2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER clock
[x] Cancel search: clockPage 1608 of 4284
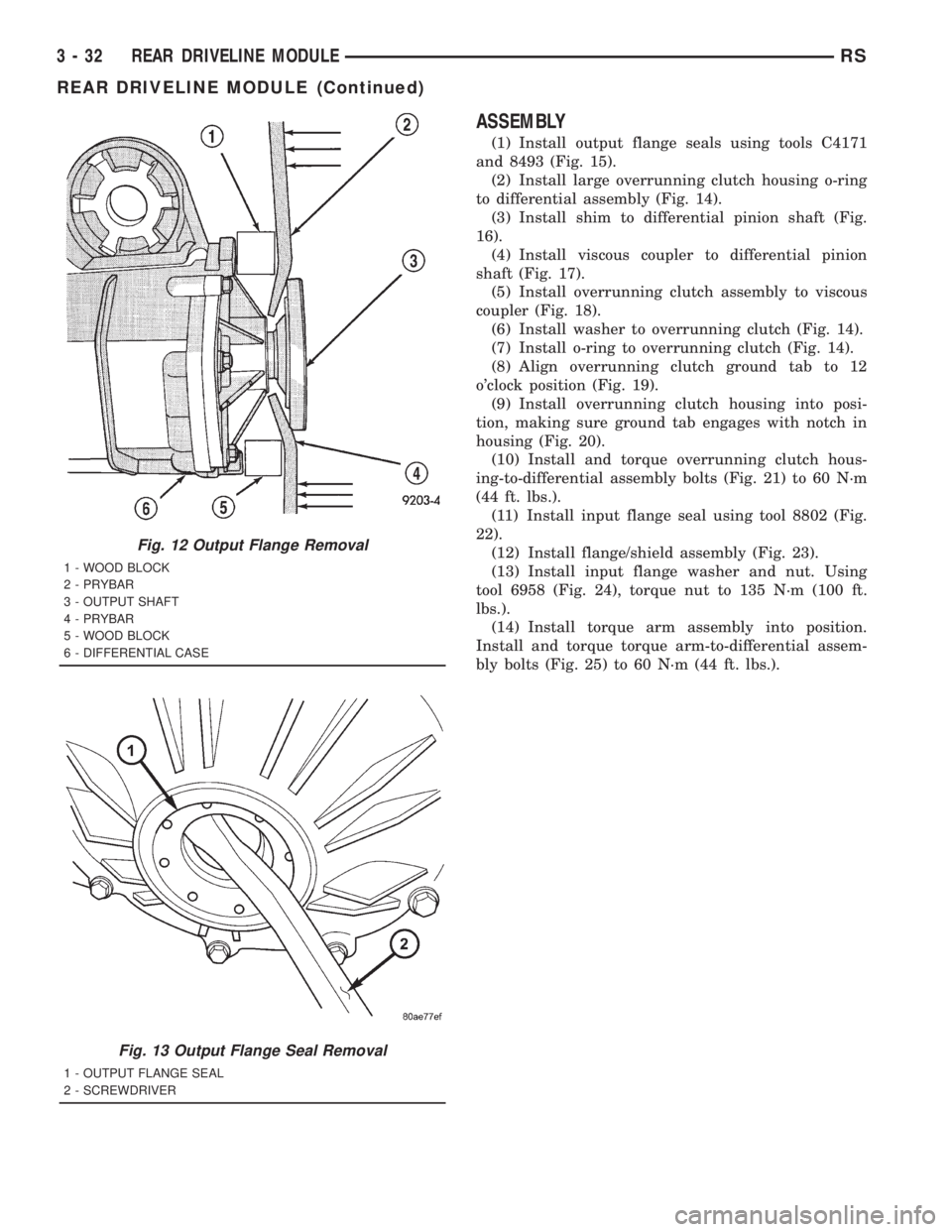
ASSEMBLY
(1) Install output flange seals using tools C4171
and 8493 (Fig. 15).
(2) Install large overrunning clutch housing o-ring
to differential assembly (Fig. 14).
(3) Install shim to differential pinion shaft (Fig.
