2000 DODGE NEON engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 9 of 1285

onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 minutes), before cranking again.
DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACHMENT
DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR LINES,
FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT. DO NOT LIFT OR TOW
VEHICLE BY FRONT OR REAR BUMPER, OR
BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER UNITS. DO NOT
VENTURE UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF NOT SUP-
PORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY STANDS. DO NOT
ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A TOWED VEHI-
CLE. USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other
under vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle. Do not attach towing device to
front or rear suspension components. Do notsecure vehicle to towing device by the use of front
or rear suspension or steering components.
Remove or secure loose or protruding objects from
a damaged vehicle before towing. Refer to state and
local rules and regulations before towing a vehicle.
Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a wheel lift or flat bed towing device (Fig. 2) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing device,
be sure the unlifted end of disabled vehicle has at
least 100 mm (4 in.) ground clearance. If minimum
ground clearance cannot be reached, use a towing
dolly. If a flat bed device is used, the approach angle
should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums or rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to
increase the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
Fig. 1 Jumper Cable Clamp Connections
1 ± BATTERY POSITIVE CABLE
2 ± POSITIVE JUMPER CABLE
3 ± TEST INDICATOR
4 ± BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE
5 ± BATTERY
6 ± NEGATIVE JUMPER CABLE
7 ± ENGINE GROUND
Fig. 2 Recommended Towing Devices
1 ± WHEEL LIFT
2 ± FLAT BED
0 - 8 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 10 of 1285

FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
²5-speed manual transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at any legal highway speed for extended dis-
tances. The gear selector must be in the neutral posi-
tion.
TOWING ± FRONT WHEEL LIFT
DaimlerChrysler Corporation recommends that a
vehicle be towed with the front end lifted, whenever
possible.
TOWING ± REAR WHEEL LIFT
If a vehicle cannot be towed with the front wheels
lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted provided the fol-
lowing guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to
secure steering wheel during towing operation.
²Unlock steering column and secure steering
wheel in straight ahead position with a clamp device
designed for towing.
²Verify that front drive line and steering compo-
nents are in good condition.
²5-speed manual transaxle vehicles can be towed
at any legal highway speed for extended distances.
The gear selector must be in the neutral position.
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The gear selector
must be in the neutral position.
HOISTING RECOMMENDATIONS
Refer to Owner's Manual provided with vehicle for
proper emergency jacking procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN THE ENGINE OR REAR SUSPENSION
IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE CENTER OF
GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME HOISTING
CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY SUPPORT OR
SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING DEVICE WHEN
THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
CAUTION: Do not position hoisting device on sus-
pension components, damage to vehicle can result.Do not attempt to raise one entire side of the
vehicle by placing a floor jack midway between the
front and rear wheels. This practice may result in
permanent damage to the body.
FLOOR JACK
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a PL vehicle (Fig. 3). Support the vehicle in the
raised position with jack stands.
A floor jack or any lifting device, must never be
used on any part of the underbody other then the
described areas.
