2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 2996 of 4284

The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit that slips and to confirm proper operation of
good units. Road testing can usually diagnose slip-
ping units, although the actual cause of the problem
may not be detected. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
Therefore, unless the condition is obvious, the
transaxle should never be disassembled until hydrau-
lic pressure tests have been performed.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, check fluid level
and condition, as well as control cable adjustments.
Fluid must be at operating temperature (150-200
degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer. Raise vehicle on a
hoist that allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Disconnect throttle cable and shift cable from
transaxle levers so they can be controlled from out-
side the vehicle.
Attach 100 psi gauges (C-3292) to ports required
for test being conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP)
is required for reverse pressure test at rear servo.
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Test Port Locations
1 - ACCUMULATOR VENT
2 - MANUAL THROTTLE LEVER SHAFT
3 - MANUAL SHIFT LEVER SHAFT
4 - LOW-REVERSE PRESSURE
5 - GOVERNER PRESSURE (BELOW DIFFERENTIAL COVER
ON RIGHT SIDE)
6 - LINE PRESSURE
7 - KICKDOWN APPLY AT ACCUMULATOR8 - TO COOLER
9 - KICKDOWN RELEASE (FRONT CLUTCH)
10 - KICKDOWN APPLY
11 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONNECTOR
12 - FROM COOLER
13 - KICKDOWN BAND ADJUSTING SCREW
21 - 32 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3002 of 4284

(12) Remove front mount and bracket (Fig. 11).
(13) Cut transaxle oil cooler lines flush with fit-
tings. a service kit will be installed upon reintalla-
tion. Plug lines and fittings to prevent debris
intrusion.
(14) Remove structural collar (Fig. 12).
(15) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor connector.
(16) Remove rear mount shield (Fig. 13).
(17) Remove rear mount thru-bolt.
(18) Support engine with screw jack and wood
block.
(19) Remove cradle plate.
(20) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(21) Remove left wheel splash shield.
(22) Remove left upper mount thru-bolt (Fig. 14).
(23) Lower engine/transaxle assembly.
(24) Obtain transmission jack and helper.
(25) Remove remaining transaxle-to-engine bolts
and remove transaxle assembly from vehicle.
Fig. 11 Front Mount and Bracket
1 - BRACKET - FRONT MOUNT
2 - NUT
3 - BOLT
4 - MOUNT - FRONT INSULATOR
5 - BOLT
6 - BOLT
7 - FRONT CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 12 Structural Collar
1 - BOLT - COLLAR TO OIL PAN
2 - BOLT - COLLAR TO TRANSAXLE
3 - STRUCTURAL COLLAR
4 - OIL PAN
