1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO Break
[x] Cancel search: BreakPage 858 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
2E-4 TIRE AND WHEELS
TIRE LABEL
The tire label is permanently located on the rear face
of the driver’s door and should be referred to for tire
information. It lists the maximum vehicle load, the tire
size (including the spare tire), and the cold inflation
pressure (including the spare tire).
S PARE TIRE
This vehicle comes equipped with a full-sized spare
tire and wheel.
The temporary spare tire is designed for emergency
use only. The original tire should be repaired or replaced
at the first opportunity and reinstall.
WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, leak air through
welds, have elongated bolt holes, or if the wheel bolts
won’t stay tight or are heavily rusted. Wheels with
excessive runout may cause vehicle vibration.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original
equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim width,
offset, and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper
size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance, and tire clearance to the body and
the chassis. The wheel offset is 49 ± 1 (1.93 ± 0.04
inches). Steel wheels may be identified by a two- or
three-letter code stamped into the rim near the valve
stem. Alloy wheels should have the code, the part
number, and the manufacturer ID cast into the back
side.
INFLATION OF TIRES
The pressure recommended for any vehicle line is care-
fully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, handling,
tread life, and load-carrying capacity.
Tire pressure should be checked monthly or before any
extended trip. Check the tires when they are cold, after
the vehicle has sat for 3 hours or more or has been
driven less than 1 mile. Set the tire pressure to the
specifications on the tire label located on the rear face
of the drive r ’s door. Tire inflation pressure is also given
under “Tire Size and Pressure Specifications” in
this section.
Valve caps or extensions should be on the valves to
keep dust and water out.
For sustained driving at speeds up to 140 km/h (85 mph),
inflate the tires to the pressure recommended on the
tire. Sustained driving at speeds faster than 140 km/h
(85 mph), even if permitted by law, is not advised unless
the vehicle has special high-speed tires available from
many tire dealers. Tire pressures may increase as much
as 41 kPa (6 psi) when the tires are hot.
Higher than recommended tire pressure can cause
Hard ride.
Tire bruising or damage.
Rapid tread wear at the center of the tire.
Lower than recommended pressure can cause
Tire squeal on turns.
Hard steering.
Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread.
Tire rim bruises and rupture.
Tire cord breakage.
High tire temperatures.
Unequal tire pressures on same axle can cause
Uneven braking.
Steering lead.
Reduced handling.
Swerve on acceleration.
Torque steer.
Page 989 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE
FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD
works in a range in which the intervention thresholds
for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively
monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip
is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are
switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically
reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes
control of the brake force distribution between the front
and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake
Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system
but for a fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD
system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD
utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed sensor
to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle
stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function.Service Precautions
Observe the following general precautions during any
ABS/TCS service. Failure to adhere to these
precautions may result in ABS/TCS system damage.
1. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector before
performing the electric welding procedures.
2. Carefully note the routing of the ABS/TCS wiring
and wring components during removal. The ABS/
TCS components are extremely sensitive to EMI
(eletromagnetic interference). Proper mounting is
critical during component service.
3. Disconnect the EBCM connector with the ignition
OFF.
4. Do not hang the suspension components from the
wheel speed sensor cables. The cables may be
damaged.
5. Do not use petroleum based fluids in the master
cylinder. Do not use any containers previously used
for petroleum based fluids. Petroleum causes
swelling and distortion of the rubber components
in the hydraulic brake system, resulting in water
entering the system and lowering the fluid boiling
point.
KAA4F020
Page 1429 of 2053

TRANSFER CASE (PART TIME - 4408) 5D2-31
SSANGYONG MY2002
Cleaning Procedure
Notice: Before cleaning, check the magnet for the
presence of metal particles which indicate internal
chipping of the transfer case.
1. Using cleaning solvent, clean the residual oil and
dirt deposits.
Notice: During cleaning, be careful not to damage
the metal surfaces.
2. After cleaning, dry the parts with low pressure(Max.
20 psi) compressed air.
3. Lubricate the ball bearings and needle bearings
with transfer case oil after cleaning.
Notice: Protect the lubricated bearings from dust.
Inspection Procedure
1. Visually check the all removed parts.
Notice: Always replace the hose coupling, O-ring
and oil seal with new parts.
2. Inspection Terms
Burr : Local rise of material forming protruding
sharp edge
Chip : An area from which a small fragment has
been broken off or cut
Crack : Surface break of line nature indicating
partial or complete separation of material.
Excessive wear : Heavy or obvious wear beyond
expectations considering conditions of
operation.
Indentation : Displacement of material caused
by localized heavy contact.
Galling : Breakdown of metal surface due to
excessive friction between parts. Particles of
the softer material are torn loose and welded to
the harder material.
Nick : Local break or notch, usually displacement
of material rather than loss.
Scoring : Tear or break in metal surface from
contact under abnormal pressure.
Page 1790 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
9L-8 GLASS AND MIRRORS
KAA9L140
Notice: The grid line repair material must be cured
with heat. In order to avoid heat damage to the
interior trim, protect the trim near the repair area
where heat will be applied.
