2001 DODGE RAM sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 1675 of 2889

(5) Fill transmission to bottom edge of fill plug
hole with Mopar Transmission Lubricant.
(6) Install and tighten fill plug to 34 N´m (25 ft.
lbs.).
(7) Check transmission vent. Be sure vent is open
and not restricted.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If a new transmission is being installed, be
sure to use all components supplied with the new
transmission. For example, if a new shift tower is
supplied with the new transmission, do not re-use
the original shift tower.
Make sure transmission front housing mounting
surface is clean. Before installation apply light coat
of Mopar high temperature bearing grease to contact
surfaces of following components:
²input shaft splines.
²release bearing slide surface of front retainer.
²release bearing bore.
²release fork.
²release fork ball stud.
²propeller shaft slip yoke.
(1) Support and secure transmission to jack with
safety chains.
(2) Raise and align transmission input shaft with
clutch disc, then slide transmission into place.
(3) Install and tighten transmission bolts to 54-61
N´m (40-45 ft. lbs.). Be sure front housing is fully
seated before tightening bolts. Install front dust
cover after all bolts are tightened.
(4) Fill transmission with Mopar lubricant. Correct
fill level is to bottom edge of fill plug hole.
(5) Connect backup lamp switch wires.(6) Connect transmission harnesses to clips on
case.
(7) Install crossmember. Tighten crossmember-to-
frame bolts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(8) Tighten crossmember-to-transmission insulator
nuts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install slave cylinder. Tighten cylinder nuts to
23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(10) Remove jack used to support transmission.
(11) Install strut bolts/nuts, if removed. Also
install oil filter if removal was necessary.
(12) Install and connect exhaust system. Align
exhaust components before tightening clamp and
bracket bolts and nuts. Be sure exhaust components
are clear of all chassis and driveline components.
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Align and install propeller shaft.
(2) Verify that all linkage components, hoses and
electrical wires have been connected.
(3) Remove any remaining support stands and
lower vehicle.
(4) Install crankshaft position sensor.
(5) Connect battery negative cable.
(6) Install shift tower and lever assembly. Tighten
shift tower bolts to 7-10 N´m (5-7 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the shift lever extension onto the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(8) Install shift boot and bezel.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Install transfer case. Align and position trans-
fer case with transmission jack or aid of helper.
(2) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install and connect transfer case shift linkage.
(4) Align and install front and rear propeller
shafts.
(5) Verify that all linkage components, hoses and
electrical wires have been connected.
(6) Check transfer case fluid level. Add Mopar
Dexron II, or ATF Plus if necessary. Correct level is
to edge of fill plug hole. Be sure transfer case is level
before checking or adding fluid.
(7) Check and adjust transfer case shift linkage if
necessary.
(8) Install transfer case skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Install crankshaft position sensor.
(10) Remove any remaining support stands and
lower vehicle.
(11) Connect battery negative cable.
(12) Install shift tower and lever assembly. Tighten
shift tower bolts to 7-10 N´m (5-7 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the shift lever extension onto the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(14) Install shift boot and bezel.
Fig. 122 Shift Tower Bolts
1 - SHIFT TOWER AND LEVER ASSEMBLY
21 - 40 MANUAL - NV3500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1682 of 2889
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot screws from floorpan and
slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from shift tower
and lever assembly.(5) Remove shift tower bolts holding tower to iso-
lator plate and transmission shift cover.
(6) Remove shift tower and isolator plate from
transmission shift cover.
(7) Raise and support vehicle.
(8) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and axle yokes for instal-
lation reference and remove shaft/shafts.
(10) Remove exhaust system Y-pipe.
(11) Disconnect speed sensor and backup light
switch connectors.
(12) Support engine with safety stand and a wood
block.
