Page 53 of 4770

The 5S±FE engine is an in±line, 4±cylinder engine with the cylinders numbered 1±2±3±4
from the front. The crankshaft is supported by five bearings inside the crankcase. These bearings
are made of aluminum alloy.
The crankshaft is integrated with eight weights for balance. Oil holes are placed in the center of
the crankshaft to supply oil to the connecting rods, bearing, pistons and other components.
The firing order is 1±3±4±2. The cylinder head is made of aluminum alloy, with a cross flow
type intake and exhaust layout and with pent±roof type combustion chambers. The spark plugs
are located in the center of the combustion chambers.
The intake manifold has four independent long ports and utilizes the inertial supercharging effect
to improve engine torque at low and medium speeds.
Exhaust and intake valves are equipped with irregular pitch springs made of special valve spring
carbon steel which are capable of functioning no matter what the engine speed.
The intake camshaft is driven by a timing belt, and a gear on the intake camshaft engages with
a gear on the exhaust camshaft to drive it. The cam journal is supported at five places between
the valve lifters of each cylinder and on the front end of the cylinder head. Lubrication of the cam
journals and gears is accomplished by oil being supplied through the oiler port in the center of the
camshaft.
Adjustment of the valve clearance is done by means of an outer shim type system, in which valve
adjusting shims are located above the valve lifters. This permits replacement of the shims without
removal of the camshafts.
Pistons are made of high temperature±resistant aluminum alloy, and a depression is built into
the piston head to prevent interference with the valves.
Piston pins are the full±floating type, with the pins fastened to neither the piston boss nor the
connecting rods. Instead, snap rings are fitted on both ends of the pins, preventing the pins from
falling out.
The No.1 compression ring is made of steel and the No.2 compression ring is made of cast iron.
The oil ring is made of a combination of steel and stainless steel. The outer diameter of each
piston ring is slightly larger than the diameter of the piston and the flexibility of the rings allows
them to hug the cylinder walls when they are mounted on the piston. Compression rings No.1 and
No.2 work to prevent gas leakage from the cylinder and the oil ring works to scrape oil off the
cylinder walls to prevent it from entering the combustion chambers.
The cylinder block is made of cast iron. It has four cylinders which are approximately twice the
length of the piston stroke. The top of each cylinder is closed off by the cylinder head and the
lower end of the cylinders becomes the crankcase, in which the crankshaft is installed. In
addition, the cylinder block contains a water jacket, through which coolant is pumped to cool the
cylinders.
The oil pan is bolted onto the bottom of the cylinder block. The oil pan is an oil reservoir made of
pressed sheet steel. A dividing plate is included 'inside the oil pan to keep sufficient oil in the
bottom of the pan even when the vehicle is tilted. This dividing plate also prevents the oil from
making waves when the vehicle is stopped suddenly and the oil shifts away from the oil pump
suction pipe.
The 5S±FE engine uses two balance shafts. The balance shafts are fitted in balance shaft
housings that are located at the bottom of the cylinder block. The No. 1 balance shaft is driven by
the drive gear of the crankshaft No.3 counterweight at twice the speed of the crankshaft. The No.
2 balance shaft is driven by the No±1 balance shaft at the same speed in the same direction as the
crankshaft. The balance shafts are designed to eliminate secondary inertia force from the engine,
thereby reducing the engine noise (booming noise).
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±3
Page 56 of 4770
Plug for vacuum hose, fuel hose
etc.
Battery specific gravity gauge09256±00030 Hose Plug Set
09904±00010 Expander Set
Piston ring compressorEngine tune±up tester Connecting rod aligner
Precision straight edge
EQUIPMENT
Piston ring expander Compression gauge
Magnetic finger Cylinder gauge
Torque wrenchDye penetrant CO/HC meterCaliper gauge
Spring tester
ThermometerDial indicator
Steel squareMicrometer
Valve spring
Valve spring Plastigage
Soft brushHeater
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±6
Page 63 of 4770

4. INSPECT VALVE CLEARANCE
(a) Check only the valves indicated.
Using a thickness gauge, measure the clearance
between the valve lifter and camshaft.
Record the out± of ±specification valve clear±
ance measurements. They will be used later to
determine the required replacement adjusting
shim.
Valve clearance (Cold):
Intake
0.19 ± 0.29 mm (0.007 ± 0.011 in.)
Exhaust
0.28 ± 0.38 mm (0.011 ± 0.015 in.) 3. SET NO.1 CYLINDER TO TDC/COMPRESSION
(a) Turn the crankshaft pulley and align its groove with
timing mark ª0º of the No.1 timing belt cover.
(b) Check that the valve lifters on the No.1 cylinder are
loose and valve lifters on the No.4 are tight.
If not, turn the crankshaft one revolution (360*) and
align the mark as above.
(b) Turn the crankshaft one revolution (360�) and align
the mark as above. (See procedure in step 3)
(c) Check only the valves indicated as shown. Measure
the valve clearance. (See procedure in step (a)) HINT: Arrange the grommets in correct order, so that
they can be reinstalled into their original positions.
This minimizes any possibility of oil leakage due to
reuse of grommets.
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±13
Page 73 of 4770
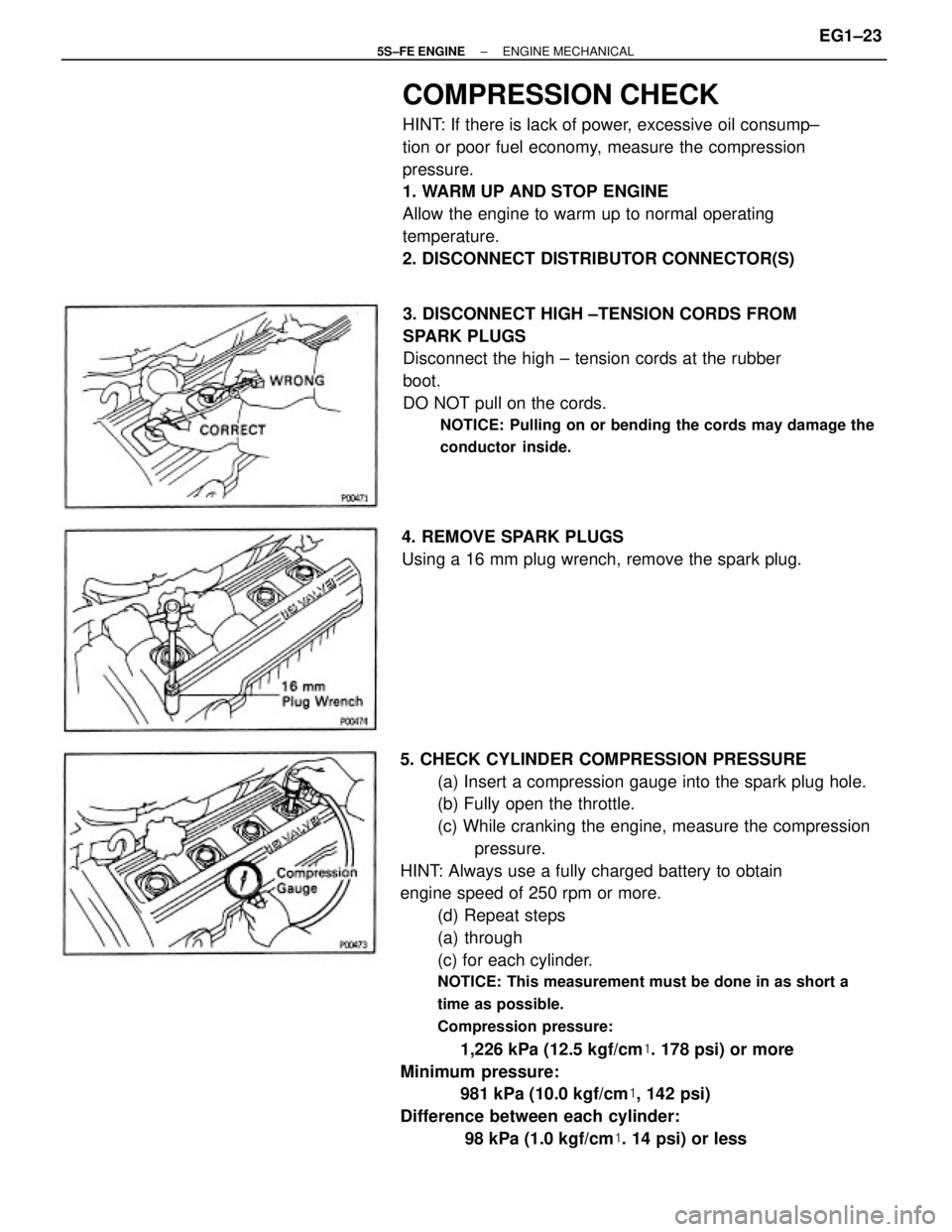
5. CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
(a) Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole.
(b) Fully open the throttle.
(c) While cranking the engine, measure the compression
pressure.
HINT: Always use a fully charged battery to obtain
engine speed of 250 rpm or more.
(d) Repeat steps
(a) through
(c) for each cylinder.
NOTICE: This measurement must be done in as short a
time as possible.
Compression pressure:
1,226 kPa (12.5 kgf/cm�. 178 psi) or more
Minimum pressure:
981 kPa (10.0 kgf/cm�, 142 psi)
Difference between each cylinder:
98 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm�. 14 psi) or less
COMPRESSION CHECK
HINT: If there is lack of power, excessive oil consump±
tion or poor fuel economy, measure the compression
pressure.
1. WARM UP AND STOP ENGINE
Allow the engine to warm up to normal operating
temperature.
2. DISCONNECT DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR(S)
3. DISCONNECT HIGH ±TENSION CORDS FROM
SPARK PLUGS
Disconnect the high ± tension cords at the rubber
boot.
DO NOT pull on the cords.
NOTICE: Pulling on or bending the cords may damage the
conductor inside.
4. REMOVE SPARK PLUGS
Using a 16 mm plug wrench, remove the spark plug.
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±23
Page 74 of 4770
(e) If the cylinder compression in one or more cylinders is
low, pour a small amount of engine oil into the cylin±
der through the spark plug hole and repeat steps (a)
through
(c) for cylinders with low compression.
wIf adding oil helps the compression, chances are
that the piston rings and/or cylinder bore are
worn or damaged.
wIf pressure stays low, a valve may be sticking or
seating is improper, or there may be leakage past
the gasket.
6. REINSTALL SPARK PLUGS
Using a 16 mm plug wrench, install the spark plug.
Torque: 18 N±m (180 kgf±cm, 13 ft±lbf)
7. RECONNECT HIGH±TENSION CORDS TO SPARK
PLUGS
8. RECONNECT DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR(S)
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±24
Page 77 of 4770
11. REMOVE SPARK PLUGS
(a) Disconnect the high ± tension cords at the rubber
boot.
DO NOT pull on the cords.
NOTICE: Pulling on or bending the cords may damage the
conductor inside.
13. SET NO.1 CYLINDER TO TDC/COMPRESSION
(a) Turn the crankshaft pulley and align its groove with
timing mark ª0º of the No.1 timing belt cover. 12. REMOVE NO.2 TIMING BELT COVER
Remove the 5 bolts, timing belt cover and 2 gaskets.10. REMOVE No.2 ENGINE MOUNTING BRACKET
Remove the 3 bolts and mounting bracket.
(b) Using a 16 mm plug wrench, remove the spark plug.
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±27
Page 85 of 4770
9. INSTALL CAMSHAFT TIMING PULLEY
(a) Align the camshaft knock pin with the knock pin
groove of the pulley, and slide on the timing pulley.
(b) Using SST, install the plate washer and bolt.
SST 09249 ± 63010 and 09278 ± 54012
Torque: 37 N±m (380 kgf±cm, 27 ft±lbf)
HINT: Use a torque wrench with a fulcrum length of
340 cm (13.39 in.)8. INSTALL CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
(a) Align the pulley set key with the key groove of the
pulley, and slide on the pulley.
(b) Using SST, install the pulley bolt.
SST 09213±54015 (91651 ±60855)
09330±00021
Torque: 108 N±m (1,100 kgf±cm, 80 ft±lbf)
10. SET No.1 CYLINDER TO TDC/COMPRESSION
(a) Turn the crankshaft pulley, and align its groove with
timing mark ª0º of the No.1 timing belt cover. 7. INSTALL NO.1 TIMING BELT COVER
(a) Install the gasket to the timing belt cover.
(b) Install the timing belt cover with the 4 bolts. 6. INSTALL TIMING BELT GUIDE
Install the guide, facing the cup side outward.
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±35
Page 190 of 4770
Warpage
Cylinder block side
Manifold side
Valve seat
Refacing angle
Contacting angle
Contacting width
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
SERVICE DATA
Deviation
Free length
Installed tension et 34.7 mm (1.366 in.) Free length
Installed load at 50.5 mm (1.988 in.)
Inside diameter
Outside diameter (for repair part)
Lifter diameter
Lifter bore diameter
Oil clearance Difference of pressure between each cylinder
Vale face angle
Stem diameter Idler pulley
tension spring Intake
manifold
vacuum
Compression
pressure
Valve guide
bushing
Valve overall length
Stem oil clearance
Margin thickness
Cylinder
head
at idle speed
Valve springet 250 rpm Idle speed
Valve lifter
Warpage Manifold Valve
± 5S±FE ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG1±140