2001 DODGE RAM transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1728 of 2889
SHIFT PATTERN
The shift pattern is in a modified H pattern (Fig.
2). Overdrive fifth and sixth gears are in line and
outboard of the first through fourth gear positions.
Reverse gear is to the right of fifth and sixth and for-
ward of the neutral gate.
GEAR RATIOS
GEAR RATIO
FIRST 5.63:1
SECOND 3.38:1
THIRD 2.04:1
FOURTH 1.39:1
FIFTH 1.00:1
SIXTH 0.73:1
REVERSE 5.63:1
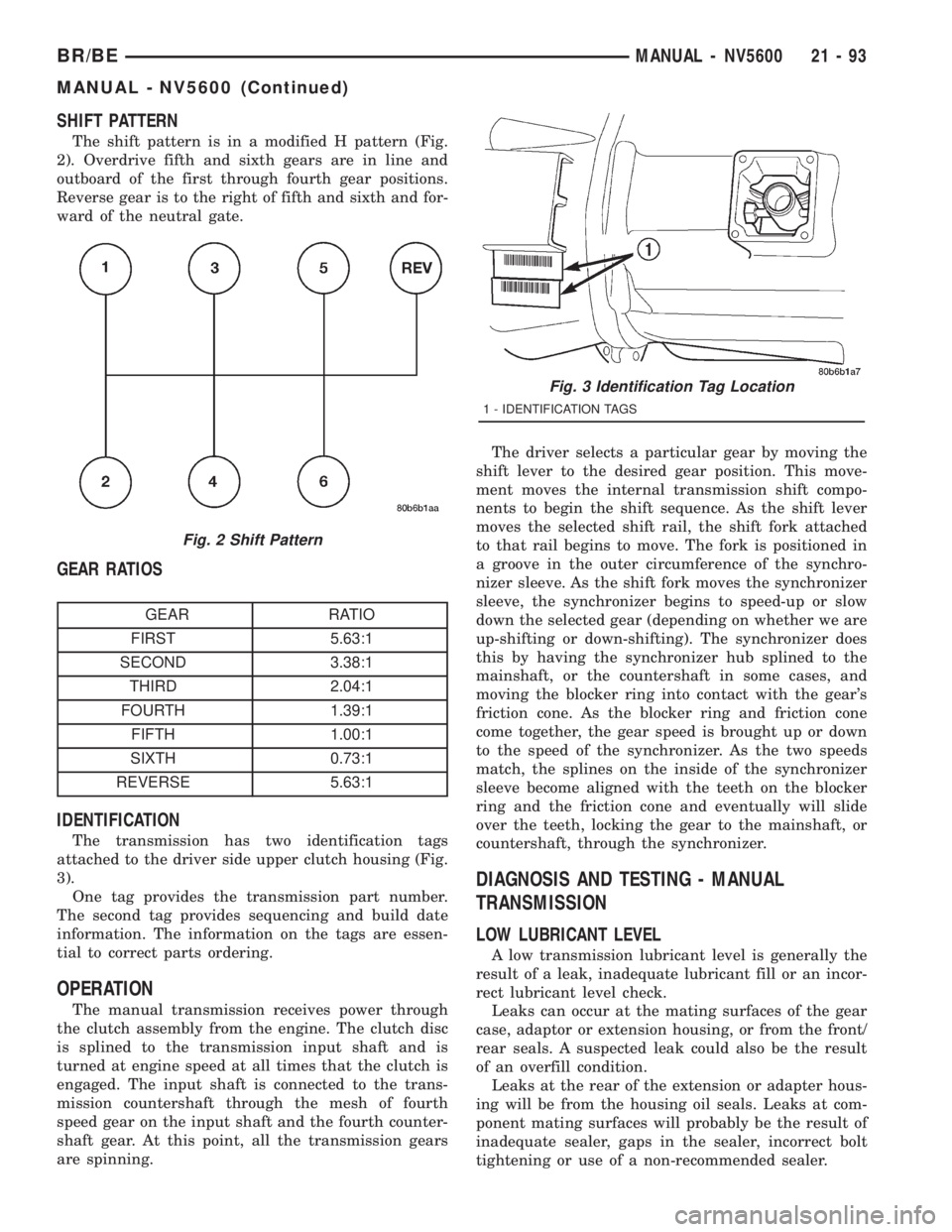
IDENTIFICATION
The transmission has two identification tags
attached to the driver side upper clutch housing (Fig.
