1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 420 of 2053

M161 ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E 2 -- 9
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Unscrew the 3 screws and remove the ignition cable
duct cover.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
3. Seperate the cable from the ignition cable and the
spark plug.
4. Remove the 2 bolts from each ignition cable and re-
move the ignition cables.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
Install the ignition cable to the cylinder 2 and 4 and
connect the cable from 1 to 4, and from 2 to 3.
-- T1/1 : Cylinder 1 and 4
-- T1/2 : Cylinder 2 and 3
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
Ignition Cable and Cable Lay- out
1. Firing Order : 1 -- 3 -- 4 -- 2
2. T1/1 : Connect the cylinder 1 + 4
3. T1/2 : Connect the cylinder 2 + 3
Inspection & Maintenance (for E2.3 MSE)
1. Measure the primary resistance between the cable
terminals 1 and 15 after removing the ignition cable
wiring connector (1 and 15) with ignition switch OFF.
Notice:Replace the ignition coil if out of the specified
resistance.
Specified Value
0.9 -- 1.6Ω
2. Measure the primary voltage(T1/1) between the ECU
terminals No.72 and No.69 during the engine crank-
ing (starter motor activated).
Specified Value
200 -- 350 v
Page 423 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1F2
ENGINE CONTROLS
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless other -
wise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Engine and ECM Problem Check Report 1F2 -- 2....
Specifications 1F2 -- 3............................
Engine Data Display Table 1F2 -- 3.................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1F2 -- 4..........
Fuel System Specification 1F2 -- 5.................
Temperature vs Resistance 1F2 -- 5................
Special Tools and Equipment 1F2 -- 6..............
Special Tools Table 1F2 -- 6.......................
Schematic and Routing Diagrams 1F2 -- 7..........
ECM Wiring Diagram
(2.3L DOHC -- MSE 3.53S) 1F2 -- 7..............
Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14................................
Failure Code Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14.....................
Clearing Failure Codes 1F2 -- 14...................
Failure Codes Table 1F2 -- 14.....................
Ignition System 1F2 -- 18...........................
Ignition Coil 1F2 -- 20.............................
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 1F2 -- 22.........
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 1F2 -- 26..........
Camshaft Actuator 1F2 -- 30......................
Knock Sensor (KS) 1F2 -- 32......................
Spark Plug 1F2 -- 34.............................
System Voltage 1F2 -- 38.........................
Ignition Switch 1F2 -- 39..........................
Fuel System 1F2 -- 40..............................
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 42.............................
Fuel Injector 1F2 -- 46............................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 50.....................
Fuel Rail 1F2 -- 52...............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 54.................
Induction System 1F2 -- 56..........................
Throttle Valve Actuator 1F2 -- 56...................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 60..........
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 1F2 -- 64.
Accelerator Pedal Module 1F2 -- 68................Cooling Fan 1F2 -- 72............................
A/C Compressor Relay 1F2 -- 73...................
Cruise Control Switch 1F2 -- 74....................
Traction Control System (TCS) 1F2 -- 75............
Stop Lamp Switch 1F2 -- 76.......................
Engine RPM 1F2 -- 77............................
Exhaust System 1F2 -- 78...........................
Catalytic Converter 1F2 -- 78......................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 80.........................
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 86.....................
Serial Data Communication 1F2--88...............
Internal Failure 1F2 -- 90..........................
Electronic Throttle Controller Safety
Malfunction 1F2 -- 92...........................
Immobilizer 1F2 -- 94.............................
Maintenance and Repair 1F2 -- 95..................
On -- Vehicle Service 1F2 -- 95........................
Discharging the Pressure in Fuel System 1F2 -- 95...
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 95.............................
Fuel Filter 1F2 -- 96..............................
Fuel Tank 1F2 -- 97..............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 98.................
Fuel Rail and Injector 1F2 -- 99....................
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 1F2 -- 100......
Throttle Body (Integrated with the
Actuator) 1F2 -- 101............................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 102.........
Knock Sensor 1F2 -- 102..........................
Pedal Position Sensor 1F2 -- 103...................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 103........................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 104....................
Canister 1F2 -- 104...............................
Camshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 104...............
Crankshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 105..............
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 105..................
