2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2742 of 4284
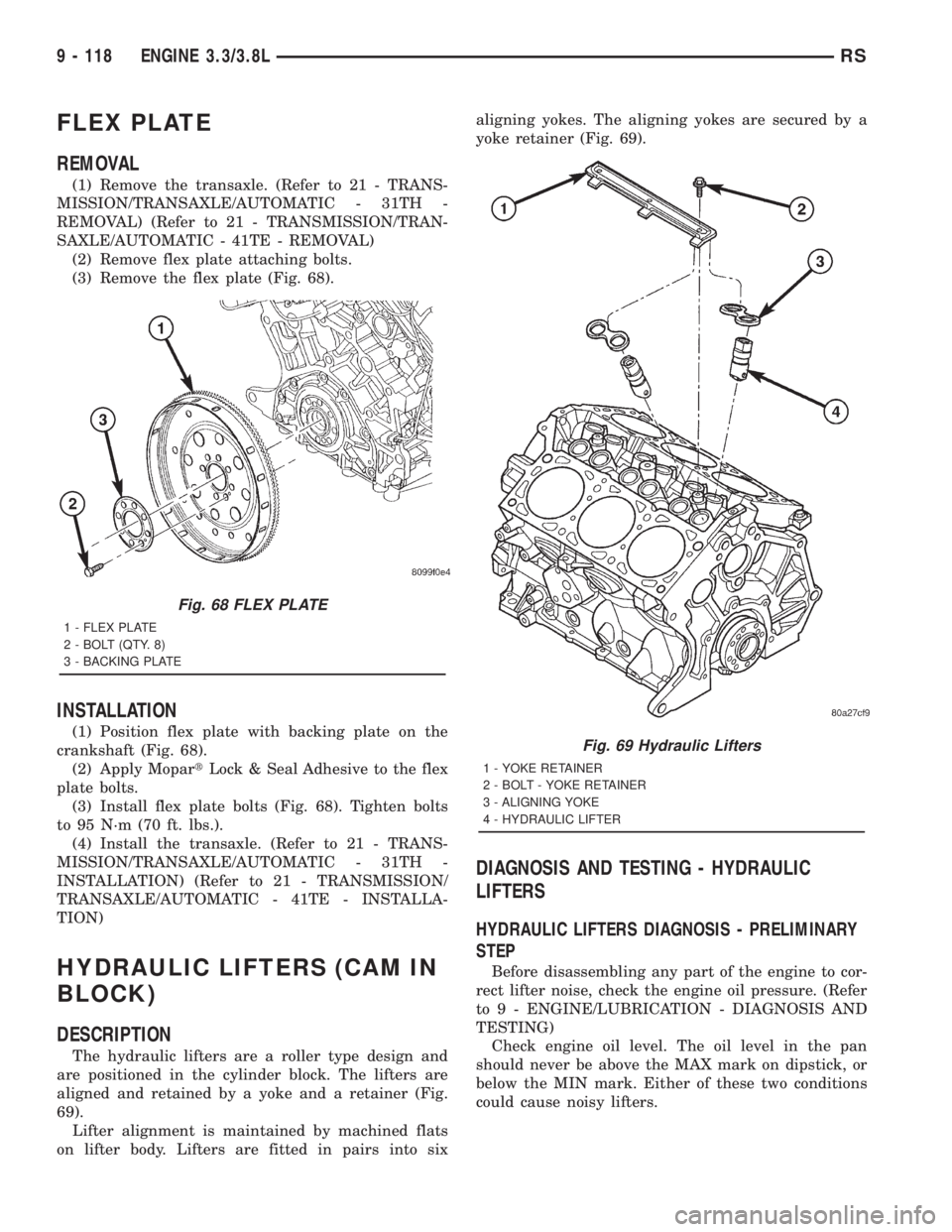
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transaxle. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 31TH -
REMOVAL) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRAN-
SAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove flex plate attaching bolts.
(3) Remove the flex plate (Fig. 68).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position flex plate with backing plate on the
crankshaft (Fig. 68).
