2000 MITSUBISHI MONTERO ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 590 of 1839

13E-1
MITSUBISHI STABILITY
CONTROL
(MITSUBISHI SC)
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 4..............
SPECIAL TOOLS 4........................
TROUBLESHOOTING 5....................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 18.................
Operation Test of MITSUBISHI SC 18.........Wheel Speed Sensor (FR) Check 18..........
Vehicle Speed Sensor Check 18..............
SC-ECU* 19...............................
G SENSOR 20.............................
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FR) 20..........
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR 20..............
WARNINGS REGARDING SERVICING OF SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) EQUIPPED VEHICLES
WARNING!
(1) Improper service or maintenance of any component of the SRS, or any SRS-related component, can lead to personal
injury or death to service personnel (from inadvertent firing of the air bag) or to the driver and passenger (from rendering
the SRS inoperative).
(2) Service or maintenance of any SRS component or SRS-related component must be performed only at an authorized
MITSUBISHI dealer.
(3) MITSUBISHI dealer personnel must thoroughly review this manual, and especially its GROUP 52B - Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) before beginning any service or maintenance of any component of the SRS or any SRS-related
component.
NOTE
The SRS includes the following components: front impact sensors, SRS-ECU, SRS warning lamp, air bag module, clock spring and
interconnecting wiring. Other SRS-related components (that may have to be removed/installed in connection with SRS service or
maintenance) are indicated in the table of contents by an asterisk (*).
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 604 of 1839
MITSUBISHI SC-Troubleshooting13E-15
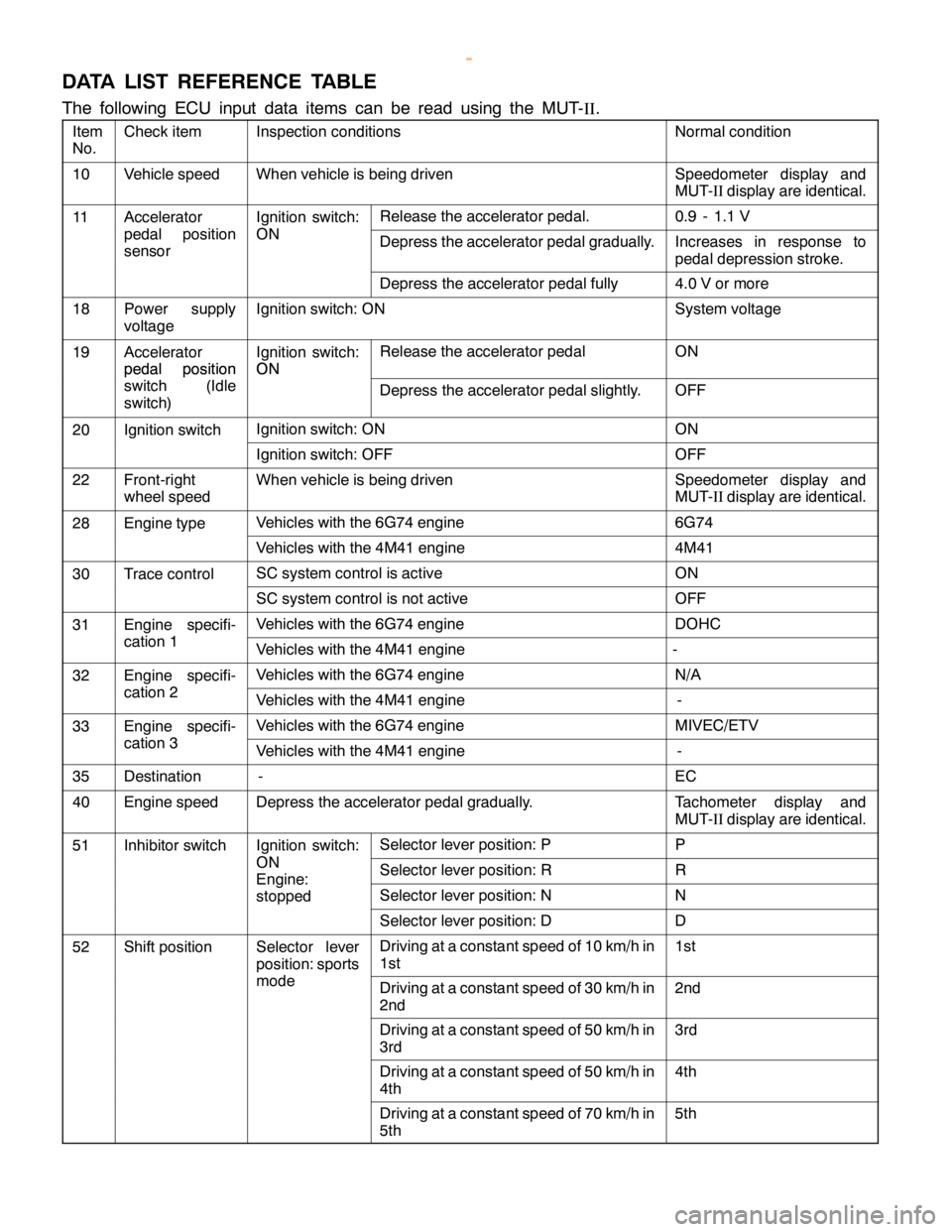
DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE
The following ECU input data items can be read using the MUT-
II.
Item