3).
One tag provides the transmission part number.
The second tag provides sequencing and build date
information. The information on the tags are essen-
tial to correct parts ordering.
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through
the clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc
is splined to the transmission input shaft and is
turned at engine speed at all times that the clutch is
engaged. The input shaft is connected to the trans-
mission countershaft through the mesh of fourth
speed gear on the input shaft and the fourth counter-
shaft gear. At this point, all the transmission gears
are spinning.The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether we are
up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchronizer does
this by having the synchronizer hub splined to the
mainshaft, or the countershaft in some cases, and
moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear's
friction cone. As the blocker ring and friction cone
come together, the gear speed is brought up or down
to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two speeds
match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer
sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker
ring and the friction cone and eventually will slide
over the teeth, locking the gear to the mainshaft, or
countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
Fig. 2 Shift Pattern
Fig. 3 Identification Tag Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION TAGS
BR/BEMANUAL - NV5600 21 - 93
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1744 of 2889
CLEANING - TRANSMISSION
Clean the gears, bearings shafts, extension/adapter
housing and gear case with solvent. Dry all parts
except the bearings with compressed air. Allow the
bearings to either air dry or wipe them dry with
clean shop towels.
Run a tap through the gear case bolt holes if the
threads need minor cleanup. Helicoil inserts can be
used to repair seriously damaged threaded holes if
necessary.
INSPECTION - TRANSMISSION
Inspect the reverse idler gear, bearings, shaft and
thrust washers. Replace the bearings if the rollers
are worn, chipped, cracked, flat-spotted or brinnelled.
Or if the bearing cage is damaged or distorted.
Replace the thrust washers if cracked, chipped or
worn. Replace the gear if the teeth are chipped,
cracked or worn thin.
Inspect the drive gear and bearings. Minor
scratches and burrs on the gear surfaces can be
reduced with an oil stone and 400 grit paper wetted
with oil. Replace either bearing if worn, or damaged.
Replace the gear if any teeth, splines, or bearing sur-
faces are also worn or damaged.
Inspect the front bearing retainer and bearing cup.
Replace the bearing cup if scored, cracked, brinnelled
or rough. Check the release bearing slide surface of
the retainer carefully. Minor corrosion, nicks, or pit-
ting can be smoothed with 400 grit emery and pol-
ished out with crocus cloth. Wet the abrasive paper
Fig. 50 COUNTERSHAFT OIL GUIDE
1 - CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - COUNTERSHAFT OIL GUIDE
Fig. 51 FRONT COUNTERSHAFT BEARING
1 - CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - REMOVER 6061-1
Fig. 52 OIL GUIDE AND SEAL
1 - INPUT SHAFT OIL GUIDE
2 - INPUT SHAFT OIL SEAL
BR/BEMANUAL - NV5600 21 - 109
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1745 of 2889

and crocus cloth with oil when smoothing/polishing.
Replace the retainer if worn or damaged in any way.
Do not reuse original retainer bolts. Install new bolts
during assembly.
Inspect the countershaft and bearings. Replace the
bearings if worn, rough, flat spotted or heat checked.
Check the countershaft gear teeth carefully. Small
nicks, scratches or burrs can be removed with an oil
stone and 400 grit paper wetted with oil. Replace the
shaft if any of the teeth are worn, cracked, broken or
severely chipped.
Be sure to check condition of the countershaft bear-
ing cups. Replace either bearings cup if worn, or
damaged.
Check condition of the mainshaft. Inspect all the
bearing surfaces, splines and threads. Also check con-
dition of the snap ring grooves in the hub area and
the speedometer drive gear teeth. Minor scratches or
burrs can be removed with an oil stone and polished
with crocus cloth. However, replace the shaft if any
surfaces exhibit considerable wear or damage.
