2000 DODGE NEON engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 157 of 1285

NOTE: It is not necessary to bleed the entire
hydraulic system after replacing just the master cyl-
inder unless the brake system has been open to air
for an excessive amount of time or air is present in
the lines. Only the master cylinder must be bled
and filled.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
Review this entire section prior to performing any
mechanical work on a vehicle equipped with ABS.
This section contains information on precautions per-
taining to potential component damage, vehicle dam-
age and personal injury which could result when
servicing an ABS equipped vehicle.
CAUTION: Only the recommended jacking or hoist-
ing positions for this vehicle are to be used when-
ever it is necessary to lift a vehicle. Failure to raise
a vehicle from the recommended locations could
result in lifting a vehicle by the hydraulic control
unit mounting bracket. Lifting a vehicle by the
hydraulic control unit mounting bracket will result
in damage to the mounting bracket and the hydrau-
lic control unit.
CAUTION: An attempt to remove or disconnect cer-
tain system components may result in improper
system operation. Only those components with
approved removal and installation procedures in
this manual should be serviced.CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted sur-
faces. If brake fluid is spilled on any painted sur-
faces, wash off with water immediately.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS do not apply a
12-volt power source to the ground circuit of the
pump motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the
pump motor and will require replacement of the
entire HCU.
CAUTION: If welding work is to be performed on
the vehicle, using an electric arc welder, the CAB
connector should be disconnected during the weld-
ing operation.
CAUTION: The CAB 25-way connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition
switch in the ON position.
Many components of the ABS System are not ser-
viceable and must be replaced as an assembly. Do not
disassemble any component which is not designed to
be serviced.
MASTER CYLINDER
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The vacuum in the power brake booster
must be pumped down before removing the master
cylinder to prevent the booster from sucking in any
contamination. This can be done by pumping the
brake pedal while the engine is not running until a
firm brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With the engine not running, pump the brake
pedal 4-5 strokes until the pedal feel is firm.
(2) Disconnect the negative (ground) cable from
the battery and isolate the cable.
(3) Disconnect the positive cable from the battery,
then remove the battery from the battery tray. There
is one nut securing the clamp on the backside of the
battery holding it in place.
(4) Disconnect the wiring harness connector from
the brake fluid level switch on the master cylinder
reservoir (Fig. 12).
Fig. 11 Bleeding Master Cylinder
1 ± WOODEN DOWEL
2 ± MASTER CYLINDER
5 - 78 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 161 of 1285
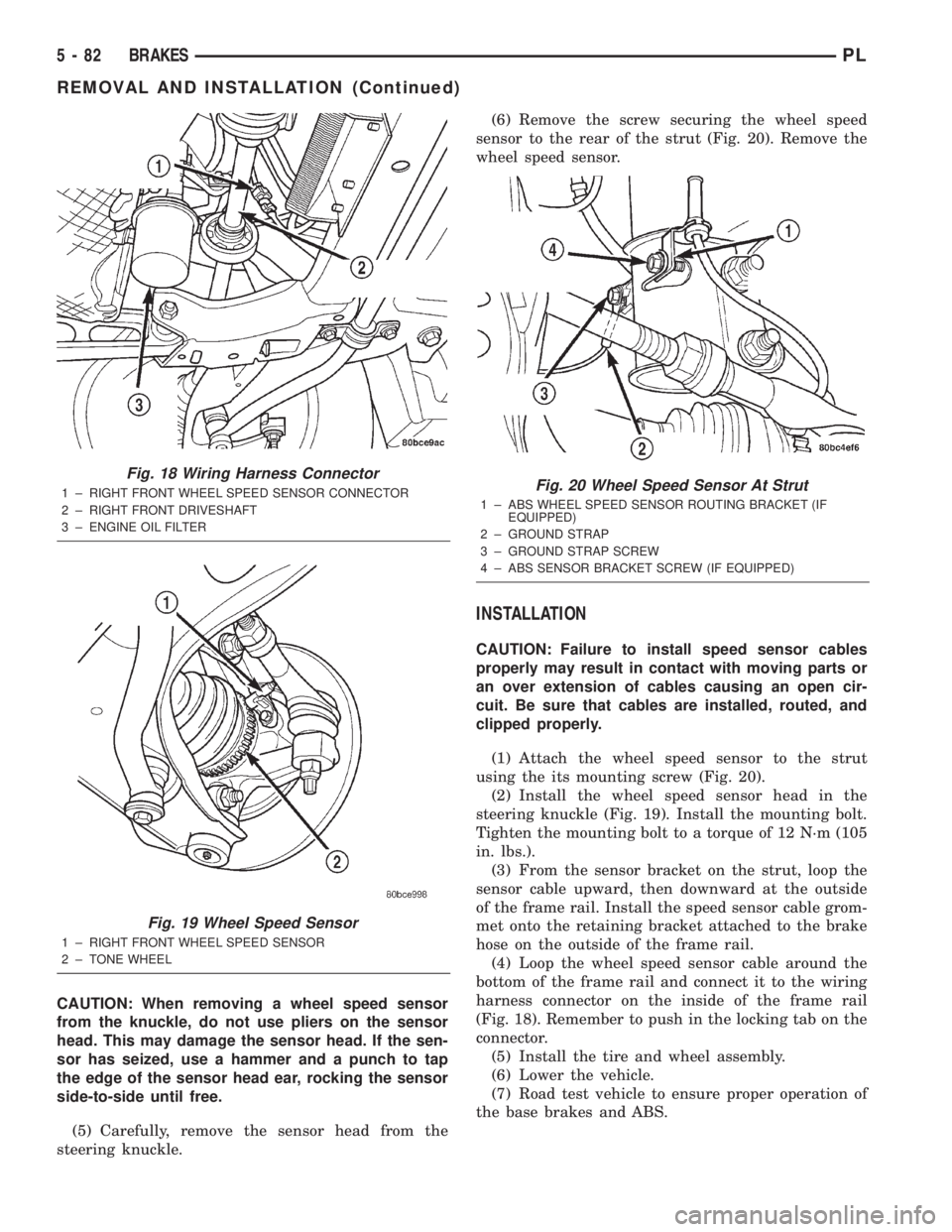
CAUTION: When removing a wheel speed sensor
from the knuckle, do not use pliers on the sensor
head. This may damage the sensor head. If the sen-
sor has seized, use a hammer and a punch to tap