16).
(4) Install viscous coupler to differential pinion
shaft (Fig. 17).
(5) Install overrunning clutch assembly to viscous
coupler (Fig. 18).
(6) Install washer to overrunning clutch (Fig. 14).
(7) Install o-ring to overrunning clutch (Fig. 14).
(8) Align overrunning clutch ground tab to 12
o'clock position (Fig. 19).
(9) Install overrunning clutch housing into posi-
tion, making sure ground tab engages with notch in
housing (Fig. 20).
(10) Install and torque overrunning clutch hous-
ing-to-differential assembly bolts (Fig. 21) to 60 N´m
(44 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install input flange seal using tool 8802 (Fig.
22).
(12) Install flange/shield assembly (Fig. 23).
(13) Install input flange washer and nut. Using
tool 6958 (Fig. 24), torque nut to 135 N´m (100 ft.
lbs.).
(14) Install torque arm assembly into position.
Install and torque torque arm-to-differential assem-
bly bolts (Fig. 25) to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 12 Output Flange Removal
1 - WOOD BLOCK
2 - PRYBAR
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - PRYBAR
5 - WOOD BLOCK
6 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 13 Output Flange Seal Removal
1 - OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - 32 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1610 of 4284
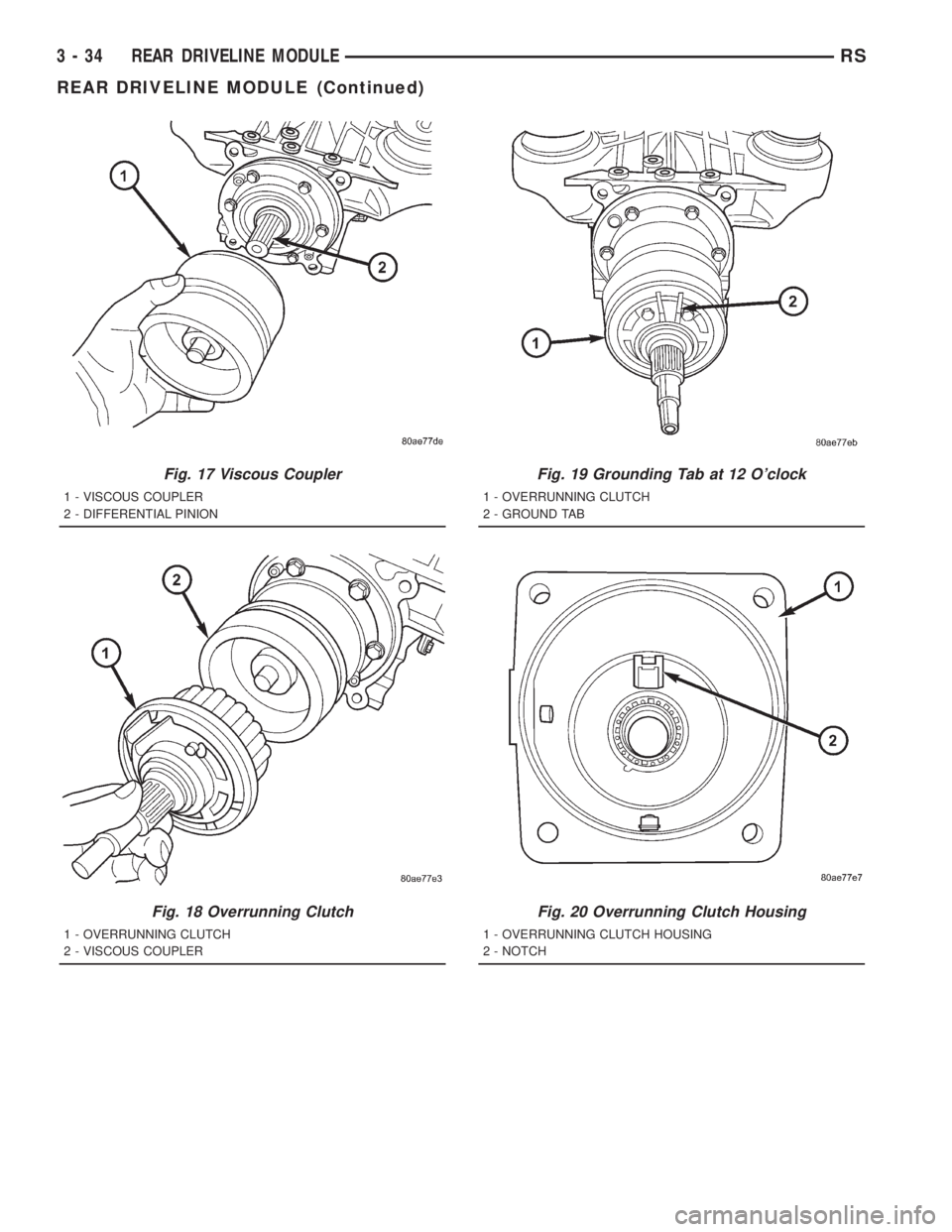
Fig. 17 Viscous Coupler
1 - VISCOUS COUPLER
2 - DIFFERENTIAL PINION
Fig. 18 Overrunning Clutch
1 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
2 - VISCOUS COUPLER
Fig. 19 Grounding Tab at 12 O'clock
1 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
2 - GROUND TAB
Fig. 20 Overrunning Clutch Housing
1 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - NOTCH