Check condition of the gear case and extension or
adapter housing. Be sure the alignment dowels in the
case top surface and in the housing/adapter are tight
and in good condition.
Run a tap through the gear case bolt holes if the
threads need minor cleanup. Helicoil inserts can be
used to repair seriously damaged threaded holes if
necessary.
Be sure all case and housing/adapter sealing and
mating surfaces are free of burrs and nicks. This is
especially important as gaskets are not used in the
transmission. Minor nicks and scratches on the seal-
ing surfaces can be dressed off with a fine tooth file
or oil stone.
Replace the gear case or housing/adapter if cracked
or broken. Do not attempt to repair this type of dam-
age by welding or brazing.
Check condition of the countershaft fifth gear com-
ponents. This includes the shift lug and rail located
in the gear case and the rail bushings.
Inspect the gear and hub assembly. Minor burrs
can be cleaned up with an oil stone. However, the
gear and hub assembly should be replaced if the
teeth or splines are excessively worn, or damaged.
The synchro sleeve should also be replaced if worn or
damaged in any way. Do not reuse synchro struts
that are worn or springs that are collapsed or
severely distorted. Replace worn distorted synchro
parts to avoid shift problems after assembly and
installation.
The shift fork should be inspected for evidence of
wear and distortion. Check fit of the sleeve in the
fork to be sure the two parts fit and work smoothly.
Replace the fork if the roll pin holes are worn over-
size or damaged. Do not attempt to salvage a wornfork. It will cause shift problems later on. Replace
shift fork roll pins if necessary or if doubt exists
about their condition.
The bearings should be examined carefully for
wear, roughness, flat spots, pitting or other damage.
Replace the bearings if necessary.
Inspect the blocker ring and clutch gear. replace
either part if worn or damaged in any way. Also be
sure replacement parts fit properly before proceeding
with assembly.
Examine the 1-2 synchro hub and sleeve for wear
or damage. Replace sleeve and hub if the splines are
worn, chipped or damaged.
Replace the synchro struts if worn, or chipped. Also
replace the springs if collapsed, distorted or broken.
Inspect the mainshaft geartrain components.
Check teeth on all gears, hubs, clutch gears, stop
rings and clutch rings. The teeth must be in good
condition and not worn, cracked or chipped. Replace
any component that exhibits wear or damage.
Examine the synchro stop rings, clutch rings and
clutch gears. Replace any part that exhibits wear,
distortion or damage. Replace the clutch rings if the
friction material is burned, flaking off or worn.
Inspect all of the thrust washers and locating pins.
Replace the pins if bent or worn. Replace the wash-
ers if worn or the locating pin notches are distorted.
Check condition of the synchro struts and springs.
Replace these parts if worn, cracked or distorted.
ASSEMBLY
NOTE: Gaskets are not used in the transmission.
Use MoparTGasket Maker or equivalent on all gear
case and extension housing sealing surfaces.
OUTPUT SHAFT
(1) Place second gear on bench with the synchro
clutch ring up.
(2) Install second gear synchro inner blocker ring
onto second gear (Fig. 53).
(3) Install second gear synchro friction cone over
the blocker ring and onto second gear (Fig. 54).
(4) Install second gear synchro outer blocker ring
over the second gear synchro friction cone. Align one
of the lugs on the outer ring with a lug on the inner
ring (Fig. 55).
(5) Install 1-2 synchro assembly onto the second
gear assembly (Fig. 56).
(6) Reverse assembly on the bench.
21 - 110 MANUAL - NV5600BR/BE
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1759 of 2889

EXTENSION/ADAPTER HOUSING
(1) Install extension housing bushing with
Installer 8156 and Handle C-4171, if necessary. The
oil feed hole must be at the 12 o'clock position when
installed.
(2) On 4X2 vehicles, install extension housing seal
with Installer 8154 and Handle C-4171, with the
weep hole at the bottom.
NOTE: Drain hole located in the dust boot portion
of the seal must face downward ( toward the
ground) when installed.