HOIST
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly
(Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 Hoisting and Jacking Points
1 Frame Contract Lift (Single Post)
Chassis Lift (Dual Post)
Outboard Lift (Dual Post)
Floor Jack
2 Drive On Lift
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 9
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 14 of 1285
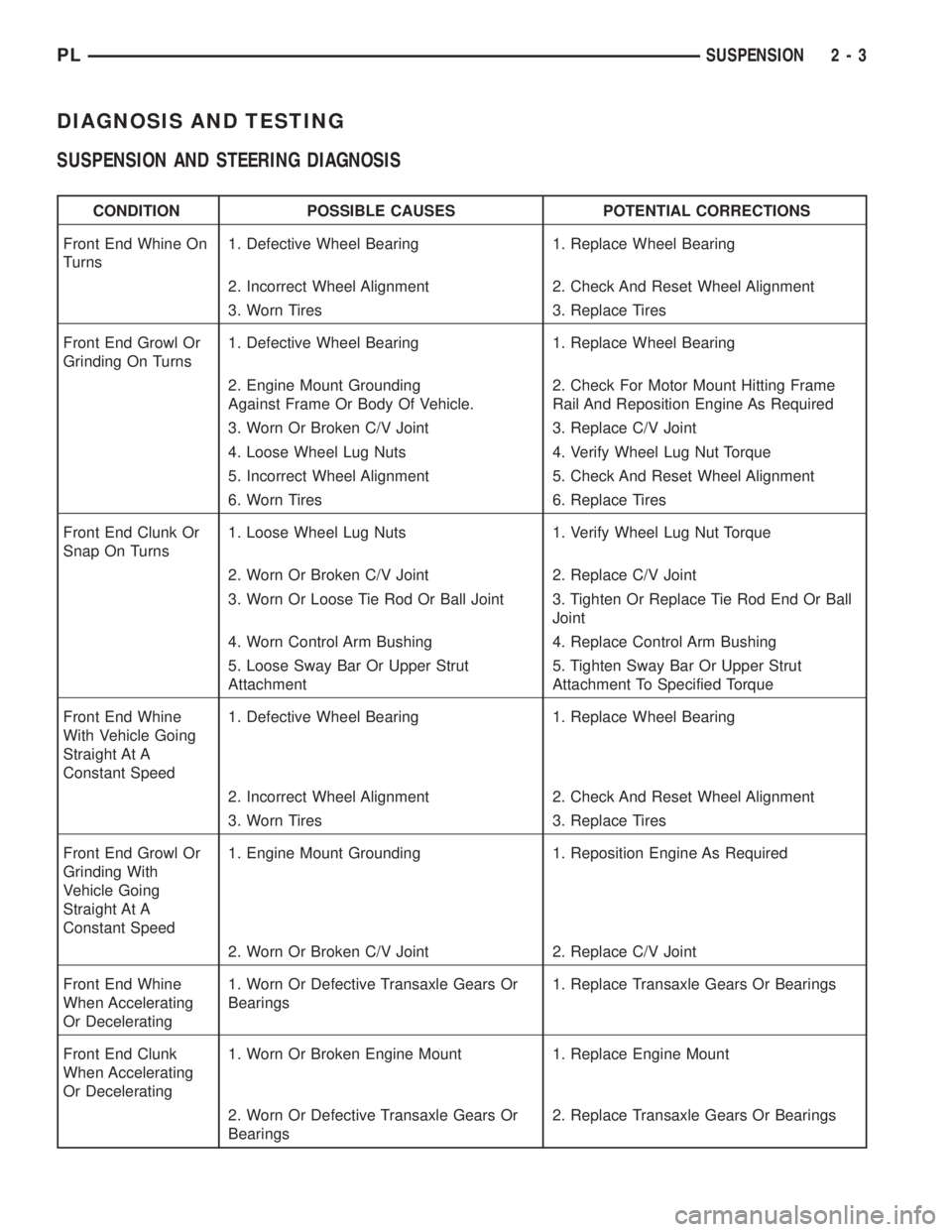
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SUSPENSION AND STEERING DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES POTENTIAL CORRECTIONS
Front End Whine On
Turns1. Defective Wheel Bearing 1. Replace Wheel Bearing
2. Incorrect Wheel Alignment 2. Check And Reset Wheel Alignment
3. Worn Tires 3. Replace Tires
Front End Growl Or
Grinding On Turns1. Defective Wheel Bearing 1. Replace Wheel Bearing
2. Engine Mount Grounding
Against Frame Or Body Of Vehicle.2. Check For Motor Mount Hitting Frame
Rail And Reposition Engine As Required
3. Worn Or Broken C/V Joint 3. Replace C/V Joint
4. Loose Wheel Lug Nuts 4. Verify Wheel Lug Nut Torque
5. Incorrect Wheel Alignment 5. Check And Reset Wheel Alignment
6. Worn Tires 6. Replace Tires
Front End Clunk Or
Snap On Turns1. Loose Wheel Lug Nuts 1. Verify Wheel Lug Nut Torque
2. Worn Or Broken C/V Joint 2. Replace C/V Joint
3. Worn Or Loose Tie Rod Or Ball Joint 3. Tighten Or Replace Tie Rod End Or Ball
Joint
4. Worn Control Arm Bushing 4. Replace Control Arm Bushing
5. Loose Sway Bar Or Upper Strut
Attachment5. Tighten Sway Bar Or Upper Strut
Attachment To Specified Torque
Front End Whine
With Vehicle Going
Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Defective Wheel Bearing 1. Replace Wheel Bearing
2. Incorrect Wheel Alignment 2. Check And Reset Wheel Alignment
3. Worn Tires 3. Replace Tires
Front End Growl Or
Grinding With
Vehicle Going
Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine Mount Grounding 1. Reposition Engine As Required
2. Worn Or Broken C/V Joint 2. Replace C/V Joint
Front End Whine
When Accelerating
Or Decelerating1. Worn Or Defective Transaxle Gears Or
Bearings1. Replace Transaxle Gears Or Bearings
Front End Clunk
When Accelerating
Or Decelerating1. Worn Or Broken Engine Mount 1. Replace Engine Mount
2. Worn Or Defective Transaxle Gears Or
Bearings2. Replace Transaxle Gears Or Bearings
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 3
Page 30 of 1285

lizer bar cushion retainer bolts a little to ease any
turning resistance.