3 - 34 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1613 of 4284
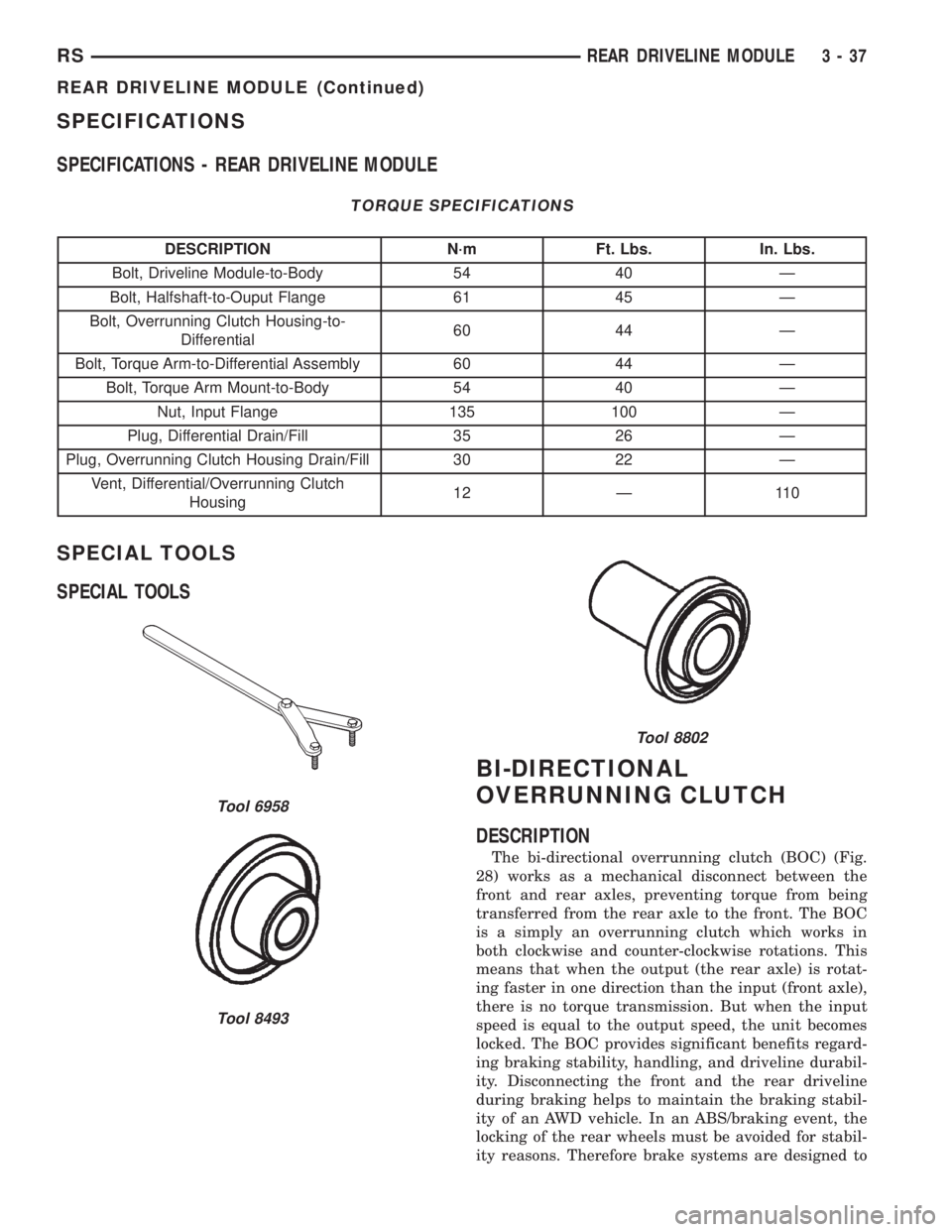
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Driveline Module-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Bolt, Halfshaft-to-Ouput Flange 61 45 Ð
Bolt, Overrunning Clutch Housing-to-
Differential60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm-to-Differential Assembly 60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm Mount-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Nut, Input Flange 135 100 Ð
Plug, Differential Drain/Fill 35 26 Ð
Plug, Overrunning Clutch Housing Drain/Fill 30 22 Ð
Vent, Differential/Overrunning Clutch
Housing12 Ð 110
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS
BI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The bi-directional overrunning clutch (BOC) (Fig.
28) works as a mechanical disconnect between the
front and rear axles, preventing torque from being
transferred from the rear axle to the front. The BOC
is a simply an overrunning clutch which works in
both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations. This
means that when the output (the rear axle) is rotat-
ing faster in one direction than the input (front axle),
there is no torque transmission. But when the input
speed is equal to the output speed, the unit becomes
locked. The BOC provides significant benefits regard-
ing braking stability, handling, and driveline durabil-
ity. Disconnecting the front and the rear driveline
during braking helps to maintain the braking stabil-
ity of an AWD vehicle. In an ABS/braking event, the
locking of the rear wheels must be avoided for stabil-
ity reasons. Therefore brake systems are designed to
Tool 6958
Tool 8493
Tool 8802
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-37