Page 441 of 2053
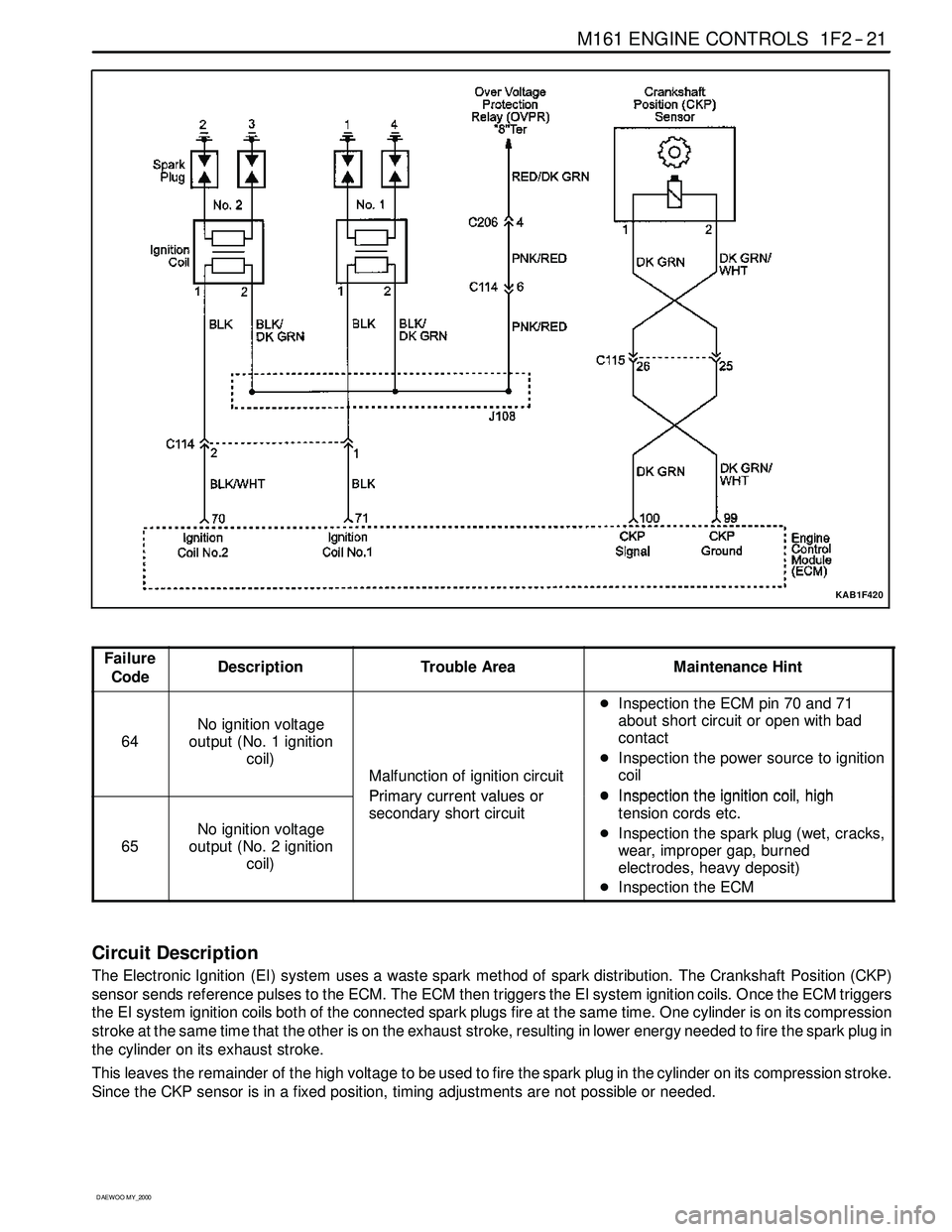
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 21
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F420
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
64
No ignition voltage
output (No. 1 ignition
coil)
Malfunction of ignition circuit
Primarycurrentvaluesor
DInspection the ECM pin 70 and 71
about short circuit or open with bad
contact
DInspection the power source to ignition
coil
DInspectiontheignitioncoilhigh
65
No ignition voltage
output (No. 2 ignition
coil)
Primary currentvalues or
secondary short circuitDInspectiontheignition coil,high
tension cords etc.
DInspection the spark plug (wet, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposit)
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses a waste spark method of spark distribution. The Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor sends reference pulses to the ECM. The ECM then triggers the EI system ignition coils. Once the ECM triggers
the EI system ignition coils both of the connected spark plugs fire at the same time. One cylinder is on its compression
stroke at the same time that the other is on the exhaust stroke, resulting in lower energy needed to fire the spark plug in
the cylinder on its exhaust stroke.