(5) Remove the nut and pinch bolt clamping the
ball joint stud to the steering knuckle (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: After removing the steering knuckle
from the ball joint stud, do not pull outward on the
knuckle. Pulling the steering knuckle outward at
this point can separate the inner C/V joint on the
driveshaft. Refer to FRONT DRIVESHAFTS in the
DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE group for further
information.
NOTE: Use caution when separating the ball joint
stud from the steering knuckle, so the ball joint seal
does not get cut.
(6) Separate the ball joint stud from the steering
knuckle by prying down on lower control arm and up
against the ball joint boss on the steering knuckle
(Fig. 12).
(7) If the right lower control arm is being serviced,
remove the bolts mounting the engine torque strut in
place (Fig. 16), then remove the engine torque strut
from the vehicle.
(8) Remove the front pivot bolt attaching the lower
control arm to the front suspension crossmember
(Fig. 17). Remove the rear pivot bolt attaching the
lower control arm to the front suspension crossmem-
ber and frame rail. Remove the lower control arm
from the crossmember.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower control arm into the cross-
member (Fig. 17). Install, but do not fully tighten,
the rear pivot bolt attaching the lower control arm to
the front suspension crossmember and frame rail.
Install the front pivot bolt attaching the lower con-
trol arm to the front suspension crossmember.
(2) Tighten the lower control arm rear pivot (and
suspension crossmember) bolt to a torque of 203 N´m
(150 ft. lbs.), then tighten the lower control arm front
pivot bolt to a torque of 163 N´m (120 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install the ball joint stud into the steering
knuckle aligning the bolt hole in the knuckle boss
Fig. 15 Ball Joint Bolt And Nut
1 ± NUT
2 ± BOLT
3 ± BALL JOINT
Fig. 16 Engine Torque Strut
1 ± MOUNTING BOLTS
2 ± ENGINE TORQUE ISOLATOR STRUT
3 ± FRONT SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 17 Lower Control Arm Attaching Bolts
1 ± LOWER CONTROL ARM
2 ± FRONT BOLT
3 ± CROSSMEMBER
4 ± REAR BOLT
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 31 of 1285

with the notch formed in the side of the ball joint
stud.
(4) If the right lower control arm has been ser-
viced, install the engine torque strut (Fig. 16). Follow
the procedure described in the ENGINE service man-
ual group to properly align and tighten the torque
strut.
(5) Install a new ball joint stud pinch bolt and nut
(Fig. 15). Tighten the nut to a torque of 95 N´m (70
ft. lbs.).
(6) Rotate the forward ends of the stabilizer bar
into mounting position.
(7) Install both stabilizer bar links back on vehicle
(Fig. 14). Start each stabilizer bar link bolt with
bushing from the bottom, through the stabilizer bar,
inner link bushings, lower control arm, and into the
upper retainer/nut and bushing (Fig. 1). Do not fully
tighten the link assemblies at this time.
(8) Lower the vehicle to ground level.
