2000 DODGE NEON check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 888 of 1285

reduces the power required to drive the pump and
holds down temperature build-up.
When steering conditions exceed maximum pres-
sure requirements, such as when the wheels are
turned against the stops, the pressure built up in the
steering gear exerts pressure on the spring end of the
flow control valve. The high pressure lifts the relief
valve ball from its seat and allows oil to flow through
a trigger orifice located in the outlet fitting. This
reduces pressure on the spring end of the flow con-
trol valve which then opens and allows the oil to
return to the intake side of the pump. This action
limits maximum pressure output of the pump to a
safe level.
Under normal power steering pump operating con-
ditions, pressure requirements of the pump are below
maximum, causing the pressure relief valve to
remain closed.
POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
The power steering fluid reservoir is mounted on
the power steering pump using 3 bolts (Fig. 1). It
stores fluid for the power steering system.
The power steering fluid reservoir is considered an
integral part of the power steering pump and is not
serviced separately.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
POWER STEERING PUMP INITIAL OPERATION
CAUTION: The fluid level should be checked with
engine off to prevent injury from moving compo-
nents. Use only MoparTPower Steering Fluid. Do
not use automatic transmission fluid. Do not over-
fill.
Wipe the filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal temperature, approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC
(70ÉF to 80ÉF).
(1) Fill the power steering fluid reservoir to the
proper level and let the fluid settle for at least two
minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Start the engine. Slowly turn the steering
wheel right and left, lightly contacting the wheel
stops.
(6) Add power steering fluid if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle and turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock to lock.(8) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and refill
as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stand a few minutes and repeat the above pro-
cedure.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
NOTE: Do not use any type of automatic transmis-
sion fluid in the power steering system.
POWER STEERING PUMP
NOTE: Before proceeding with this removal and
installation procedure, review SERVICE WARNINGS
AND CAUTIONS at the beginning of REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove battery cable from the negative post on
the battery.
(2) Siphon as much fluid as possible from the
power steering fluid reservoir.
(3) Remove the power steering pump drive belt
from the power steering pump pulley. Refer to
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS in the COOLING SYS-
TEM service manual group for the required removal
and installation procedure.
(4) Remove the hose clamp securing the return
hose to the power steering fluid reservoir. Slide the
hose off the end of the reservoir fitting. (Fig. 2).
(5) Back out the tube nut securing the power
steering fluid pressure hose to the power steering
pump and remove the hose from the pump (Fig. 2).
PLSTEERING 19 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 893 of 1285

NOTE: The power steering gear should not be ser-
viced or adjusted. If a malfunction or oil leak occurs
with the steering gear, the complete steering gear
needs to be replaced.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
NOTE: Do not use any type of automatic transmis-
sion fluid in the power steering system.
POWER STEERING GEAR
NOTE: Before proceeding with this removal and
installation procedure, review SERVICE WARNINGS
AND CAUTIONS at the beginning of REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Place the steering wheel in the STRAIGHT-
AHEAD position. Using a steering wheel holder, lock
the steering wheel in place to keep it from rotating
(Fig. 2). This keeps the clockspring in the proper ori-
entation.
(2) Inside the passenger compartment, remove the
steering column coupling retainer pin, back off the
pinch bolt nut, and remove the steering column cou-
pling pinch bolt (Fig. 3) (the pinch bolt nut is caged
to the coupling and is not removable). Separate the
upper and lower steering column couplings.
(3) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group in this
service manual for the correct lifting procedure.(4) Remove both front tire and wheel assemblies
from the vehicle.
(5) Remove nuts attaching both outer tie rods to
the steering knuckles (Fig. 4). Remove each nut by
holding the tie rod stud stationary while loosening
and removing the nut with a wrench.
(6) Remove the outer tie rod from the steering
knuckles using Remover, Special Tool MB991113
(Fig. 5).
(7) Remove the tie rod heat shield.