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1614 of 4284

lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on a
slippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
through to the rear wheels. The rear driveline mod-
ule, with the BOC, will perform the same as a front
wheel drive vehicle during these events. The gear
ratio offset between the front and rear differentials
force the BOC into the overrunning mode most of the
time. This allows BOC to significantly reduce the
rolling resistance of the vehicle, which improves fuel
consumption, allows the downsizing of the driveline
components, and prevents the PTU and propshaft
joints from overheating.
OPERATION
In order to achieve all-wheel drive operation in
reverse, the overrunning clutch locking functional
direction must be reversible. The bi-directional over-
running clutch (BOC) changes the operational mode
direction depending on the propeller shaft direction.
The propeller shaft rotates in the clockwise (when
viewed from the front) direction when the vehicle is
moving forward, which indexes the BOC to the for-
ward overrunning position. When the vehicle is in
reverse, the propeller shaft will rotate counter-clock-
wise and index the BOC to the reverse overrunning
position.
The BOC acts as a mechanical stator. It is active
(transmitting torque), or it is not active and in over-
running mode (not transmitting torque). This ªall or
nothingº approach to torque transfer would cause a
sudden application of all available power to the rear
wheels, which is not desirable. Therefore it is run in
series with a viscous coupler to smooth, dampen, and
limit the transmission of torque to the rear axle and
to prevent a step style torque input to the rear axle.