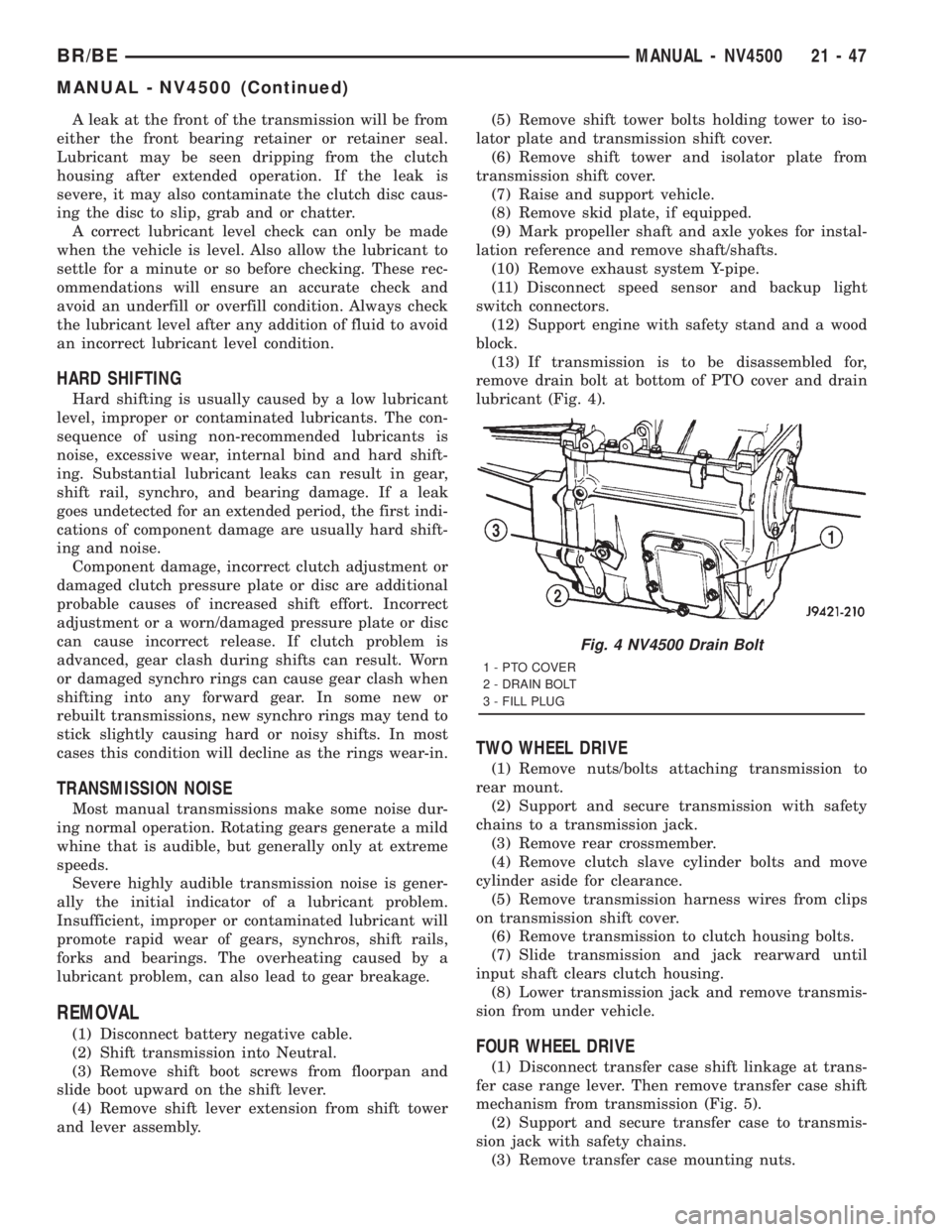
(13) If transmission is to be disassembled for,
remove drain bolt at bottom of PTO cover and drain
lubricant (Fig. 4).
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Remove nuts/bolts attaching transmission to
rear mount.
(2) Support and secure transmission with safety
chains to a transmission jack.
(3) Remove rear crossmember.
(4) Remove clutch slave cylinder bolts and move
cylinder aside for clearance.
(5) Remove transmission harness wires from clips
on transmission shift cover.
(6) Remove transmission to clutch housing bolts.
(7) Slide transmission and jack rearward until
input shaft clears clutch housing.
(8) Lower transmission jack and remove transmis-
sion from under vehicle.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Disconnect transfer case shift linkage at trans-
fer case range lever. Then remove transfer case shift
mechanism from transmission (Fig. 5).
