1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO wheel torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel torquePage 1374 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
5D1-4 TRANSFER CASE
COMPONENTS OF THE TOD
TRANSFER CASE SYSTEM
Shift Motor
It locates backside transfer case, which drives rotary
helical cam. When mode select switch changes to 4L,
shift fork is on position for 2.48 : 1 by rotation of helical
cam.
Rear Speed Sensor
A hall effect speed sensor which produces a square
wave. 0 to 5 volts direct current signal in response to
a rotating 30-tooth wheel coupled to the rear propeller
shaft inside the transfer case. Each rotation of the rear
propeller shaft will result in 30 speed sensor pulse.
Front Speed Sensor
A hall effect speed sensor which produces a square
wave. 0 to 5 volts direct current signal in response to
a rotating 30-tooth wheel coupled to the front propeller
shaft inside the transfer case. Each rotation of the front
propeller shaft will result in 30 speed sensor pulse.
Electro-Magnetic Clutch
An electromagnetic clutch used to control the amount
of torque applied to the front propeller shaft.
Position Encoder
A set of 4 gray code switches which provide feedback
to the TCCU indicating the position of the shift motor.
Clutch Pedal Position Switch
A switch on vehicles equipped with a manual transmis-
sion which indicates that the clutch pedal is depressed
Park/Neutral Position Switch
A switch on vehicles equipped with an automatic trans-
mission which indicates that the transmission is in neu-
tral.
4H/4L Switch
A switch selects the desired gear ratio.
DEFINITION OF TERMINOLOGY
Shift Inhibit Speed
The vehicle speed limit, which transfer case shifts, is
disallowed. Vehicle speed is indicated by propeller
shaft speed measurement.
Duty Cycle
Duty cycle is the time the electromagnetic clutch is on
divided by the period in which it is being modulated.
Touch-off
A minimum amount of duty cycle applied to the electro
magnetic clutch.
Front Overrun
A condition where the front propeller shaft is turning at
a rate which is faster than the rear propeller shaft.
Rear Overrun
A condition where the rear propeller shaft is turning at
a rate which is faster than the front propeller shaft.
High Range
The highest (numerically lowest = 1 : 1) gear ratio be-
tween the input and outputs of the transfer case.
Low Range
The lowest (numerically highest = 2.48 : 1) gear ratio
between the input and outputs of the transfer case.
OPERATION OF THE TOD
TRANSFER CASE SYSTEM
Initial Operation of TOD Control Unit
When ignition switch is turned to ON, 4WD LOW and
4WD CHECK lamp illuminates for 0.6 second to check
bulb in instrument panel, then perform diagnosis of
system. Refer to “Self-Diagnosis Test” in this section.
Electric Shift System Operation
The electric shift system is responsible for changing
the transfer case gear ratio by controlling the electric
shift motor. The TCCU monitors the 4H/4L switch, park/
neutral position switch, speed sensors, position
encoder, and ignition switch.
A range change is initiated when:
The 4H/4L switch is changed from 4H to 4L or from
4L to 4H.
The motor position (as indicated by the position
encoder) does not match the 4H/4L switch
immediately after the ignition is turned on.
Shift Criteria
When a range change is initiated a diagnostic test will
be completed on the motor, speed sensors, and
position encoder. If the diagnostic test fails, the shift
will not be attempted. If all components are operating
properly, the TCCU will attempt a range change after
the following shift criteria are met:
The transmission is in neutral for 2 seconds after
the shift is requested.
Both propeller shaft speeds are below 87 rpm (2580
pulses/minute). If the transmission is taken out of
neutral before 2 seconds has passed, or either
propeller shaft speed increases above the limit, the
shift will be suspended and the 4L indicator will
continue to blink until the criteria are met again or
the 4H/4L switch is returned to the original position.
Range Change
When the shift criteria are met, the motor is rotated in
the appropriate direction (as determined by the selector
switch) until one of the following occurs:
Page 1375 of 2053
TRANSFER CASE 5D1-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
The motor reaches its destination.
The motor is on for 5 seconds without reaching its
destination. The shift has failed and the TCCU will
respond as default mode.
A fault occurs with either the motor or position
encoder. Refer to the diagnosis requirement.
When the motor is energized, the Ignition, 4H/4L
switch, propeller shaft speeds, and transmission
neutral inputs are ignored.
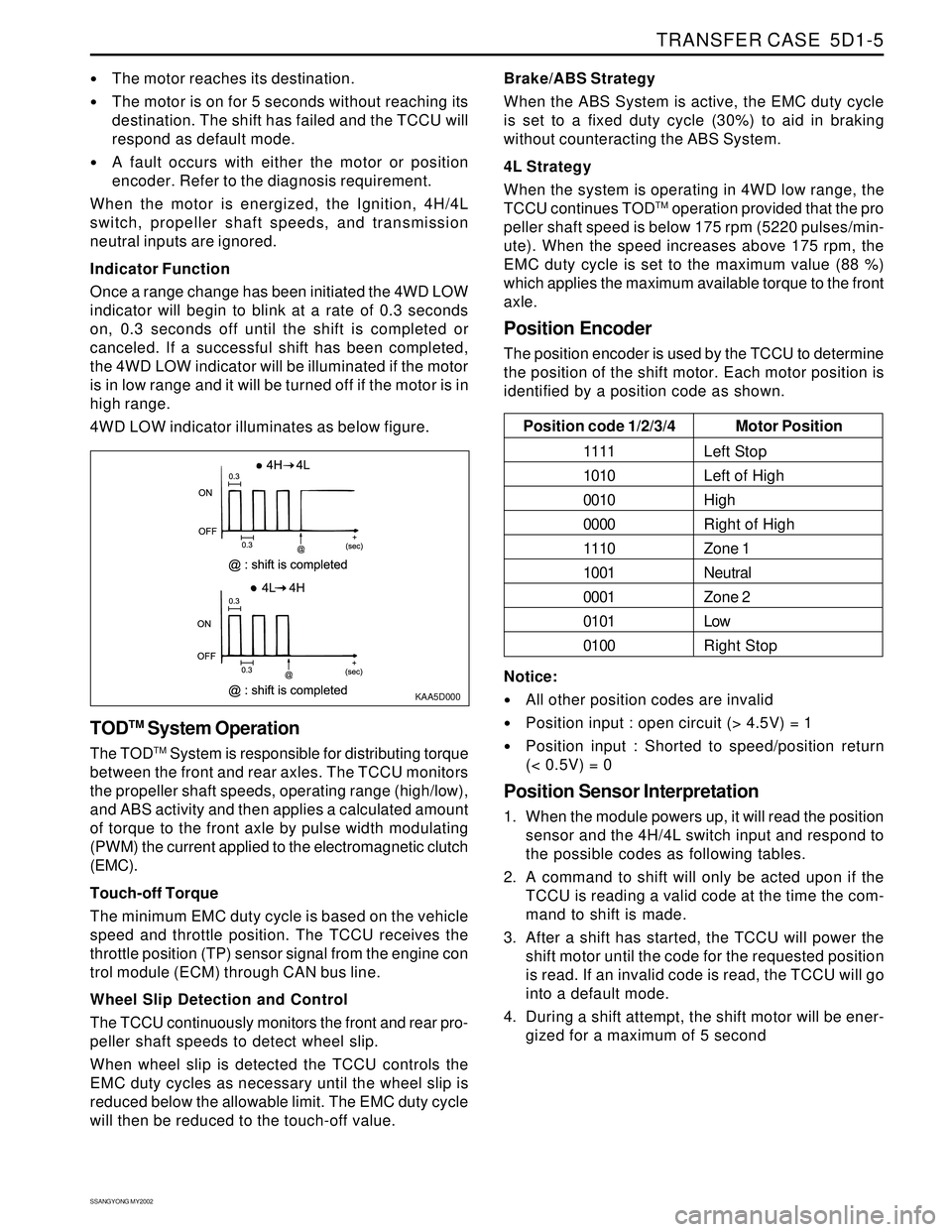
Indicator Function
Once a range change has been initiated the 4WD LOW
indicator will begin to blink at a rate of 0.3 seconds
on, 0.3 seconds off until the shift is completed or
canceled. If a successful shift has been completed,
the 4WD LOW indicator will be illuminated if the motor
is in low range and it will be turned off if the motor is in
high range.
4WD LOW indicator illuminates as below figure.
