2001 DODGE RAM service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 46 of 2889

down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot bar
inward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 52 of 2889

SPECIAL TOOLS
INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION
HUB / BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the caliper adapter bolts from the
steering knuckle and remove caliper adapter assem-
bly (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANI-
CAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Do not allow brake hose to support caliper
adapter assembly.
(4) Remove the rotor from the hub/bearing wheel
studs.
(5) Remove the hub/bearing nut (Fig. 3) and slide
the hub/bearing off the spindle.
CAUTION: The hub/bearing nut can not be re-used.
INSTALLATION
(1) On models with all-wheel antilock system
(ABS), check condition of tone wheel on hub/bearing.
If teeth on wheel are damaged, hub/bearing assembly
will have to be replaced (tone wheel is not serviced
separately).
(2) Slide the hub/bearing onto the spindle.
(3) Install thenewhub/bearing nut and tighten
to:
²LD 1500: 251N´m (185 ft. lbs.)
²HD 2500/3500: 380 N´m (280 ft lbs.)(4) Install the rotor onto hub/bearing wheel studs.
(5) Install the caliper adapter assembly (Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION), and tighten
adapter bolts to:
²LD 1500: 176 N´m (130 ft lbs.)
²HD 2500/3500: 285 N´m (210 ft lbs.)
(6) Install the wheel and tire assembly and lower
the vehicle, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Apply brakes several times to seat brake shoes.
Be sure to obtain firm pedal before moving vehicle.
JOUNCE BUMPER
DESCRIPTION
The jounce bumpers are mounted under the coil
spring bracket.
OPERATION
The jounce bumpers are used to limit suspension
travel in compression.
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION
The knuckles are a single casting with legs
machined for the upper and lower ball joints. The
knuckles also has machined mounting locations for
the front brake calipers adapters and hub bearing
assembly.
Remover, Tie Rod End MB-990635
Puller Tie Rod C-3894-A
Fig. 3 Caliper Adapter Assembly
1 - HUB/BEARING
2 - SPINDLE
BR/BEFRONT - 2WD 2 - 9
FRONT - 2WD (Continued)
Page 84 of 2889
to maintain compression of the rubber insulator
around the bearing. Do not use washers. Replace the
original bolts with the appropriate increased length
bolts.
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
Individual components of cardan universal joints
are not serviceable. If worn or leaking, they must be
replaced as an assembly.
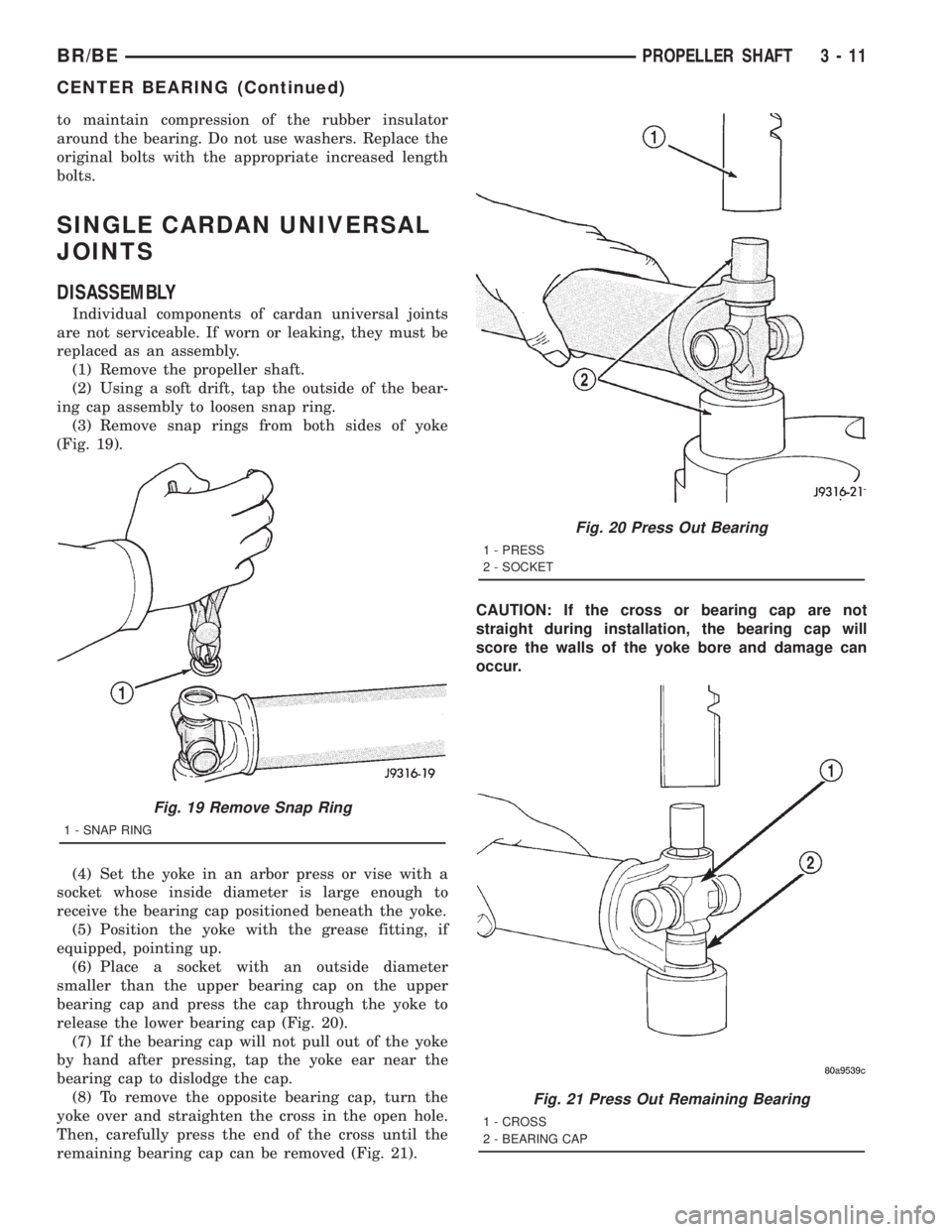
(1) Remove the propeller shaft.
(2) Using a soft drift, tap the outside of the bear-
ing cap assembly to loosen snap ring.
(3) Remove snap rings from both sides of yoke
(Fig. 19).
(4) Set the yoke in an arbor press or vise with a
socket whose inside diameter is large enough to
receive the bearing cap positioned beneath the yoke.
(5) Position the yoke with the grease fitting, if
equipped, pointing up.
(6) Place a socket with an outside diameter
smaller than the upper bearing cap on the upper
bearing cap and press the cap through the yoke to
release the lower bearing cap (Fig. 20).