(2) Support and secure transfer case to transmis-
sion jack with safety chains.
(3) Remove transfer case mounting nuts.
Fig. 4 NV4500 Drain Bolt
1 - PTO COVER
2 - DRAIN BOLT
3 - FILL PLUG
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 47
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1717 of 2889

INSTALLATION
NOTE: If a new transmission is being installed, be
sure to use all components supplied with the new
transmission. For example, if a new shift tower is
supplied with the new transmission, do not re-use
the original shift tower.
Befor installation apply light coat of Mopar high
temperature bearing grease to contact surfaces of fol-
lowing components:
²input shaft splines.
²release bearing slide surface of front retainer.
²release bearing bore.
²release fork.
²release fork ball stud.
²propeller shaft slip yoke.
(1) Apply sealer to threads of bottom PTO cover
bolt and install bolt in case.
(2) Mount transmission on jack and position trans-
mission under vehicle.
(3) Raise transmission until input shaft is centered
in release bearing and clutch disc hub.
(4) Move transmission forward and start input
shaft in release bearing, clutch disc and pilot bush-
ing.
(5) Work transmission forward until seated against
clutch housing. Do not allow transmission to remain
unsupported after input shaft has entered clutch
disc.
(6) Install and tighten transmission-to-clutch hous-
ing bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install transmission mount on transmission or
rear crossmember.
(8) Install rear crossmember.
(9) Remove transmission jack and engine support
fixture.
(10) Position transmission harness wires in clips
on shift cover.
(11) Install clutch slave cylinder and install slave
cylinder shield, if equipped.
(12) Connect speed sensor and backup light switch
wires.
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Fill transmission with recommended lubricant.
Correct fill level is bottom edge of fill plug hole.
(2) Align and install propeller shaft.
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower, isola-
tor plate, and shift cover with suitable wax and
grease remover.
(5) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker, or equivalent, to
the sealing surface of the shift cover. Do not over
apply sealant.(6) Install the isolator plate onto the shift cover,
metal side down.
(7) Install the shift tower onto the isolator plate.
No sealant is necessary between the shift tower and
the isolator plate.
(8) Verify that the shift tower, isolator plate, and
the shift tower bushings are properly aligned.
(9) Install the bolts to hold the shift tower to the
isolator plate and the shift cover. Tighten the shift
tower bolts to 10.2±11.25 N´m (7.5±8.3 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install the shift lever extension onto the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(11) Install shift boot and bezel.
(12) Connect battery negative cable.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Install transfer case shift mechanism on trans-
mission.
(2) Install transfer case on transmission jack.
Secure transfer case to jack with safety chains.
(3) Raise jack and align transfer case input gear
with transmission mainshaft.
(4) Move transfer case forward and seat it on
adapter.
(5) Install and tighten transfer case attaching
nuts. Tighten nuts to 41-47 N´m (30-35 ft. lbs.) if
case has 3/8 studs, or 30-41 N´m (22-30 ft. lbs.) if
case has 5/16 studs.
(6) Install transfer case shift mechanism to side of
transfer case.
(7) Connect transfer case shift lever to range lever
on transfer case.
(8) Align and connect propeller shafts.
(9) Fill transmission with required lubricant.
Check lubricant level in transfer case and add lubri-
cant if necessary.
(10) Install transfer case skid plate, if equipped,
and crossmember. Tighten attaching bolts/nuts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Install exhaust system components.
(12) Lower vehicle.
(13) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower, iso-
lator plate, and shift cover with suitable wax and
grease remover.
(14) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker, or equivalent, to
the sealing surface of the shift cover. Do not over
apply sealant.
(15) Install the isolator plate onto the shift cover,
metal side down.
(16) Install the shift tower onto the isolator plate.
No sealant is necessary between the shift tower and
the isolator plate.
(17) Verify that the shift tower, isolator plate, and
the shift tower bushings are properly aligned.