the edge of the sensor head ear, rocking the sensor
side-to-side until free.
(5) Carefully, remove the sensor head from the
steering knuckle.(6) Remove the screw securing the wheel speed
sensor to the rear of the strut (Fig. 20). Remove the
wheel speed sensor.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Failure to install speed sensor cables
properly may result in contact with moving parts or
an over extension of cables causing an open cir-
cuit. Be sure that cables are installed, routed, and
clipped properly.
(1) Attach the wheel speed sensor to the strut
using the its mounting screw (Fig. 20).
(2) Install the wheel speed sensor head in the
steering knuckle (Fig. 19). Install the mounting bolt.
Tighten the mounting bolt to a torque of 12 N´m (105
in. lbs.).
(3) From the sensor bracket on the strut, loop the
sensor cable upward, then downward at the outside
of the frame rail. Install the speed sensor cable grom-
met onto the retaining bracket attached to the brake
hose on the outside of the frame rail.
(4) Loop the wheel speed sensor cable around the
bottom of the frame rail and connect it to the wiring
harness connector on the inside of the frame rail
(Fig. 18). Remember to push in the locking tab on the
connector.
(5) Install the tire and wheel assembly.
(6) Lower the vehicle.
(7) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
the base brakes and ABS.
Fig. 18 Wiring Harness Connector
1 ± RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 ± RIGHT FRONT DRIVESHAFT
3 ± ENGINE OIL FILTER
Fig. 19 Wheel Speed Sensor
1 ± RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 ± TONE WHEEL
Fig. 20 Wheel Speed Sensor At Strut
1 ± ABS WHEEL SPEED SENSOR ROUTING BRACKET (IF
EQUIPPED)
2 ± GROUND STRAP
3 ± GROUND STRAP SCREW
4 ± ABS SENSOR BRACKET SCREW (IF EQUIPPED)
5 - 82 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 166 of 1285

CLUTCH
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY..............1
CLUTCH CABLE..........................1
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS...............2
DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT..............5
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS............5
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS........5
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........5REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CLUTCH CABLE..........................7
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........8
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY..............8
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK.............12
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION.................12
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS.................13
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
All 2.0L SOHC engines equipped with the A578
5-speed transaxle use a modular clutch assembly
(Fig. 1). The transaxle must be removed to gain
access to and replace the modular clutch, drive plate,
and/or clutch release bearing and lever.
The modular clutch assembly used in this vehicle
consists of a single, dry-type clutch disc, a diaphragm
style clutch cover, and an integrated flywheel. The
clutch cover is riveted to the flywheel, containing theclutch disc within. The modular clutch can only be
serviced as an assembly.
