2002 DODGE RAM fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 16 of 2255

²The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal
law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine perfor-
mance, damage the emission control system, and
could result in loss of warranty coverage.
²An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition
malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to
overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or
some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or
malfunctioning and may require immediate service.
Contact your dealer for service assistance.
²When pulling a heavy load or driving a fully
loaded vehicle when the humidity is low and the tem-
perature is high, use a premium unleaded fuel to
help prevent spark knock. If spark knock persists,
lighten the load, or engine piston damage may result.
²The use of fuel additives which are now being
sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Most
of these products contain high concentrations of
methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle perfor-
mance problems resulting from the use of such fuels
or additives is not the responsibility of
DaimlerChrysler Corporation and may not be covered
under the new vehicle warranty.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control
systems can result in civil penalties being assessed
against you.
DESCRIPTION - FUEL REQUIREMENTS -
DIESEL ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Do not use alcohol or gasoline as a fuel
blending agent. They can be unstable under certain
conditions and hazardous or explosive when mixed
with diesel fuel.
Use good quality diesel fuel from a reputable sup-
plier in your Dodge truck. For most year-round ser-
vice, number 2 diesel fuel meeting ASTM
specification D-975 will provide good performance. If
the vehicle is exposed to extreme cold (below 0ÉF/-
18ÉC), or is required to operate at colder-than-normal
conditions for prolonged periods, use climatized No. 2
diesel fuel or dilute the No. 2 diesel fuel with 50%
No. 1 diesel fuel. This will provide better protection
from fuel gelling or wax-plugging of the fuel filters.
Diesel fuel is seldom completely free of water. To
prevent fuel system trouble, including fuel line freez-
ing in winter, drain the accumulated water from the
fuel/water separator using the fuel/water separator
drain provided. If you buy good-quality fuel and fol-
low the cold-weather advice above, fuel conditioners
should not be required in your vehicle. If available in
your area, a high cetane ªpremiumº diesel fuel mayoffer improved cold starting and warm-up perfor-
mance.
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. DISPOSE OF
GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROPERLY, CONTACT
YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT AGENCY FOR
LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER IN YOUR
AREA. DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN
THE ENGINE IS AT OPERATING TEMPERATURE OR
HOT UNDER PRESSURE, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT. AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHEN
ENGINE COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS
PERFORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants
is not recommended, as they provide less freeze
protection and less corrosion protection.
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves and
engine block. Then coolant carries the heat to the
radiator where the tube/fin radiator can transfer the
heat to the air.
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769), or the equiva-
lent ethylene glycol base coolant with organic corro-
sion inhibitors (called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% Ethylene Glycol and 50% distilled
water to obtain a freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it
loses color or becomes contaminated, drain, flush,
and replace with fresh properly mixed coolant solu-
tion.
CAUTION: MoparTAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769) may not be
mixed with any other type of antifreeze. Mixing of
coolants other than specified (non-HOAT or other
HOAT), may result in engine damage that may not
be covered under the new vehicle warranty, and
decreased corrosion protection.
BR/BELUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 3
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 19 of 2255

DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in this
group for the recommended maintenance (fluid/filter
change) intervals for this transmission.
NOTE: Refer to Service Procedures in this group for
fluid level checking procedures.
MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic Transmis-
sion Fluid is the recommended fluid for
DaimlerChrysler automatic transmissions.
Dexron II fluid IS NOT recommended. Clutch
chatter can result from the use of improper
fluid.
MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic Transmis-
sion Fluid when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown.This is normal.A dark brown/black fluid
accompanied with a burnt odor and/or deterioration
in shift quality may indicate fluid deterioration or
transmission component failure.
FLUID ADDITIVES
DaimlerChrysler strongly recommends against the
addition of any fluids to the transmission, other than
those automatic transmission fluids listed above.
Exceptions to this policy are the use of special dyes
to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel and/or quality. These
additives and others also claim to improve converter
clutch operation and inhibit overheating, oxidation,
varnish, and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to the satisfaction of DaimlerChrysler and
these additivesmust not be used.The use of trans-
mission ªsealersº should also be avoided, since they
may adversely affect the integrity of transmission
seals.
OPERATION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
The automatic transmission fluid is selected based
upon several qualities. The fluid must provide a high
level of protection for the internal components by
providing a lubricating film between adjacent metal
components. The fluid must also be thermally stable
so that it can maintain a consistent viscosity through
a large temperature range. If the viscosity stays con-
stant through the temperature range of operation,transmission operation and shift feel will remain con-
sistent. Transmission fluid must also be a good con-
ductor of heat. The fluid must absorb heat from the
internal transmission components and transfer that
heat to the transmission case.