No.Check itemInspection conditionsNormal condition
10Vehicle speedWhen vehicle is being drivenSpeedometer display and
MUT-IIdisplay are identical.
11AcceleratorIgnition switch:Release the accelerator pedal.0.9 - 1.1 V
pedal position
sensorONDepress the accelerator pedal gradually.Increases in response to
pedal depression stroke.
Depress the accelerator pedal fully4.0 V or more
18Power supply
voltageIgnition switch: ONSystem voltage
19Accelerator
pedal positionIgnition switch:
ONRelease the accelerator pedalON
pedal position
switch (Idle
switch)ON
Depress the accelerator pedal slightly.OFF
20Ignition switchIgnition switch: ONON
Ignition switch: OFFOFF
22Front-right
wheel speedWhen vehicle is being drivenSpeedometer display and
MUT-IIdisplay are identical.
28Engine typeVehicles with the 6G74 engine6G74
Vehicles with the 4M41 engine4M41
30Trace controlSC system control is activeON
SC system control is not activeOFF
31Engine specifi-Vehicles with the 6G74 engineDOHC
cation 1Vehicles with the 4M41 engine-
32Engine specifi-Vehicles with the 6G74 engineN/A
cation 2Vehicles with the 4M41 engine-
33Engine specifi-Vehicles with the 6G74 engineMIVEC/ETV
cation 3Vehicles with the 4M41 engine-
35Destination-EC
40Engine speedDepress the accelerator pedal gradually.Tachometer display and
MUT-IIdisplay are identical.
51Inhibitor switchIgnition switch:Selector lever position: PP
ONSelector lever position: RREngine:
stopped
Selector lever position: NN
Selector lever position: DD
52Shift positionSelector lever
position: sportsDriving at a constant speed of 10 km/h in
1st1st
modeDriving at a constant speed of 30 km/h in
2nd2nd
Driving at a constant speed of 50 km/h in
3rd3rd
Driving at a constant speed of 50 km/h in
4th4th
Driving at a constant speed of 70 km/h in
5th5th
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 612 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4D5-stepIII>-General/General Information13E-2
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGE
An electronically-controlled injection pump has been added in order to comply with Regulation STEP