The clutch disc has cushion springs riveted to the
disc hub assembly. The clutch disc facings are riveted
to the cushion springs. The facings are made from a
non-asbestos material.
The clutch cover pressure plate assembly is a dia-
phragm type unit with a one-piece diaphragm spring
with multiple release fingers. The pressure plate
release fingers are preset during manufacture and
are not adjustable.
CLUTCH CABLE
The clutch cable assembly (Fig. 2) carries the
movement of the clutch pedal to the clutch release
bearing. The cable is designed to maintain tension
against the clutch fork, or lever, and has a built in
self-adjusting mechanism, which compensates for
clutch disc wear.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The clutch interlock/upstop switch is an assembly
consisting of two switches: an engine starter inhibit
switch (interlock) and a clutch pedal upstop switch
(Fig. 3). The switch assembly is located in the clutch/
brake pedal bracket assembly (Fig. 4), each switch
being fastened by four plastic wing tabs.
OPERATION
Clutch Interlock Switch
The clutch interlock switch prevents engine starter
operation and inadvertent vehicle movement with the
clutch engaged and the transaxle in gear.
Fig. 1 Modular Clutch Assembly
1 ± MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
PLCLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 167 of 1285
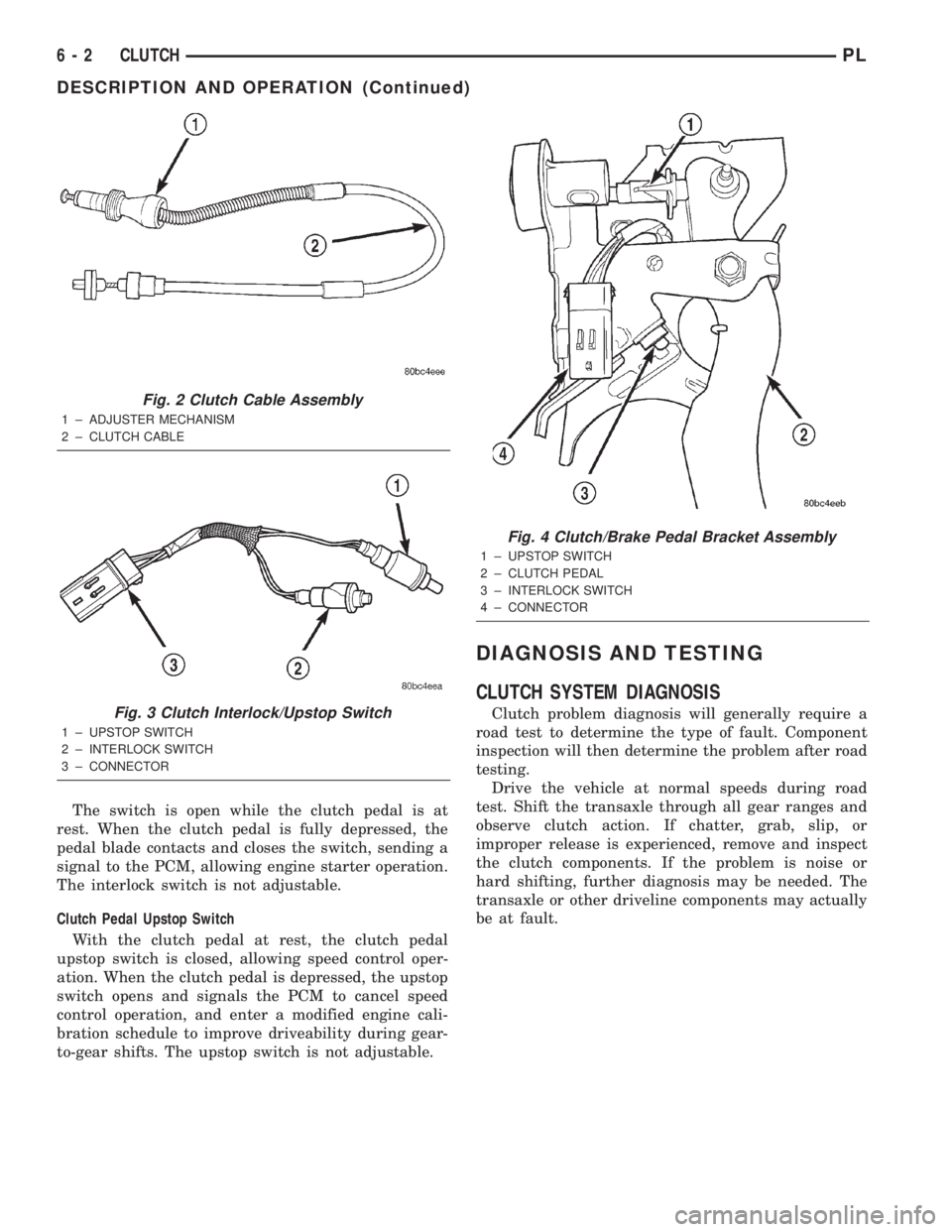
The switch is open while the clutch pedal is at
rest. When the clutch pedal is fully depressed, the
pedal blade contacts and closes the switch, sending a
signal to the PCM, allowing engine starter operation.
The interlock switch is not adjustable.
Clutch Pedal Upstop Switch
With the clutch pedal at rest, the clutch pedal
upstop switch is closed, allowing speed control oper-
ation. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the upstop
switch opens and signals the PCM to cancel speed
control operation, and enter a modified engine cali-
bration schedule to improve driveability during gear-
to-gear shifts. The upstop switch is not adjustable.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Clutch problem diagnosis will generally require a
road test to determine the type of fault. Component
inspection will then determine the problem after road
testing.
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds during road
test. Shift the transaxle through all gear ranges and
observe clutch action. If chatter, grab, slip, or
improper release is experienced, remove and inspect
the clutch components. If the problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed. The
transaxle or other driveline components may actually
be at fault.
Fig. 2 Clutch Cable Assembly
1 ± ADJUSTER MECHANISM
2 ± CLUTCH CABLE
Fig. 3 Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
3 ± CONNECTOR
Fig. 4 Clutch/Brake Pedal Bracket Assembly
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± CLUTCH PEDAL
3 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
4 ± CONNECTOR
6 - 2 CLUTCHPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 168 of 1285

SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC
FACING COVERED
WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or transaxle
input shaft sealCorrect leak and replace modular clutch
assembly
Too much grease applied to splines of disc
and input shaftApply lighter coating of grease to splines
NO FAULT FOUND
WITH CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to suspension or
driveline componentFurther diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems Check EFI and ignition systems
PARTIAL
ENGAGEMENT OF
CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release fingers
bent, distorted (rough handling, improper
assembly)Replace modular clutch assembly
Clutch disc damaged or distorted Replace modular clutch assembly
Clutch misalignment Check alignment and runout of flywheel,
disc, or cover. Check clutch housing to
engine dowels and dowel holes for damage.
Correct as necessary.
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING
WORN OUTNormal wear. Replace modular clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch, results
in rapid wear overheating.Replace modular clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm spring
tensionReplace modular clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC
FACING
CONTAMINATED
WITH OIL OR
GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or transaxle input
shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace modular
clutch assembly.
Excessive amount of grease applied to
input shaft splinesApply less grease to input shaft. Replace
modular clutch assembly
Road splash, water entering housing Seal housing. Inspect clutch assembly.
CLUTCH IS
RUNNING
PARTIALLY
DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding, does
not return to normal running position.Verify that bearing is actually binding. Then,
replace bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer if sleeve surface is
damaged.
Cable self-adjuster mechanism sticking or
binding causing high preloadVerify that self-adjuster is free to move
PLCLUTCH 6 - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 170 of 1285

DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft bolts
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists:
(2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly.
(3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(6) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
stud and fork fingers. Replace all worn parts.
(7) Check clutch assembly for contamination (dirt,
oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if nec-
essary.
(9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace,
if necessary.
(10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(11) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS
Certain NV T350 (A-578) manual transaxles are
equipped with a reverse brake. It prevents clash
when shifting into reverse, but only if the vehicle is
not moving. See Group 21, Transaxle for further
diagnosis.
(1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time, and the reverse brake
may not be functioning.(2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc
splines, and release bearing for dry rust. If present,
clean rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease
to the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. Verify
that the clutch disc slides freely along the input shaft
spline.
(4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, and replace with new clutch assembly if
required.
(5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines.
Replace as necessary.
(6) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers.
(7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
The clutch interlock/upstop switch is an assembly
consisting of two switches: an engine starter inhibit
switch (clutch interlock) and a clutch pedal upstop
switch (Fig. 5). The switch assembly is located in the
clutch/brake pedal bracket assembly (Fig. 6), each
switch being fastened by four plastic wing tabs.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK SWITCH
Mechanical Test
(1) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,turn the ignition key to the start posi-
tion. The engine starter should not crank with the
clutch pedal at rest (not depressed). If the starter
cranks, proceed to the electrical test to determine
whether the switch is defective or the circuit is
shorted. If the vehicle does not crank, proceed to the
next step.