NOTE: It may be necessary to put the vehicle on a
platform hoist or alignment rack to gain access to
the stabilizer bar mounting bolts with the vehicle at
curb height.
(9) Tighten each stabilizer bar link by holding the
upper retainer/nut with a wrench and turning the
link bolt. Tighten each link bolt to a torque of 23
N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(10) If previously loosened, tighten the stabilizer
bar cushion retainer bolts to a torque of 28 N´m (250
in. lbs.).
STABILIZER BAR (FRONT)
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group for the
proper lifting procedure.
(2) Remove both stabilizer bar links from the vehi-
cle (Fig. 18). Remove each link by holding the upper
retainer/nut with a wrench and turning the link bolt.
(3) Remove the stabilizer bar cushion retainer
bolts and retainers (Fig. 18), and remove the stabi-
lizer bar with cushions attached from the vehicle.
(4) To remove the cushions from the stabilizer bar,
peel back each cushion at the slit and roll it off the
bar.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Before stabilizer bar installation, inspect the
cushions and links for excessive wear, cracks, dam-
age and distortion. Replace any pieces failing
inspection.
(1) If removed, install the stabilizer bar cushions
on the stabilizer bar utilizing the slit in each cush-
ion. Position the cushions at each end of the bar's
straight beam, just before it begins to curve.
NOTE: Before installing the stabilizer bar, make
sure the bar is not upside-down. The stabilizer bar
must be installed with the curve on the outboard
ends of the bar facing downward to clear the con-
trol arms once fully installed (Fig. 19).
(2) First, place the stabilizer bar in position on the
front suspension crossmember. The slits in each
cushion must point toward the front of the vehicle
and sit directly on top of the raised beads formed
into the stamping on the crossmember. Next, install
the cushion retainers, matching the raised beads
formed into the cushion retainers to the grooves
formed into the cushions. Install the cushion retainer
bolts, but do not completely tighten them at this
time.
(3) Install both stabilizer bar links back on vehicle
(Fig. 18). Start each stabilizer bar link bolt with
bushing from the bottom, through the stabilizer bar,
inner link bushings, lower control arm, and into the
upper retainer/nut and bushing (Fig. 1). Do not fully
tighten the link assemblies at this time.
Fig. 18 Stabilizer Bar
1 ± STABLILIZER BAR CUSION RETAINERS
2 ± CUSHIONS
3 ± FRONT STABLIZER BAR
4 ± STABILIZER BAR LINKS
2 - 20 SUSPENSIONPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 81 of 1285

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
and proportioning valves (rear only) to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly.
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes as standard equipment. Rear disc brakes and
an antilock brake system (ABS) with traction control
are optional.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock and antilock braking systems.
This means the left front and right rear brakes are
on one hydraulic circuit and the right front and left
rear are on the other.
Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e.
This system shares most base brake hardware used
on vehicles without ABS. A vehicle equipped with
ABS, however, uses a different master cylinder and
brake tubes. Also included in the ABS system is an
integrated control unit (ICU) and four wheel speed
sensors. These components are described in detail in
the ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM section in this
group of the service manual. All vehicles with ABS
come standard with four-wheel-disc brakes and trac-
tion control.
The parking brakes are hand-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. The parking
brake lever has an automatic adjusting feature that
takes up any excessive slack in the parking brake
cable system.
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
BRAKE PEDAL
A suspended-type brake pedal is used on this vehi-
cle. The pedal pivots on a shaft mounted in the pedal
support bracket under the instrument panel. The
pedal connects to the power brake booster input rod
and pushes it in when the pedal is applied.
The brake pedal and it's pad are serviceable sepa-
rately.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
There are two different power brake booster
designs, although externally they appear the same.
All vehicles use a 205 mm tandem diaphragm power
brake booster. The two boosters are internally tuned
differently depending on whether the vehicle is
equipped with the standard front disc/rear drum
brake combination or the optional front disc/rear disc
(four-wheel disc) brake combination. If the power
brake booster requires replacement, be sure it is
replaced with the correct part.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig.
1). This tag contains the following information: The
production part number of the power brake booster,
the date it was built and who manufactured it.