STEADY STATE, LOW TO MODERATE SPEED, NO
FRONT WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
During normal driving conditions, (no wheel slip),
the inner shaft (front axle) and outer race (viscous
coupler) are running at different speeds due to the
different gear ratios between the front and rear dif-
ferentials. In this condition, the outer race is always
spinning faster (overdriving between 5-32 rpm) than
the inner shaft. When the BOC (Fig. 29) is running
under these conditions, at low vehicle speeds the
drag shoes and the cage keep the rollers up on the
left side (forward side) of the inner shaft flats. This is
what is known as ªoverrunning mode.º Notice that
when the clutch is in overrunning mode, the rollers
are spinning clockwise and with the outer race, thus
no torque is being transferred.
NOTE: Low speed, forward and reverse operation is
identical, just in opposite directions. (Fig. 29)
shows forward direction in reverse the rollers are
on the other side of the flats due to a reversal of
the cage force.
TRANSIENT CONDITION (BOC LOCKED), FRONT
WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
When the front wheels lose traction and begin to
slip, the propeller shaft and rear axle pinion speed
difference decreases to zero. At this point the input
shaft (cam) becomes the driving member of the BOC
(Fig. 30), compressing the rollers against the outer
race. This locks the input shaft with the outer race
and transmits torque to the housing of the viscous
coupler, that in turn transmits torque to the rear
axle pinion. It should also be noted that when the
device is locked, the inner shaft and the outer race
are rotating at the same speed. The rollers are
pinched at this point and will stay locked until a
torque reversal (no front wheel slip) occurs. When
locked, the viscous coupler slips during the torque
transfer and the amount of torque transferred is
dependent on the coupling characteristic and the
amount of front wheel slip.
3 - 38 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1692 of 4284

INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(LEFT REAR)
(1) Install the rear parking brake cable in the
brake support plate. Insert cable housing retainer
into brake support plate making certain that cable
housing retainer fingers lock the housing and
retainer firmly into place.
(2) Attach the parking brake cable onto the park
brake actuator lever.
(3) Install the brake shoes on the rear brake sup-
port plate. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/ME-
CHANICAL/BRAKE PADS/SHOES -
INSTALLATION).
(4) Insert cable housing retainer into body outrig-
ger bracket making certain that cable housing
retainer fingers lock the housing firmly into place.
(5) Connect rear parking brake cable to the equal-
izer bracket (Fig. 114).
(6) Install brake drum, and wheel and tire assem-
bly.
(7) Remove the locking pliers from the front park
brake cable. This will automatically adjust the park
brake cables.
(8) Apply and release park brake pedal 1 time.
This will seat the park brake cables.
ADJUSTMENT - CABLES
The park brake cables on this vehicle have an
automatic self adjuster built into the park brake
pedal mechanism. When the foot operated park brake
pedal is in its released (upward most) position, a
clock spring automatically adjusts the park brake
cables. The park brake cables are adjusted (ten-
sioned) just enough to remove all the slack from the
cables. The automatic adjuster system will not over
adjust the cables causing rear brake drag.
Due to the automatic adjust feature of the park
brake pedal, adjustment of the parking brake cables
on these vehicles relies on proper drum brake and
park brake shoe adjustment. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DRUM - ADJUST-
MENTS) and (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/PARKING
BRAKE/SHOES - ADJUSTMENTS).
When the park brake pedal is applied the self
adjuster is by-passed and the pedal operates nor-
mally to engage the park brakes.
When a service procedure needs to be performed on
the park brake pedal or the park brake cables, the
automatic self adjuster can be manually locked out
by the service technician.