(7) If the bearing cap will not pull out of the yoke
by hand after pressing, tap the yoke ear near the
bearing cap to dislodge the cap.
(8) To remove the opposite bearing cap, turn the
yoke over and straighten the cross in the open hole.
Then, carefully press the end of the cross until the
remaining bearing cap can be removed (Fig. 21).CAUTION: If the cross or bearing cap are not
straight during installation, the bearing cap will
score the walls of the yoke bore and damage can
occur.
Fig. 19 Remove Snap Ring
1 - SNAP RING
Fig. 20 Press Out Bearing
1 - PRESS
2 - SOCKET
Fig. 21 Press Out Remaining Bearing
1 - CROSS
2 - BEARING CAP
BR/BEPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 11
CENTER BEARING (Continued)
Page 85 of 2889

FRONT AXLE - 216FBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................13
AXLE................................13
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................17
ADJUSTMENTS..........................17
SPECIFICATIONS........................25
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................25
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................28
AXLE SHAFTS - INTERMEDIATE
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................28
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL..............................29
INSTALLATION...........................29
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR
DESCRIPTION...........................29
OPERATION.............................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................31VACUUM MOTOR.......................31
REMOVAL..............................33
DISASSEMBLY...........................33
ASSEMBLY.............................33
INSTALLATION...........................33
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
REMOVAL..............................33
INSTALLATION...........................34
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL..............................34
INSTALLATION...........................34
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL..............................36
DISASSEMBLY...........................36
ASSEMBLY.............................37
INSTALLATION...........................37
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL..............................39
INSTALLATION...........................39
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL..............................40
INSTALLATION...........................42
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI
DESCRIPTION
The housing for the 216 Front Beam-design Iron
(FBI) axles consists of an iron center casting with
tubes on each side. The tubes are pressed into and
welded to the differential housing.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set below the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a vent used to relieve internal pres-
sure caused by lubricant vaporization and internal
expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the hub
bearings. The axle shafts are retained by nuts at the
hub bearings. The hub bearings are bolted to the
steering knuckle at the outboard end of the axle tube
yoke. The hub bearings are serviced as an assembly.
The axles are equipped with ABS brake sensors.
The sensors are attached to the knuckle assemblies
and the tone rings are pressed onto the axle shaft.
Use care when removing axle shafts as NOT to
damage the tone wheel or the sensor.The stamped steel cover provides a means for
inspection and servicing the differential.
The 216 axle have the assembly part number and
gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to the
housing cover by one of the cover bolts. Build date
identification codes are stamped on the cover side of
a axle tube.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a roll
pin. Differential bearing preload and ring gear back-
lash is adjusted by the use of shims. The shims are
located between the differential bearing cones and
case. Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained by
the use of a collapsible spacer.
The axle differential covers can be used for identi-
fication of the axle (Fig. 1). A tag is also attached to
the cover.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transfer case
through the front propeller shaft. The front propeller
shaft is connected to the pinion gear which rotates
the differential through the gear mesh with the ring
gear bolted to the differential case. The engine power
is transmitted to the axle shafts through the pinion
3 - 12 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
Page 88 of 2889
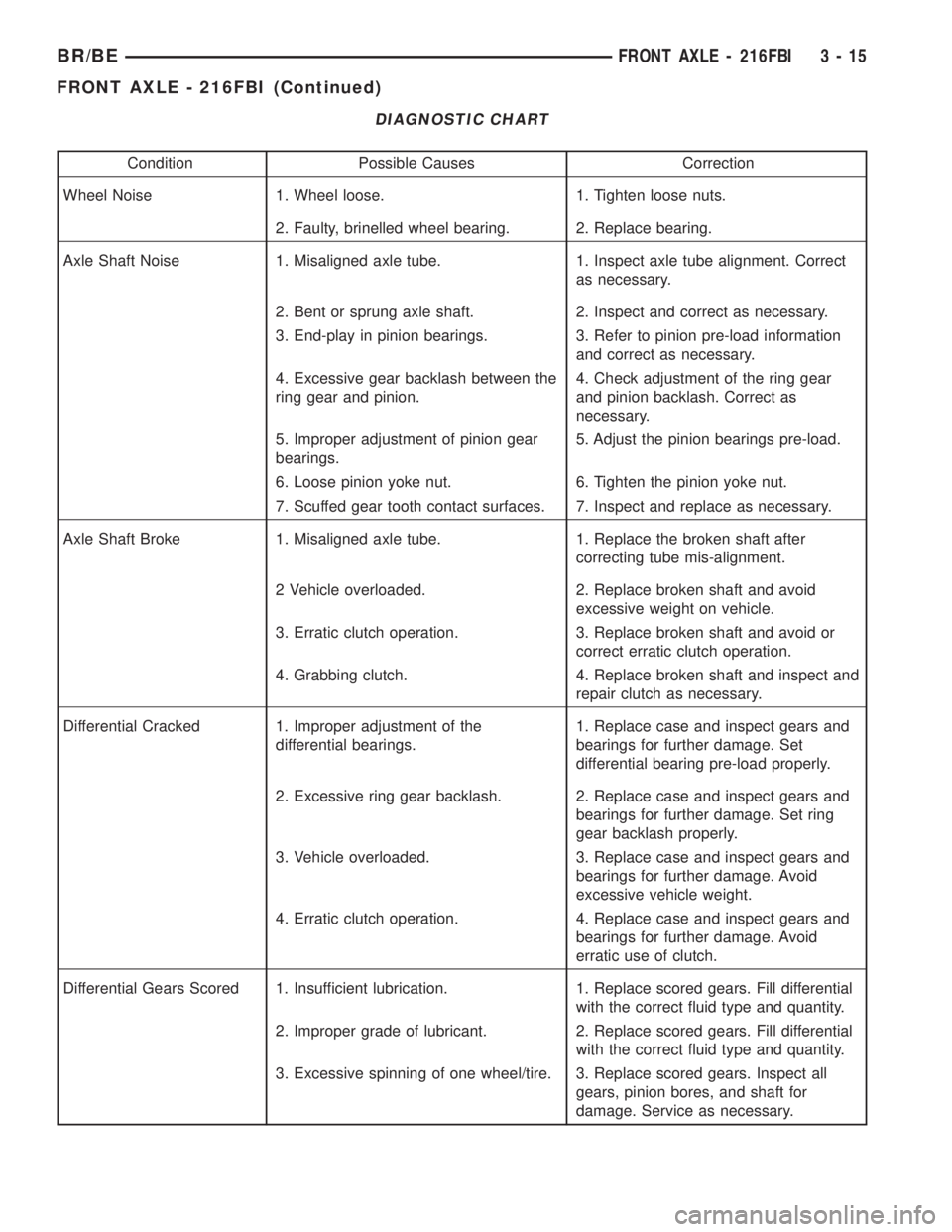