FLUID CAPACITIES
SPECIFICATIONS
FLUID CAPACITIES
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
FUEL TANK
2500 Series Club Cab
and Quad Cab with 6.5'
Short Box129 L (34 gal.)*****
All 8' Long Box 132 L (35 gal.)*****
All Cab/Chassis Models 132 L (35 gal.)*****
ENGINE OIL WITH FILTER
5.9L 4.7 L (5.0 qts.)
8.0L 6.6 L (7.0 qts.)
5.9L DIESEL 10.4 L (11.0 qts.)
COOLING SYSTEM
5.9L 19 L (20 qts.)****
8.0L 24.5 L (26.0 qts.)****
5.9L DIESEL 22.7 L (24.0 qts.)****
POWER STEERING
Power steering fluid capacities are dependent on
engine/chassis options as well as steering gear/cooler
options. Depending on type and size of internal
cooler, length and inside diameter of cooler lines, or
use of an auxiliary cooler, these capacities may vary.
Refer to 19, Steering for proper fill and bleed
procedures.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Service Fill - 46RE 3.8 L (4.0 qts.)
O-haul - 46RE 9-9.5L (19-20 pts.)*
Service Fill - 47RE 3.8 L (4.0 qts.)
O-haul - 47RE 14-16 L (29-33 pts.)*
0 - 6 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 86 of 2255

AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(2) Remove axle shaft seal from the differential
housing with a long drift or punch.Be careful not
to damage housing.
(3) Clean the inside perimeter of the differential
housing with fine crocus cloth.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(2) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 25).
(3) Install axles and hub bearings.
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The disconnect axle control system consists of:
²Shift motor.
²Indicator switch.
²Vacuum switch.
²Vacuum harness (Fig. 26).
OPERATION
The shift motor receives a vacuum signal from the
switch mounted on the transfer case when the vehi-
cle operator wants to switch from two wheel drive
mode to four wheel drive mode, or vice versa. When
this signal is received, the shift motor begins to move
the shift fork and collar within the axle housing. In
the four wheel drive mode, the shift collar connects
the axle intermediate shaft to the axle shaft to sup-
ply engine power to both front wheels. In two wheel
drive mode, the shift collar is disengaged from the
intermediate shaft and the intermediate shaft is
allowed to free-spin. When the two shafts are disen-
gaged, the load on the engine is reduced, thereby pro-
viding better fuel economy and road handling.
Fig. 25 SEAL INSTALLATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - POSITION FOR OPEN-END WRENCH
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8417
5 - SEAL
6 - SPECIAL TOOL 8411
Fig. 26 VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM
1 - CHECK VALVE
2 - CONTROL SWITCH ON TRANSFER CASE
3 - AIR VENT FILTER
4 - AXLE SHIFT MOTOR
5 - INDICATOR SWITCH
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 31
Page 378 of 2255

ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION - ECM
The ECM is bolted to the left side of the engine
behind the fuel filter (Fig. 14). It is a separate com-
ponent and can be serviced. The FPCM is internal to
the fuel injection pump (Fig. 15) and cannot be ser-
viced.
OPERATION - ECM
The main functions of the Engine Control Module
(ECM) and Fuel Injection Pump Control Module
(FPCM) are to electrically control the fuel system.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM)does not
controlthe fuel system.
The ECM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.If the ECM has
been replaced, flashed or re-calibrated, the
ECM must learn the Accelerator Pedal Position
Sensor (APPS) idle voltage. Failure to learn
this voltage may result in unnecessary diagnos-
tic trouble codes. Refer to ECM Removal/Instal-
lation for learning procedures.
The ECM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
ECM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to asECM Outputs.The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the ECM are
consideredECM Inputs.NOTE: ECM Inputs:
²Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) Volts
²APPS Idle Validation Switches #1 and #2
²Battery voltage
²Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²(FPCM) Fuel Injection Pump Control Module
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
²Ground circuits
²Intake manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
²Manifold Air Pressure Sensor (Boost Pressure
Sensor)
²Oil pressure sensor
²PCM
²Power Take Off (PTO)
²Power ground
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor
Fig. 14 Engine Control Module (ECM) Location
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - HEX HEADED BOLT
3 - 50-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
5 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
Fig. 15 Fuel Injection Pump Control Module (FPCM)
Location
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
BR/BEELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 13
Page 379 of 2255

NOTE: ECM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the ECM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the ECM. These are consideredECM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²CKP and APPS outputs to the PCM
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Five volt sensor supply
²Fuel injection pump
²Fuel injection pump relay
²(FPCM) Fuel Pump Control Module
²Fuel transfer (lift) pump
²Intake manifold air heater relays #1 and #2 con-
trol circuits
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp)
²Oil pressure gauge/warning lamp
²PCM
²Wait-to-start warning lamp
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) warning lamp
REMOVAL
The ECM is bolted to the engine block behind the
fuel filter (Fig. 16).(1) Record any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
found in the PCM or ECM.
To avoid possible voltage spike damage to either
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or ECM, igni-
tion key must be off, and negative battery cables
must be disconnected before unplugging ECM con-
nectors.
(2) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(3) Remove 50±way electrical connector bolt at
ECM (Fig. 16). Note: Connector bolt is female 4mm
hex head. To remove bolt, use a ball-hex bit or ball-
hex screwdriver such as Snap-Ont4mm SDABM4
(5/32º may also be used). As bolt is being removed,
very carefully remove connector from ECM.
(4) Remove three ECM mounting bolts and remove
ECM from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
Do not apply paint to back of ECM. Poor ground
will result.
(1) Clean ECM mounting points at engine block.
(2) Position ECM to engine block and install 3
mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(3) Check pin connectors in ECM and 50±way con-
nector for corrosion or damage. Repair as necessary.
(4) Clean pins in 50±way electrical connector with
a quick-dry electrical contact cleaner.
(5) Very carefully install 50±way connector to
ECM. Tighten connector hex bolt.
(6) Install battery cables.
(7)Turn key to ON position. Without starting
engine, slowly press throttle pedal to floor and
then slowly release. This step must be done
(one time) to ensure accelerator pedal position
sensor calibration has been learned by ECM. If
not done, possible DTC's may be set.
(8) Use DRB scan tool to erase any stored compan-
ion DTC's from PCM.
Fig. 16 Engine Control Module (ECM) Location and
Mounting
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - HEX HEADED BOLT
3 - 50-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
5 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 515 of 2255

INDICATOR DOES NOT ILLUMINATE WITH WASHER
RESERVOIR EMPTY
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the washer fluid level switch from
the washer fluid level switch connector receptacle.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity of the headlamp and dash wire harness connector
for the washer fluid level switch and a good ground.
There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 2. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground (G100)
as required.
(2) Remove the instrument cluster from the instru-
ment panel. Check for continuity between the washer
fluid switch sense circuit cavities of the headlamp
and dash wire harness connector for the washer fluid
level switch and the instrument panel wire harness
connector (Connector C2) for the instrument cluster.
If OK, replace the faulty washer fluid level switch. If
not OK, repair the open washer fluid switch sense
circuit between the washer fluid level switch and the
instrument cluster as required.
INDICATOR STAYS ILLUMINATED WITH WASHER
RESERVOIR FULL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the washer fluid level switch from
the washer fluid level switch connector receptacle.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit ter-
minal and the washer fluid switch sense terminal in
the washer fluid level switch connector receptacle.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to Step 2. If
not OK, replace the faulty washer fluid level switch.
(2) Remove the instrument cluster from the instru-
ment panel. Check for continuity between the washer
fluid switch sense circuit cavity of the headlamp and
dash wire harness connector for the washer fluid
level switch and a good ground. There should be no
continuity. If not OK, repair the shorted washer fluid
switch sense circuit between the washer fluid level
switch and the instrument cluster as required.
WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
A water-in-fuel indicator is standard equipment on
all instrument clusters, but is only functional in vehi-
cles equipped with an optional diesel engine. The
water-in-fuel indicator is located near the lower edge
of the instrument cluster overlay, to the left of center.
The water-in-fuel indicator consists of a stencilled
cutout of the text ªWATER IN FUELº in the opaque
layer of the instrument cluster overlay. The dark
outer layer of the overlay prevents the indicator from
being clearly visible when it is not illuminated. A redlens located behind the cutout causes the ªWATER
IN FUELº text to appear in red through the translu-
cent outer layer of the overlay when the indicator is
illuminated from behind by a Light Emitting Diode
(LED) soldered onto the instrument cluster electronic
circuit board. The water-in-fuel indicator is serviced
as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The water-in-fuel indicator gives an indication to
the vehicle operator when the water accumulated in
the diesel engine fuel filter/separator filter bowl
requires draining. This indicator is controlled by a
transistor on the instrument cluster circuit board
based upon cluster programming and electronic mes-
sages received by the cluster from the Engine Control
Module (ECM) over the Chrysler Collision Detection
(CCD) data bus. The water-in-fuel indicator Light
Emitting Diode (LED) receives battery current on the
instrument cluster electronic circuit board through
the fused ignition switch output (st-run) circuit
whenever the ignition switch is in the On or Start
positions; therefore, the indicator will always be off
when the ignition switch is in any position except On
or Start. The LED only illuminates when it is
switched to ground by the instrument cluster transis-
tor. The instrument cluster will turn on the water-in-
fuel indicator for the following reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position the indicator is illuminated
for about two seconds as a bulb test.
²Water-In-Fuel Lamp-On Message- Each time
the cluster receives a water-in-fuel lamp-on message
from the ECM, the indicator will be illuminated. The
indicator remains illuminated until the cluster
receives a water-in-fuel lamp-off message from the
ECM or until the ignition switch is turned to the Off
position, whichever occurs first.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the indicator will be
turned on during the bulb check portion of the test to
confirm the functionality of the LED and the cluster
control circuitry.
The ECM continually monitors the water-in-fuel
sensor, then sends the proper messages to the instru-
ment cluster. For further diagnosis of the water-in-
fuel indicator or the instrument cluster circuitry that
controls the indicator, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING). For proper diagnosis of the water-in-fuel
sensor, the ECM, the CCD data bus, or the message
inputs to the instrument cluster that control the
water-in-fuel indicator, a DRBIIItscan tool is
required. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic
information.
8J - 36 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERBR/BE
WASHER FLUID INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 1021 of 2255

CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(V8)BK Near Distributor 5
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(V10)Near Oil Filter 8
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(Diesel)Left Side of Engine 15
Fuel Heater (Diesel) Left Side of Engine 13
Fuel Injection Pump (Diesel) Left Side of Engine, Below ECM 13
Fuel Injector No.1 BK At Fuel Injector 7
Fuel Injector No. 2 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 3 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 4 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 5 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 6 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 7 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 8 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 9 BK At Fuel Injector 8
Fuel Injector No. 10 BK At Fuel Injector 8
Fuel Pump Module (Gas) LTGY At Frame Rail 29
Fuel Tank Module (Diesel) LTGY At Frame Rail N/S
Fuel Transfer Pump (Diesel) Left Rear of Engine Bottom of Pump 13
Generator BK Front of Engine 10, 11
Glove Box Lamp At Glove Box 30
Headlamp Switch C1 BK Left Side of Instrument Panel 30, 34
Headlamp Switch C2 Left Side of Instrument Panel 30, 34
Heated Mirror Switch Center of Instrument Panel 33
High Note Horn BK Front Bumper Right Support 22
Idle Air Control Motor BK On Throttle Body 12
Ignition Coil (5.9L) GY Right Front of Engine 7, 12
Ignition Coil 4 Pack (8.0L) BK Right Side of Engine 12
Ignition Coil 6 Pack (8.0L) BK Right Side of Engine 12
Ignition Switch C1 BK Steering Column 32
Ignition Switch C2 GY Steering Column 32
Instrument Cluster C1 Rear of Instrument Cluster 30
Instrument Cluster C2 Rear of Instrument Cluster 30
Intake Air Heater Relay
(Diesel)Left Fender Side Shield 21
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor (Diesel)Left Rear of Engine 13
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor (Gas)BK On Intake Manifold 7, 8
Joint Connector No. 1 In Power Distribution Center N/S
Joint Connector No. 2 In Power Distribution Center N/S
8W - 91 - 4 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONBR/BE
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1025 of 2255
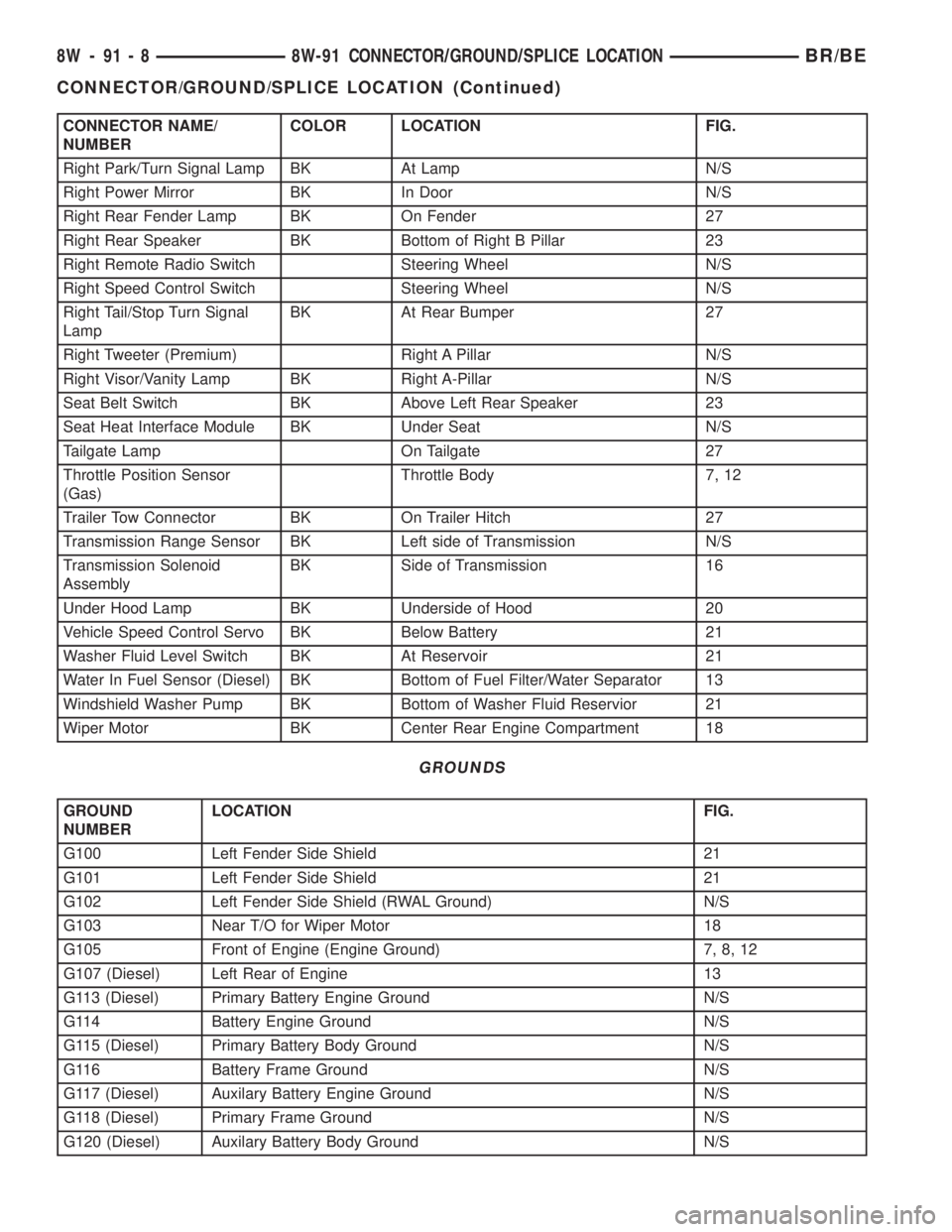
CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Right Park/Turn Signal Lamp BK At Lamp N/S
Right Power Mirror BK In Door N/S
Right Rear Fender Lamp BK On Fender 27
Right Rear Speaker BK Bottom of Right B Pillar 23
Right Remote Radio Switch Steering Wheel N/S
Right Speed Control Switch Steering Wheel N/S
Right Tail/Stop Turn Signal
LampBK At Rear Bumper 27
Right Tweeter (Premium) Right A Pillar N/S
Right Visor/Vanity Lamp BK Right A-Pillar N/S
Seat Belt Switch BK Above Left Rear Speaker 23
Seat Heat Interface Module BK Under Seat N/S
Tailgate Lamp On Tailgate 27
Throttle Position Sensor
(Gas)Throttle Body 7, 12
Trailer Tow Connector BK On Trailer Hitch 27
Transmission Range Sensor BK Left side of Transmission N/S
Transmission Solenoid
AssemblyBK Side of Transmission 16
Under Hood Lamp BK Underside of Hood 20
Vehicle Speed Control Servo BK Below Battery 21
Washer Fluid Level Switch BK At Reservoir 21
Water In Fuel Sensor (Diesel) BK Bottom of Fuel Filter/Water Separator 13
Windshield Washer Pump BK Bottom of Washer Fluid Reservior 21
Wiper Motor BK Center Rear Engine Compartment 18
GROUNDS
GROUND
NUMBERLOCATION FIG.
G100 Left Fender Side Shield 21
G101 Left Fender Side Shield 21
G102 Left Fender Side Shield (RWAL Ground) N/S
G103 Near T/O for Wiper Motor 18
G105 Front of Engine (Engine Ground) 7, 8, 12
G107 (Diesel) Left Rear of Engine 13
G113 (Diesel) Primary Battery Engine Ground N/S
G114 Battery Engine Ground N/S
G115 (Diesel) Primary Battery Body Ground N/S
G116 Battery Frame Ground N/S
G117 (Diesel) Auxilary Battery Engine Ground N/S
G118 (Diesel) Primary Frame Ground N/S
G120 (Diesel) Auxilary Battery Body Ground N/S
8W - 91 - 8 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONBR/BE
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)