2001 DODGE RAM tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 1507 of 2889

(6)Open fuel fill door and remove screws mounting
fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not disconnect
rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting strap nuts from
mounting strap studs (Fig. 35). If equipped, remove
fuel tank shield bolts.
(9) Lower fuel tank only enough to allow access to
top of tank. The 2 tank fittings (where rubber fuel fill
and vent hose connections are made) must be posi-
tioned above tank level. Rotate tank slightly to allow
these fittings to be above tank level.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(10) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect rubber fuel vent hose at fuel tank (Fig. 35)
(vent hose is the smallest of 2 hoses). Position fuel
siphoning/drain hose into this fitting at tank. Drain
fuel into an approved portable holding tank or a
properly labeled gasoline (or diesel fuel) safety con-
tainer.
(11) Disconnect rubber fuel fill hose at fuel tank
(Fig. 35).
(12)Gas Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 36) or
(Fig. 37).
(b) If equipped with 26 or 34 gallon fuel tank,
two EVAP lines are connected to rollover valves.
Disconnect EVAP line from rollover valve at top of
module (Fig. 36). Disconnect other EVAP line from
rollover valve near rear of tank (Fig. 36).
(c) If equipped with 35 gallon fuel tank, two
EVAP lines are connected to rollover valves. Dis-
connect EVAP lines from rollover valves at top-
front and top-rear of fuel tank (Fig. 38).
(d) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel filter/fuel
pressure regulator supply fitting (Fig. 36) or (Fig.
37). Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for proce-
dures.
(13)Diesel Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel tank module (Fig. 39).
(b) Disconnect fuel supply and fuel return lines
at the fuel tank module fittings (Fig. 39). Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures.
(14) Gasoline Engines: If fuel pump module
removal is necessary, refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation in this group. Diesel Engines: If
fuel tank module removal is necessary, refer to Fuel
Tank Module Removal/Installation in this group.
INSTALLATION
(1) Gasoline Engines: If fuel pump module is being
installed, refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Instal-
lation in this group. Diesel Engines: If fuel tank mod-
ule is being installed, refer to Fuel Tank Module
Removal/Installation in this group.
(2) Place fuel tank on top of transmission jack.
(3) Install rubber fill and vent lines to tank.
Tighten hose clamps to 2.3 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Raise tank into position while guiding fill and
vent hoses to body. Raise tank only enough to allow
access to top of tank.
(5)Gas Powered Engines:
(a) Connect electrical connector to fuel pump
module.
(b) Connect EVAP hoses at rollover valves.
(c) Connect fuel supply line at fuel filter/fuel
pressure regulator. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings
for procedures.
(6)Diesel Powered Engines:
(a) Connect electrical connector to fuel tank
module.
Fig. 35 Fuel Tank MountingÐTypical
1 - STRAP MOUNTING STUDS (AT FRAME)
2 - FUEL FILL HOSE
3 - FUEL VENT HOSE
4 - STRAP MOUNTING NUTS (2)
5 - FUEL TANK STRAPS (2)
6 - FUEL TANK
7 - CLAMPS
14 - 20 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1569 of 2889

(5) Using key, crank engine over while observing
gauge. Pressure should be 5±7 psi.
(6) Re-install fuel system relay to PDC.
(7) Start engine and record fuel pressure. Pressure
should be aminimumof 69 kPa (10 psi) at idle
speed.
(8) Because fuel pump relay was removed, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) may have been set. After
testing is completed, and relay has been installed,
use DRB scan tool to remove DTC.
Pressure Drop Test:
(9) Shut engine off and remove test gauge from
inlet port test fitting. Re-attach 6828 test gauge to
outlet port (Fig. 55). Start engine and record fuel
pressure. Pressure should not be more than 34 kPa
(5 psi) lower than inlet port pressure test. If so,
replace fuel filter.
Fuel Supply Restriction Test:
Due to very small vacuum specifications, the DRB
scan tool along with the Periphal Expansion Port
(PEP) Module and 0±15 psi transducer must be used.
(10) Verify transfer pump pressure is OK before
performing restriction test.
(11) Locate and disconnect fuel supply line quick-
connect fitting at left-rear of engine (Fig. 56). After
disconnecting line, plastic clip will remain attached
to metal fuel line at engine. Carefully remove clip
from metal line. Snap same clip into fuel supply
hose.
(12) Install Special Rubber Adapter Hose Tool
6631 (3/8º) into ends of disconnected fuel supply line.(13) Install transducer from PEP module to brass
ªTº fitting on tool 6631.
(14) Hook up DRB scan tool to transducer.
WARNING: DO NOT STAND IN LINE WITH THE
COOLING FAN FOR THE FOLLOWING STEPS.
(15) Start engine and record vacuum reading with
engine speed at high-idle (high-idle means engine
speed is at 100 percent throttle and no load). The
fuel restriction testMUSTbe done with engine speed
at high-idle.
(16) If vacuum reading islessthan 6 in/hg. (0±152
mm hg.), test is OK. If vacuum reading ishigher
than 6 in/hg. (152 mm hg.), restriction exists in fuel
supply line or in fuel tank module. Check fuel supply
line for damage, dents or kinking. If OK, remove
module and check module and lines for blockage.
Also check fuel pump inlet filter at bottom of module
for obstructions.
Testing For Air Leaks in Fuel Supply Side:
(17) A 3±foot section of 3/8º I.D. clear tubing is
required for this test.
(18) Using a tire core valve removal tool, carefully
remove core valve from inlet fitting test port.
(19) Attach and clamp the 3/8ºclear hose to fitting
nipple.
(20) Place other end of hose into a large clear con-
tainer. Allow hose to loop as high as possibleabove
test port.
(21) The fuel transfer pump can be put into a 25
second run (test) mode if key is quickly turned to
crank position and released back to run position
without starting engine.
To prevent engine from starting in this test, first
remove fuel system relay (fuel injection pump relay).
Relay is located in Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to label under PDC cover for relay location.
Because fuel pump relay was removed, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may have been set. After test-
ing is completed, and relay has been installed, use
DRB scan tool to remove DTC.
(22) Allow air to purge from empty hose before
examining for air bubbles. Air bubbles should not be
present.
(23) If bubbles are present, check for leaks in sup-
ply line to fuel tank.
(24) If supply line is not leaking, remove fuel tank
module and remove filter at bottom of module (filter
snaps to module). Check for leaks between supply
nipple at top of module, and filter opening at bottom
of module. Replace module if necessary.
(25) After performing test, install core back into
test fitting. Before installing protective cap, be sure
fitting is not leaking.
Fig. 56 Fuel Return and Supply Line Quick-Connect
Locations
1 - FUEL RETURN LINE
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
3 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
14 - 82 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL TRANSFER PUMP (Continued)
Page 1595 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill parking. Or when the steering wheel is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar
to that of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing
through an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
STEERING NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Repair steering gear.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Loose or damaged steering linkage. 3. Inspect and repair steering
linkage.
4. Internal gear noise. 4. Repair steering gear.
5. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.5. Reposition hose.
6. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.6. Inspect and repair or replace.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
5. Reservoir cap not installed correctly. 5. Install reservoir cap correctly.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
2. Wrong gear. 2. Verify gear.
19 - 2 STEERINGBR/BE
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1596 of 2889

BINDING AND STICKING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
DIFFICULT TO TURN WHEEL
STICKS OR BINDS1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Tire pressure. 2. Adjust tire pressure.
3. Steering components (ball
joints/tie rod ends).3. Lube, inspect and repair as
necessary.
4. Loose belt. 4. Adjust or replace.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and replace if
necessary.
6. Column shaft coupler binding. 6. Replace coupler.
7. Steering gear worn or out of
adjustment.7. Repair or replace gear.
INSUFFICIENT ASST. OR POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HARD TURNING OR MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN TURNING EFFORT1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Low fluid level. 2. Fill to proper level.
3. Loose belt. 3. Adjust or replace.
4. Lack of lubrication. 4. Inspect and lubricate steering and
suspension compnents.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and repair as
necessary.
6. Internal gear leak. 6. Pressure and flow test, and repair
as necessary.
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
WANT TO RETURN TO CENTER
POSITION1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Wheel alignment. 2. Align front end.
3. Lack of lubrication. 3. Inspect and lubricate steering and
suspension compnents.
4. High friction in steering gear. 4. Test and adjust gear as
necessary.
LOOSE STEERING AND VEHICLE LEAD
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING
WHEEL1. Worn or loose suspension or
steering components.1. Inspect and repair as necessary.
2. Worn or loose wheel bearings. 2. Inspect and repair or adjust
bearings.
3. Steering gear mounting. 3. Tighten gear mounting bolts to
specification.
4. Gear out of adjustment. 4. Adjust gear to specification.
5. Worn or loose steering coupler. 5. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
BR/BESTEERING 19 - 3
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
VEHICLE PULLS OR LEADS TO
ONE SIDE.1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Rotate tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align front end.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
FLOW AND PRESSURE
The following procedure is used to test the opera-
tion of the power steering system on the vehicle. This
test will provide the flow rate of the power steering
pump along with the maximum relief pressure. Per-
form test any time a power steering system problem
is present. This test will determine if the power
steering pump or power steering gear is not function-
ing properly. The following pressure and flow test is
performed using Power Steering Analyzer Tool kit
6815 (Fig. 2) and Adapter Kit 6893.
POWER STEERING ANALYZER INSTALLATION
WITHOUT HYDRAULIC BOOSTER
(1) Remove the high pressure hose from the power
steering pump.
(2) Connect Tube 6844 into the pump hose fitting.(3) Connect pressure gauge hose from the Power
Steering Analyzer to Tube 6844.
(4) Connect Adapter 6826 to Power Steering Ana-
lyzer test valve end.
(5) Connect the power steering hose from the
steering gear to Adapter 6826.
WITH HYDRAULIC BOOSTER
(1) Remove high pressure hose which goes to the
steering gear from the tube coming out of the booster.
(2) Connect Adapter 6826 to the Power Steering
Analyzer pressure gauge hose.
(3) Connect pressure gauge hose to the tube com-
ing out of the booster.
(4) Connect Tube 6844 to the steering gear hose
and Power Steering Analyzer test valve end.
FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check belt condition and tension.
(2) Open the test valve completely.
(3) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through flow/pressure test
gauge and to get air out of the fluid. Then shut off
engine.
(4) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary. Start
engine again and let idle.
(5) Gauge should read below 1034 kPa (150 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure reading should be in
the range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
(6) Increase the engine speed to 1500 RPM and
read the flow meter. If the flow rate (GPM) is below
specification (Refer to pump specification chart for
GPM) the pump should be replaced.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than three seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
Fig. 2 Pressure Test Gauge
1 - GAUGE HOSE
2 - TUBE
3 - ADAPTER FITTINGS
4 - ANALYZER
19 - 4 STEERINGBR/BE
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1883 of 2889

materials will adhere to component surfaces and
could restrict or block fluid passages after assembly.
INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 218) and (Fig.
219).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 220). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 217).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 221). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 221). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 216).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
216).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
Fig. 217 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2054 of 2889

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 216) and (Fig.
217).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 218). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 217).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 219). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 219). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 216).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
216).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
Fig. 215 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 419
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2196 of 2889
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 119).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.
(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.
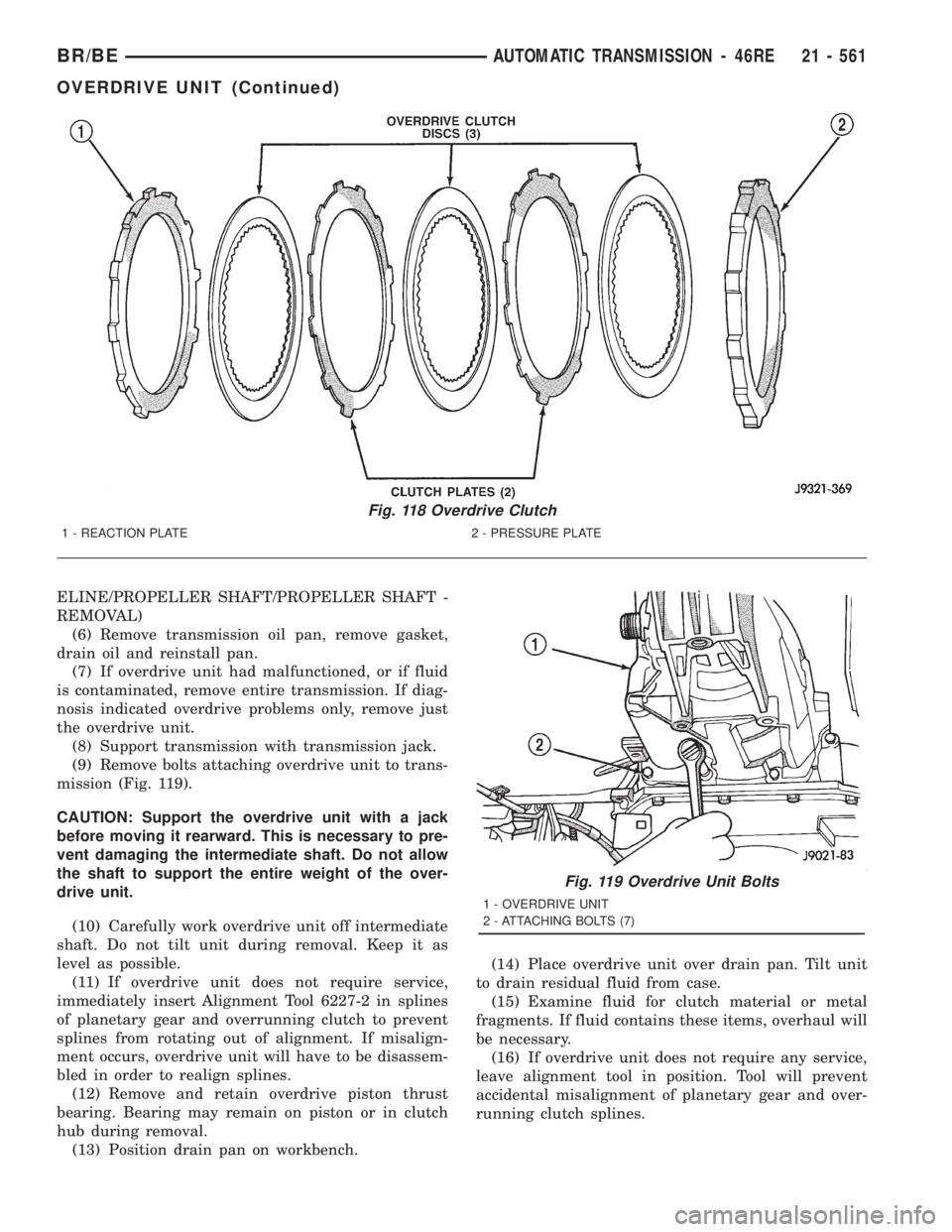
Fig. 118 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
Fig. 119 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 561
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)