21 - 82 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1770 of 2889

OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE
PISTON RETAINER
DESCRIPTION..........................235
OPERATION............................235
DISASSEMBLY..........................235
CLEANING.............................236
INSPECTION...........................236
ASSEMBLY............................236
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................237
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH.......237
REMOVAL.............................238
INSTALLATION..........................238
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION..........................238
OPERATION............................238
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION..........................240
OPERATION............................240
DISASSEMBLY..........................240
INSPECTION...........................241
ASSEMBLY............................241
REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION..........................246
OPERATION............................246
DISASSEMBLY..........................247
CLEANING.............................247
INSPECTION...........................248
ASSEMBLY............................248
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION..........................250
OPERATION............................250
DISASSEMBLY..........................251
CLEANING.............................251
ASSEMBLY............................251
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION..........................251OPERATION............................251
ADJUSTMENTS.........................252
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION..........................252
OPERATION............................253
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................253
OPERATION............................253
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION..........................253
ADJUSTMENTS.........................254
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION..........................256
OPERATION............................260
REMOVAL.............................261
INSTALLATION..........................261
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION..........................262
OPERATION............................262
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................262
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE . 262
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................262
OPERATION............................262
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION..........................263
OPERATION............................267
REMOVAL.............................281
DISASSEMBLY..........................282
CLEANING.............................293
INSPECTION...........................293
ASSEMBLY............................294
INSTALLATION..........................303
ADJUSTMENTS.........................304
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
42RE
DESCRIPTION
The 42RE is a four speed fully automatic transmis-
sion (Fig. 1) with an electronic governor. The 42RE is
equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.
The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and thelow/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1778 of 2889

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1782 of 2889

PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS CHART
TEST CONDITION INDICATION
Line pressure OK during
any one testPump and regulator
valve OK
Line pressure OK in R
but low in D, 2, 1Leakage in rear clutch
area (seal rings, clutch
seals)
Pressure low in D Fourth
Gear RangeOverdrive clutch piston
seal, or check ball
problem
Pressure OK in 1, 2 but
low in D3 and RLeakage in front clutch
area
Pressure OK in 2 but low
in R and 1Leakage in rear servo
Front servo pressure in 2 Leakage in servo; broken
servo ring or cracked
servo piston
Pressure low in all
positionsClogged filter, stuck
regulator valve, worn or
faulty pump, low oil level
Governor pressure too
high at idle speedGovernor pressure
solenoid valve system
fault. Refer to diagnostic
book.
Governor pressure low at
all mph figuresFaulty governor pressure
solenoid, transmission
control module, or
governor pressure
sensor
Lubrication pressure low
at all throttle positionsClogged fluid cooler or
lines, seal rings leaking,
worn pump bushings,
pump, clutch retainer, or
clogged filter.
Line pressure high Output shaft plugged,
sticky regulator valve
Line pressure low Sticky regulator valve,
clogged filter, worn pump
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH AND BAND
OPERATION
Air-pressure testing can be used to check transmis-
sion front/rear clutch and band operation. The test
can be conducted with the transmission either in the
vehicle or on the work bench, as a final check, after
overhaul.
Air-pressure testing requires that the oil pan and
valve body be removed from the transmission. The
servo and clutch apply passages are shown (Fig. 10).
Front Clutch Air Test
Place one or two fingers on the clutch housing and
apply air pressure through front clutch apply pas-
sage. Piston movement can be felt and a soft thump
heard as the clutch applies.
Rear Clutch Air Test
Place one or two fingers on the clutch housing and
apply air pressure through rear clutch apply passage.
Fig. 10 Air Pressure Test Passages
1 - REAR SERVO APPLY
2 - FRONT SERVO APPLY
3 - PUMP SUCTION
4 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLY
5 - FRONT SERVO RELEASE
6 - LINE PRESSURE TO ACCUMULATOR
7 - PUMP PRESSURE
8 - TO CONVERTER
9 - REAR CLUTCH APPLY
10 - FROM CONVERTER
11 - TO COOLER
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 147
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1788 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
6. TPS Malfunction. 6. Replace sensor, check with DRBTscan
tool.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if required.
8. Valve Body Malfunction. 8. Repair sticking 1-2, 2-3 shift valves,
governor plugs, 3-4 solenoid, 3-4 shift
valve, 3-4 timing valve.
STUCK IN LOW GEAR
(WILL NOT UPSHIFT)1. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted/
Stuck.1. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn
or damaged. Check for binding cable or
missing return spring.
2. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn
or damaged.
3. Governor Component Electrical
Fault.3. Check operating pressures and test with
DRBTscan tool, repair faulty component.
4. Front Band Out of Adjustment. 4. Adjust Band.
5. Clutch or Servo Malfunction. 5. Air pressure check operation of clutches
and bands. Repair faulty component.
CREEPS IN NEUTRAL 1. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 1. Adjust linkage.
2. Rear Clutch Dragging/Warped. 2. Disassemble and repair.
3. Valve Body Malfunction. 3. Perform hydraulic pressure test to
determine cause and repair as required.
BUZZING NOISE 1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Mis-assembled. 2. Route cable away from engine and bell
housing.
3. Valve Body Mis-assembled. 3. Remove, disassemble, inspect valve
body. Reassemble correctly if necessary.
Replace assembly if valves or springs are
damaged. Check for loose bolts or screws.
4. Pump Passages Leaking. 4. Check pump for porous casting, scores
on mating surfaces and excess rotor
clearance. Repair as required. Loose pump
bolts.
5. Cooling System Cooler Plugged. 5. Flow check cooler circuit. Repair as
needed.
6. Overrunning Clutch Damaged. 6. Replace clutch.
SLIPS IN REVERSE ONLY 1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage.
3. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust band.
4. Rear Band Worn. 4. Replace as required.
5. Overdrive Direct Clutch Worn. 5. Disassemble overdrive. Repair as
needed.
6. Hydraulic Pressure Too Low. 6. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to
determine cause.
7. Rear Servo Leaking. 7. Air pressure check clutch-servo operation
and repair as required.
8. Band Linkage Binding. 8. Inspect and repair as required.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 153
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1791 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3-4 UPSHIFT OCCURS
IMMEDIATELY AFTER 2-3
SHIFT1. Overdrive Solenoid Connector or
Wiring Shorted.1. Test connector and wiring for loose
connections, shorts or ground and repair as
needed.
2. TPS Malfunction. 2. Test TPS and replace as necessary.
Check with DRBTscan tool.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3. Test PCM with DRBTscan tool and
replace controller if faulty.
4. Overdrive Solenoid Malfunction. 4. Replace solenoid.
5. Valve Body Malfunction. 5. Remove, disassemble, clean and inspect
valve body components. Make sure all
valves and plugs slide freely in bores.
Polish valves with crocus cloth if needed.
WHINE/NOISE RELATED
TO ENGINE SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing.
Should not touch engine or bell housing.
NO 3-4 UPSHIFT 1. O/D Switch In OFF Position. 1. Turn control switch to ON position.
2. Overdrive Circuit Fuse Blown. 2. Replace fuse. Determine why fuse failed
and repair as necessary (i.e., shorts or
grounds in circuit).
3. O/D Switch Wire Shorted/Open
Cut.3. Check wires/connections with 12V test
lamp and voltmeter. Repair damaged or
loose wire/connection as necessary.
4. Distance or Coolant Sensor
Malfunction.4. Check with DRBTscan tool and repair or
replace as necessary.
5. TPS Malfunction. 5. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
6. Neutral Sense to PCM Wire
Shorted/Cut.6. Test switch/sensor as described in
service section and replace if necessary.
Engine no start.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
8. Overdrive Solenoid Shorted/Open. 8. Replace solenoid if shorted or open and
repair loose or damaged wires (DRBTscan
tool).
9. Solenoid Feed Orifice in Valve
Body Blocked.9. Remove, disassemble, and clean valve
body thoroughly. Check feed orifice.
10. Overdrive Clutch Failed. 10. Disassemble overdrive and repair as
needed.
11. Hydraulic Pressure Low. 11. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause.
12. Valve Body Valve Stuck. 12. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing
valve.
13. O/D Piston Incorrect Spacer. 13. Remove unit, check end play and install
correct spacer.
14. Overdrive Piston Seal Failure. 14. Replace both seals.
15. O/D Check Valve/Orifice Failed. 15. Check for free movement and secure
assembly (in piston retainer). Check ball
bleed orifice.
21 - 156 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)