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment. Correct
as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load information
and correct as necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash between the
ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring gear
and pinion backlash. Correct as
necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion gear
bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact surfaces. 7. Inspect and replace as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect and
repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set ring
gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one wheel/tire. 3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 15
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 92 of 2889
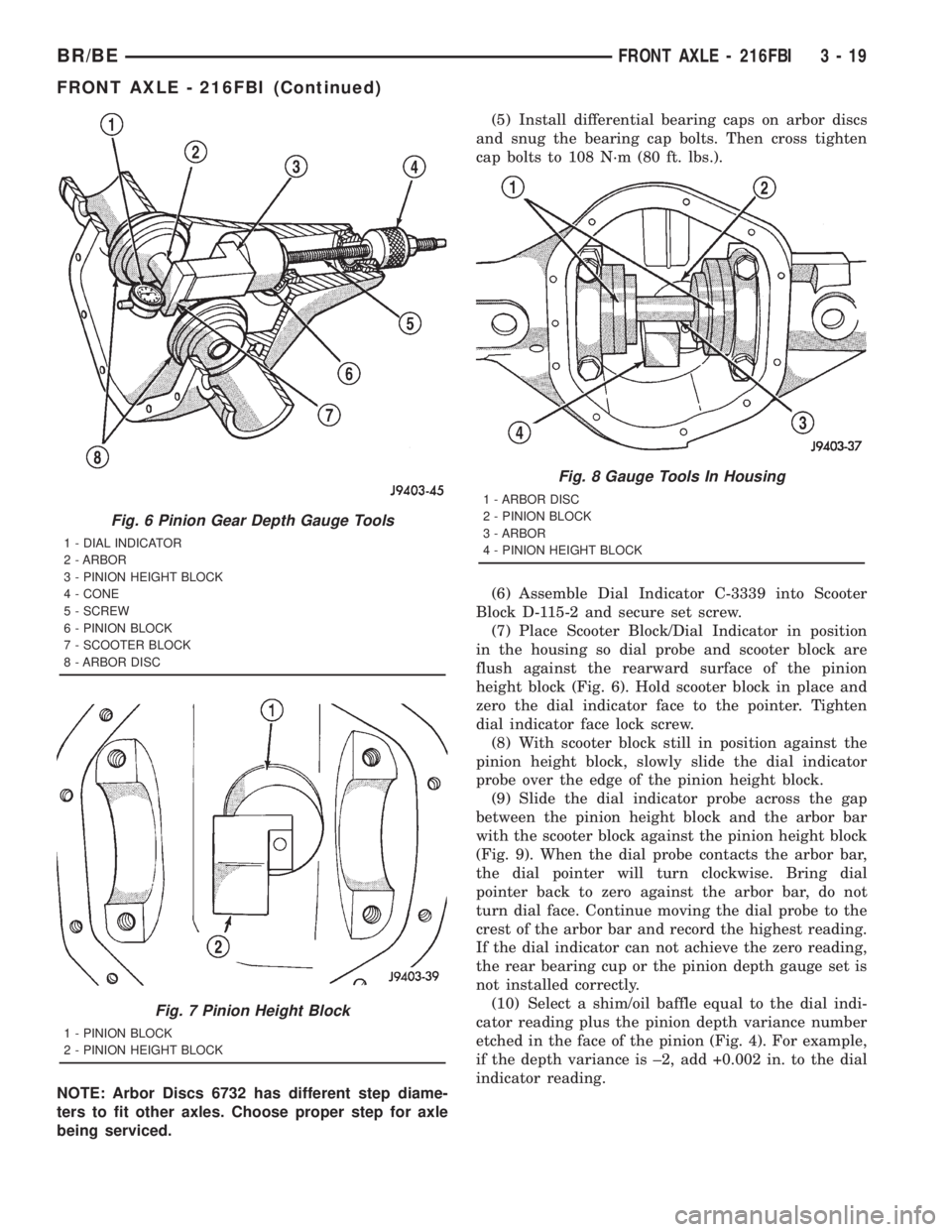
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 6). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(8) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(9) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 9). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(10) Select a shim/oil baffle equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 4). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 8 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 106 of 2889

REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
(3) Remove shift motor housing cover, gasket and
shield from the housing (Fig. 28).
