2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 2727 of 4284

(8) Locate the forcing screw and spring retainer
adapter assembly over the spring requiring removal
(Fig. 36).
(9) Slowly turn the forcing screw clockwise (com-
pressing the valve spring) until the valve keepers can
be removed.
(10) Turn forcing screw counterclockwise to relieve
spring tension. Remove retainer and valve spring.
(11) Repeat procedure for each cylinder requiring
valve spring removal.
INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested (Fig. 37).As an example;the compression
length of a spring to be tested is 38.00 mm (1.496
in.). Turn the table of Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the 38.00 mm (1.496 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by two. This will give
the spring load at test length. Fractional measure-
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to Engine Specifications to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace any springs
that do not meet specifications.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) If removed, install a new valve stem seal.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
STEM SEALS - INSTALLATION)
(2) Position valve spring and retainer on spring
seat.(3) Using Special Tool C-3422-C with 8464 Adapter
(Fig. 35), compress the spring only enough to install
the valve retainer locks.
(4) Slowly release the spring tension. Ensure the
retainer locks are seated properly.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1)The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the
valve stem as guide.Do Not Force
seal against top of
guide. When installing the valve retainer locks, com-
press the springonly enoughto install the locks.
CAUTION: Do not pinch seal between retainer and
top of valve guide.
(2) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6.Make
sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve
spring that is being covered.
(3) Remove spark plug adapter tool.
(4) Install rocker arms and shaft assembly. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
INSTALLATION)
(5) Install cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install spark plugs and connect wires.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arms are installed on the rocker arm
shaft. The rocker arms and shaft assembly is attached
to the cylinder head with seven bolts and retainers.
The rocker arms are made of stamped steel.
Fig. 36 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL (HEAD ON)
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8453
2 - BOLTS - SPECIAL TOOL ATTACHING
3 - AIR SUPPLY HOSE ADAPTER
Fig. 37 TESTING VALVE SPRING
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 103
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 2732 of 4284

TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
(CAM IN BLOCK) - REMOVAL). Identify each tappet
for reinstallation in original location.
(4) Remove camshaft thrust plate (Fig. 45).
(5) Install a long bolt into front of camshaft to
facilitate removal of the camshaft.
(6) Remove the camshaft (Fig. 45), being careful
not to damage cam bearings with the cam lobes.
NOTE: The camshaft bearings are serviced with the
engine block.
INSPECTION
(1) Check the cam lobes and bearing surfaces for
abnormal wear and damage (Fig. 47). Replace cam-
shaft as required.
NOTE: If camshaft is replaced due to lobe wear or
damage, always replace the lifters.
(2) Measure the lobe actual wear (unworn area -
wear zone = actual wear) (Fig. 47) and replace cam-
shaft if out of limit. Standard value is 0.0254 mm
(0.001 in.), wearlimitis 0.254 mm (0.010 in.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate camshaft lobes and camshaft bearing
journals with engine oil.
(2) Install a long bolt into the camshaft to assist in
the installation of the camshaft.
(3) Carefully install the camshaft in engine block.
(4) Install camshaft thrust plate and bolts (Fig.
45). Tighten to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Measure camshaft end play. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) If not within specifi-
cations, replace thrust plate.
(6) Install the timing chain and sprockets. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/
CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
NOTE: When camshaft is replaced, all of the
hydraulic lifters must be replaced also.
(7) Install the hydraulic lifters (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
(CAM IN BLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Each lifter
Fig. 45 CAMSHAFT AND BEARINGS
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - THRUST PLATE
3 - BOLT
4 - CAMSHAFT BEARINGS (SERVICED WITH BLOCK)
Fig. 46 CAMSHAFT IDENTIFICATION
1 - CAMSHAFT - 3.3L ENGINE
2 - CAST-IN RING
3 - CAMSHAFT - 3.8L ENGINE
4 - MACHINED CAST-IN RING
Fig. 47 Checking Camshaft for Wear (Typical)
1 - UNWORN AREA
2 - ACTUAL WEAR
3 - BEARING JOURNAL
4 - LOBE
5 - WEAR ZONE
9 - 108 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 2733 of 4284

reused must be installed in the same position from
which it was removed.
(8) Install the timing chain cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(9) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(10) Install the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(11) Install the lower and upper intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION)
(12) Install the engine assembly. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - INSTALLATION)
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
The bearing caps are not interchangeable and
should be marked at removal to ensure correct
assembly. The bearing shells must be installed with
the tangs inserted into the machined grooves in the
rods and caps. Install cap with the tangs on the same
side as the rod. Fit all rods on one bank until com-
plete. Connecting rod bearings are available in the
standard size and the following undersizes: 0.025
mm (0.001 in.) and 0.250 mm (0.010 in.).
CAUTION: Install the bearings in pairs. Do not use a
new bearing half with an old bearing half. Do not
file the rods or bearing caps.
Measure connecting rod journal for taper and out-
of-round. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT - INSPECTION)
The connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage or the equivalent.
The following is the recommended procedure for the
use of Plastigage:
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod
to be checked is at the bottom of its stroke.
(2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approx-
imately 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from
the oil hole. In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing Plastigage in that area.
(4) Assemble the rod cap with Plastigage in place.
Tighten the rod cap to the specified torque.Do not
rotate the crankshaft while assembling the cap
or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving inac-
curate results.(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the scale pro-
vided on the package (Fig. 48). Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band indicates the
amount of oil clearance. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper
present. Record all readings taken. Refer to Engine
Specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).Plastigage generally is accompanied by
two scales. One scale is in inches, the other is a
metric scale. If the bearing clearance exceeds
wear limit specification, replace the bearing.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION - 3.3L
The nodular iron crankshaft is supported by four
main bearings, with number two position the thrust
bearing (Fig. 49). Crankshaft end sealing is provided
by front and rear rubber seals.
DESCRIPTION - 3.8L
The nodular iron crankshaft is supported by four
main bearings, with number two position providing
thrust bearing location (Fig. 50). Each main bearing
cap has two vertical retaining bolts. The two center
main caps have horizontal bolts to add increased
rigidity to the lower engine block (Fig. 50). Crank-
shaft end sealing is provided by front and rear rub-
ber seals.
Fig. 48 Measuring Connecting Rod Bearing
Clearance
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 109
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 2738 of 4284

(2) Alternative Method:
²Support the weight of the crankshaft with a jack
under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
(3) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(4) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 58). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 59) with the scale
provided on the package. Locate the band closest to
the same width. This band shows the amount of
clearance in thousandths. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper
present. Record all readings taken. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.PLASTIGAGE METHODÐENGINE OUT-OF-VEHICLE
(1) With engine in the inverted position (crank-
shaft up) and mounted on a repair stand, remove
main journal cap.
(2) Remove oil from journal and bearing shell.
(3) Cut Plastigage to same length as width of the
bearing and place it in parallel with the journal axis
(Fig. 58).
(4) Carefully install the main bearing cap and
tighten the bolts to specified torque.
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plasti-
gage will be smeared.
(5) Carefully remove the bearing cap and measure
the width of the Plastigage at the widest part using
the scale on the Plastigage package (Fig. 59). Refer
to Engine Specifications for proper clearances (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If the clearance
exceeds the specified limits, replace the main bear-
ing(s) with the appropriate size, and if necessary,
have the crankshaft machined to next undersize.
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
(1) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(2) Identify main bearing caps before removal.
(3) Remove bearing caps one at a time. Remove
upper half of bearing by inserting Special Main Bear-
ing Tool C-3059 (Fig. 60) into the oil hole of crank-
shaft.
(4) Slowly rotate crankshaft clockwise, forcing out
upper half of bearing shell.
Fig. 58 Plastigage Placed in Lower
1 - PLASTIGAGE
Fig. 59 Clearance Measurement
Fig. 60 Upper Main Bearing Removing/Installing
With Special Tool C-3059
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
2 - BEARING
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
4 - BEARING
9 - 114 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 2743 of 4284

OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the yoke retainer and aligning yokes
(Fig. 71).
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. If necessary use
Special Tool C-4129, or equivalent to remove liftersfrom bores. If lifters are to be reused, identify each
lifter to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the lifters with engine oil.
NOTE: Position the lifter in bore with the lubrication
hole facing upward (Fig. 70).
(2) Install the hydraulic lifters with the lubrication
hole facing upward towards middle of block (Fig. 70).
Install lifters in original positions, if reused.
(3) Install lifter aligning yokes (Fig. 71).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 71).
(5) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic lifters have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
Fig. 70 LIFTER LUBRICATION HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 2744 of 4284

OPERATION
The piston and connecting rod is the link between
the combustion force to the crankshaft.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS
The bearing caps are not interchangeable or
reversible, and should be marked at removal to
ensure correct reassembly. The bearing shells must
be installed with the tangs inserted into the
machined grooves in the rods and caps. Install cap
with the tangs on the same side as the rod. For con-
necting rod bearing fitting (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Fit all connecting rods
on one bank until complete.NOTE: The connecting rod cap bolts should be
examined before reuse. Bolt stretch can be checked
by holding a scale or straight edge against the
threads. If all the threads do not contact the scale
the bolt must be replaced (Fig. 72).
(1) Before installing the nuts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil.
(2) Install nuts finger tight on each bolt then alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(3) Tighten the nuts to 54 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (40
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn).
(4) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 73). Refer to Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 71 Lifter Aligning Yoke and Retainer
1 - YOKE RETAINER
2 - BOLT - YOKE RETAINER
3 - ALIGNING YOKE
4 - HYDRAULIC LIFTER
Fig. 72 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 73 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
9 - 120 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2751 of 4284
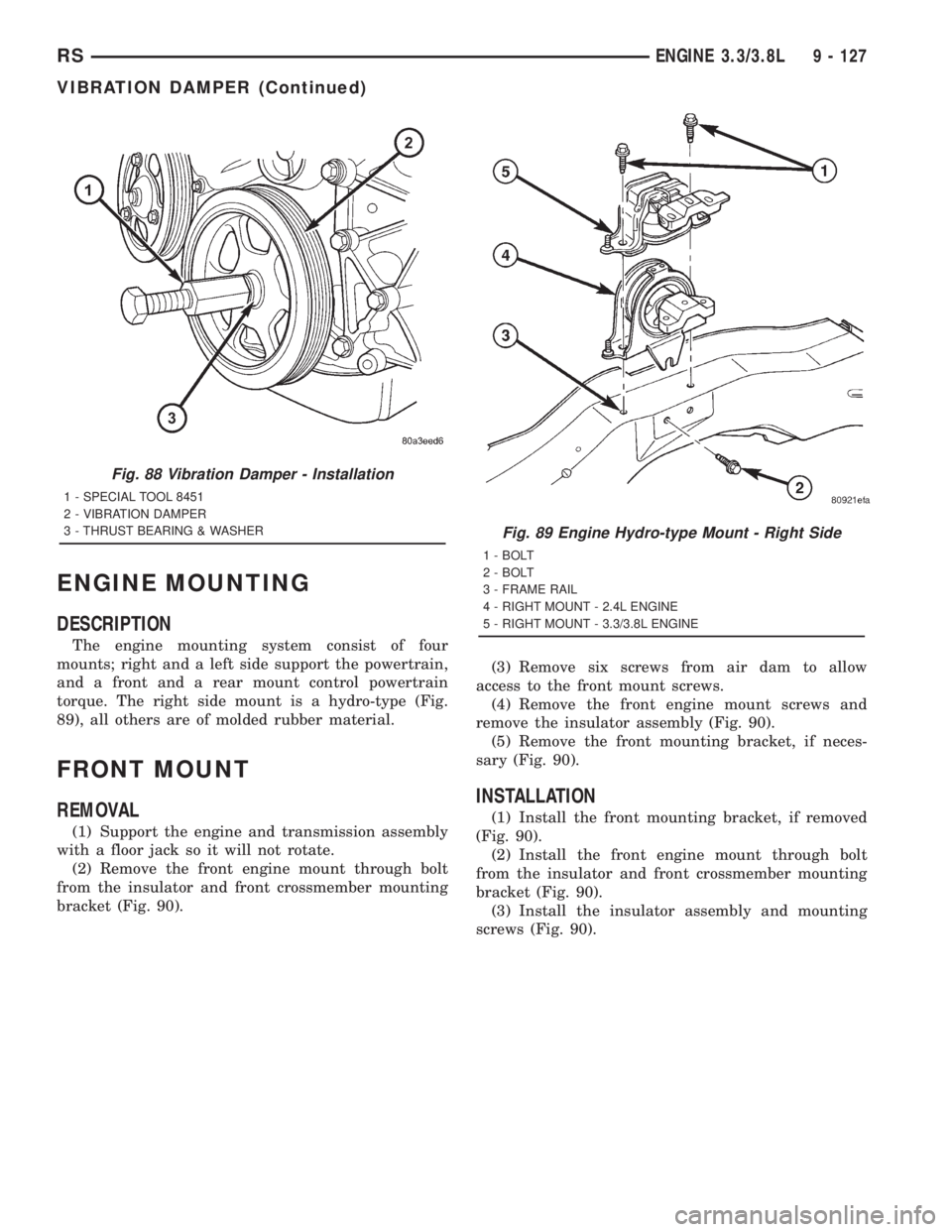
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION
The engine mounting system consist of four
mounts; right and a left side support the powertrain,
and a front and a rear mount control powertrain
torque. The right side mount is a hydro-type (Fig.
89), all others are of molded rubber material.
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate.
(2) Remove the front engine mount through bolt
from the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 90).(3) Remove six screws from air dam to allow
access to the front mount screws.
(4) Remove the front engine mount screws and
remove the insulator assembly (Fig. 90).
(5) Remove the front mounting bracket, if neces-
sary (Fig. 90).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the front mounting bracket, if removed
(Fig. 90).
(2) Install the front engine mount through bolt
from the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 90).
(3) Install the insulator assembly and mounting
screws (Fig. 90).
Fig. 88 Vibration Damper - Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8451
2 - VIBRATION DAMPER
3 - THRUST BEARING & WASHER
Fig. 89 Engine Hydro-type Mount - Right Side
1 - BOLT
2 - BOLT
3 - FRAME RAIL
4 - RIGHT MOUNT - 2.4L ENGINE
5 - RIGHT MOUNT - 3.3/3.8L ENGINE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 127
VIBRATION DAMPER (Continued)
Page 2765 of 4284

between cylinder heads and houses the coolant ther-
mostat (Fig. 121).
The intake manifold utilizes a compact design with
very low restriction and outstanding flow balance.
This design allows the engine to perform with a wide
torque curve while increasing higher rpm horse-
power.
The composite upper intake for the 3.3L engine has
a unique cover over the upper portion of the manifold
(Fig. 119). This cover is designed to absorb intake
noises and also offers styling to the engine. This
cover, under any circumstance, should never be
removed. The fasteners attaching the upper intake
manifold can be accessed without removing this
cover. If, for some reason, the molded-in vacuum
ports break, the composite manifold can salvaged.
The vacuum ports are designed to break at the shoul-
der, if overloaded. Additional material in the shoulder
area provides sufficient stock to repair. For more
information and procedure, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Also, if the special screws that attach
the MAP sensor, power steering reservoir, throttle
cable bracket, and the EGR tube become stripped, an
oversized screw is available to repair the stripped-out
condition. For more information and procedure,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
OPERATION
The intake manifold delivers air to the combustion
chambers. This air allows the fuel delivered by the
fuel injectors to ignite when the spark plug fire.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
3.3L
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR
The composite upper intake manifold thread
bosses, if stripped out, can be repaired by utilizing a
repair screw available through Mopartparts. Repair
screws are available for the following manifold
attached components:
²MAP sensor
²Power steering reservoir
²EGR tube
²Throttle cable bracket
The repair screws require a unique tightening
torque specification from the original screw. Refer to
the following chart for specification.
Fig. 119 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L
1 - BOLT
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - SCREW
4 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
5 - WIRE HARNESS
6 - GASKET (3 PER CYL. BANK)
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 141
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)