The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop the vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum-operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 2).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power booster
input rod moves forward. This opens and closes
valves in the power brake booster, allowing atmo-
spheric pressure to enter on one side of a diaphragm.
Engine vacuum is always present on the other side.
This difference in pressure forces the output rod of
the power booster out against the primary piston of
the master cylinder. As the pistons in the master cyl-
inder move forward, hydraulic pressure is created in
the brake system.
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder and Power Brake Booster
1 ± POWER BRAKE BOOSTER PARTS IDENTIFICATION TAG
2 ± POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
3 ± BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE SWITCH
4 ± MASTER CYLINDER
5 - 2 BRAKESPL
Page 82 of 1285

The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel. The booster
input push rod connects to the brake pedal. A vac-
uum line connects the power booster to the intake
manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the front
of the power brake booster.
MASTER CYLINDER
The base brakes on a vehicle not equipped with
ABS use a standard compensating port master cylin-
der, while vehicles equipped with ABS use a center
valve design master cylinder. The information pro-
vided here applies only to the non-ABS master cylin-
der. For information on the master cylinder used on
vehicles with ABS, refer to the ANTILOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM section in this service manual group.
The non-ABS master cylinder is a four-outlet
design with two screw-in proportioning valves. One is
attached directly to the inboard side of the master
cylinder housing while the other is attached to the
bottom (Fig. 3). Vehicles equipped with rear drum
brakes use a master cylinder with a 22.23 mm (0.875
in.) bore diameter, while vehicles equipped with rear
disc brakes use a 23.82 mm (0.937 in.) bore diameter
master cylinder.
The master cylinder body is an anodized aluminum
casting. It has a machined bore to accept the master
cylinder piston and also has threaded ports with
seats for hydraulic brake line connections.
The master cylinder's primary outlet ports supply
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rearbrakes while the secondary outlet ports supply
hydraulic pressure to the left front and right rear
brakes (Fig. 3).
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR
The master cylinder has the brake fluid reservoir
mounted on top of it which gravity feeds brake fluid
to the master cylinder when it is required. The res-
ervoir is made of see-through plastic and it houses
the brake fluid level switch.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
The brake fluid level switch is located in the brake
fluid reservoir on the master cylinder (Fig. 1). It
senses the level of the brake fluid within the reser-
voir and when the level drops below an acceptable
level, the switch closes and completes the ground cir-
cuit for the red BRAKE warning lamp. This turns on
the red BRAKE warning lamp. For additional infor-
mation, refer to RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP also
in this section.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
NOTE: Only vehicles without antilock brakes have
proportioning valves. Vehicles with antilock brakes
have electronic brake distribution that is built into
the integrated control unit.
Fig. 2 Power Brake Booster
1 ± MOUNTING STUD
2 ± PARTS IDENTIFICATION TAG
3 ± MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING STUDS
4 ± VACUUM CHECK VALVE
Fig. 3 Non-ABS Master Cylinder
1 ± RIGHT FRONT BRAKE TUBE
2 ± LEFT FRONT BRAKE TUBE
3 ± LEFT REAR BRAKE TUBE
4 ± REAR PROPORTIONING VALVES
5 ± RIGHT REAR BRAKE TUBE
PLBRAKES 5 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 89 of 1285
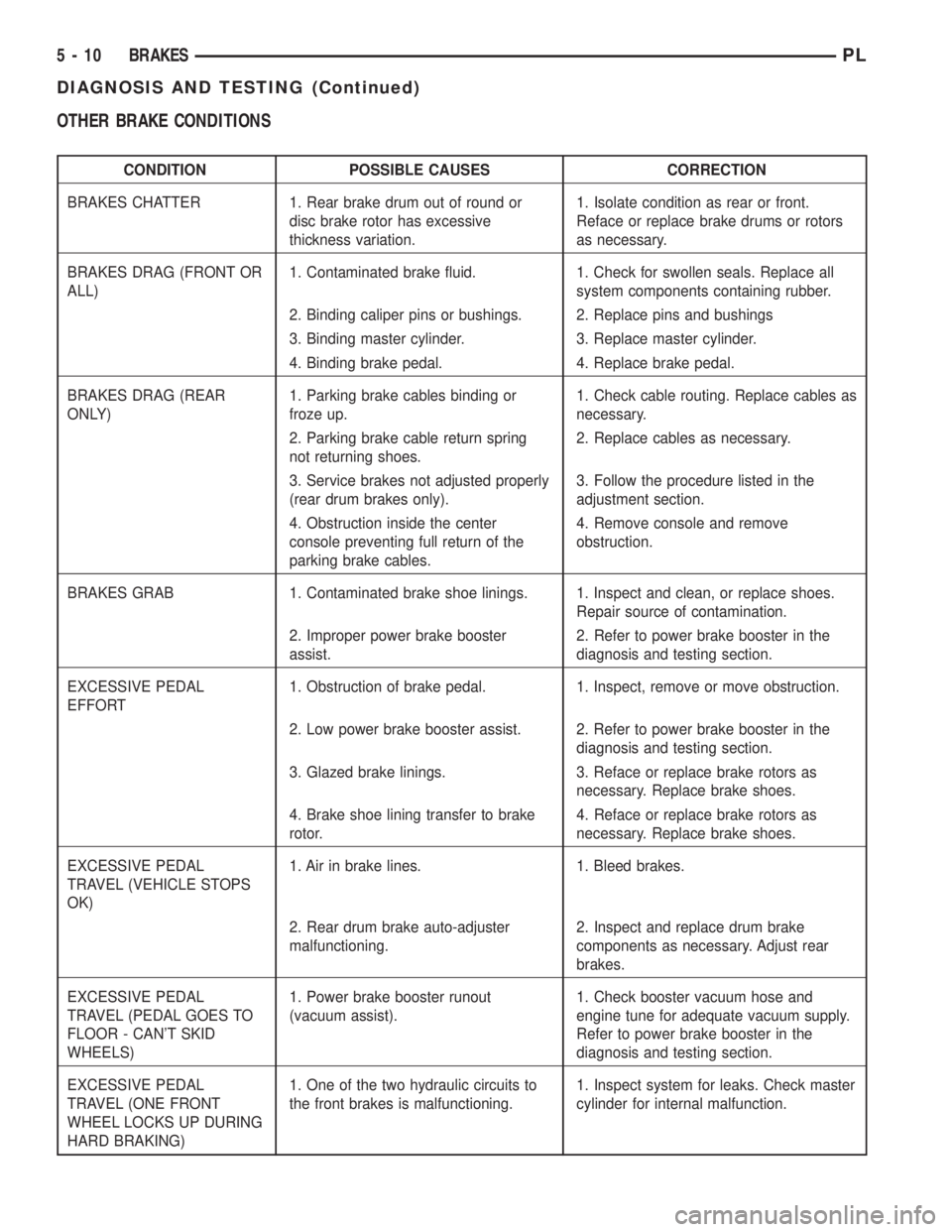
OTHER BRAKE CONDITIONS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKES CHATTER 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or rotors
as necessary.
BRAKES DRAG (FRONT OR
ALL)1. Contaminated brake fluid. 1. Check for swollen seals. Replace all
system components containing rubber.
2. Binding caliper pins or bushings. 2. Replace pins and bushings
3. Binding master cylinder. 3. Replace master cylinder.
4. Binding brake pedal. 4. Replace brake pedal.
BRAKES DRAG (REAR
ONLY)1. Parking brake cables binding or
froze up.1. Check cable routing. Replace cables as
necessary.
2. Parking brake cable return spring
not returning shoes.2. Replace cables as necessary.
3. Service brakes not adjusted properly
(rear drum brakes only).3. Follow the procedure listed in the
adjustment section.
4. Obstruction inside the center
console preventing full return of the
parking brake cables.4. Remove console and remove
obstruction.
BRAKES GRAB 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Improper power brake booster
assist.2. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist. 2. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor.4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK)1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (PEDAL GOES TO
FLOOR - CAN'T SKID
WHEELS)1. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).1. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum supply.
Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP DURING
HARD BRAKING)1. One of the two hydraulic circuits to
the front brakes is malfunctioning.1. Inspect system for leaks. Check master
cylinder for internal malfunction.
5 - 10 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)