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove E-clips from the shift motor housing
and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove O-ring seal from the shift motor shaft.
(3) Clean and inspect all components. Replaced
any component that is excessively worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert shift motor shaft through the hole in the
housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset should be
toward the differential.
(3) Install E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shift motor housing gasket and cover.
Ensure shift fork is correctly guided into the shift
collar groove.
(2) Install shift motor housing shield and tighten
the bolts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.).(3) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5
hypoid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(4) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
REMOVAL
Single cardan U-joint components are not service-
able. If defective they must be replaced as a unit.
CAUTION: Clamp only the narrow forged portion of
the yoke in the vise. To avoid distorting the yoke,
do not over tighten the vise jaws.
(1) Remove axle shaft.
(2) Remove the bearing cap retaining snap rings
(Fig. 30).
NOTE: Saturate bearing caps with penetrating oil
prior to removal.
(3) Locate a socket with an inside diameter is
larger than the bearing cap. Place the socket (receiv-
er) against the yoke and around the perimeter of the
bearing cap to be removed.
(4) Locate a socket with an outside diameter is
smaller than the bearing cap. Place the socket (driv-
er) against the opposite bearing cap.
Fig. 28 Shift Motor Housing
1 - INDICATOR LAMP SWITCH
2 - DISCONNECT HOUSING
3 - VACUUM SHIFT MOTOR
4 - AXLE SHAFT
5 - SEAL
6 - SHIFT COLLAR
7 - SHIFT FORK
8 - BEARING
9 - INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFT
Fig. 29 Shift Motor Components
1 - INDICATOR SWITCH
2 - E-CLIP
3 - O-RING
4 - SHIFT MOTOR
