2001 NISSAN ALMERA engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1028 of 2898

9 CHECK INJECTOR
1. Disconnect all ignition coil harness connectors.
2. Place pans or saucers under each injector.
3. Crank engine for about 3 seconds. Make sure that fuel sprays out from injectors.
SEF595Q
Fuel should be sprayed evenly for each cylinder.
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 10.
NG©Replace injectors from which fuel does not spray out. Always replace O-ring with new
one.
10 CHECK INTERMITTENT INCIDENT
Perform ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR INTERMITTENT INCIDENTº, EC-177.
©INSPECTION END
DTC P0171 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FUNCTION (LEAN SIDE)QG
Diagnostic Procedure (Cont'd)
EC-304
Page 1035 of 2898

6 CHECK FUNCTION OF INJECTORS
With CONSULT-II
1. Install all parts removed.
2. Start engine.
3. Perform ªPOWER BALANCEº in ªACTIVE TESTº mode with CONSULT-II.
SEF190Y
4. Make sure that each circuit produces a momentary engine speed drop.
Without CONSULT-II
1. Install all parts removed.
2. Start engine.
3. Listen to each injector operating sound.
MEC703B
Clicking noise should be heard.
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 7.
NG©Perform trouble diagnosis for ªINJECTORSº, EC-542.
7 REMOVE INJECTOR
1. Confirm that the engine is cooled down and there are no fire hazards near the vehicle.
2. Turn ignition switch ªOFFº.
3. Remove injector assembly. Refer to EC-41.
Keep fuel hose and all injectors connected to injector gallery.
©GO TO 8.
8 CHECK INJECTOR
1. Disconnect all injector harness connectors.
2. Disconnect all ignition coil harness connectors.
3. Prepare pans or saucers under each injectors.
4. Crank engine for about 3 seconds.
Make sure fuel does not drip from injector.
OK or NG
OK (Does not drip)©GO TO 9.
NG (Drips)©Replace the injectors from which fuel is dripping. Always replace O-ring with new one.
DTC P0172 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FUNCTION (RICH SIDE)QG
Diagnostic Procedure (Cont'd)
EC-311
Page 1045 of 2898

6 CHECK IGNITION SPARK
1. Turn Ignition switch ªOFFº.
2. Disconnect ignition coil assembly from rocker cover.
3. Connect a known good spark plug to the ignition coil assembly.
4. Place end of spark plug against a suitable ground and crank engine.
5. Check for spark.
SEF575Q
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 7.
NG©Check ignition coil, power transistor and their circuits. Refer to EC-547.
7 CHECK SPARK PLUGS
Remove the spark plugs and check for fouling, etc.
SEF156I
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 8.
NG©Repair or replace spark plug(s) with standard type one(s). For spark plug type, refer to
EM-19, ªChecking and changingº.
8 CHECK COMPRESSION PRESSURE
Refer to EM section.
+Check compression pressure.
Standard:
1,324 kPa (13.24 bar, 13.5 kg/cm
2, 192 psi)/350 rpm
Minimum:
1,128 kPa (11.28 bar, 11.5 kg/cm
2, 164 psi)/350 rpm
Difference between each cylinder:
98 kPa (0.98 bar, 1.0 kg/cm
2, 14 psi)/350 rpm
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 9.
NG©Check pistons, piston rings, valves, valve seats and cylinder head gaskets.
DTC P0300 - P0304 NO.4-1CYLINDER MISFIRE, MULTIPLE CYLINDER
MISFIRE
QG
Diagnostic Procedure (Cont'd)
EC-321
Page 1067 of 2898

DescriptionNJEC0227SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONNJEC0227S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
EGR vol-
ume controlEGR volume control valve Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Battery Battery voltage
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering load signal
Electrical load Electrical load signal
PNP switch Park/Neutral position signal
This system controls flow rate of EGR led from exhaust manifold
to intake manifold. The opening of the EGR by-pass passage in the
EGR volume control valve changes to control the flow rate. A
built-in step motor moves the valve in steps corresponding to the
ECM output pulses. The opening of the valve varies for optimum
engine control. The optimum value stored in the ECM is determined
by considering various engine conditions. The EGR volume control
valve remains close under the following conditions.
+Low engine coolant temperature
+Engine starting
+High-speed engine operation
+Extremely light load engine operation
+Engine idling
+Excessively high engine coolant temperature
+Wide open throttle
+Mass air flow sensor malfunction
+Low battery voltage
SEF551W
DTC P0400 EGR FUNCTION (CLOSED) (WHERE FITTED)QG
Description
EC-343
Page 1076 of 2898