(2) Apply MopartLock & Seal Adhesive to the flex
plate bolts.
(3) Install flex plate bolts (Fig. 68). Tighten bolts
to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the transaxle. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 31TH -
INSTALLATION) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/
TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - INSTALLA-
TION)
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN
BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic lifters are a roller type design and
are positioned in the cylinder block. The lifters are
aligned and retained by a yoke and a retainer (Fig.
69).
Lifter alignment is maintained by machined flats
on lifter body. Lifters are fitted in pairs into sixaligning yokes. The aligning yokes are secured by a
yoke retainer (Fig. 69).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LIFTERS
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS DIAGNOSIS - PRELIMINARY
STEP
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect lifter noise, check the engine oil pressure. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
Check engine oil level. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the MAX mark on dipstick, or
below the MIN mark. Either of these two conditions
could cause noisy lifters.
Fig. 68 FLEX PLATE
1 - FLEX PLATE
2 - BOLT (QTY. 8)
3 - BACKING PLATE
Fig. 69 Hydraulic Lifters
1 - YOKE RETAINER
2 - BOLT - YOKE RETAINER
3 - ALIGNING YOKE
4 - HYDRAULIC LIFTER
9 - 118 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
Page 2743 of 4284

OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the yoke retainer and aligning yokes
(Fig. 71).
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. If necessary use
Special Tool C-4129, or equivalent to remove liftersfrom bores. If lifters are to be reused, identify each
lifter to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the lifters with engine oil.
NOTE: Position the lifter in bore with the lubrication
hole facing upward (Fig. 70).
(2) Install the hydraulic lifters with the lubrication
hole facing upward towards middle of block (Fig. 70).
Install lifters in original positions, if reused.
(3) Install lifter aligning yokes (Fig. 71).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 71).
(5) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic lifters have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
Fig. 70 LIFTER LUBRICATION HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 2744 of 4284

OPERATION
The piston and connecting rod is the link between
the combustion force to the crankshaft.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS
The bearing caps are not interchangeable or
reversible, and should be marked at removal to
ensure correct reassembly. The bearing shells must
be installed with the tangs inserted into the
machined grooves in the rods and caps. Install cap
with the tangs on the same side as the rod. For con-
necting rod bearing fitting (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Fit all connecting rods
on one bank until complete.NOTE: The connecting rod cap bolts should be
examined before reuse. Bolt stretch can be checked
by holding a scale or straight edge against the
threads. If all the threads do not contact the scale
the bolt must be replaced (Fig. 72).
(1) Before installing the nuts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil.
(2) Install nuts finger tight on each bolt then alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(3) Tighten the nuts to 54 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (40
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn).
(4) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 73). Refer to Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 71 Lifter Aligning Yoke and Retainer
1 - YOKE RETAINER
2 - BOLT - YOKE RETAINER
3 - ALIGNING YOKE
4 - HYDRAULIC LIFTER
Fig. 72 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 73 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
9 - 120 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2745 of 4284
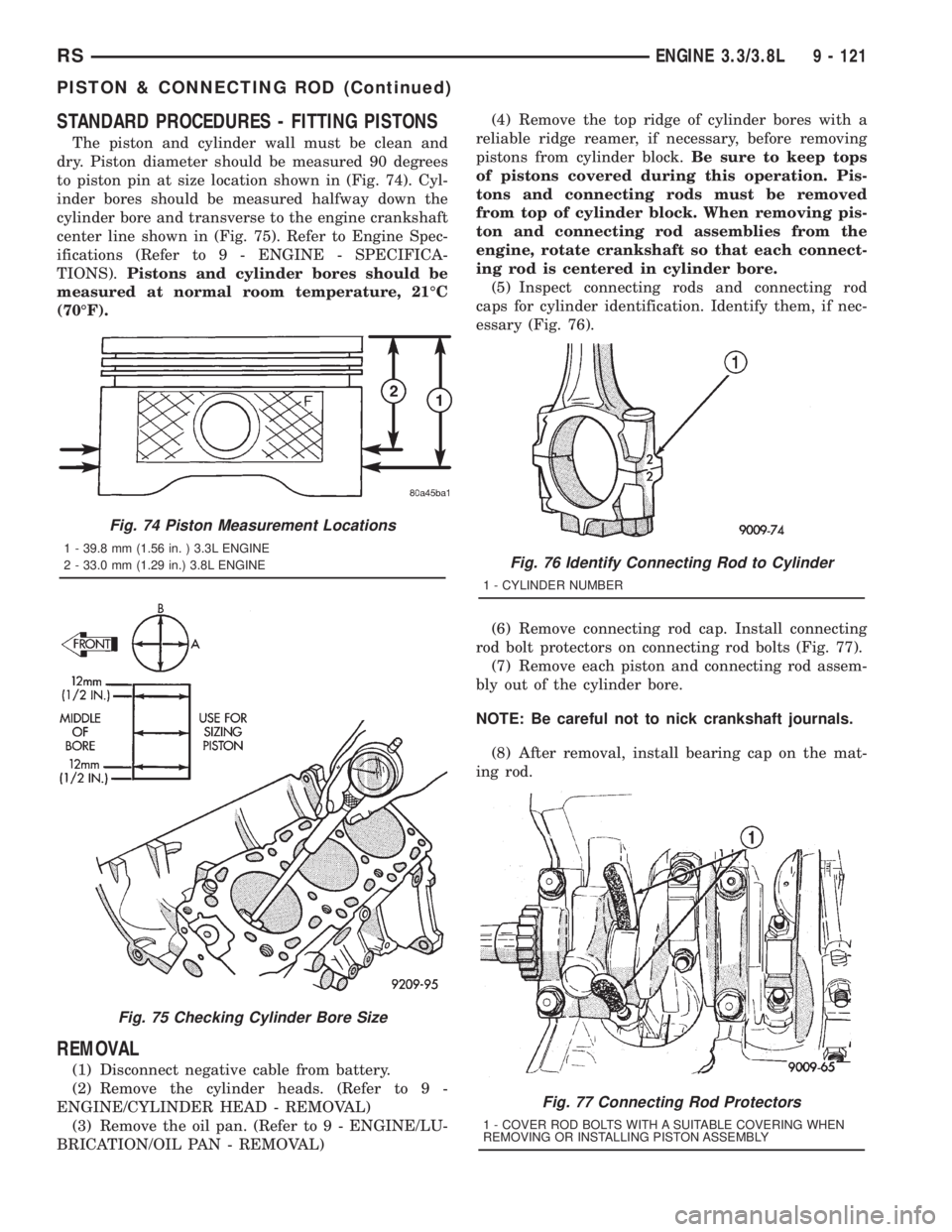
STANDARD PROCEDURES - FITTING PISTONS
The piston and cylinder wall must be clean and
dry. Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees
to piston pin at size location shown in (Fig. 74). Cyl-
inder bores should be measured halfway down the
cylinder bore and transverse to the engine crankshaft
center line shown in (Fig. 75). Refer to Engine Spec-
ifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).Pistons and cylinder bores should be
measured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC
(70ÉF).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)(4) Remove the top ridge of cylinder bores with a
reliable ridge reamer, if necessary, before removing
pistons from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops
of pistons covered during this operation. Pis-
tons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. When removing pis-
ton and connecting rod assemblies from the
engine, rotate crankshaft so that each connect-
ing rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Inspect connecting rods and connecting rod
caps for cylinder identification. Identify them, if nec-
essary (Fig. 76).
(6) Remove connecting rod cap. Install connecting
rod bolt protectors on connecting rod bolts (Fig. 77).
(7) Remove each piston and connecting rod assem-
bly out of the cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(8) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
Fig. 74 Piston Measurement Locations
1 - 39.8 mm (1.56 in. ) 3.3L ENGINE
2 - 33.0 mm (1.29 in.) 3.8L ENGINE
Fig. 75 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
Fig. 76 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
1 - CYLINDER NUMBER
Fig. 77 Connecting Rod Protectors
1 - COVER ROD BOLTS WITH A SUITABLE COVERING WHEN
REMOVING OR INSTALLING PISTON ASSEMBLY
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 121
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2746 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, ensure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap (Fig. 78).
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, ensure
the oil ring expander ends are butted and the rail
gaps located as shown in (Fig. 78).
(3) Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings, and tighten the compressor (Fig. 79).Be
sure position of rings does not change during
this operation.(4) Position upper bearing onto connecting rod.
Lubricate bearing with oil.
(5) Install connecting rod bolt protectors (rubber
hose or equivalent) on the connecting rod bolts (Fig.
79).
(6) The pistons are marked with a ªFº located near
the piston pin. Install piston with this mark posi-
tioned to front of engine on both cylinder banks. The
connecting rod oil squirt hole faces the major thrust
(right) side of the engine block (Fig. 80).
(7) Rotate crankshaft until the connecting rod
journal is located in the center of the cylinder bore.
Insert connecting rod and piston into cylinder bore.
Carefully guide connecting rod over the crankshaft
journal (Fig. 79).
(8) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
(9) Install lower bearing shell and connecting rod
cap (Fig. 79). Install nuts on cleaned and oiled rod
bolts and tighten to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) PLUS
1¤4
turn.
(10) Repeat procedure for each piston and connect-
ing rod installation.
(11) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(12) Install the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION)
(13) Fill engine crankcase with proper oil to cor-
rect level.
(14) Connect negative cable to battery.Fig. 78 Piston Ring End Gap Position
1 - SIDE RAIL UPPER
2 - NO. 1 RING GAP
3 - PISTON PIN
4 - SIDE RAIL LOWER
5 - NO. 2 RING GAP AND SPACER EXPANDER GAP
9 - 122 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2747 of 4284
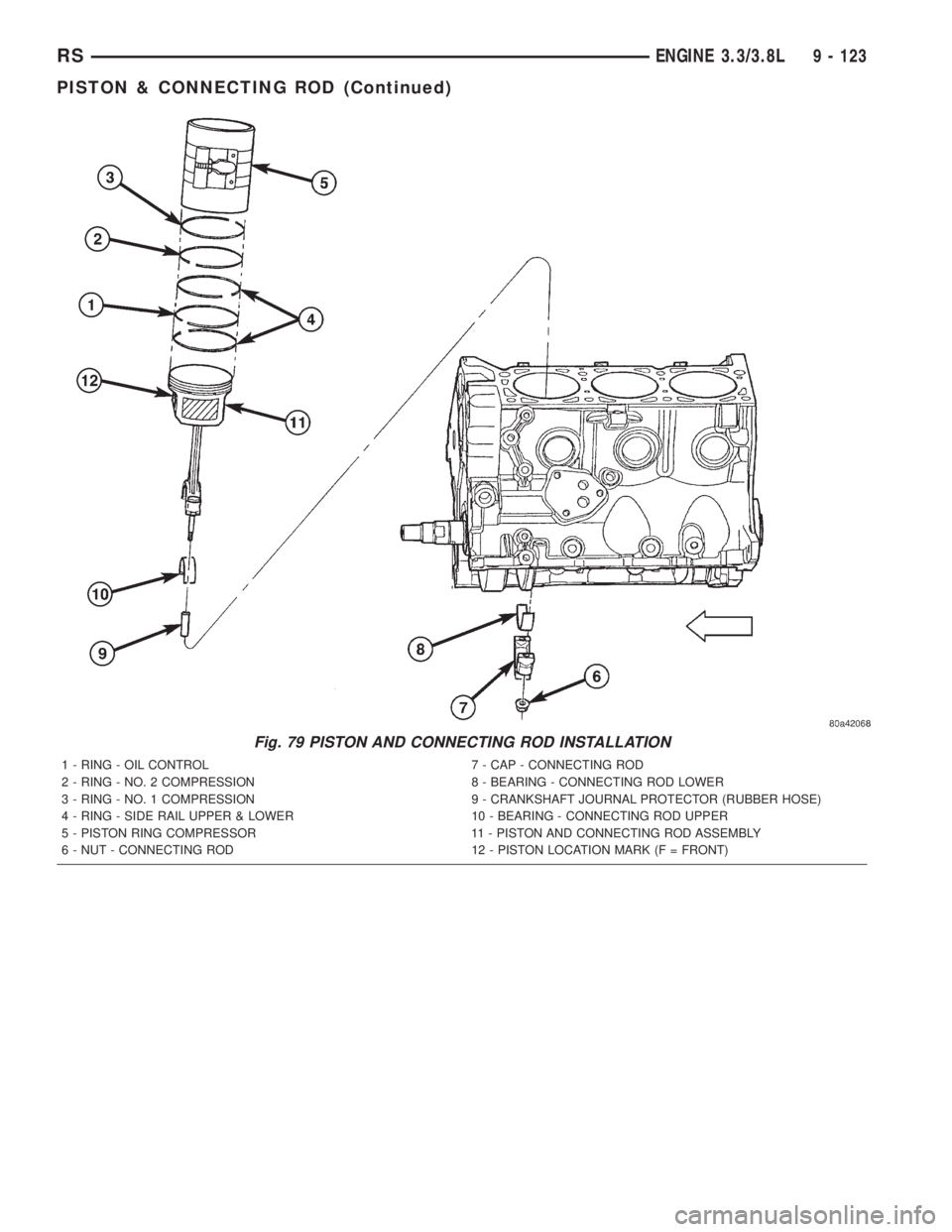
Fig. 79 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD INSTALLATION
1 - RING - OIL CONTROL 7 - CAP - CONNECTING ROD
2 - RING - NO. 2 COMPRESSION 8 - BEARING - CONNECTING ROD LOWER
3 - RING - NO. 1 COMPRESSION 9 - CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL PROTECTOR (RUBBER HOSE)
4 - RING - SIDE RAIL UPPER & LOWER 10 - BEARING - CONNECTING ROD UPPER
5 - PISTON RING COMPRESSOR 11 - PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
6 - NUT - CONNECTING ROD 12 - PISTON LOCATION MARK (F = FRONT)
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 123
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2748 of 4284
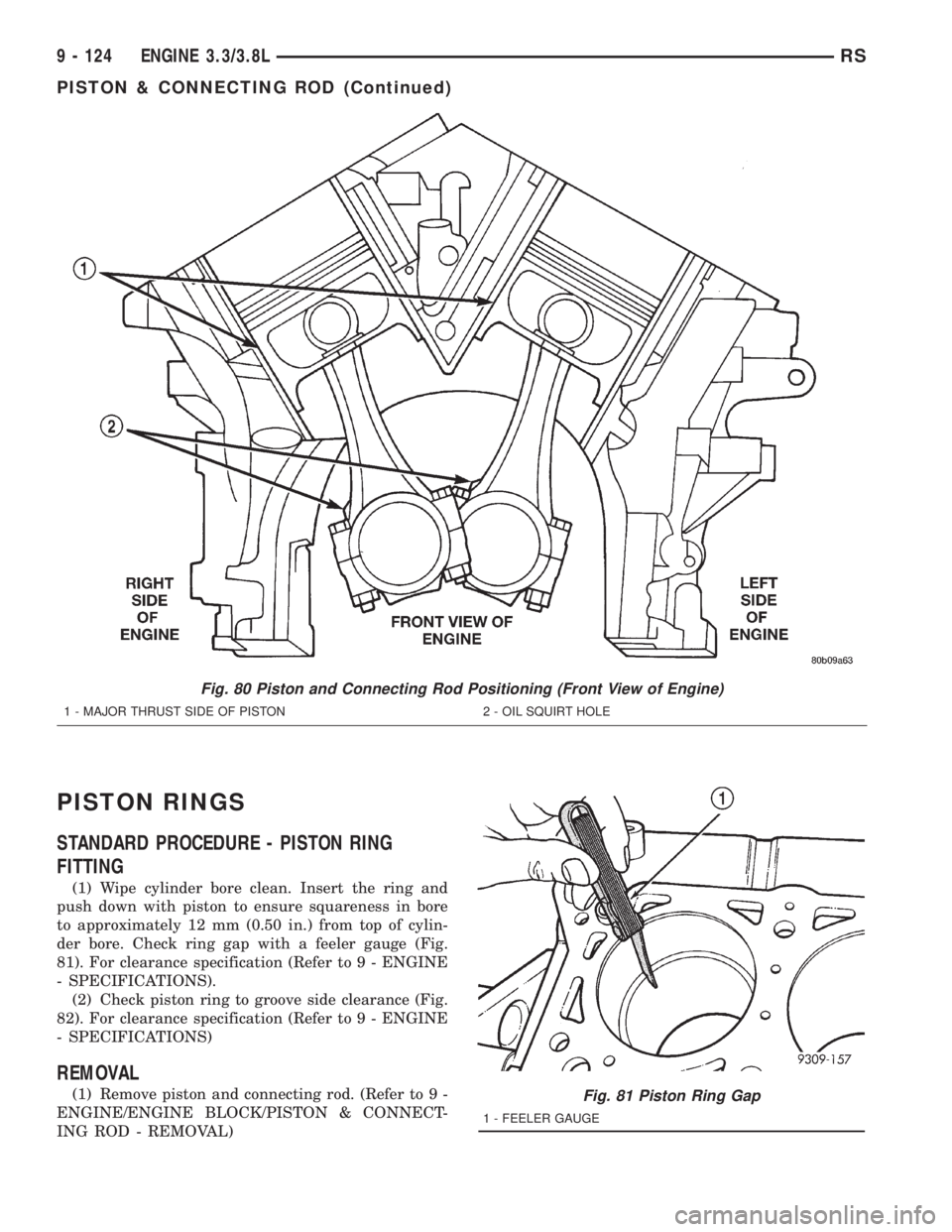
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert the ring and
push down with piston to ensure squareness in bore
to approximately 12 mm (0.50 in.) from top of cylin-
der bore. Check ring gap with a feeler gauge (Fig.
81). For clearance specification (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- SPECIFICATIONS).
(2) Check piston ring to groove side clearance (Fig.
82). For clearance specification (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- SPECIFICATIONS)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove piston and connecting rod. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - REMOVAL)
Fig. 80 Piston and Connecting Rod Positioning (Front View of Engine)
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON 2 - OIL SQUIRT HOLE