5 - 66 BRAKES - BASERS
CABLES (Continued)
Page 1731 of 4284
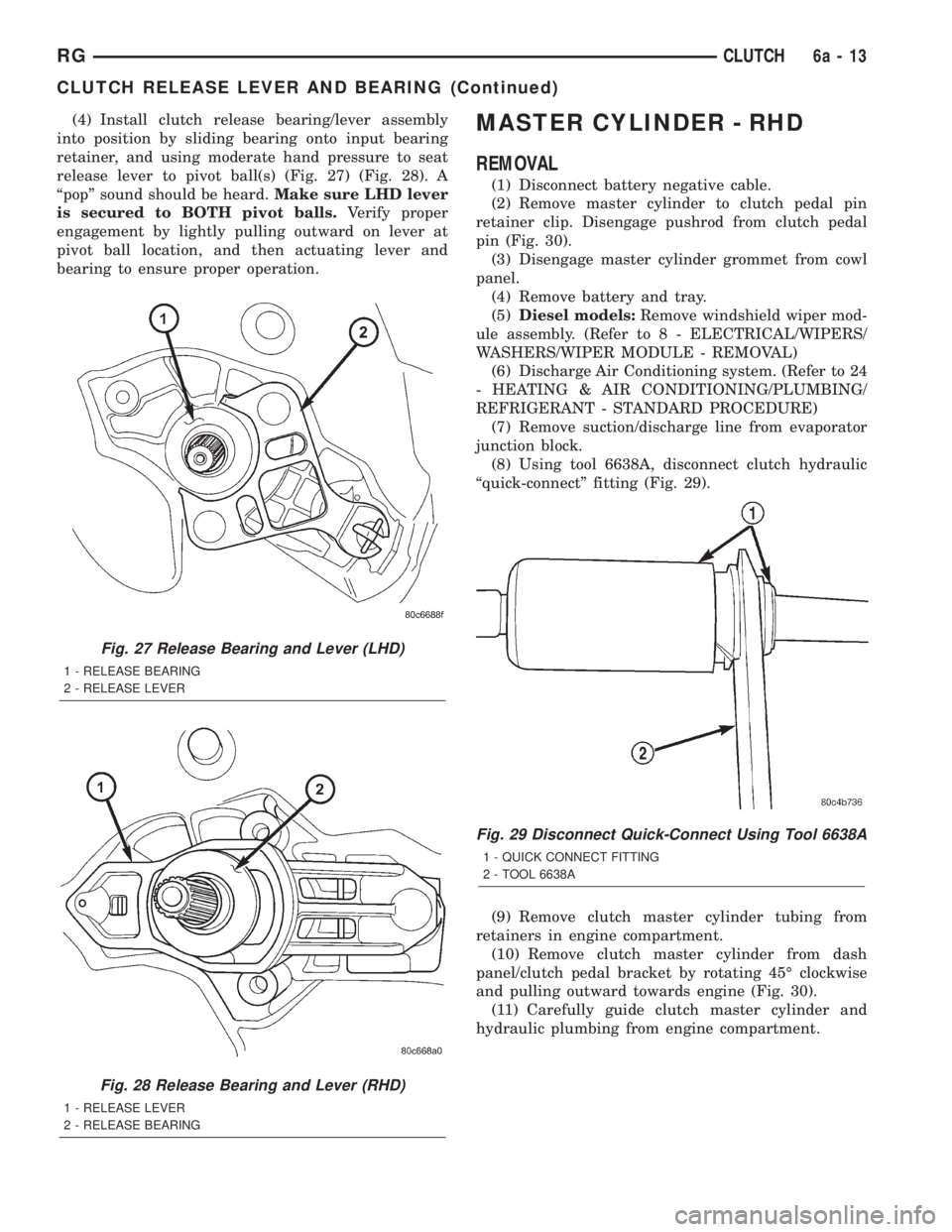
(4) Install clutch release bearing/lever assembly
into position by sliding bearing onto input bearing
retainer, and using moderate hand pressure to seat
release lever to pivot ball(s) (Fig. 27) (Fig. 28). A
ªpopº sound should be heard.Make sure LHD lever
is secured to BOTH pivot balls.Verify proper
engagement by lightly pulling outward on lever at
pivot ball location, and then actuating lever and
bearing to ensure proper operation.MASTER CYLINDER - RHD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove master cylinder to clutch pedal pin
retainer clip. Disengage pushrod from clutch pedal
pin (Fig. 30).
(3) Disengage master cylinder grommet from cowl
panel.
(4) Remove battery and tray.
(5)Diesel models:Remove windshield wiper mod-
ule assembly. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/
WASHERS/WIPER MODULE - REMOVAL)
(6) Discharge Air Conditioning system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(7) Remove suction/discharge line from evaporator
junction block.
(8) Using tool 6638A, disconnect clutch hydraulic
ªquick-connectº fitting (Fig. 29).