(2) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,fully depress the clutch pedal and turn
Fig. 5 Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
3 ± CONNECTOR
PLCLUTCH 6 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 171 of 1285

the ignition key to the start position. The engine
starter should crank. If the starter does not crank,
visually inspect the clutch pedal for obstructions
(floor mat, etc.). Also make sure the clutch pedal
blade contacts and fully
Electrical Test
(1) Move ignition key to the ªOFF/LOCKº position
and remove key.
(2) Set park brake.
(3) Disconnect the clutch interlock/upstop switch
connector.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between terminals2&3with the interlock switchnot depressed (clutch pedal at rest). There should be
no continuity between the terminals (open circuit).
(5) Fully depress the clutch pedal to close the
switch at least 1.25 mm (0.050 in.). The ohmmeter
should show continuity (0 ohms).
(6) If ohmmeter readings do not fall within these
ranges, the switch assembly is defective and should
be replaced. If the switch tests ok, wiring is defective.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams and repair
defective wiring.
UPSTOP SWITCH
Mechanical Test
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Start engine and operate speed control to main-
tain speed.
(3) Depress clutch pedal at least 33 mm (1.30 in.).
Speed control operation should terminate. If speed
control does not terminate, the upstop switch is
defective or the related wiring is shorted. Proceed to
the upstop switch electrical test.
Electrical Test
(1) Move ignition key to the ªOFF/LOCKº position
and remove key.
(2) Set park brake.
(3) Disconnect the clutch interlock/upstop switch
connector.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between terminals1&2with the upstop switch
depressed (clutch pedal at rest). The ohmmeter
should show continuity (0 ohms).
(5) Depress the clutch pedal at least 33 mm (1.30
in.) check for continuity between terminals1&2.
There should be no continuity between the terminals
(open circuit).
(6) If ohmmeter readings do not fall within these
ranges, the switch assembly is defective and should
be replaced. If the switch tests ok, wiring is defective.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams and repair
defective wiring.
Fig. 6 Clutch/Brake Pedal Bracket Assembly
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± CLUTCH PEDAL
3 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
4 ± CONNECTOR
6 - 6 CLUTCHPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 172 of 1285

SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE STARTER
WON'T CRANK
WHEN CLUTCH
PEDAL IS
PRESSED TO THE
FLOORClutch interlock switch does not have
continuity when plunger is depressed 1.25
mm (1.30 in.)Defective switch or open wiring circuit.
Replace switch if necessary.
Interlock switch plunger is not depressed
when clutch pedal is pushed to the floorFloor mat interferes with clutch pedal
movement or clutch pedal bracket is bent.
Problem is related to other components in
the starting circuit.Check other components in the starting
circuit. Refer to Battery/Starting/Charging
System in Group 8.
SPEED CONTROL
DOES NOT
TERMINATE WHEN
CLUTCH PEDAL IS
DEPRESSED BY AT
LEAST 33 mm (1.30
in.)Upstop switch circuit is closed when clutch
pedal is depressed, or harness is shorted.Refer to Upstop Switch Electrical Test in
this group. Repair wiring or replace switch
assembly as necessary.
Other speed control system failure. Refer to Group 8H, Speed Control for
further diagnosis and testing procedures.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CLUTCH CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect both battery cables.
(2) Remove battery clamp and remove battery
from vehicle.
(3) Remove battery tray from mount bracket.
(4) Remove bellhousing cap (Fig. 7).
(5) Disconnect clutch cable from transaxle housing
and clutch release lever as shown in (Fig. 7).
(6) Disconnect the clutch cable from the clutch
pedal spacer (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Use care when handling clutch cable
assembly. Improper handling can cause adjuster
mechanism to come apart, making re-installation
difficult.
(7) Carefully guide cable through pedal assembly
bore and remove from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the clutch pedal end of the cable into
position and connect the cable to the clutch pedal
spacer as shown in (Fig. 8).
(2) Verify adjuster mechanism function as follows:
(a) With slight pressure, pull the clutch release
lever end of the cable to draw the cable taut.(b) Push the clutch cable housing toward the
dash panel (With less than 25 lbs. of effort, the
cable housing should move 30-50mm.). If the cable
Fig. 7 Clutch Cable at Transaxle
1 ± CLUTCH CABLE
2 ± TRANSAXLE
3 ± BELLHOUSING CAP
PLCLUTCH 6 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)