
it has been drained from a vehicle's engine.
OIL COOLER & LINES
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean the sealing surfaces.
Apply 483 kPa (70 psi) air pressure to the element
to check for leaks. If the element leaks, replace the
element.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Clean the area around the oil filter head.
Remove the filter using a 90-95 mm filter wrench.
(2) Clean the gasket surface of the filter head. The
filter canister O-Ring seal can stick on the filter
head. Make sure it is removed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fill the oil filter element with clean oil before
installation. Use the same type oil that will be used
in the engine.
(2) Apply a light film of lubricating oil to the seal-
ing surface before installing the filter.
CAUTION: Mechanical over-tightening may distort
the threads or damage the filter element seal.
(3) Install the filter until it contacts the sealing
surface of the oil filter adapter. Tighten filter an
additional ó turn.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(4) Remove flywheel.
(5) Disconnect starter cables from starter motor.
(6) Remove starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL)
and transmission adapter plate assembly.
WARNING: HOT OIL CAN CAUSE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(7) Drain the engine oil (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Install the oil pan drain plug with a new seal-
ing washer and tighten to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove oil pan bolts, break the pan to block
seal, and lower pan slightly and remove oil suction
tube fasteners.
(10) Remove oil pan and suction tube (Fig. 151).
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from the oil pan and
cylinder block sealing surfaces. Extra effort may be
required around T-joint areas. Clean oil pan and
flush suction tube with a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect the oil pan, suction tube, and tube braces
for cracks and damage. Replace any defective compo-
nent. Inspect the oil drain plug and drain hole
threads. Inspect the oil pan sealing surface for
straightness. Repair any minor imperfections with a
ball-peen hammer. Do not attempt to repair an oil
pan by welding.
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 179
OIL (Continued)
Page 1285 of 2255

CHARGE AIR COOLER AND
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION
The charge air system (Fig. 29) consists of the
charge air cooler piping, charge air cooler and intake
air grid heater.
The charge air cooler is a heat exchanger that uses
air flow from vehicle motion to dissipate heat from
the intake air. As the turbocharger increases air
pressure, the air temperature increases. Lowering
the intake air temperature increases engine effi-
ciency and power.
OPERATION
Intake air is drawn through the air cleaner and
into the turbocharger compressor housing. Pressur-
ized air from the turbocharger then flows forward
through the charge air cooler located in front of the
radiator. From the charge air cooler the air flows
back into the intake manifold.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGE AIR
COOLER SYSTEM - LEAKS
Low turbocharger boost pressure and low engine
preformance can be caused by leaks in the charge air
cooler or it's plumbing. The following procedure out-
lines how to check for leaks in the charge air cooler
system.(1) Loosen clamp and remove turbocharger to air
inlet duct rubber sleeve from turbocharger (Fig. 30).
(2) Insert Special Tool 8442 Adapter into the rub-
ber sleeve. Tighten existing clamp to 8 N´m (72
in.lbs.).
CAUTION: Do not apply more than 138 kpa (20 psi)
air pressure to the charge air cooler system, sever
damage to the charge air cooler system may occur.
(3) Connect regulated air supply to air fitting on
Special Tool 8442 Adapter. Set air pressure to a Max-
imum of 138 kpa (20 psi).
(4) Using soapy water check the air inlet ducts,
rubber sleeves, charge air cooler and intake manifold
for leaks.
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF THE ENGINE WAS JUST TURNED
OFF, THE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM TUBES MAY BE
HOT.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove the front bumper (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
BUMPER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the front support bracket.
Fig. 29 Intake Air Circulation
1 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
2 - AIRFILTER
3 - TURBOCHARGER
Fig. 30 AIR INLET DUCT RUBBER SLEEVE
1 - CLAMP
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR DUCT RUBBER SLEEVE
4 - AIR INLET DUCT
11 - 18 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE