2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1623 of 4284

When a high speed difference (shear) occurs
because of loss of traction (one axle spinning faster
than the other), the silicone fluid expands as it heats
from this shearing. When the silicone expands to fill
the viscous coupler completely, this pressure differ-
ence is high enough to squeeze each pair of plates
together. The resulting hump torque is up to 8 times
higher than the shear torque. When the viscous cou-
pler is in the hump mode, it does not lock the axles
(undifferentiated 4-Wheel Drive). It controls the
amount of slippage while delivering maximum power
to the axle having greatest traction. Once the speed
difference equalizes the fluid and plates cool down
and the viscous coupler goes back to the shear mode.
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove rear driveline module assembly. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR DRIV-
ELINE MODULE - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove six torque arm-to-differential assembly
bolts (Fig. 47). Remove torque arm.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install six torque arm-to-differential assembly
bolts (Fig. 47) and torque to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install rear driveline module assembly. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR DRIV-
ELINE MODULE - INSTALLATION)
(3) Lower vehicle.
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(3) Using tool 6958, remove input flange nut and
washer (Fig. 48).
(4) Remove input flange (Fig. 49).
(5) Using suitable screwdriver, remove input
flange seal from overrunning clutch housing (Fig.
50).
INSTALLATION
(1) Using tool 8802, install input flange seal to
overrunning clutch case (Fig. 51).
(2) Install input flange (Fig. 52).
(3) Install flange nut and washer. Using tool 6958,
torque flange nut to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 53).
(4) Install propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
(5) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 47 Torque Arm Fasteners
1 - TORQUE ARM ASSEMBLY
2 - BOLT (SIX)
Fig. 48 Input Flange Nut
1 - INPUT FLANGE
2 - TOOL 6958
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-47
VISCOUS COUPLER (Continued)
Page 1625 of 4284
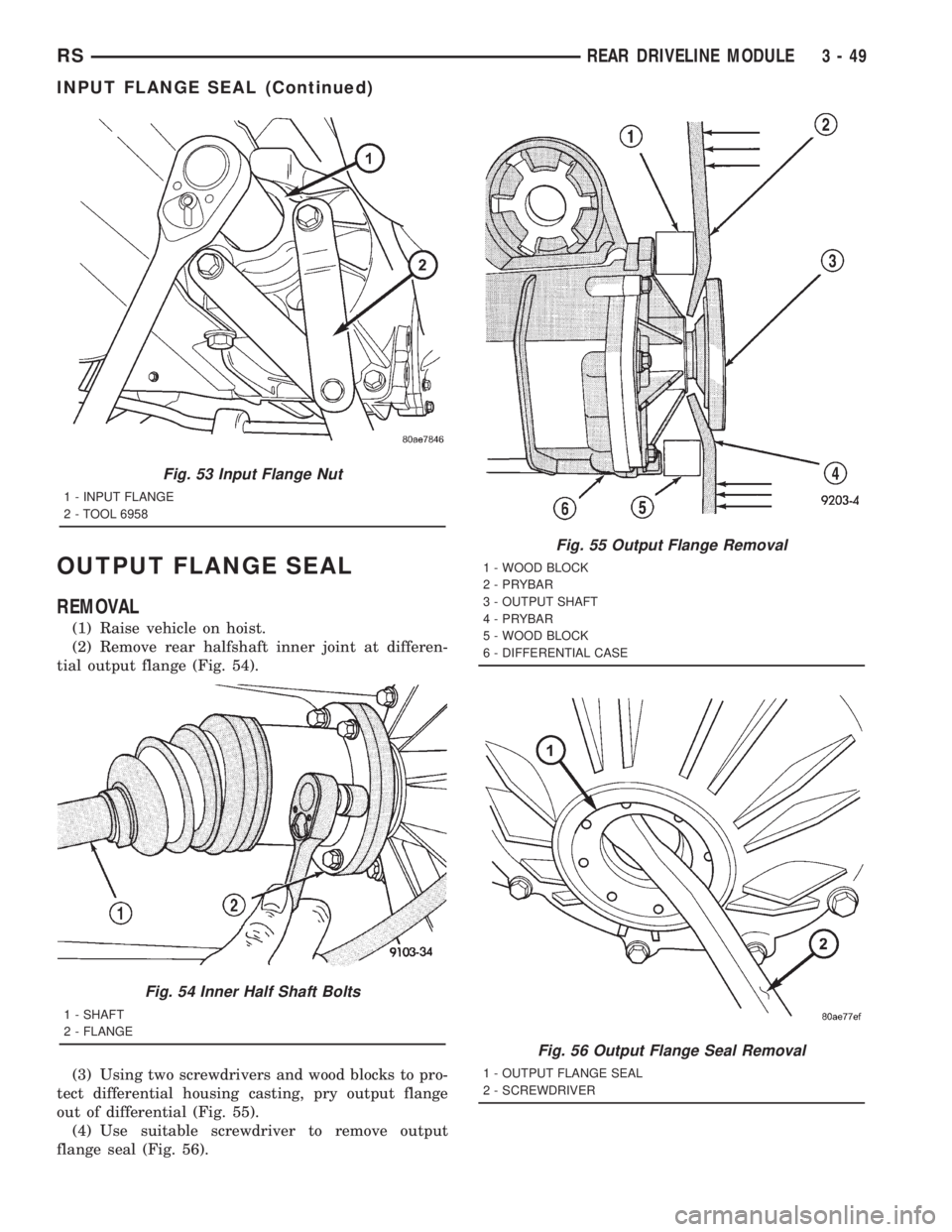
OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove rear halfshaft inner joint at differen-
tial output flange (Fig. 54).
(3) Using two screwdrivers and wood blocks to pro-
tect differential housing casting, pry output flange
out of differential (Fig. 55).
(4) Use suitable screwdriver to remove output
flange seal (Fig. 56).
Fig. 53 Input Flange Nut
1 - INPUT FLANGE
2 - TOOL 6958
Fig. 54 Inner Half Shaft Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 55 Output Flange Removal
1 - WOOD BLOCK
2 - PRYBAR
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - PRYBAR
5 - WOOD BLOCK
6 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 56 Output Flange Seal Removal
1 - OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
2 - SCREWDRIVER
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-49
INPUT FLANGE SEAL (Continued)
Page 1628 of 4284

JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................32
OPERATION.............................32
REMOVAL..............................32
INSTALLATION...........................33
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION...........................33
OPERATION.............................34
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................34
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING...........34
REMOVAL..............................34
DISASSEMBLY...........................35
ASSEMBLY.............................36
INSTALLATION...........................36
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................37
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................38
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER...............38
REMOVAL..............................38
INSTALLATION...........................40
PROPORTIONING VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................41
OPERATION.............................42
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................42
PROPORTIONING VALVE (HEIGHT
SENSING).............................42
REMOVAL..............................43
INSTALLATION...........................43
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................44BRAKE ROTOR........................44
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................47
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING..............47
REMOVAL..............................48
INSTALLATION...........................48
SUPPORT PLATE - DRUM BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................48
INSTALLATION...........................49
WHEEL CYLINDERS
REMOVAL..............................50
INSPECTION............................50
INSTALLATION...........................50
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION...........................50
OPERATION.............................51
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................51
PARKING BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
MECHANISM RELEASE..................51
PARKING BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
RESET...............................51
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................52
INSTALLATION...........................53
SHOES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................58
ADJUSTMENTS..........................59
CABLES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................61
INSTALLATION...........................65
ADJUSTMENTS..........................66
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES
The base brake system consists of the following
components:
²Brake pedal
²Power brake booster
²Master cylinder
²Brake tubes and hoses
²Proportioning valve (non-ABS vehicles only)
²Disc brakes
²Drum brakes
²Brake lamp switch
²Brake fluid level switch
²Parking brakes
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes or rear disc brakes depending on options.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock braking systems and antilock
braking systems. That means the left front and right
rear brakes are on one hydraulic circuit and the right
front and left rear are on the other.For information on the brake lamp switch, (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERI-
OR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION)
Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e. It
is available with or without traction control. This
system shares most base brake hardware used on
vehicles without ABS. ABS components are described
in detail in ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM.
OPERATION - BASE BRAKES
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
to the brakes at each tire and wheel assembly.
The parking brakes are foot-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. These shoes
come in contact with a hub mounted drum (drum for
5 - 2 BRAKES - BASERS
Page 1630 of 4284
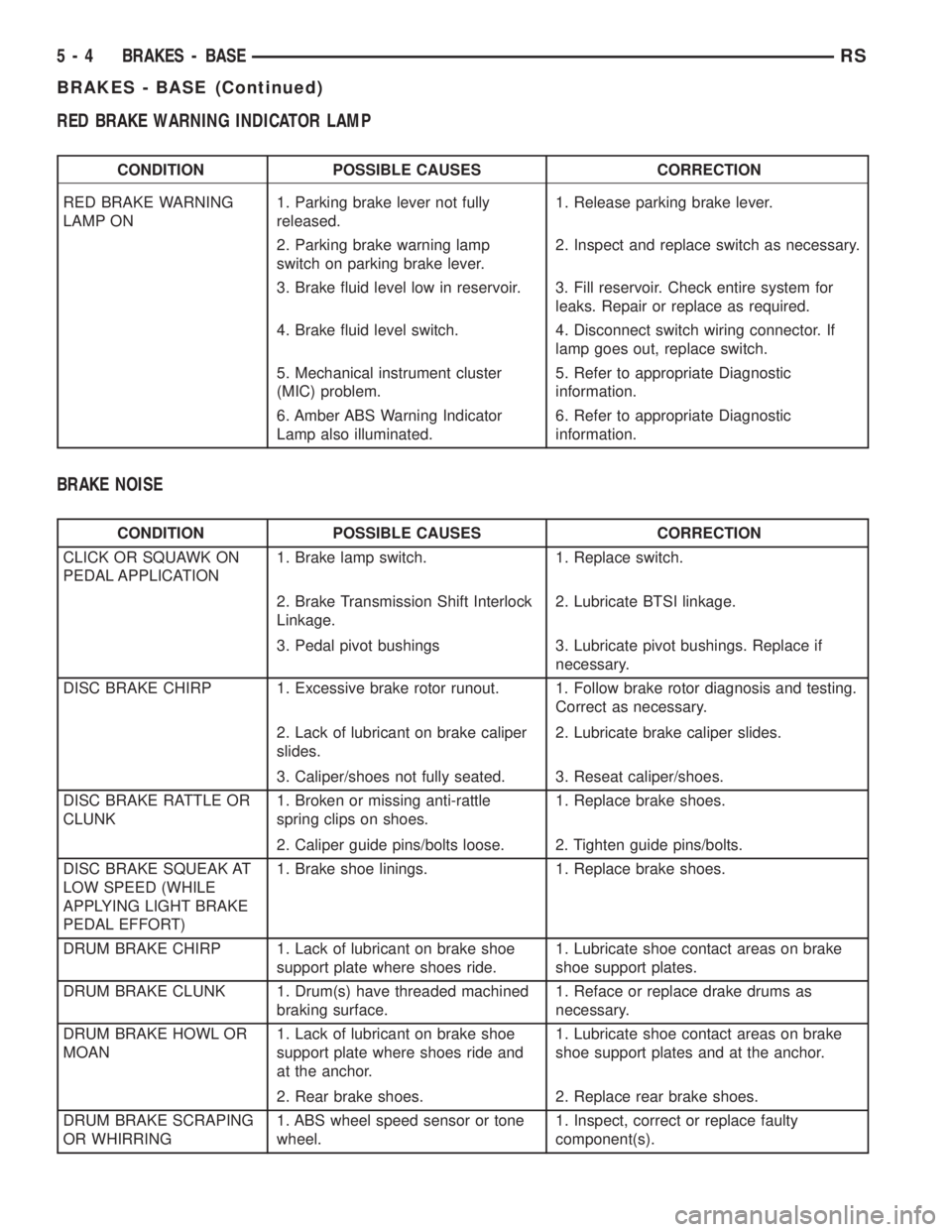
RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR LAMP
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
RED BRAKE WARNING
LAMP ON1. Parking brake lever not fully
released.1. Release parking brake lever.
2. Parking brake warning lamp
switch on parking brake lever.2. Inspect and replace switch as necessary.
3. Brake fluid level low in reservoir. 3. Fill reservoir. Check entire system for
leaks. Repair or replace as required.
4. Brake fluid level switch. 4. Disconnect switch wiring connector. If
lamp goes out, replace switch.
5. Mechanical instrument cluster
(MIC) problem.5. Refer to appropriate Diagnostic
information.
6. Amber ABS Warning Indicator
Lamp also illuminated.6. Refer to appropriate Diagnostic
information.
BRAKE NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLICK OR SQUAWK ON
PEDAL APPLICATION1. Brake lamp switch. 1. Replace switch.
2. Brake Transmission Shift Interlock
Linkage.2. Lubricate BTSI linkage.
3. Pedal pivot bushings 3. Lubricate pivot bushings. Replace if
necessary.
DISC BRAKE CHIRP 1. Excessive brake rotor runout. 1. Follow brake rotor diagnosis and testing.
Correct as necessary.
2. Lack of lubricant on brake caliper
slides.2. Lubricate brake caliper slides.