(3) On 4X4 vehicles, install adapter housing seal
with Installer C-3860-A and Handle C-4171.
(4) Install the crossover cam bushing into the
extension/adapter housing with Installer 8239 and
Handle C-4171.
(5) Clean the rear of the transmission case of all
sealer.
(6) Install reverse countershaft gear bearing race
onto the reverse countershaft gear bearing.
(7) Measure the distance from the back of the
bearing race to Gauge Bar 6311 (Fig. 94).(8) Measure thickness of the gauge bar and record
the total of the two measurements.
(9) Clean all the sealer from the extension/adapter
housing.
(10) Place Gauge Bar 6311 across the housing face.
Measure the distance from the top of the bar to the
bottom of the reverse countershaft bearing race bore
(Fig. 95).
(11) Subtract thickness of the gauge bar from the
measurement and record the result.
(12) The difference between the two measurements
is the end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly.
(13) Install shims to achieve 0.15-0.25 mm (0.006-
0.010 in.) end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly into the reverse countershaft bearing race
bore.
(14) Use Installer to install the reverse counter-
shaft bearing race into the extension/adapter hous-
ing.
(15) Install back-up lamp switch and a new gasket
into the extension/adapter housing. Tighten switch to
28 N´m (20 ft.lbs.).
(16) Install crossover cam into the extension/
adapter housing.
(17) Install bolt to hold the crossover cam to the
extension/adapter housing (Fig. 96).
Fig. 94 Measure Height of Reverse Countershaft
1 - MEASURE DISTANCE FROM RACE TO GAUGE BAR 6311
Fig. 95 Reverse Countershaft Gear Bearing Race
Bore
1 - GAUGE BAR 6311 TO BEARING RACE BORE
MEASUREMENT
21 - 124 MANUAL - NV5600BR/BE
MANUAL - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1769 of 2889

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
DESCRIPTION..........................135
OPERATION............................137
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................143
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION.............143
PRELIMINARY........................143
ROAD TESTING.......................143
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST...........144
AIR CHECKING TRANSMISSION CLUTCH
AND BAND OPERATION.................147
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAK......148
DIAGNOSIS CHARTS...................149
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................159
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR.............159
REMOVAL.............................159
DISASSEMBLY..........................160
CLEANING.............................165
INSPECTION...........................165
ASSEMBLY............................166
INSTALLATION..........................173
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS.............174
SPECIFICATIONS........................186
SPECIAL TOOLS........................188
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION..........................191
OPERATION............................191
INSPECTION...........................192
BANDS
DESCRIPTION..........................192
OPERATION............................192
ADJUSTMENTS.........................193
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION..........................194
OPERATION............................194
REMOVAL.............................196
INSTALLATION..........................197
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
REMOVAL.............................198
INSTALLATION..........................198
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL.............................198
INSTALLATION..........................198
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................199
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL . . . 199
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID..............199
FLUID CONTAMINATION................199
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................199
FLUID LEVEL CHECK...................199FLUID AND FILTER REPLACEMENT.......201
TRANSMISSION FILL...................201
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION..........................202
OPERATION............................202
DISASSEMBLY..........................202
INSPECTION...........................205
ASSEMBLY............................206
FRONT SERVO
DESCRIPTION..........................206
OPERATION............................207
DISASSEMBLY..........................207
CLEANING.............................207
INSPECTION...........................207
ASSEMBLY............................208
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION..........................208
OPERATION............................208
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................209
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK..............209
DISASSEMBLY..........................209
CLEANING.............................211
INSPECTION...........................211
ASSEMBLY............................212
OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING
REMOVAL.............................213
INSTALLATION..........................213
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING
REMOVAL.............................213
INSTALLATION..........................213
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION..........................214
OPERATION............................214
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................215
OPERATION............................215
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................215
OVERDRIVE ELECTRICAL CONTROLS.....215
REMOVAL.............................215
INSTALLATION..........................215
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL.............................216
DISASSEMBLY..........................217
CLEANING.............................224
INSPECTION...........................224
ASSEMBLY............................225
INSTALLATION..........................234
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
Page 1770 of 2889

OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE
PISTON RETAINER
DESCRIPTION..........................235
OPERATION............................235
DISASSEMBLY..........................235