Fig. 81 Piston Ring Gap
1 - FEELER GAUGE
9 - 124 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2749 of 4284

(2) Remove No. 1 and No.2 piston rings from pis-
ton using a ring expander tool (Fig. 85).
(3) Remove upper oil ring side rail (Fig. 74).
(4) Remove lower oil ring side rail (Fig. 74).
(5) Remove oil ring expander (Fig. 74).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install rings with manufacturers I.D. mark (if
present) facing up, to the top of the piston (Fig. 83).
CAUTION: Install piston rings in the following
order:
²Oil ring expander.
²Upper oil ring side rail.
²Lower oil ring side rail.
²No. 2 Intermediate piston ring.
²No. 1 Upper piston ring.
(2) Install the side rail by placing one end
between the piston ring groove and the expander.
Hold end firmly and press down the portion to be
installed until side rail is in position.Do not use a
piston ring expander(Fig. 84).
(3) Install upper side rail first and then the lower
side rail.
(4) Install No. 2 piston ring and then No. 1 piston
ring (Fig. 85).(5) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in (Fig.
86).
(6) Position oil ring expander gap at least 45É
from the side rail gaps butnoton the piston pin cen-
ter or on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is
important for oil control.
Fig. 82 Piston Ring Side Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 83 Piston Ring Installation
1 - NO. 1 PISTON RING
2 - NO. 2 PISTON RING
3 - SIDE RAIL
4 - OIL RING
5 - SPACER EXPANDER
Fig. 84 Oil Ring Side Rail
1 - SIDE RAIL END
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 125
PISTON RINGS (Continued)