Fig. 2 Steering Wheel Holder
1 ± STEERING WHEEL
2 ± STEERING WHEEL HOLDER
3 ± DRIVERS SEAT
Fig. 3 Steering Column Couplings
1 ± STEERING COLUMN UPPER COUPLING
2 ± PINCH BOLT
3 ± STEERING COLUMN LOWER COUPLING
4 ± BRAKE PEDAL
5 ± NUT
6 ± RETAINER PIN
19 - 22 STEERINGPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 897 of 1285

(7) Using a soft face hammer, tap the front suspen-
sion crossmember back-and-forth or side-to-side until
it is aligned with the previously scribed positioning
marks on the body of the vehicle (Fig. 9). Once the
front suspension crossmember is correctly positioned,
tighten the rear two crossmember (and rear lower
control arm) mounting bolts to a torque of 203 N´m
(150 ft. lbs.), then tighten the front two crossmember
mounting bolts to a torque of 142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.).
(8) Fasten the engine torque strut to the right for-
ward corner of the front suspension crossmember
using its mounting bolt (Fig. 8). Follow the procedure
described in the ENGINE service manual group to
properly align and tighten the torque strut and it's
mounting bolts.
(9) Using a lint free towel, wipe clean the open
power steering hose ends and the power steering
gear ports. Replace the pressure hose used O-ring
with new. Lubricate the O-ring with power steering
fluid.
(10) Attach the power steering fluid pressure hose
to it's port on the power steering gear (Fig. 7). Start
the tube nut threads into the gear, but do not tighten
them at this time. On vehicles equipped with a power
steering fluid cooler, reconnect the cooler line to the
gear in place of the power steering fluid return hose.
(11) Open the routing clips on the front of the
steering gear housing and install the power steering
fluid pressure hose into the routing clips.
(12) On vehicles equipped with a power steering
fluid cooler, place the cooler in mounting position and
snap the cooler tube going to the gear into the right
routing clip.
(13) Close both routing clips.
(14) Tighten the power steering fluid pressure
hose tube nut at the gear to a torque of 34 N´m (25
ft. lbs.).
(15) If the vehicle is equipped with a power steer-
ing fluid cooler, install the two screws securing the
cooler to the front suspension crossmember. They are
located behind the cooler.
(16) On vehicle's with a power steering fluid cooler,
place the hose clamp on the hose far enough from the
end to clear the steel fitting on the gear. Do the same
for the fluid return hose on a vehicle that is not
equipped with a cooler.
(17) Push either hose listed in the above step onto
the steel fitting, then move and secure the clamp on
the hose past the bead on the steel fitting in the
steering gears outlet port (Fig. 7).
(18) Route the fluid return hose along the front of
the steering gear, clipping it into place in the
C-clamps on the outside of the routing clips on the
front of the power steering gear housing.
(19) Reconnect the wiring harness connector from
the power steering fluid pressure switch (Fig. 6). Besure the locking tab on the wiring harness connector
is securely latched.
(20) Perform the following to each outer tie rod:
²Place the tie rod heat shield on the knuckle's
steering arm, aligning the hole in the shield with the
hole in the knuckle and the tangs on the outside of
the shield with the outside configuration of the steer-
ing arm. The shield should now be facing outboard,
away from the power steering gear and tie rod (Fig.
4).
²Attach the outer tie rod end to its steering
knuckle.
²Start the attaching nut onto the stud of the
outer tie rod.
²While holding the stud of the tie rod stationary
with a wrench, tighten the attaching nut (Fig. 4).
²Using a crowfoot wrench attached to a torque
wrench, tighten the attaching nut to 55 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.).
(21) Install the tire and wheel assemblies back on
vehicle. Tighten the wheel mounting nuts to 135 N´m
(100 ft. lbs.) torque.
(22) Lower the vehicle to ground level.
(23) Install the dash-to-lower coupling seal in
place over the lower coupling's plastic collar.
NOTE: Verify that grease is present on the lip of
the dash-to-coupling seal where it contacts the cou-
pling's plastic collar.
(24) Inside the passenger compartment, reconnect
the steering column lower coupling to the steering
column upper coupling (Fig. 3). Install the coupling
pinch bolt and tighten the pinch bolt nut to a torque
of 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.). Install the pinch bolt
retainer pin.
(25) Remove the steering wheel holder.
(26) While looking under the instrument panel at
the lower coupling, rotate the steering wheel back-
and-forth to verify that the lower coupling does not
squeak against the dash-to-coupling seal.
(27) Perform the POWER STEERING PUMP INI-
TIAL OPERATION service procedure which can be
found in the POWER STEERING PUMP section of
this group to properly fill and bleed the power steer-
ing system.
(28) Check for fluid leaks.
(29) Adjust the front toe setting on the vehicle.
Refer to WHEEL ALIGNMENT in the SUSPENSION
service manual group.
OUTER TIE ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group in this
service manual for the correct lifting procedure.
19 - 26 STEERINGPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 917 of 1285

LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
Insufficient transaxle lubricant is usually the
result of leaks, or inaccurate fluid level check or refill
method. Leakage is evident by the presence of oil
around the leak point. If leakage is not evident, the
condition is probably the result of an underfill.
If air±powered lubrication equipment is used to fill
a transaxle, be sure the equipment is properly cali-
brated. Equipment out of calibration can lead to an
underfill condition.
FLUID LEAKS
Fluid leaks can occur around the input shaft seal,
axleshaft seals, case split lines, and the end cover. Be
careful not to misdiagnose an input shaft seal leak
for an engine rear main seal leak. Also, the transaxle
case sealer (split line) will accumulate dirt and look
like an oil leak.
CLUTCH PROBLEMS
Worn, damaged, or misaligned clutch components
can cause difficult shifting, gear clash, and noise.
A worn or damaged clutch disc, pressure plate, or
release bearing can cause hard shifting and gear
clash.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FLUID DRAIN AND FILL
All NV T350 (A-578) transaxles are equipped with
a fill plug. The fill plug is located on the left side of
the transaxle differential area (Fig. 3). The fluid level
should be within 3/16 inch from the bottom of the
transaxle fill hole (vehicle must be level when check-
ing).All NV T350 (A-578) transaxles are equipped with
a drain plug. The drain plug is located on the lower
right side of the transaxle differential housing (Fig.
4). Tighten drain plug to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
Dry fill lubricant capacity is approximately 1.9-2.2
liters (4.0-4.6 pints). Wipe the outside of the tran-
saxle if any lubricant spills.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
GEARSHIFT KNOB
REMOVAL
(1)Pull shifter boot down and away from shifter knob.
(2) Push down on knob and rotate clockwise to
remove (Fig. 5).
Fig. 3 Fill Plug Location
1 ± RUBBER FILL PLUG
2 ± LEFT DRIVESHAFT SEAL
Fig. 4 Drain Plug Location
1 ± RIGHT DRIVESHAFT SEAL
2 ± DRAIN PLUG
Fig. 5 Gearshift Knob Removal
1 ± GEARSHIFT KNOB
21 - 4 TRANSAXLEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 964 of 1285

(8) Remove case bolts. Remove clutch bellhousing
differential bearing cup. Install shim(s) selected in
Step 7. Then press the bearing cup into clutch bell-
housing.
(9) Install clutch bellhousing. Install and torque
case bolts to 26 N´m (19 ft. lbs.).
(10) Using Special Tool C-4995 and an inch-pound
torque wrench, check turning torque of the differen-
tial assembly (Fig. 164).The turning torque
should be 6 to 12 in. lbs. If the turning torque is
too high, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner
shim. If the turning torque is too low, install a
0.05mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim.(11) Recheck turning torque. Repeat Step 10until
the proper turning torque is obtained.
SPECIFICATIONS
NV T350 (A-578) SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Back-up Lamp Switch........ 24N´m(18ft.lbs.)
Crossover Cable Adj. Screw.... 8N´m(70in.lbs.)
Drain Plug............... 28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Differential Ring Gear Bolts . . . 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.)
Dust Shield to Transaxle.... 12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
End Plate Cover Bolts........ 29N´m(21ft.lbs.)
Lateral Bending Strut to Engine......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Lateral Bending Strut to Trans.......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Left Mount Through Bolt.... 108N´m(80ft.lbs.)