Fig. 13 Rear Mount Heat Shield
1 - BOLT - HEAT SHIELD
2 - HEAT SHIELD
3 - CLIP
4 - REAR MOUNT
21 - 38 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3024 of 4284
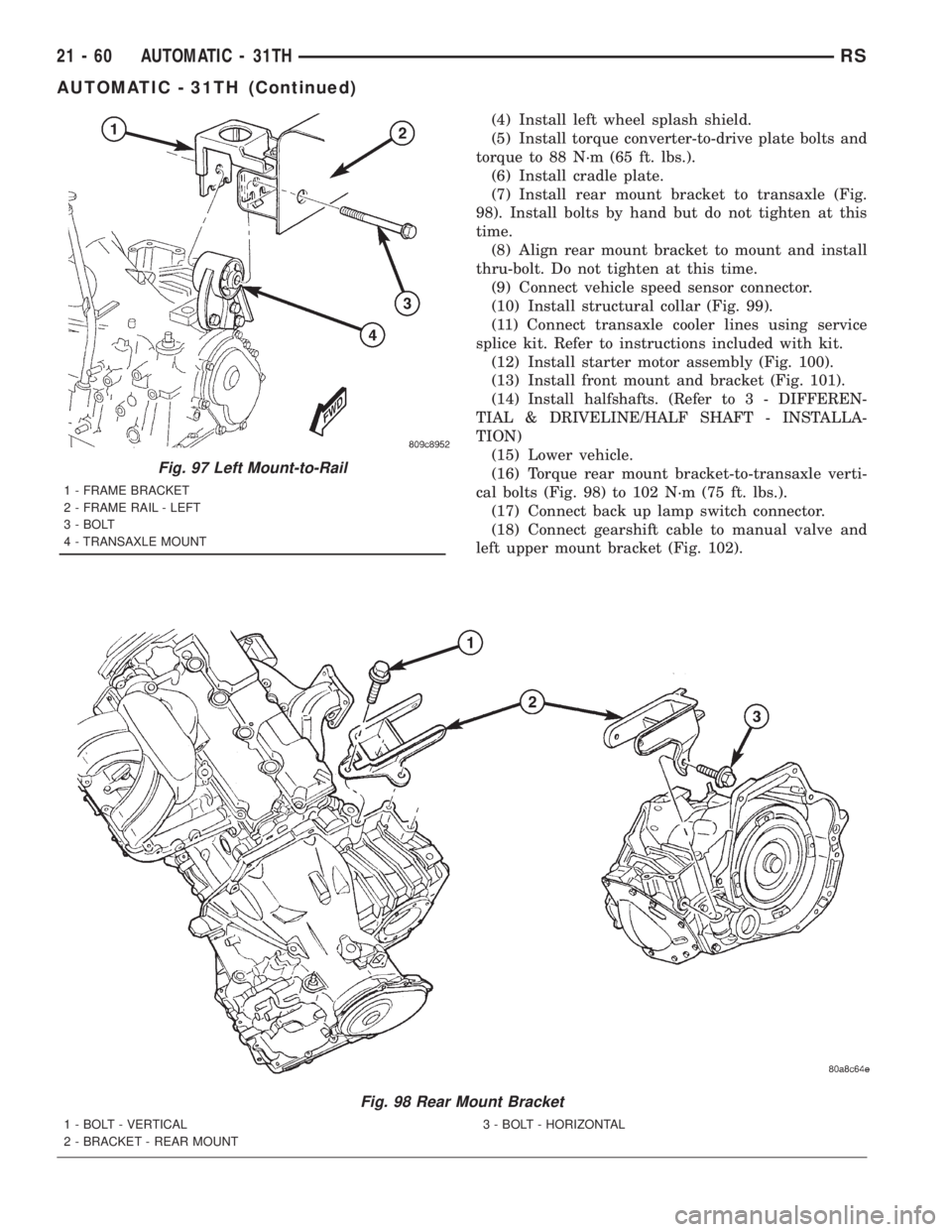
(4) Install left wheel splash shield.
(5) Install torque converter-to-drive plate bolts and
torque to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install cradle plate.
(7) Install rear mount bracket to transaxle (Fig.
98). Install bolts by hand but do not tighten at this
time.
(8) Align rear mount bracket to mount and install
thru-bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(9) Connect vehicle speed sensor connector.
(10) Install structural collar (Fig. 99).
(11) Connect transaxle cooler lines using service
splice kit. Refer to instructions included with kit.
(12) Install starter motor assembly (Fig. 100).
(13) Install front mount and bracket (Fig. 101).
(14)
Install halfshafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - INSTALLA-
TION)
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Torque rear mount bracket-to-transaxle verti-
cal bolts (Fig. 98) to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(17) Connect back up lamp switch connector.
(18) Connect gearshift cable to manual valve and
left upper mount bracket (Fig. 102).
Fig. 98 Rear Mount Bracket
1 - BOLT - VERTICAL
2 - BRACKET - REAR MOUNT3 - BOLT - HORIZONTAL
Fig. 97 Left Mount-to-Rail
1 - FRAME BRACKET
2 - FRAME RAIL - LEFT
3 - BOLT
4 - TRANSAXLE MOUNT
21 - 60 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3088 of 4284
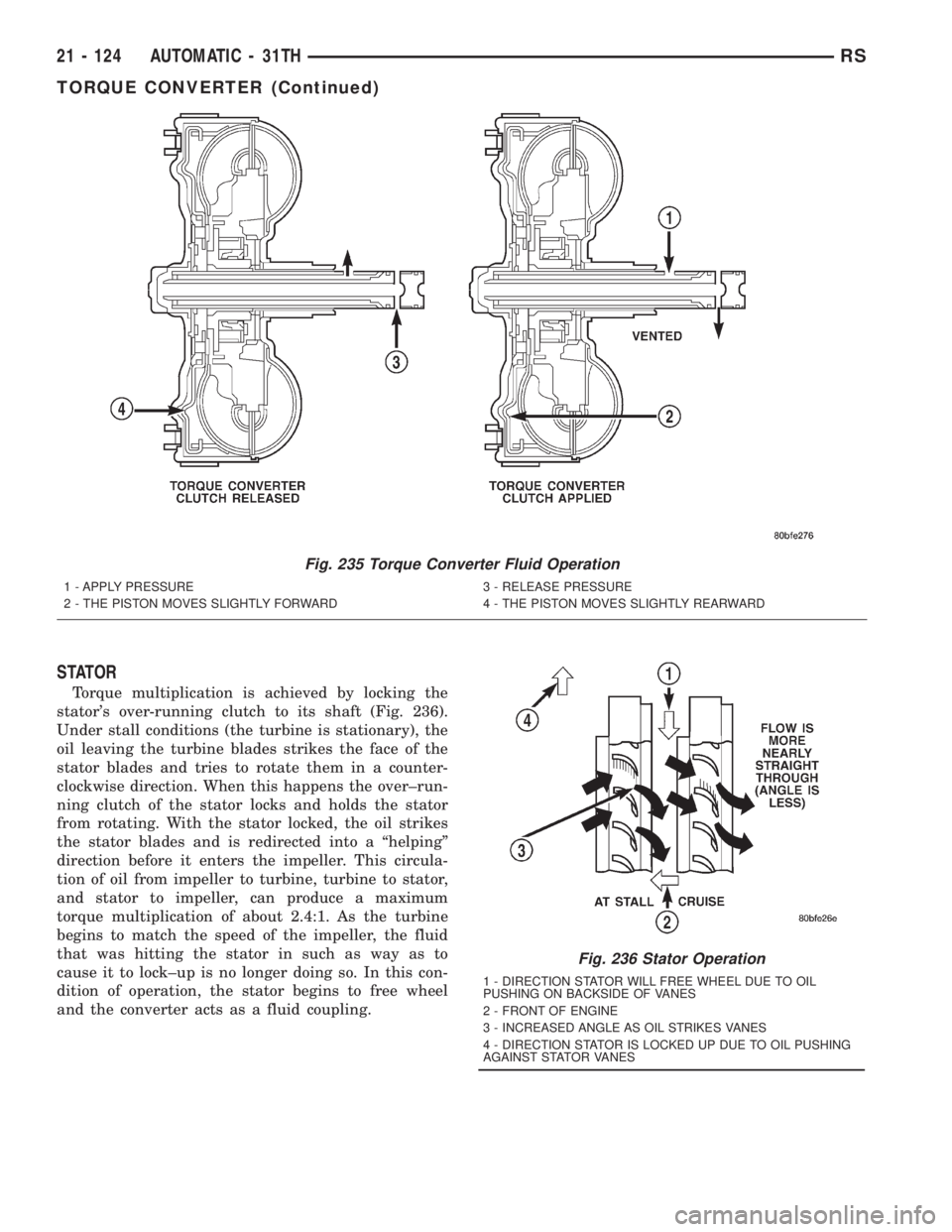
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 236).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 235 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 236 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 124 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3089 of 4284

TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 31TH - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 237). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 31TH - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 237 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 125
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3126 of 4284

The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can diagnose slip-
ping units, but the cause of the malfunction cannot
be determined. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most hydraulic transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP) to port(s)
required for test(s) being conducted. Use adapter set
L-4559 to adapt gauge(s) to transaxle.
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 3).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW (1st GEAR)
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (L) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
to 20 mph.
(4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi.(5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE (2nd GEAR)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3 position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph.
(4) In second gear the underdrive clutch pressure
should read 110 to 145 psi.
TEST TWO A±SELECTOR IN OD (4th Gear)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow wheels to rotate freely and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated speed of 40
mph.
(4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read below
5 psi. If not, then either the solenoid assembly or
TCM is at fault.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK (3rd and
2nd Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 20 mph. Vehicle should be in 3rd gear.
(4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi.
(5) Move selector lever to the (3) position and
increase indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph.
(6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi.
(7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear.
(4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi.
(5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Fig. 3 Pressure Taps
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER OFF
3 - LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
4 - 2/4 CLUTCH
5 - REVERSE CLUTCH
6 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
21 - 162 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
Page 3127 of 4284

TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear-CC
on)
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear, CC on.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same
speed.
(4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi.
(5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauges to the reverse and LR clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (R) position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm.(4) Reverse and LR clutch pressure should read
165 to 235 psi.
(5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working prop-
erly.
(2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regu-
lator valve.
(3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures
do not fall within the specified pressure range.
(4) If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than
5 psi in Step 4 of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft
seal ring or a defective solenoid assembly is indi-
cated.
(5) If the underdrive clutch pressure is greater
than 5 psi in Step 4 of Test Two A, a defective sole-
noid assembly or TCM is the cause.
PRESSURE CHECK SPECIFICATIONS
Gear Selector
PositionActual
GearPressure Taps
Underdrive
ClutchOverdrive
ClutchReverse
ClutchTorque
Converter
Clutch Off2/4 ClutchLow/
Reverse
Clutch
Park *
PARK 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
REVERSE *
REVERSE 0-2 0-7 165-235 50-100 0-2 165-235
0 mph
NEUTRAL *
NEUTRAL 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
L#
FIRST 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
20 mph
3#
SECOND 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 115-145 0-2
30 mph
3#
DIRECT 75-95 75-95 0-2 60-90 0-2 0-2
45 mph
OD #
OVER-
DRIVE0-2 75-95 0-2 60-90 75-95 0-2
30 mph
OD #OVER-
DRIVE
WITH
TCC0-2 75-95 0-2 0-5 75-95 0-2
50 mph
* Engine speed at 1500 rpm
# CAUTION: Both front wheels must be turning at the same speed.
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 163
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
Page 3130 of 4284
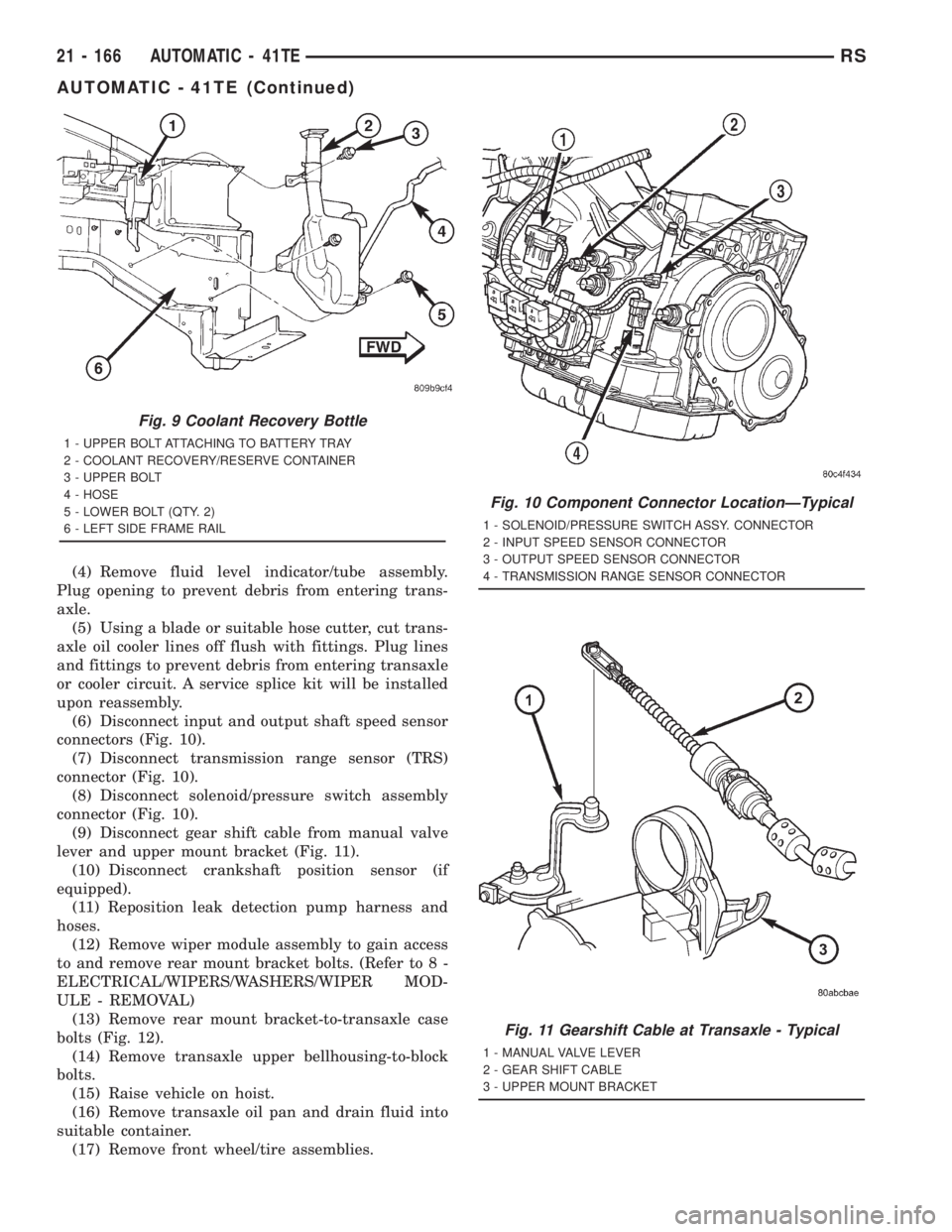
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 10).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 10).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 10).
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 11).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped).
(11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
(12) Remove wiper module assembly to gain access
to and remove rear mount bracket bolts. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - REMOVAL)
(13) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 12).
(14) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(15) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(16) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(17) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
Fig. 9 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY/RESERVE CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
Fig. 10 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 11 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)