This leaves the remainder of the high voltage to be used to fire the spark plug in the cylinder on its compression stroke.
Since the CKP sensor is in a fixed position, timing adjustments are not possible or needed.
Page 443 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 23
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F150
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
17
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure (no
engine revolution signal)Even through cam position
recognition is normal, no
crankshaft position signal
recognition.
DMonitoring the actual rpm through or
scan tool
18
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(rpm > max. value)When more than applicable
revolution values or
implausibleto60–2teeth.
scantool
DInspection the ECM pin 100, 99 about
short circuit with bad contact
DInspection the CKP sensor
20
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(gap recognition failure)
When implausible recognition
of cam and crank angle signal
or intermittent sensing the
signal or error count of
undetected gap.
p
DInspection the air gap between sensor
and drive plate
DInspection the drive plate (teeth
condition)
DInspection the ECM
67Crankshaft position
sensor adaptation failureWhen faulty crank angle
sensor adaption.
p
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the CKP sensor. During one crankshaft revolution, 58 crankshaft pulseswill
be produced. The ECM uses the 58X reference signal to calculate engine rpm and CKP. The ECM constantly monitors
the number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit and compares them to the number of Camshaft Position (CMP)
signal pulses being received. If the ECM receives and incorrect number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit, this
failure code will set.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling “E” of ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 99 and No. 100 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
1,050 ~ 1,400Ω
Notice:Measure the insulator resistance of the CKP sensor if out of the specified value.
Page 447 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 27
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F430
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
19
Camshaft position
sensor signal :
No. 1 cylinder
recognition failureWhen no cam recognition
signal during TN 24 counts
more. (maintain the constant
low or high level)DInspection the source voltage of CMP
sensor
DInspection the ECM pin 106, 104
about short circuit or open with bad
contact
58
Camshaft position
sensor signal : No. 1
cylinder synchronization
failure
When synchronization fault of
cylinder 1 (TDC recognition)
contact
DInspection the CMP sensor
DInspection the damage of sensor or
sprocket
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The CMP sensor sends a cam position signal to the ECM. If the cam position signal is lost while the engine is running,
the fuel injection system shifts to a calculated sequential fuel injection mode based on the last fuel injection pulse, and
the engine continuous to run.
Camshaft Position Sensor Signal Voltage Inspection
1. Measure the voltage between the ECM terminal No. 11 and No. 106 while the engine speed is at idle.
Specified Value
1.2~1.7v
Notice:The signal voltagewill be changed in the range of 1.2 ~ 1.7 v.
Page 451 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 33
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F440
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
56No. 1 knock sensor
signal failure
When recognition in more
than control gain threshold at
normal operational condition
of other system during over
75 and 3,000 rpm running
area (cylinder 1, 2, 3, 4)DInspection the ECM pin 118, 117 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the KS 1 malfunction
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The KS system is used to detect engine detonation, allowing the ECM to retard the ignition control spark timing based
on the KS signal being received. The KS signal’s amplitude and frequency depend upon the amount of knock being
experienced. The ECM monitors the KS signal and can diagnose the KS sensor and circuitry.
Knock Sensor Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling from ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 118 and No. 117 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
>10 MΩ
Notice:Replace the KS if the measured values is out of the specified values. Check the connector and wire connec-
tion between ECM and the KS if the measured values are normal.
Page 453 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 35
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F450
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
68Random / Multiple
Misfire
When detection misfire of
multiple cylinder for source of
over the emission threshold or
catalyst damage
DInspection the ignition system
DInspection the injection system
DInspection the fuel pressure
DInspection the compression pressure
DInspection the valve timing or
clearance
DInspection the air flow sensor
DInspection the crankshaft position
sensor and air gap
DInspection the engine wiring system
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM)
Circuit Description
The ECM monitors the crankshaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is misfiring. The ECM looks for a quick
drop in crankshaft speed. Misfire multiple cylinder is monitored by engine roughness measuring. The actual roughness
value is compared with the actual (emission and catalyst damage) threshold.
Page 456 of 2053

1F2 -- 38 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
SYSTEM VOLTAGE
KAB1F190
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
08System voltage too low
Malfunction in recognition of
system source voltage.
Less than minimum 8 volts in
2,000 rpm below, or less than
10 volts in 2,000 rpm above.
DMonitoring the actual battery voltages
through the scan tool
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 12, 11, 10, 5 about short
circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the over voltage protection
relay
DInspection the battery
DInspection ECM