3. Caliper/shoes not fully seated. 3. Reseat caliper/shoes.
DISC BRAKE RATTLE OR
CLUNK1. Broken or missing anti-rattle
spring clips on shoes.1. Replace brake shoes.
2. Caliper guide pins/bolts loose. 2. Tighten guide pins/bolts.
DISC BRAKE SQUEAK AT
LOW SPEED (WHILE
APPLYING LIGHT BRAKE
PEDAL EFFORT)1. Brake shoe linings. 1. Replace brake shoes.
DRUM BRAKE CHIRP 1. Lack of lubricant on brake shoe
support plate where shoes ride.1. Lubricate shoe contact areas on brake
shoe support plates.
DRUM BRAKE CLUNK 1. Drum(s) have threaded machined
braking surface.1. Reface or replace drake drums as
necessary.
DRUM BRAKE HOWL OR
MOAN1. Lack of lubricant on brake shoe
support plate where shoes ride and
at the anchor.1. Lubricate shoe contact areas on brake
shoe support plates and at the anchor.
2. Rear brake shoes. 2. Replace rear brake shoes.
DRUM BRAKE SCRAPING
OR WHIRRING1. ABS wheel speed sensor or tone
wheel.1. Inspect, correct or replace faulty
component(s).
5 - 4 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 1632 of 4284

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP
DURING HARD
BRAKING)1. One of the two hydraulic circuits to
the front brakes is malfunctioning.1. Inspect system for leaks. Check
master cylinder for internal malfunction.
PEDAL PULSATES/
SURGES DURING
BRAKING1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
PEDAL IS SPONGY 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).2. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum
supply. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
PREMATURE REAR
WHEEL LOCKUP1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Inoperative proportioning valve
(non-ABS vehicles).2. Refer to proportioning valve
diagnosis and testing. Replace valve as
necessary.
3. Improper power brake booster
assist.3. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
STOP/BRAKE LAMPS
S TAY O N1. Brake lamp switch out of
adjustment.1. Replace brake lamp switch.
2. Brake pedal binding. 2. Inspect and replace as necessary.
3. Obstruction in pedal linkage. 3. Remove obstruction.
4. Power Brake Booster not allowing
pedal to return completely.4. Replace power brake booster.
VEHICLE PULLS TO
RIGHT OR LEFT ON
BRAKING1. Frozen brake caliper piston. 1. Replace frozen piston or caliper.
Bleed brakes.
2. Contaminated brake shoe lining. 2. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
3. Pinched brake lines. 3. Replace pinched line.
4. Leaking piston seal. 4. Replace piston seal or brake caliper.
5. Suspension problem. 5. Refer to the Suspension group.
PARKING BRAKE -
EXCESSIVE HANDLE
TRAVEL1. Rear drum brakes or rear disc
brake parking brake shoes out of
adjustment.1. Adjust rear drum brake shoes, or
rear parking brake shoes on vehicles
with rear disc brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BASE BRAKE
BLEEDING
NOTE: This bleeding procedure is only for the vehi-
cle's base brakes hydraulic system. For bleeding
the antilock brakes hydraulic system, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - ABS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, thoroughly clean the cover and master cylin-
der fluid reservoir to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 1634 of 4284

(6) Check pedal travel. If pedal travel is excessive
or has not been improved, enough fluid has not
passed through the system to expel all the trapped
air. Be sure to monitor the fluid level in the pressure
bleeder, so it stays at a proper level so air will not
enter the brake system through the master cylinder.
(7) Perform a final adjustment of the rear brake
shoes (when applicable), then test drive vehicle to be
sure brakes are operating correctly and that pedal is
solid.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
ABS ICU Mounting Bolts To
Bracket11 Ð 9 7
ABS ICU Mounting
Bracket-To-Cradle Bolts28 21 250
ABS CAB-To-HCU Mounting
Screws2Ð17
ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
Mounting Bolt12 Ð 105
Brake Tube Nuts 17 Ð 145
Brake Hose Intermediate
Bracket Bolt12 Ð 105
Brake Hose-To-Caliper
Mounting Bolt47 35 Ð
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Disc Brake Caliper Guide
Pin Bolts35 26 Ð
Disc Brake Caliper Bleeder
Screw15 Ð 125
Drum Brake Wheel Cylinder
Mounting Bolts8Ð75
Drum Brake Wheel Cylinder
Mounting Bleeder screw10 Ð 80
Drum Brake Support Plate
Mounting Bolts130 95 Ð
Junction Block (Non-ABS
Brakes) Mounting Bolts28 21 250
Master Cylinder Mounting
Nuts25 19 225
Power Brake Booster
Mounting Nuts28 21 250
Proportioning Valve
Mounting Bolts54 40 Ð
Proportioning Valve Axle
Bracket Mounting Bolt20 Ð 175
Parking Brake Lever (Pedal)
Mounting Bolts And Nut28 21 250
Wheel Mounting (Lug) Nuts 135 100 Ð
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM
Fig. 3 TOOL 6921 INSTALLED ON MASTER
CYLINDER
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6921
2 - FLUID RESERVOIR
Tubes, Master Cylinder Bleeding 6920
5 - 8 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 1635 of 4284
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The brake fluid level switch is located in the brake
fluid reservoir of the master cylinder (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The purpose of the brake fluid level switch is to
provide the driver with an early warning that the
brake fluid level in the master cylinder fluid reser-
voir has dropped below a normal level. This may
indicate:
²Abnormal loss of brake fluid in the master cyl-
inder fluid reservoir resulting from a leak in the
hydraulic system.