5 - SHIFT FORK
6 - VACUUM PORTS
7 - DISCONNECT HOUSING AND GASKET
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 33
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR (Continued)
Page 113 of 2889
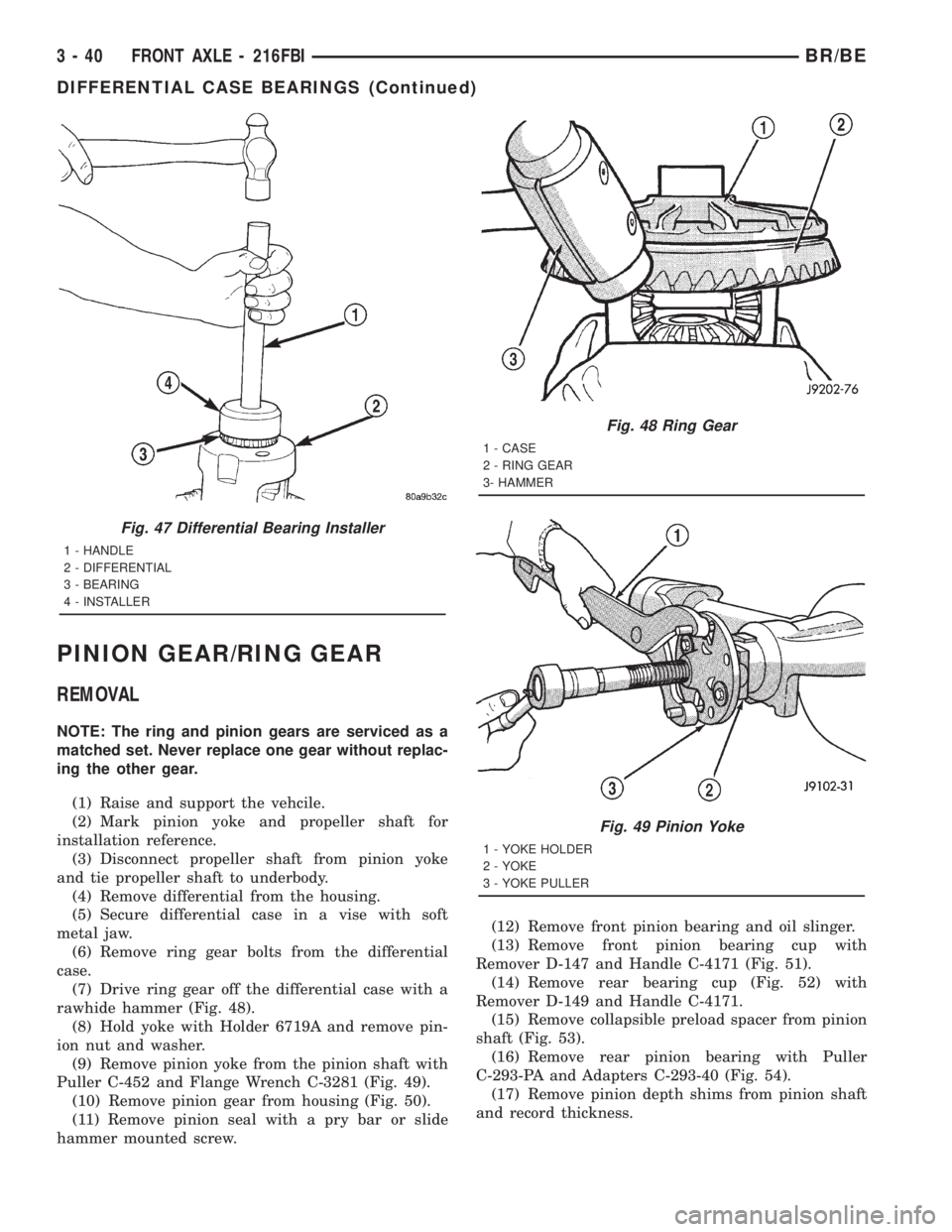
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL
NOTE: The ring and pinion gears are serviced as a
matched set. Never replace one gear without replac-
ing the other gear.
(1) Raise and support the vehcile.
(2) Mark pinion yoke and propeller shaft for
installation reference.
(3) Disconnect propeller shaft from pinion yoke
and tie propeller shaft to underbody.
(4) Remove differential from the housing.
(5) Secure differential case in a vise with soft
metal jaw.
(6) Remove ring gear bolts from the differential
case.
(7) Drive ring gear off the differential case with a
rawhide hammer (Fig. 48).
(8) Hold yoke with Holder 6719A and remove pin-
ion nut and washer.
(9) Remove pinion yoke from the pinion shaft with
Puller C-452 and Flange Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 49).
(10) Remove pinion gear from housing (Fig. 50).
(11) Remove pinion seal with a pry bar or slide
hammer mounted screw.(12) Remove front pinion bearing and oil slinger.
(13) Remove front pinion bearing cup with
Remover D-147 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 51).
(14) Remove rear bearing cup (Fig. 52) with
Remover D-149 and Handle C-4171.
(15) Remove collapsible preload spacer from pinion
shaft (Fig. 53).
(16) Remove rear pinion bearing with Puller
C-293-PA and Adapters C-293-40 (Fig. 54).
(17) Remove pinion depth shims from pinion shaft
and record thickness.
Fig. 47 Differential Bearing Installer
1 - HANDLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL
3 - BEARING
4 - INSTALLER
Fig. 48 Ring Gear
1 - CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3- HAMMER
Fig. 49 Pinion Yoke
1 - YOKE HOLDER
2 - YOKE
3 - YOKE PULLER
3 - 40 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS (Continued)