CLEANING.............................236
INSPECTION...........................236
ASSEMBLY............................236
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................237
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH.......237
REMOVAL.............................238
INSTALLATION..........................238
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION..........................238
OPERATION............................238
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION..........................240
OPERATION............................240
DISASSEMBLY..........................240
INSPECTION...........................241
ASSEMBLY............................241
REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION..........................246
OPERATION............................246
DISASSEMBLY..........................247
CLEANING.............................247
INSPECTION...........................248
ASSEMBLY............................248
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION..........................250
OPERATION............................250
DISASSEMBLY..........................251
CLEANING.............................251
ASSEMBLY............................251
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION..........................251OPERATION............................251
ADJUSTMENTS.........................252
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION..........................252
OPERATION............................253
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................253
OPERATION............................253
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION..........................253
ADJUSTMENTS.........................254
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION..........................256
OPERATION............................260
REMOVAL.............................261
INSTALLATION..........................261
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION..........................262
OPERATION............................262
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................262
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE . 262
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................262
OPERATION............................262
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION..........................263
OPERATION............................267
REMOVAL.............................281
DISASSEMBLY..........................282
CLEANING.............................293
INSPECTION...........................293
ASSEMBLY............................294
INSTALLATION..........................303
ADJUSTMENTS.........................304
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
42RE
DESCRIPTION
The 42RE is a four speed fully automatic transmis-
sion (Fig. 1) with an electronic governor. The 42RE is
equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.
The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and thelow/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1772 of 2889

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS The 42RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.74:1
2nd................................1.54:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.21:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch will disengage momen-
tarily when an increase in engine load is sensed by
the PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go
uphill or the throttle pressure is increased. The
torque converter clutch feature increases fuel econ-
omy and reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - CONVERTER CLUTCH 15 - HOUSING
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER 16 - REAR BEARING
3 - OIL PUMP AND REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT ASSEMBLY 17 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - FRONT BAND 18 - SEAL
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 19 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - DRIVING SHELL 20 - OVERDRIVE PLANETARY GEAR
7 - REAR BAND 21 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
8 - TRANSMISSION OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 22 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PISTON
9 - OVERDRIVE UNIT 23 - VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY
10 - PISTON RETAINER 24 - FILTER
11 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH 25 - FRONT PLANETARY GEAR
12 - DIRECT CLUTCH 26 - REAR CLUTCH
13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT 27 - TRANSMISSION
14 - FRONT BEARING 28 - REAR PLANETARY GEAR
Fig. 2 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 137
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1773 of 2889

PARK POWERFLOW
As the engine is running and the crankshaft is
rotating, the flexplate and torque converter, which
are also bolted to it, are all rotating in a clockwise
direction as viewed from the front of the engine. The
notched hub of the torque converter is connected to
the oil pump's internal gear, supplying the transmis-
sion with oil pressure. As the converter turns, it
turns the input shaft in a clockwise direction. As the
input shaft is rotating, the front clutch hub-rear
clutch retainer and all their associated parts are also
rotating, all being directly connected to the input
shaft. The power flow from the engine through the
front clutch hub and rear clutch retainer stops at the
rear clutch retainer. Therefore, no power flow to the
output shaft occurs because no clutches are applied.
The only mechanism in use at this time is the park-
ing sprag (Fig. 3), which locks the parking gear on
the output shaft to the transmission case.
NEUTRAL POWERFLOW
With the gear selector in the NEUTRAL position
(Fig. 4), the power flow of the transmission is essen-
tially the same as in the park position. The only
operational difference is that the parking sprag has
been disengaged, unlocking the output shaft from the
transmission case and allowing it to move freely.
Fig. 3 Park Powerflow
1 - PAWL ENGAGED FOR PARK
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 4 Neutral Powerflow
1 - PAWL DISENGAGED FOR NEUTRAL
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - CAM
5-PAWL
21 - 138 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)