²Brake shoe linings which have worn to a point
requiring replacement.
As the brake fluid drops below the minimum level,
the brake fluid level switch closes to complete the red
BRAKE warning indicator (lamp) circuit. This will
turn on the red BRAKE warning indicator. The mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir should be checked and
refilled to the Full mark with DOT 3 brake fluid.If
the brake fluid level has dropped below the add
line in the master cylinder fluid reservoir, the
entire brake hydraulic system should be
checked for evidence of a leak.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wiring harness connector from brake
fluid reservoir level switch (Fig. 4).
(2) Using fingers, compress the retaining tabs on
the opposite end of brake fluid level switch.
(3) With retaining tabs compressed, grasp the con-
nector end of brake fluid level switch and pull it out
of master cylinder brake fluid reservoir.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert brake fluid level switch into left side of
brake fluid reservoir. Be sure switch is pushed in
until retaining tabs lock it to brake fluid reservoir.
(2) Connect vehicle wiring harness connector to
brake fluid level switch (Fig. 4).
Tubes, Master Cylinder Bleed 8358
Adapter, Master Cylinder Pressure Bleed Cap 6921
Dial Indicator, C-3339
Gauge, Brake Safe-Set
Handle, Universal C±4171
Installer, Dust Boot C-4689 or C-4842
RSBRAKES - BASE5-9
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 1639 of 4284

observed if the automatic adjuster is working prop-
erly. If one or more adjusters do not function prop-
erly, the respective drum must be removed for
adjuster servicing.
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The brake tubes are steel with a corrosion-resis-
tant nylon coating applied to the external surfaces.
The flex hoses are made of reinforced rubber with fit-
tings at each end.
The primary and secondary brake tubes leading
from the master cylinder to the ABS ICU Hydraulic
Control Unit (HCU) or the non-ABS junction block
have a special flexible section. This flexible section is
required due to cradle movement while the vehicle is
in motion (The ICU and non-ABS junction block are
mounted to the cradle).If replacement of these
lines is necessary, only the original factory
brake line containing the flexible section must
be used.
OPERATION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the chassis brake tubes and flex
hoses is to transfer the pressurized brake fluid devel-
oped by the master cylinder to the wheel brakes of
the vehicle. The flex hoses are made of rubber to
allow for the movement of the vehicle's suspension.
INSPECTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The brake tubing should be inspected periodically
for evidence of physical damage or contact with mov-
ing or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections must also be inspected. This flexible tub-
ing must be inspected for kinks, fraying and contact
with other components or with the body of the vehi-
cle.
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - FRONT
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(DISC/DISC BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(2) Remove both front wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Begin on one side of the vehicle.
(4) Remove the anti-rattle clip from the outboard
side of the caliper and adapter.
(5) Remove the two caliper guide pin bolts.
(6) Remove caliper from caliper adapter and brake
rotor.
CAUTION: Supporting weight of caliper by the flex-
ible brake fluid hose can damage the hose.
(7) Using wire or cord, hang the caliper from the
front strut assembly (Fig. 12). Support the caliper
firmly to prevent weight of caliper from being sup-
ported by the brake fluid hose.
(8) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per adapter.
(9) Pull the inboard brake shoe away from the cal-
iper piston until the retaining clip on shoe is free
from the cavity in the caliper piston (Fig. 13).
(10) Repeat the above procedure on other side of
the vehicle.
Fig. 12 Stored Front Disc Brake Caliper
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - BRAKE FLEX HOSE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - WIRE HANGER
5 - STRUT ASSEMBLY
RSBRAKES - BASE5-13
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)