KAA5D000
TODTM System Operation
The TODTM System is responsible for distributing torque
between the front and rear axles. The TCCU monitors
the propeller shaft speeds, operating range (high/low),
and ABS activity and then applies a calculated amount
of torque to the front axle by pulse width modulating
(PWM) the current applied to the electromagnetic clutch
(EMC).
Touch-off Torque
The minimum EMC duty cycle is based on the vehicle
speed and throttle position. The TCCU receives the
throttle position (TP) sensor signal from the engine con
trol module (ECM) through CAN bus line.
Wheel Slip Detection and Control
The TCCU continuously monitors the front and rear pro-
peller shaft speeds to detect wheel slip.
When wheel slip is detected the TCCU controls the
EMC duty cycles as necessary until the wheel slip is
reduced below the allowable limit. The EMC duty cycle
will then be reduced to the touch-off value.Brake/ABS Strategy
When the ABS System is active, the EMC duty cycle
is set to a fixed duty cycle (30%) to aid in braking
without counteracting the ABS System.
4L Strategy
When the system is operating in 4WD low range, the
TCCU continues TOD
TM operation provided that the pro
peller shaft speed is below 175 rpm (5220 pulses/min-
ute). When the speed increases above 175 rpm, the
EMC duty cycle is set to the maximum value (88 %)
which applies the maximum available torque to the front
axle.
Position Encoder
The position encoder is used by the TCCU to determine
the position of the shift motor. Each motor position is
identified by a position code as shown.
Motor Position
Left Stop
Left of High
High
Right of High
Zone 1
Neutral
Zone 2
Low
Right Stop Position code 1/2/3/4
1111
1010
0010
0000
1110
1001
0001
0101
0100
Notice:
All other position codes are invalid
Position input : open circuit (> 4.5V) = 1
Position input : Shorted to speed/position return
(< 0.5V) = 0
Position Sensor Interpretation
1. When the module powers up, it will read the position
sensor and the 4H/4L switch input and respond to
the possible codes as following tables.
2. A command to shift will only be acted upon if the
TCCU is reading a valid code at the time the com-
mand to shift is made.
3. After a shift has started, the TCCU will power the
shift motor until the code for the requested position
is read. If an invalid code is read, the TCCU will go
into a default mode.
4. During a shift attempt, the shift motor will be ener-
gized for a maximum of 5 second
Page 1399 of 2053
TRANSFER CASE 5D1-77
SSANGYONG MY2002
KAA5D420
KAA5D590
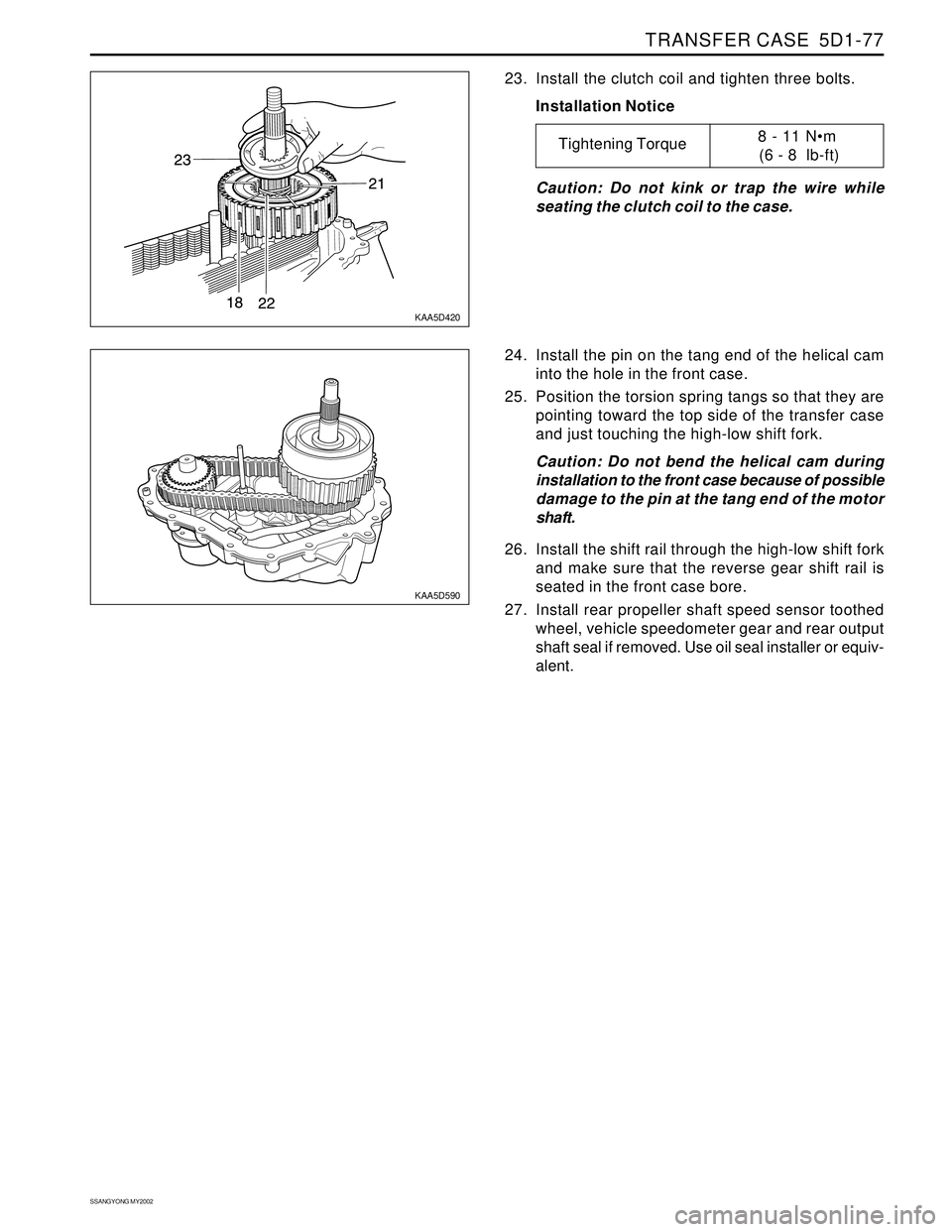
23. Install the clutch coil and tighten three bolts.
Installation Notice
Caution: Do not kink or trap the wire while
seating the clutch coil to the case.
24. Install the pin on the tang end of the helical cam
into the hole in the front case.
25. Position the torsion spring tangs so that they are
pointing toward the top side of the transfer case
and just touching the high-low shift fork.
Caution: Do not bend the helical cam during
installation to the front case because of possible
damage to the pin at the tang end of the motor
shaft.
26. Install the shift rail through the high-low shift fork
and make sure that the reverse gear shift rail is
seated in the front case bore.
27. Install rear propeller shaft speed sensor toothed
wheel, vehicle speedometer gear and rear output
shaft seal if removed. Use oil seal installer or equiv-
alent.
Tightening Torque8 - 11 Nm
(6 - 8 lb-ft)
Page 1446 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
6A-4 POWER STEERING SYSTEM
KAA6A020
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
PRESSURE TEST
Tools Required
124 589 06 21 00 Power Steering Pump Testing Unit
Check the fluid pressure as follow to trouble is in the
pump or gear unit.
Test Procedure
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the oil pump
and connect a pressure gauge between the oil
pump and pressure hose.
2. Bleed the system. Start the engine and turn the
steering wheel form lock several times until oil
temperature is up to 50 °C.
3. Run the engine at 1,000 rpm.
4. Close the gauge valve fully, and read pressure.
The pump pressure with the valve closed should
be between 7,355 kPa to 8,041 kPa (1,067 psi to
1,166 psi).
Notice: Do not keep the valve closed for more
than 10 seconds.
5. Remove the pressure gauge and connect the pres-
sure hose.
6. Do bleeding procedure.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
LEAK TEST
General Procedure
Inspect the following :
The power steering fluid reservoir for overfill.
Fluid for aeration and overflow.
The hoses for loose connections.
The torsion bar, stub shaft and adjuster seals for
leaks.
The component sealing surfaces for damage.
Important: Verify the exact point of the leak. The point
from which the fluid is dripping is not necessarily the
point at which the system is leaking. When service is
required, clean the leak area upon disassembly,
replace the leaking seal, check the component sealing
surfaces for damage and reset the torque bolt to
specifications required.
External Leak Check
The purpose of this procedure is to pinpoint the location
of the leak. In some cases, the leak can be easily lo-
cated, but seepage-type leaks may be harder to find.
To locate seepage leaks, use the following method:
1. With the engine off, wipe dry the complete power
steering system.
2. Check the power steering fluid level in the pump’s
reservoir. Adjust the fluid level as necessary.
Refer to “Checking and Adding Fluid” in this
section.
Notice: Do not hold the steering wheel at a stop
for any length of time as this can damage the
power steering pump.
3. Start the engine. Turn the steering wheel counter-
clockwise and clockwise from stop to stop several
times.
4. Find the exact area of the leak and repair it.
Page 1455 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
6A-4 POWER STEERING SYSTEM
KAA6A020
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
PRESSURE TEST
Tools Required
124 589 06 21 00 Power Steering Pump Testing Unit
Check the fluid pressure as follow to trouble is in the
pump or gear unit.
Test Procedure
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the oil pump
and connect a pressure gauge between the oil
pump and pressure hose.
2. Bleed the system. Start the engine and turn the
steering wheel form lock several times until oil
temperature is up to 50 °C.
3. Run the engine at 1,000 rpm.
4. Close the gauge valve fully, and read pressure.
The pump pressure with the valve closed should
be between 7,355 kPa to 8,041 kPa (1,067 psi to
1,166 psi).
Notice: Do not keep the valve closed for more
than 10 seconds.
5. Remove the pressure gauge and connect the pres-
sure hose.
6. Do bleeding procedure.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
LEAK TEST
General Procedure
Inspect the following :
The power steering fluid reservoir for overfill.
Fluid for aeration and overflow.
The hoses for loose connections.
The torsion bar, stub shaft and adjuster seals for
leaks.
The component sealing surfaces for damage.
Important: Verify the exact point of the leak. The point
from which the fluid is dripping is not necessarily the
point at which the system is leaking. When service is
required, clean the leak area upon disassembly,
replace the leaking seal, check the component sealing
surfaces for damage and reset the torque bolt to
specifications required.
External Leak Check
The purpose of this procedure is to pinpoint the location
of the leak. In some cases, the leak can be easily lo-
cated, but seepage-type leaks may be harder to find.
To locate seepage leaks, use the following method:
1. With the engine off, wipe dry the complete power
steering system.
2. Check the power steering fluid level in the pump’s
reservoir. Adjust the fluid level as necessary.
Refer to “Checking and Adding Fluid” in this
section.
Notice: Do not hold the steering wheel at a stop
for any length of time as this can damage the
power steering pump.
3. Start the engine. Turn the steering wheel counter-
clockwise and clockwise from stop to stop several
times.
4. Find the exact area of the leak and repair it.
Page 1476 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
6C-8 POWER STEERING GEAR
KAA6C040
KAA6C030
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
RACK AND PINION ASSEMBLY
Tools Required
661 589 13 33 00 Ball Joint Remover
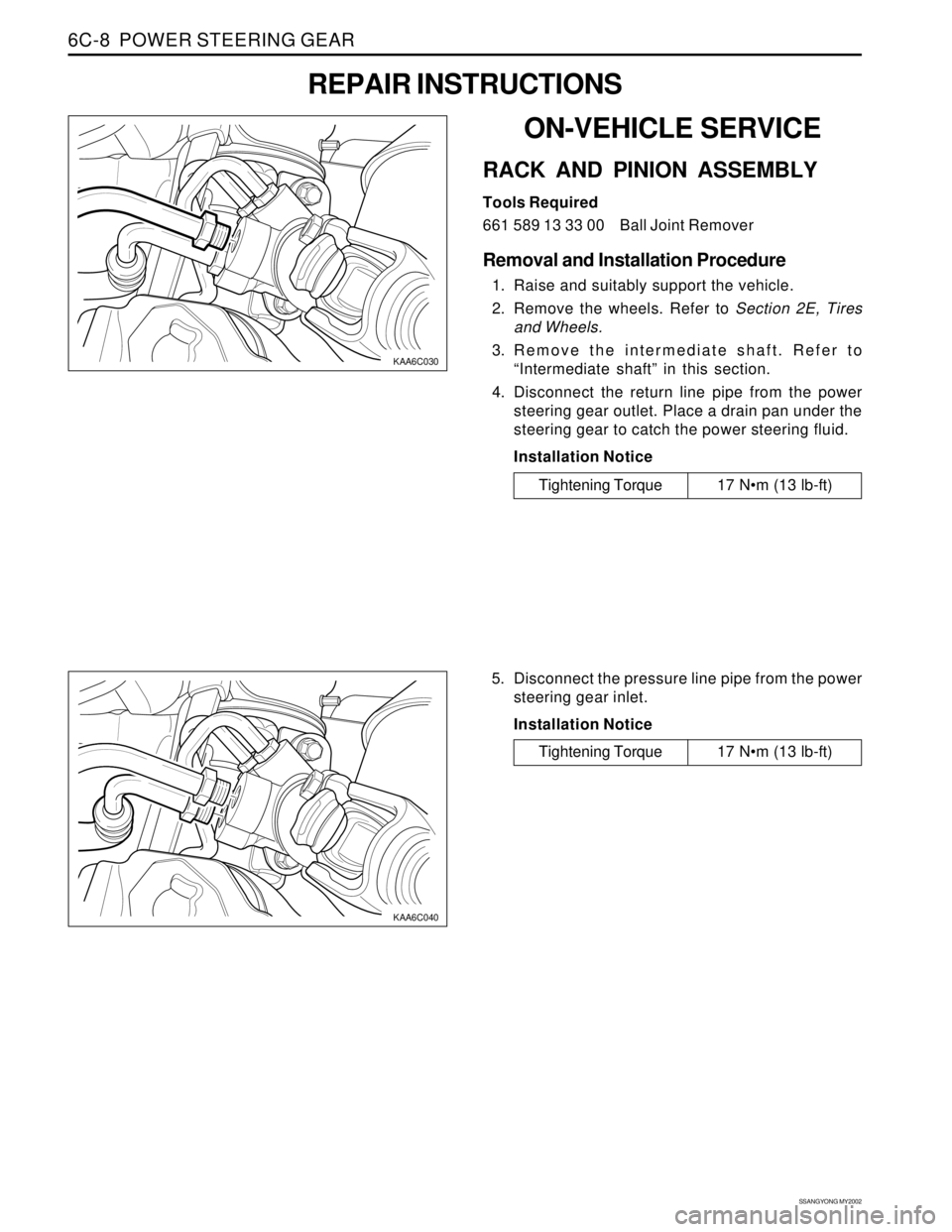
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheels. Refer to Section 2E, Tires
and Wheels.
3. Remove the intermediate shaft. Refer to
“Intermediate shaft” in this section.
4. Disconnect the return line pipe from the power
steering gear outlet. Place a drain pan under the
steering gear to catch the power steering fluid.
Installation Notice
REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
Tightening Torque 17 Nm (13 lb-ft)
5. Disconnect the pressure line pipe from the power
steering gear inlet.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 17 Nm (13 lb-ft)
Page 1477 of 2053
POWER STEERING GEAR 6C-9
SSANGYONG MY2002
KAA6C140
KAA6C050
KAA6C050
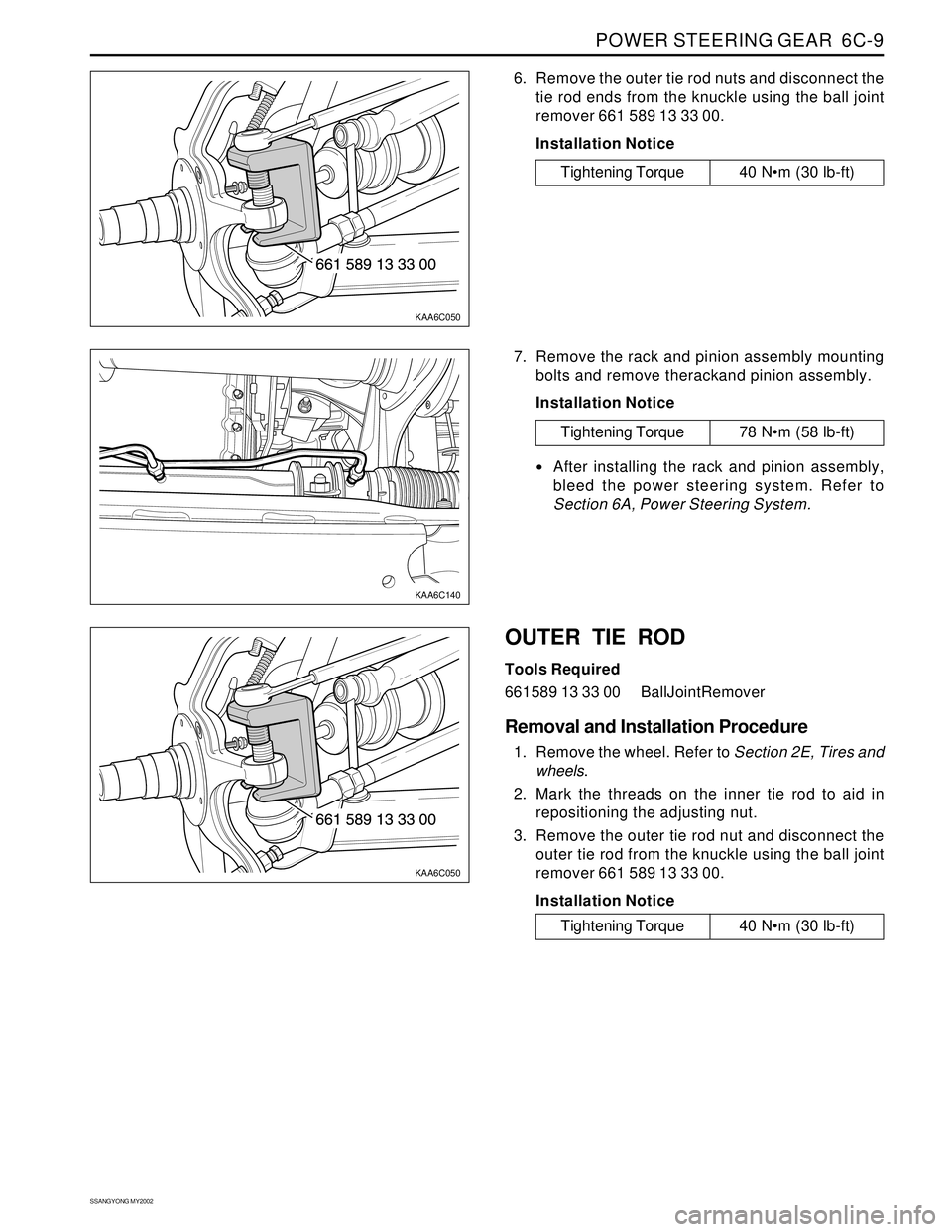
6. Remove the outer tie rod nuts and disconnect the
tie rod ends from the knuckle using the ball joint
remover 661 589 13 33 00.
Installation Notice
7. Remove the rack and pinion assembly mounting
bolts and remove therackand pinion assembly.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 40 Nm (30 lb-ft)
After installing the rack and pinion assembly,
bleed the power steering system. Refer to
Section 6A, Power Steering System.
OUTER TIE ROD
Tools Required
661589 13 33 00 BallJointRemover
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Remove the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
wheels.
2. Mark the threads on the inner tie rod to aid in
repositioning the adjusting nut.
3. Remove the outer tie rod nut and disconnect the
outer tie rod from the knuckle using the ball joint
remover 661 589 13 33 00.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 78 Nm (58 lb-ft)
Tightening Torque 40 Nm (30 lb-ft)
Page 1484 of 2053
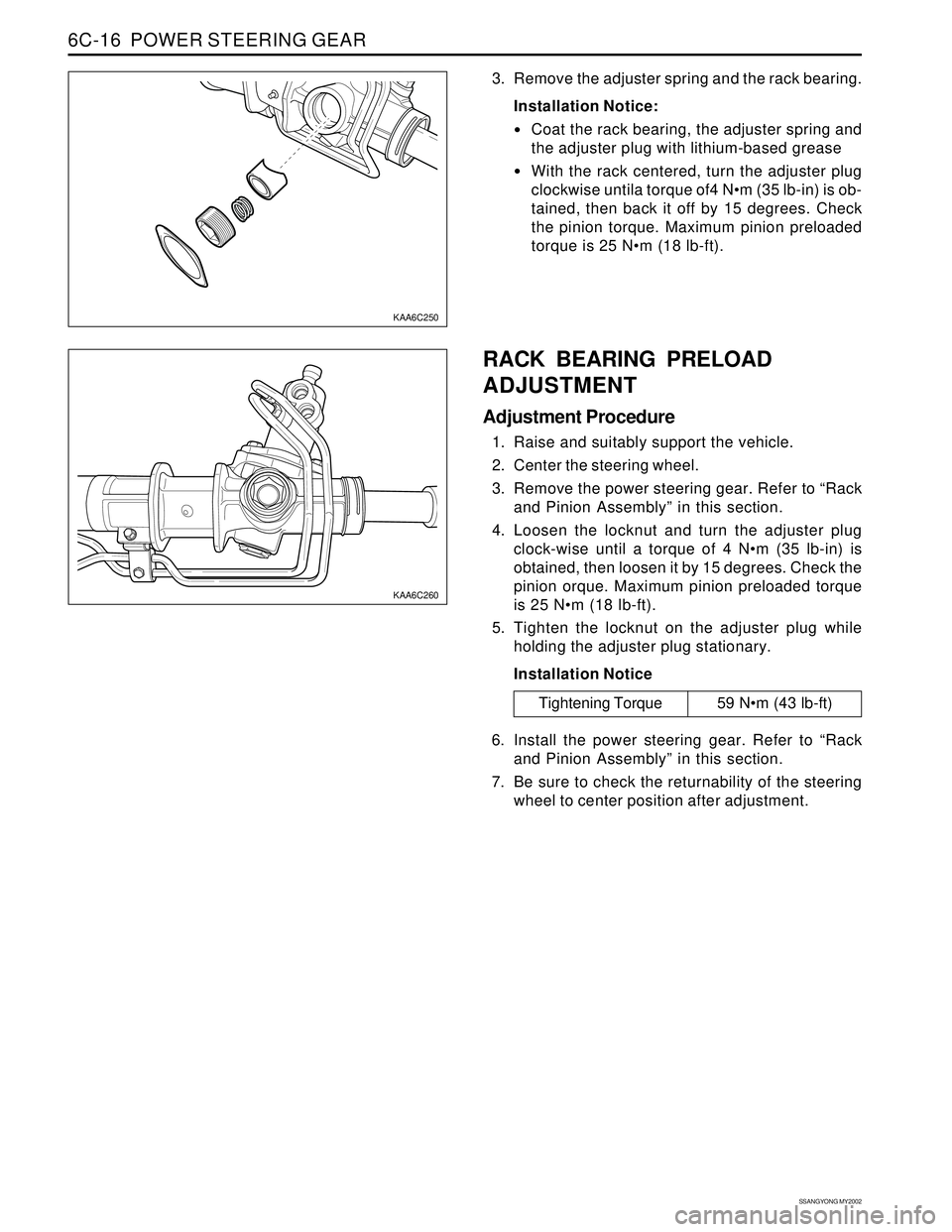
SSANGYONG MY2002
6C-16 POWER STEERING GEAR
KAA6C250
KAA6C260
3. Remove the adjuster spring and the rack bearing.
Installation Notice:
Coat the rack bearing, the adjuster spring and
the adjuster plug with lithium-based grease
With the rack centered, turn the adjuster plug
clockwise untila torque of4 Nm (35 lb-in) is ob-
tained, then back it off by 15 degrees. Check
the pinion torque. Maximum pinion preloaded
torque is 25 Nm (18 lb-ft).
RACK BEARING PRELOAD
ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment Procedure
1. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
2. Center the steering wheel.
3. Remove the power steering gear. Refer to “Rack
and Pinion Assembly” in this section.
4. Loosen the locknut and turn the adjuster plug
clock-wise until a torque of 4 Nm (35 lb-in) is
obtained, then loosen it by 15 degrees. Check the
pinion orque. Maximum pinion preloaded torque
is 25 Nm (18 lb-ft).
5. Tighten the locknut on the adjuster plug while
holding the adjuster plug stationary.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 59 Nm (43 lb-ft)
6. Install the power steering gear. Refer to “Rack
and Pinion Assembly” in this section.
7. Be sure to check the returnability of the steering
wheel to center position after adjustment.