(9) Remove clutch master cylinder tubing from
retainers in engine compartment.
(10) Remove clutch master cylinder from dash
panel/clutch pedal bracket by rotating 45É clockwise
and pulling outward towards engine (Fig. 30).
(11) Carefully guide clutch master cylinder and
hydraulic plumbing from engine compartment.
Fig. 27 Release Bearing and Lever (LHD)
1 - RELEASE BEARING
2 - RELEASE LEVER
Fig. 28 Release Bearing and Lever (RHD)
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE BEARING
Fig. 29 Disconnect Quick-Connect Using Tool 6638A
1 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
2 - TOOL 6638A
RGCLUTCH6a-13
CLUTCH RELEASE LEVER AND BEARING (Continued)
Page 1732 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Carefully route master cylinder plumbing into
engine compartment as removed and position master
cylinder to dash panel hole.
(2) Rotate master cylinder 45É clockwise, insert
into dash panel hole, engaging clutch pedal bracket.
Rotate master cylinder 45É counter-clockwise, secur-
ing it to pedal bracket (Fig. 30).
(3) Install and secure grommet to dash panel.
(4) Connect pushrod to clutch pedal pin. Install
retainer clip (Fig. 30).
(5) Secure master cylinder plumbing to retainers
in engine compartment.
(6) Connect clutch master cylinder plumbing to
slave cylinder ªquick connectº fitting. An audible
ªclickº should be heard. Verify connection by pulling
outward.(7) Connect A/C suction/discharge line to evapora-
tor junction block.
(8)Diesel models:Install wiper module assembly.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/
WIPER MODULE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Install battery and tray.
(10) Connect battery negative cable
(11) Charge Air Conditioning system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/RE-
FRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSY -
2.4L GAS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle from vehicle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove modular clutch assembly from input
shaft (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 Clutch Master Cylinder at Pedal Bracket
1 - CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER
2 - RETAINER CLIP
3 - CLUTCH PEDAL PIN
4 - PUSH ROD
Fig. 31 Modular Clutch Assembly
1 - MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 - INPUT SHAFT
6a - 14 CLUTCHRG
MASTER CYLINDER - RHD (Continued)
Page 1733 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Install modular clutch assembly to transaxle
input shaft (Fig. 31).
(2) Install transaxle to vehicle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL - INSTAL-
LATION)
SLAVE CYLINDER - RHD
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.Diesel models:Remove
underbody splash shield.
(2) Using Tool 6638A, disconnect hyrdraulic clutch
circuit quick connect fitting.
(3) Remove clutch slave cylinder (Fig. 32) by lifting
nylon tab with a small screwdriver, and then
depressing cylinder inward towards case and rotating
cylinder 60É counter-clockwise.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install clutch slave cylinder into position, not-
ing orientation of different sized lugs. While depress-
ing inward, rotate slave cylinder clockwise until
nylon locating tab rests in transaxle case cutout, and
the hydraulic tube is vertical (Fig. 32).
(2) Connect ªquick-connectº connection until an
audible ªclickº is heard. Verify connection by pulling
outward on connection.
(3)Diesel models:Install underbody splash
shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
CLUTCH DISC AND PRESSURE
PLATE - 2.5L TD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle assembly. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove six (6) clutch pressure plate-to-fly-
wheel bolts. Remove pressure plate and disc from fly-
wheel (Fig. 33).
(3) Inspect flywheel. Resurface/replace as neces-
sary.
(4) Inspect clutch release bearing and lever.
Replace as necessary. (Refer to 6 - CLUTCH/
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
(1) Install clutch release bearing and lever (if
removed). (Refer to 6 - CLUTCH/CLUTCH RELEASE
BEARING - INSTALLATION)
(2) Install clutch disc and pressure plate to fly-
wheel (Fig. 33). Install clutch alignment tool, and
install and torque pressure plate-to-flywheel bolts to
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Install transaxle assembly. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL - INSTAL-
LATION)
Fig. 32 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
RGCLUTCH6a-15
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSY - 2.4L GAS (Continued)