Left Mount to Transaxle...... 68N´m(50ft.lbs.)
Output Bearing Race Ret. Strap......... 11N´m
(96 in. lbs.)
Reverse Fork Bracket........ 11N´m(96in.lbs.)
Reverse Idler Shaft Bolt...... 26N´m(19ft.lbs.)
Shift Cable Bracket to Transaxle........ 28N´m
(250 in. lbs.)
Transaxle Case Bolts......... 29N´m(21ft.lbs.)
Transaxle to Engine Bolt...... 95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Trans. to Eng. Intake Bkt. Bolts......... 95N´m
(70 ft. lbs.)
Vehicle Speed Sensor......... 7N´m(60in.lbs.)
Vertical Bending Strut to Engine........ 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Vertical Bending Strut to Trans.......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
NOTE: Bolts that have thread sealer or torque lock
patches should not be reused. Always install new
bolts in these applications.
Fig. 163 Checking Differential Bearing End Play to
Determine Shim Thickness
1 ± T-HANDLE
2 ± DIAL INDICATOR SET
3 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-4995
Fig. 164 Checking Differential Bearing Turning
Torque
1 ± INCH-POUND TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-4995
NV T350 (A-578) MANUAL TRANSAXLE FLUID
FILL
TRANSAXLE METRIC
MEASUREU. S.
MEASURE
NV T350 1.9-2.2 Liters 2.0-2.3 Quarts
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 51
ADJUSTMENTS (Continued)
Page 969 of 1285

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
The torque converter fills in both the P (Park) and
N (Neutral) positions. Place the selector lever in P
(Park) to be sure that the fluid level check is accu-
rate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground. This will ensure complete oil
level stabilization between differential and
transmission.The fluid should be at normal operat-
ing temperature (approximately 82É C. or 180É F.).
The fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region
(cross-hatched area) on the dipstick (Fig. 1).
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions,
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy therefore, pressures will be
low and will build up slowly.
Improper filling also can raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
that occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming also can result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle dipstick, where it may be mistaken for a
leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
or is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, remove the
oil pan and inspect.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH
A torque converter clutch is standard on all vehi-
cles. The torque converter clutch is activated only in
direct drive and is controlled by the engine electron-
ics. A solenoid on the valve body, is powered by the
powertrain control module to activate the torque con-
verter clutch.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic control system makes the transaxle
fully automatic, and has four important functions to
perform. The components of any automatic control
system may be grouped into the following basic
groups:
²Pressure supply system
²Pressure regulating valves
²Flow control valves
²Clutches
²Band servos
Taking each of these basic groups or systems in
turn, the control system may be described as follows:
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM
The pressure supply system consists of an oil pump
driven by the engine through the torque converter.
The single pump furnishes pressure for all hydraulic
and lubrication requirements.Oil pump housing
assemblies are available with preselected pump
gears.
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES
The pressure regulating valve controls line pres-
sure dependent on throttle opening. The governor
valve transmits regulated pressure to the valve body
(in conjunction with vehicle speed) to control upshift
and downshift.
The throttle valve transmits regulated pressure to
the transaxle (dependent on throttle position) to con-
trol upshift and downshift.
FLOW CONTROL VALVES
The manual valve provides the different transaxle
drive ranges selected by the vehicle operator.
The 1-2 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from first to second or from second to first,
depending on the vehicle operation.
The 2-3 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from second to third or from third to second
depending on the vehicle operation.
Fig. 1 Transaxle Dipstick
1 ± TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 56 TRANSAXLEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 970 of 1285

The kickdown valve makes possible a forced down-
shift from third to second, second to first, or third to
first (depending on vehicle speed). This can be done
by depressing the accelerator pedal past the detent
feel near wide open throttle.
The shuttle valve has two separate functions and
performs each independently of the other. The first is
providing fast release of the kickdown band, and
smooth front clutch engagement when a lift-foot
upshift from second to third is made. The second
function is to regulate the application of the kick-
down servo and band when making third±to±second
kickdown.
The bypass valve provides for smooth application
of the kickdown band on 1-2 upshifts.
The torque converter clutch solenoid allows for the
electronic control of the torque converter clutch. It
also disengages the torque converter at closed throt-
tle. This is done during engine warm-up and part-
throttle acceleration.
The switch valve directs oil to apply the torque
converter clutch in one position. The switch valve
releases the torque converter clutch in the other posi-
tion.
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR
The front and rear clutch pistons, and both servo
pistons, are moved hydraulically to engage the
clutches and apply the bands. The pistons are
released by spring tension when hydraulic pressure
is released. On the 2-3 upshift, the kickdown servo
piston is released by spring tension and hydraulic
pressure.
The accumulator controls the hydraulic pressure
on the apply±side of the kickdown servo during the
1-2 upshift; thereby cushioning the kickdown band
application at any throttle position.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
The Brake Transmission Shifter/Ignition Interlock
(BTSI) is a cable and solenoid operated system. It
interconnects the automatic transmission floor
mounted shifter to the steering column ignition
switch. The system locks the shifter into the PARK
position. The interlock system is engaged whenever
the ignition switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY
position. An additional electrically activated feature
will prevent shifting out of the PARK position unless
the brake pedal is depressed at least one-half inch. A
magnetic holding device integral to the interlock
cable is energized when the ignition is in the RUN
position. When the key is in the RUN position and
the brake pedal is depressed, the shifter is unlocked
and will move into any position. The interlock systemalso prevents the ignition switch from being turned
to the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, unless the
shifter is in the gated PARK position.
The following chart describes the normal operation
of the Brake Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI) sys-
tem. If the ªexpected responseº differs from the vehi-
cle's response, then system repair and/or adjustment
is necessary.
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS
The transaxle is controlled by alever typegear-
shift incorporated within the console. The control has
six selector lever positions: P (Park), R (Reverse), N
(Neutral), and D (Drive), 2 (Second), and 1 (First).
The parking lock is applied by moving the selector
lever past a gate to the (P) position.Do not apply
the parking lock until the vehicle has stopped;
otherwise, a severe banging noise will occur.
COOLER BYPASS VALVE
Some 31TH transaxles are equipped with a cooler