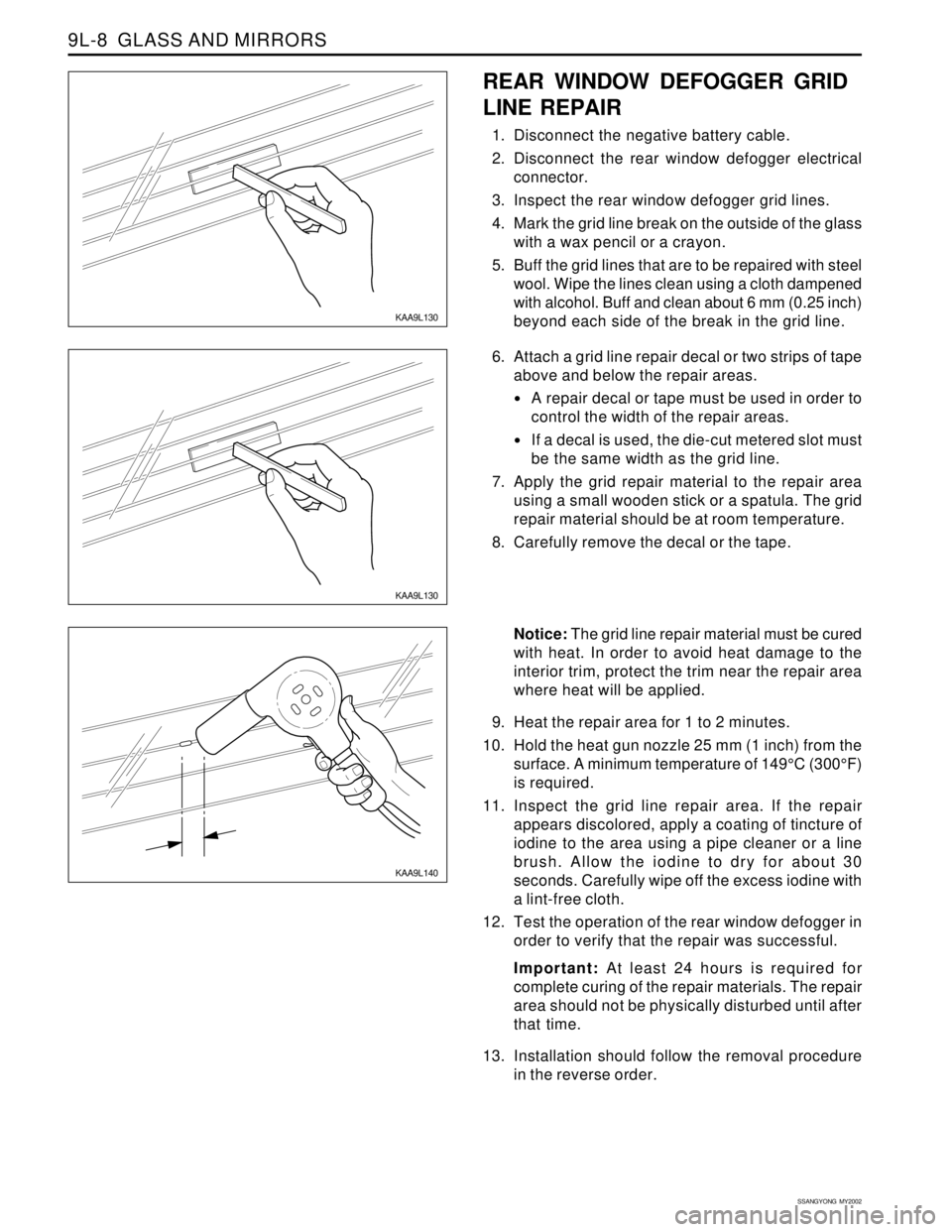
9. Heat the repair area for 1 to 2 minutes.
10. Hold the heat gun nozzle 25 mm (1 inch) from the
surface. A minimum temperature of 149°C (300°F)
is required.
11. Inspect the grid line repair area. If the repair
appears discolored, apply a coating of tincture of
iodine to the area using a pipe cleaner or a line
brush. Allow the iodine to dry for about 30
seconds. Carefully wipe off the excess iodine with
a lint-free cloth.
12. Test the operation of the rear window defogger in
order to verify that the repair was successful.
Important: At least 24 hours is required for
complete curing of the repair materials. The repair
area should not be physically disturbed until after
that time.
13. Installation should follow the removal procedure
in the reverse order.
KAA9L130
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID
LINE REPAIR
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the rear window defogger electrical
connector.
3. Inspect the rear window defogger grid lines.
4. Mark the grid line break on the outside of the glass
with a wax pencil or a crayon.
5. Buff the grid lines that are to be repaired with steel
wool. Wipe the lines clean using a cloth dampened
with alcohol. Buff and clean about 6 mm (0.25 inch)
beyond each side of the break in the grid line.
KAA9L130
6. Attach a grid line repair decal or two strips of tape
above and below the repair areas.
A repair decal or tape must be used in order to
control the width of the repair areas.
If a decal is used, the die-cut metered slot must
be the same width as the grid line.
7. Apply the grid repair material to the repair area
using a small wooden stick or a spatula. The grid
repair material should be at room temperature.
8. Carefully remove the decal or the tape.