DescriptionNJEC0504SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONNJEC0504S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
EGR vol-
ume controlEGR volume control valve Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Battery Battery voltage
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering load signal
Electrical load Electrical load signal
PNP switch Park/Neutral position signal
This system controls flow rate of EGR led from exhaust manifold
to intake manifold. The opening of the EGR by-pass passage in the
EGR volume control valve changes to control the flow rate. A
built-in step motor moves the valve in steps corresponding to the
ECM output pulses. The opening of the valve varies for optimum
engine control. The optimum value stored in the ECM is determined
by considering various engine conditions. The EGR volume control
valve remains close under the following conditions.
+Low engine coolant temperature
+Engine starting
+High-speed engine operation
+Extremely light load engine operation
+Engine idling
+Excessively high engine coolant temperature
+Wide open throttle
+Mass air flow sensor malfunction
+Low battery voltage
SEF551W
DTC P0403 EGR VOLUME CONTROL VALVE (CIRCUIT)
(WHERE FITTED)
QG
Description
EC-352
Page 1086 of 2898
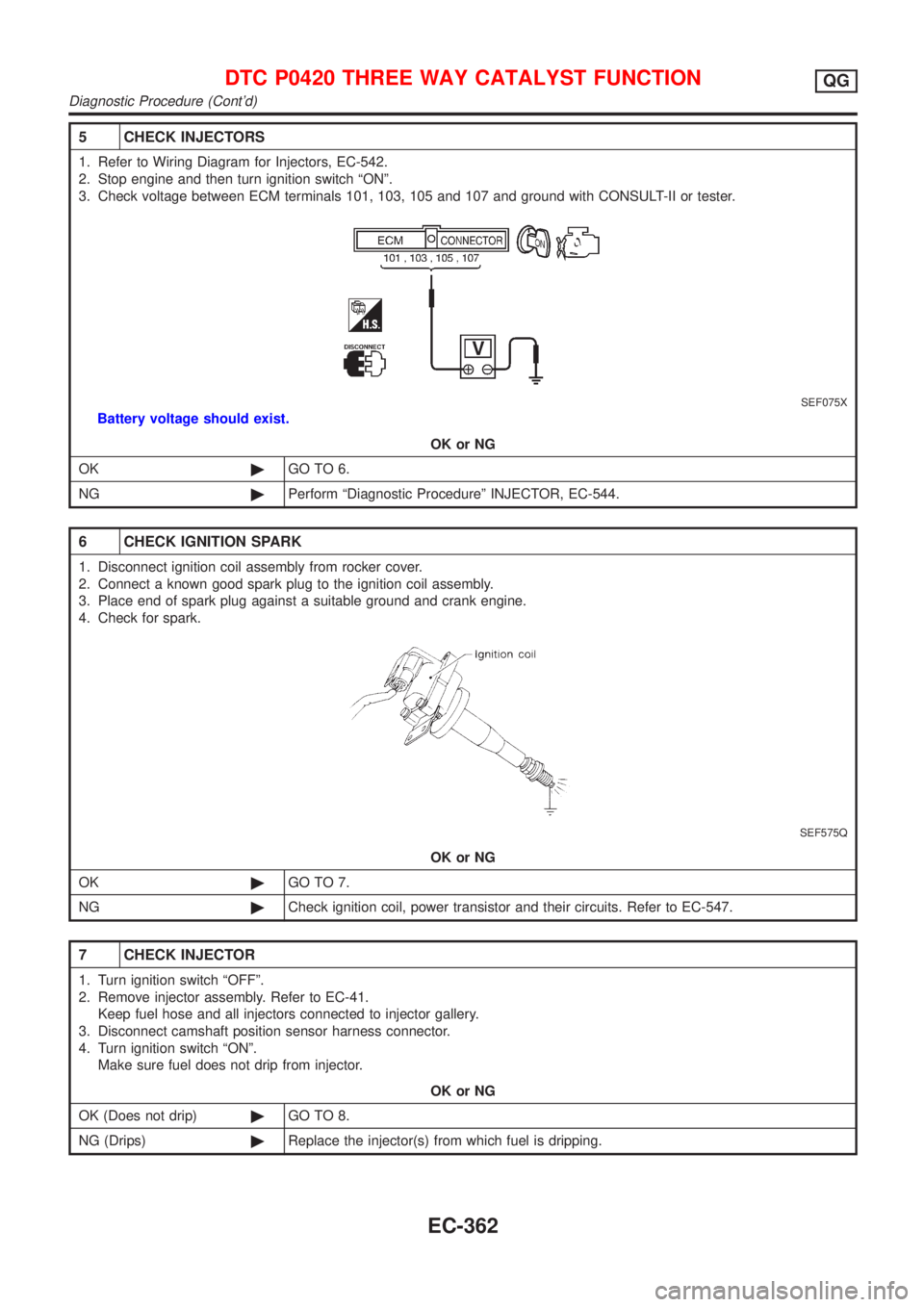
5 CHECK INJECTORS
1. Refer to Wiring Diagram for Injectors, EC-542.
2. Stop engine and then turn ignition switch ªONº.
3. Check voltage between ECM terminals 101, 103, 105 and 107 and ground with CONSULT-II or tester.
SEF075X
Battery voltage should exist.
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 6.
NG©Perform ªDiagnostic Procedureº INJECTOR, EC-544.
6 CHECK IGNITION SPARK
1. Disconnect ignition coil assembly from rocker cover.
2. Connect a known good spark plug to the ignition coil assembly.
3. Place end of spark plug against a suitable ground and crank engine.
4. Check for spark.
SEF575Q
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 7.
NG©Check ignition coil, power transistor and their circuits. Refer to EC-547.
7 CHECK INJECTOR
1. Turn ignition switch ªOFFº.
2. Remove injector assembly. Refer to EC-41.
Keep fuel hose and all injectors connected to injector gallery.
3. Disconnect camshaft position sensor harness connector.
4. Turn ignition switch ªONº.
Make sure fuel does not drip from injector.
OK or NG
OK (Does not drip)©GO TO 8.
NG (Drips)©Replace the injector(s) from which fuel is dripping.
DTC P0420 THREE WAY CATALYST FUNCTIONQG
Diagnostic Procedure (Cont'd)
EC-362
Page 1100 of 2898

DescriptionNJEC0279SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONNJEC0279S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Idle air
controlIACV-AAC valve Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
PNP switch Park/Neutral position
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering load signal
Battery Battery voltage
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Cooling fan Cooling fan operation
Electrical load Electrical load signal
This system automatically controls engine idle speed to a specified
level. Idle speed is controlled through fine adjustment of the
amount of air which by-passes the throttle valve via IACV-AAC
valve. The IACV-AAC valve changes the opening of the air by-pass
passage to control the amount of auxiliary air. This valve is actu-
ated by a step motor built into the valve, which moves the valve in
the axial direction in steps corresponding to the ECM output sig-
nals. One step of IACV-AAC valve movement causes the respec-
tive opening of the air by-pass passage. (i.e. when the step
advances, the opening is enlarged.) The opening of the valve is
varied to allow for optimum control of the engine idling speed. The
crankshaft position sensor (POS) detects the actual engine speed
and sends a signal to the ECM. The ECM then controls the step
position of the IACV-AAC valve so that engine speed coincides with
the target value memorized in ECM. The target engine speed is the
lowest speed at which the engine can operate steadily. The opti-
mum value stored in the ECM is determined by taking into consid-
eration various engine conditions, such as during warm up,
deceleration, and engine load (air conditioner, power steering, cool-
ing fan operation and electrical load).
SEF937W
COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONNJEC0279S02IACV-AAC ValveNJEC0279S0202The IACV-AAC valve is operated by a step motor for centralized
control of auxiliary air supply. This motor has four winding phases
and is actuated by the output signals of ECM which turns ON and
OFF two windings each in sequence. Each time the IACV-AAC
valve opens or closes to change the auxiliary air quantity, the ECM
sends a pulse signal to the step motor. When no change in the
auxiliary air quantity is needed, the ECM does not issue the pulse
signal. A certain voltage signal is issued so that the valve remains
at that particular opening.
DTC P0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IACV) Ð AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL
(AAC) VALVE
QG
Description
EC-376
Page 1117 of 2898
SEF095X
Component DescriptionNJEC0513The valve timing control system is utilized to control intake valve
opening and closing timing. Engine coolant temperature signals,
engine speed and throttle position are used to determine intake
valve timing.
The intake camshaft sprocket position is regulated by oil pressure
controlled by the intake valve timing control.
When ECM sends ON signal to intake valve timing control solenoid
valve, oil pressure is transmitted to camshaft sprocket. Then, intake
side camshaft is advanced.
OperationNJEC0514
Engine operating condition
Intake valve tim-
ing control sole-
noid valveIntake valve
opening and
closing timeValve overlap
Engine coolant
temperatureEngine speed B/FUEL SCHDL Neutral switch
20ÉC (68ÉF) -
70ÉC (158ÉF)
1,150 - 4,600
rpmAbove 3 msec
OFF ON Advance Increased
Above 70ÉC
(158ÉF)Above 7 msec
Conditions other than those above OFF Normal Normal
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode
NJEC0515
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
INT/V SOL-B1+Engine: After warming up
+Lift up drive wheels and suitable
gear positionIdle OFF
Revving engine from 2,000 to
3,000 rpmON
ECM Terminals and Reference ValueNJEC0516Specification data are reference values and are measured between each terminal and ground.
CAUTION:
Do not use ECM ground terminals when measuring input/output voltage. Doing so may result in dam-
age to the ECM's transistor. Use a ground other than ECM terminals, such as the ground.
TER-
MINAL
NO.WIRE
COLORITEM CONDITION DATA (DC Voltage)
1 Y/RIntake valve timing control
solenoid valve[Engine is running]
+Idle speedBATTERY VOLTAGE
(11 - 14V)
On Board Diagnosis LogicNJEC0517
DTC No. Malfunction is detected when ... Check Items (Possible Cause)
P 1111
1111+An improper voltage signal is entered to ECM through
intake valve timing control solenoid valve.+Harness or connectors
(The intake valve timing control solenoid valve
circuit is open or shorted.)
+Intake valve timing control solenoid valve
D T C P 1111INTAKE VALVE TIMING CONTROL SOLENOID VALVEQG
Component Description
EC-393