bypass valve (Fig. 2). The valve is designed to bypass
the transaxle oil cooler circuit in cold weather condi-
tions, or when circuit restriction exceeds 25±30 p.s.i.
The valve consists of an integrated check ball and
spring, and a return tube to carry bypassed oil back
to the pump. The bypass valve is mounted to the
valve body transfer plate and is sealed with a rubber
o-ring seal (Fig. 3).
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the ªOFFº
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUNº position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
ªON/RUNº position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the ªLOCKº or9ACCº
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the ªLOCKº or
ªACCº position.
5. Return shifter to
ªPARKº and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to ªLOCKº
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of ªPARKº.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of ªPARKº.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 57
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 971 of 1285
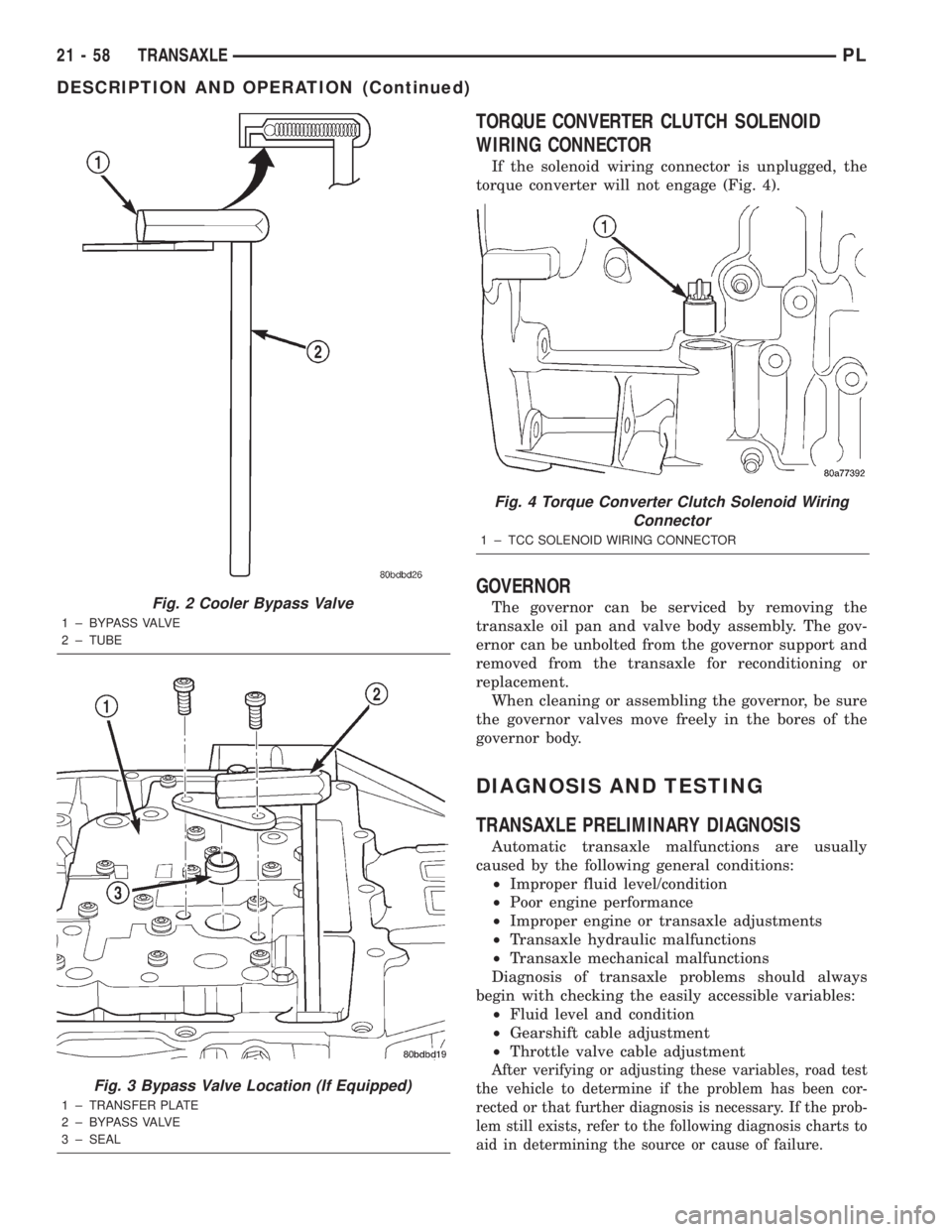
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
WIRING CONNECTOR
If the solenoid wiring connector is unplugged, the
torque converter will not engage (Fig. 4).
GOVERNOR
The governor can be serviced by removing the
transaxle oil pan and valve body assembly. The gov-
ernor can be unbolted from the governor support and
removed from the transaxle for reconditioning or
replacement.
When cleaning or assembling the governor, be sure
the governor valves move freely in the bores of the
governor body.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TRANSAXLE PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
Automatic transaxle malfunctions are usually
caused by the following general conditions:
²Improper fluid level/condition
²Poor engine performance
²Improper engine or transaxle adjustments
²Transaxle hydraulic malfunctions
²Transaxle mechanical malfunctions
Diagnosis of transaxle problems should always
begin with checking the easily accessible variables:
²Fluid level and condition
²Gearshift cable adjustment
²Throttle valve cable adjustment
After verifying or adjusting these variables, road test
the vehicle to determine if the problem has been cor-
rected or that further diagnosis is necessary. If the prob-
lem still exists, refer to the following diagnosis charts to
aid in determining the source or cause of failure.
Fig. 2 Cooler Bypass Valve
1 ± BYPASS VALVE
2 ± TUBE
Fig. 3 Bypass Valve Location (If Equipped)
1 ± TRANSFER PLATE
2 ± BYPASS VALVE
3 ± SEAL
Fig. 4 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Wiring
Connector
1 ± TCC SOLENOID WIRING CONNECTOR
21 - 58 TRANSAXLEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)