III. Due to this, the following service procedures have been added.
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine-ECU detects an abnormality in any of the sensors or actuators, the throttle valve
is half opened to restrict the amount of intake air in order to prevent the vehicle from running away.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Condenser Fan Motor Relay Control
Controls the condenser fan motor relay based on the A/C switch, engine coolant temperature and
vehicle speed input signals.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 658 of 1839
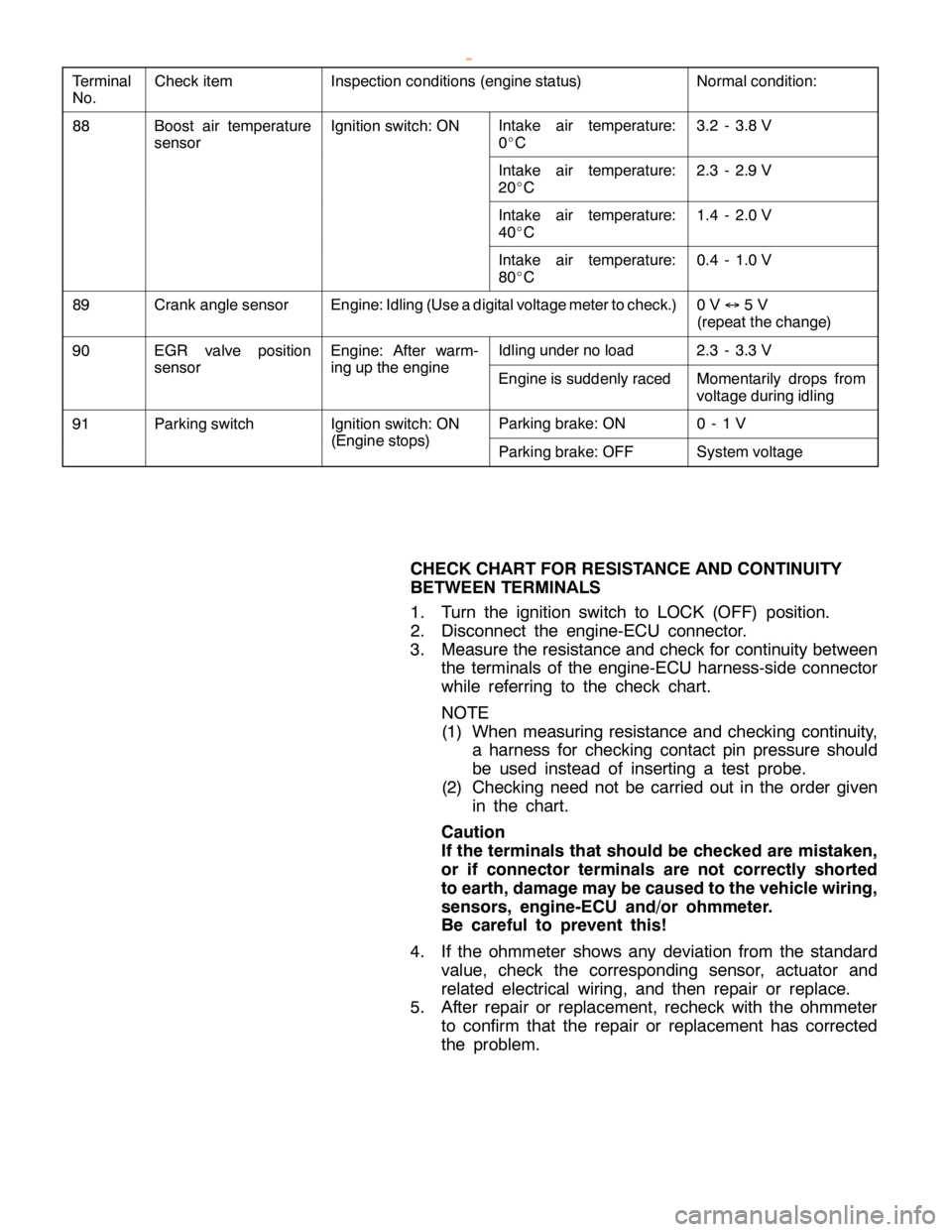
DIESEL FUEL <4D5-stepIII>-Troubleshooting13E-48
Terminal
No.Normal condition: Inspection conditions (engine status) Check item
88Boost air temperature
sensorIgnition switch: ONIntake air temperature:
0_C3.2 - 3.8 V
Intake air temperature:
20_C2.3 - 2.9 V
Intake air temperature:
40_C1.4 - 2.0 V
Intake air temperature:
80_C0.4 - 1.0 V
89Crank angle sensorEngine: Idling (Use a digital voltage meter to check.)0V↔5V
(repeat the change)
90EGR valve position
sensor
Engine: After warm-
inguptheengine
Idling under no load2.3 - 3.3 V
sensoring up the engineEngine is suddenly racedMomentarily drops from
voltage during idling
91Parking switchIgnition switch: ON
(Enginestops)
Parking brake: ON0-1V
(Engine stops)Parking brake: OFFSystem voltage
CHECK CHART FOR RESISTANCE AND CONTINUITY
BETWEEN TERMINALS
1. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK (OFF) position.
2. Disconnect the engine-ECU connector.
3. Measure the resistance and check for continuity between
the terminals of the engine-ECU harness-side connector
while referring to the check chart.
NOTE
(1) When measuring resistance and checking continuity,
a harness for checking contact pin pressure should
be used instead of inserting a test probe.
(2) Checking need not be carried out in the order given
in the chart.
Caution
If the terminals that should be checked are mistaken,
or if connector terminals are not correctly shorted
to earth, damage may be caused to the vehicle wiring,
sensors, engine-ECU and/or ohmmeter.
Be careful to prevent this!
4. If the ohmmeter shows any deviation from the standard
value, check the corresponding sensor, actuator and
related electrical wiring, and then repair or replace.
5. After repair or replacement, recheck with the ohmmeter
to confirm that the repair or replacement has corrected
the problem.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 801 of 1839

ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Glow System <4D5-StepIII>16-1
GROUP 16
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
GLOW SYSTEM <4D5-STEPIII>
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGE
Glow system control is now carried out by the engine-ECU to correspond to the adoption of an
electronically-controlled fuel injection system.
Refer to GROUP 13E - Troubleshooting for details on measuring the ECU terminal voltage as a result
of this.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 833 of 1839

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System <6G7>17-31
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <6G7>
GENERAL INFORMATION
The emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
DCrankcase emission control system
DEvaporative emission control system
DExhaust emission control system
ItemsNameSpecification
Crankcase emission
control systemPositive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission
control systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission
control systemAir-fuel ratio control device - GDI systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valveEquipped
Stepper motor type
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converterMonolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE REFERENCE TABLE
Related partsCrankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel
ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust
gas
recirculation
systemReference
page
PCV valve´17-35
Purge control solenoid valve´17-38
GDI system component´´GROUP
13A
Catalytic converter´17-44
EGR valve´17-40
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 854 of 1839

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System
<4M4-Vehicles with EGR>17-52
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <4M4-VEHICLES WITH
EGR>
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled EGR system and the
fuel injection timing control system (load timer)
reduce the level of exhaust gases (NO
x).
ItemsNameSpecification
Exhaust emission
control systemExhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valve
DEGR solenoid valve No.1
DEGR solenoid valve No.2Electronically-controlled EGR system
Single type
Duty cycle solenoid valve
ON-OFFsolenoid valve
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
EGR solenoid valve No.1/No. 2 resistance (at 20_C)W36 - 44
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 860 of 1839

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -EngineControlSystem/EmissionControl
System <4D5-Step III>17-2
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGE
Electronic-controlled throttle valve system has been used instead of a conventional cable-type accelerator
mechanism <4D5>.
Its service procedure is the same as for previous models with 6G7 or 4M4 engine.
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <4D5-STEP
III>
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGES
Some service procedures have been established as the following changes have been made due to the
compliance with the Emission Regulation Step III.
DAn electronic-controlled EGR valve and EGR cooler have been used.
DA catalytic converter has been added.
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled EGR system reduces
the level of exhaust gases (NO
x).
ItemsNameSpecification
Exhaust emission
control systemExhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valve
DEGR solenoid valve No.1
DEGR solenoid valve No.2
DEGR valve position sensorElectronically-controlled EGR system
Single type
ON-OFF solenoid valve
ON-OFF solenoid valve
Variable resistor type
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
EGR solenoid valve Nos. 1 and 2 resistance (at 20_C)Ω36 - 44
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk