1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1204 of 1938
(2) Using a suitable ring expander, remove upper
and intermediate piston rings (Fig. 77).
(3) Remove the upper oil ring side rail, lower oil
ring side rail and then oil ring expander from piston.
(4) Clean ring grooves of any carbon deposits.
PISTON RINGSÐINSTALLATION
(1) Install rings with manufacturers I.D. mark fac-
ing up, to the top of the piston (Fig. 78).
CAUTION: Install piston rings in the following
order:
a. Oil ring expander.b. Upper oil ring side rail.
c. Lower oil ring side rail.
d. No. 2 Intermediate piston ring.
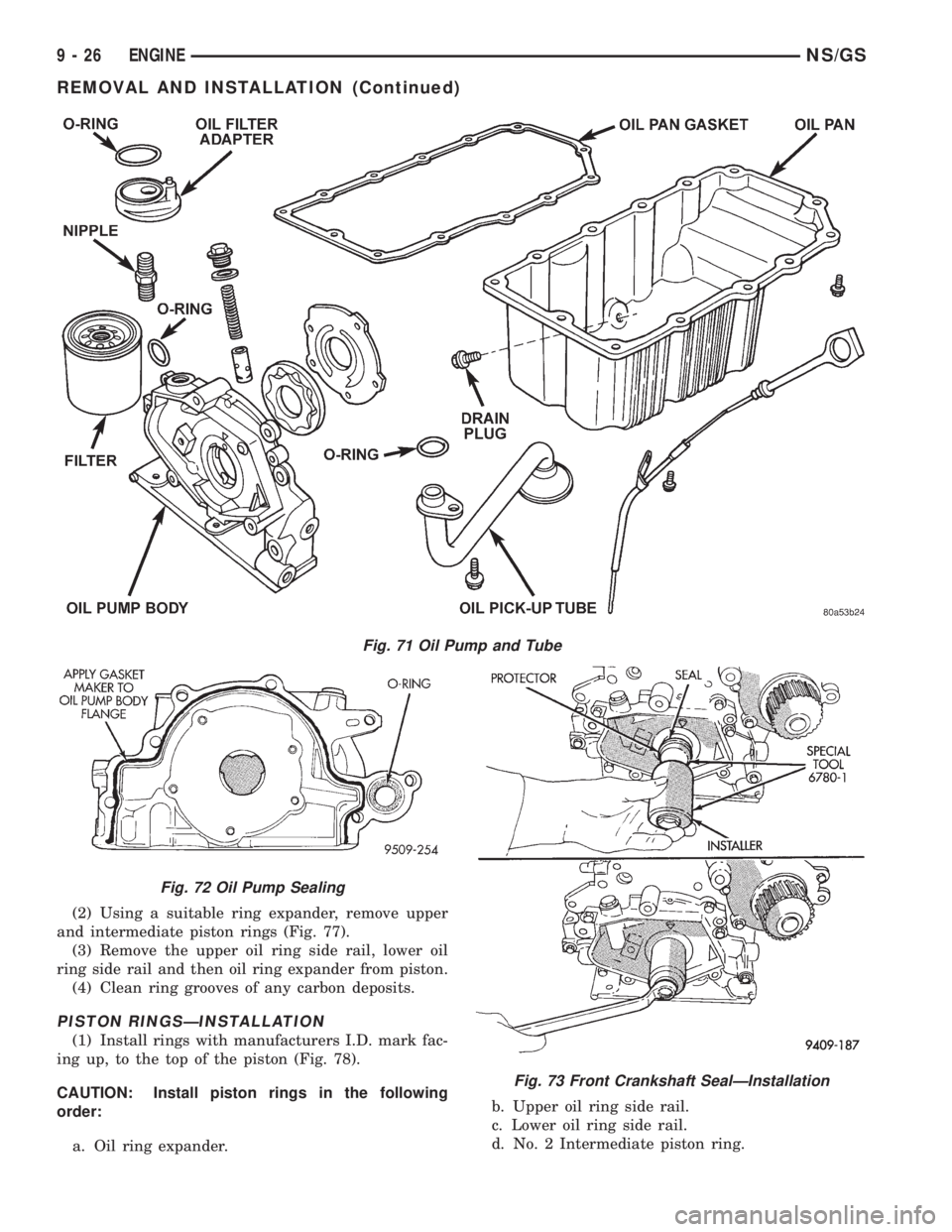
Fig. 71 Oil Pump and Tube
Fig. 72 Oil Pump Sealing
Fig. 73 Front Crankshaft SealÐInstallation
9 - 26 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1205 of 1938
e. No. 1 Upper piston ring.
f. Install the side rail by placing one end between
the piston ring groove and the expander. Hold end
firmly and press down the portion to be installed
until side rail is in position.Do not use a piston
ring expander (Fig. 79).
(2) Install upper side rail first and then the lower
side rail.
(3) Install No. 2 piston ring and then No. 1 piston
ring (Fig. 78).(4) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in (Fig.
80).
(5) Position oil ring expander gap at least 45É from
the side rail gaps butnoton the piston pin center or
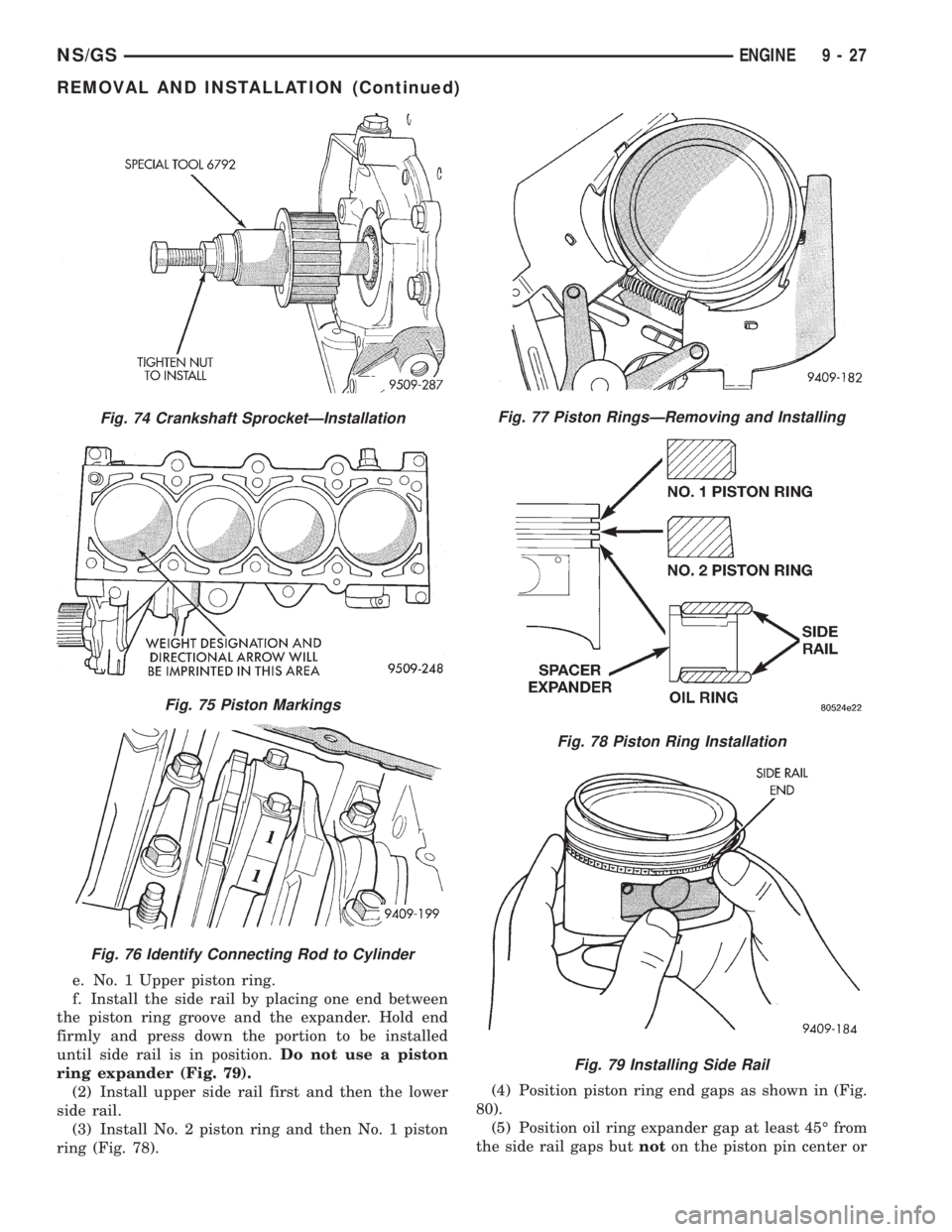
Fig. 74 Crankshaft SprocketÐInstallation
Fig. 75 Piston Markings
Fig. 76 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
Fig. 77 Piston RingsÐRemoving and Installing
Fig. 78 Piston Ring Installation
Fig. 79 Installing Side Rail
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 27
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1206 of 1938

on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is impor-
tant for oil control.
PISTON AND ROD ÐINSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap.
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located as shown in (Fig. 80).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
(Fig. 81).Be sure position of rings does not
change during this operation.
(4) The weight stamp designation L or H will be in
the front half of the piston should face toward the
front of the engine for SOHC engine. The arrow
should face toward the front of the engine for DOHC
engine (Fig. 75).
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insertrod and piston assembly into cylinder bore and guide
rod over the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
(7) Install rod caps. InstallNewbolts and tighten
to 27 N´m (20 ft.lb.) Plus 1/4 turn.
VIBRATION DAMPER
NOTE: If a gap is found in the crankshaft damper,
in the area where the Poly-V Generator belt rides
this is normal and is acceptable (Fig. 82).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure outlined in that sec-
tion.
(2) Remove crankshaft damper bolt. Remove
damper using the large side of Special Tool 1026 and
insert 6827±A (Fig. 83).
Fig. 80 Piston Ring End Gap Position
Fig. 81 Installing Piston
Fig. 82 Weld Gap
Fig. 83 Crankshaft DamperÐRemoval
9 - 28 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1207 of 1938

INSTALLATION
(1) Install crankshaft damper using M12-1.75 x
150 mm bolt, washer, thrust bearing and nut from
Special Tool 6792. Install crankshaft damper bolt and
tighten to 142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 84).
(2) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive section for proce-
dure.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP
(1) To remove the relief valve, proceed as follows:
(2) Remove the threaded plug and gasket from the
oil pump (Fig. 85).
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve must be
installed as shown in (Fig. 85) or serious damage
may occur.
(3) Remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 85).(4) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover.
(5) Remove pump rotors.
(6) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear (Fig. 86).
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Special Tool C-3422-B or equivalent.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear. Measure stem
about 60 mm beneath the valve lock grooves.
(3) If valve stems are worn more than 0.05 mm
(.002 in.), replace valve.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 87). Refer to Valve Guide Specification
Chart for specifications. Replace guides if they are
not within specification.
(3) Check valve guide height (Fig. 88).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
Fig. 84 Crankshaft DamperÐInstallation
Fig. 85 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
Fig. 86 Oil Pump
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1208 of 1938
should be tested Special Tool C-647. As an example,
the compression length of the spring to be tested is
33.34 mm (1-5/16 inches). Turn tool table until sur-
face is in line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 inch) mark
on the threaded stud and the zero mark on the front.
Place spring over stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device (Fig. 89). Pull on torque
wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two.
This will give the spring load at test length. Frac-
tional measurements are indicated on the table for
finer adjustments. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications. The Following specifications
apply to both intake and exhaust valve springs.²Valve Closed Nominal ForceÐ 67 lbs. @ 39.8 mm
(1.57 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal ForceÐ 160 lbs. @ 32.6 mm
(1.28 in.)
(2) Verify springs are not distorted with a steel
square and surface plate, check springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle.
(2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 90). Intake valves with less than
0.95 mm (1/32 inch.) margin and Exhaust valves
with less than 1.05 mm (3/64 inch) margin should be
discarded.
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained. For valve specifications see Valve Specifica-
tion Chart.
(4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat and
valve guide using a valve seat runout dial indicator.
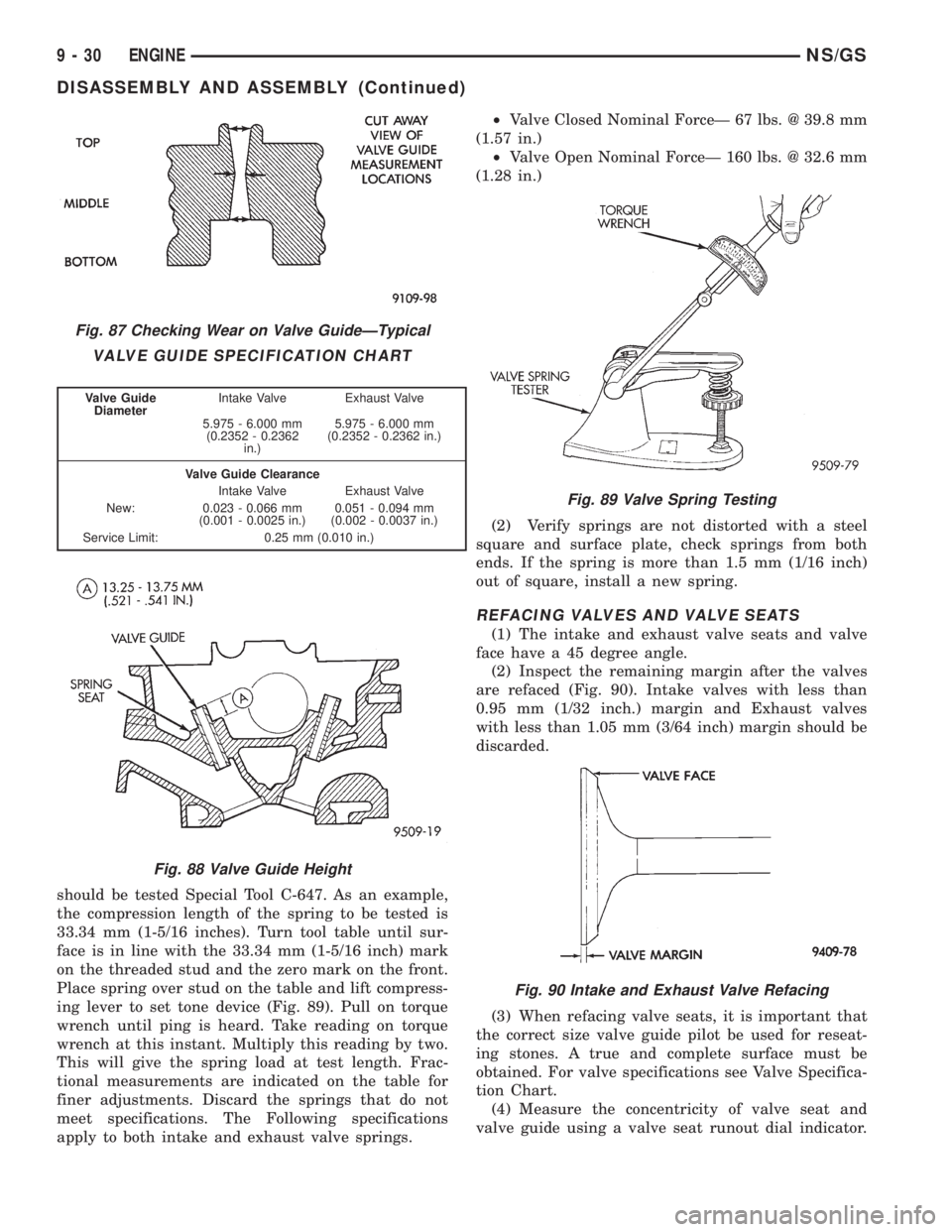
Fig. 87 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
VALVE GUIDE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Guide
DiameterIntake Valve Exhaust Valve
5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362
in.)5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362 in.)
Valve Guide Clearance
Intake Valve Exhaust Valve
New: 0.023 - 0.066 mm
(0.001 - 0.0025 in.)0.051 - 0.094 mm
(0.002 - 0.0037 in.)
Service Limit: 0.25 mm (0.010 in.)
Fig. 88 Valve Guide Height
Fig. 89 Valve Spring Testing
Fig. 90 Intake and Exhaust Valve Refacing
9 - 30 ENGINENS/GS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1209 of 1938

Total runout should not exceed. 0.051 mm (0.002
inch.) (total indicator reading).
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
²Intake valve seat diameter is 33 mm (1.299 in.)
²Exhaust valve seat diameter is 28 mm (1.102
in.)
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75 to 1.25 mm
(0.030 to 0.049 in.) (Fig. 91).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip to 43.51 - 44.57 mm (1.71 - 1.75 in.) for exhaust
valve and 45.01 - 46.07 mm (1.77 - 1.81 in.) for
intake valve over spring seat when installed in the
head (Fig. 92). The valve tip chamfer may need to be
reground to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 93). The valve stem seals
should be pushed firmly and squarely over valve
guide.
CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Face Angle
Intake and
Exhaust:45 - 45 1/2É
Head Diameter
Intake: 33.12 - 33.37 mm (1.303 - 1.313 in.)
Exhaust: 28.57 - 28.83 mm (1.124 - 1.135 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake: 114.69 - 115.19 mm (4.515 - 4.535 in.)
Exhaust: 116.94 - 117.44 mm (4.603 - 4.623 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake: 5.934 - 5.952 mm (0.2337 - 0.2344 in.)
Exhaust: 5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.2326 - 0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake: 1.15 - 1.48 mm (0.0452 - 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust: 1.475 - 1.805 mm (0.0580 - 0.0710 in.)
Fig. 91 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 92 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 31
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1210 of 1938

CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring
retainers with valve spring compressor the locks
can become dislocated. Check to make sure both
locks are in their correct location after removing
tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height B after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 92). Make sure mea-
surements are taken from top of spring seat to the
bottom surface of spring retainer. If height is greater
than 40.18 mm (1.58 in.), install a 0.762 mm (0.030
in.) spacer under the valve spring seat to bring
spring height back within specification.
(5) Install rocker arm shafts as previously
described in this section.
(6) Checking dry lash. Dry lash is the amount of
clearance that exists between the base circle of an
installed cam and the rocker arm roller when the
adjuster is drained of oil and completely collapsed.
Specified dry lash is 1.17 mm (0.046 in.) for intake
and 1.28 mm (0.050 in.) for exhaust. After performing
dry lash check, refill adjuster with oil and allow 10
minutes for adjuster/s to bleed down before rotating
cam.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT JOURNALS
INSPECTING CYLINDER HEAD
Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm (0.004
inch) (Fig. 94).
Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for wear.
Check camshaft journals for scratches and worn
areas. If light scratches are present, they may be
removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep scratches
are present, replace the camshaft and check the cyl-
inder head for damage. Replace the cylinder head if
worn or damaged. Check the lobes for pitting and
wear. If the lobes show signs of wear, check the cor-
responding rocker arm roller for wear or damage.Replace rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster if worn or
damaged. If lobes show signs of pitting on the nose,
flank or base circle; replace the camshaft.
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block. Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
OIL PUMP
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the oil pump should be smooth. Replace pump cover
if scratched or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 95). If a 0.076 mm (0.003 inch.) feeler
gauge can be inserted between cover and straight
edge, cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301
inch.) or less (Fig. 96), or if the diameter is 79.95 mm
(3.148 inches) or less, replace outer rotor.
Fig. 93 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
Fig. 94 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
Fig. 95 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
9 - 32 ENGINENS/GS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1211 of 1938
(4) If inner rotor measures 7.64 mm (.301 inch) or
less replace inner rotor (Fig. 97).
(5) Slide outer rotor into pump housing, press to
one side with fingers and measure clearance between
rotor and housing (Fig. 98). If measurement is 0.39
mm (0.015 inch.) or more, replace housing only if
outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into pump housing. If clear-
ance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 99) is .203
mm (.008 inch) or more, replace both rotors.
(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
pump housing, between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge
of .102 mm (.004 inch) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 100).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
(8) Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for
scoring and free operation in its bore. Small marks
may be removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
(9) The relief valve spring has a free length of
approximately 60.7 mm (2.39 inches) it should test
between 18 and 19 pounds when compressed to 40.5
mm (1.60 inches). Replace spring that fails to meet
specifications.(10) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings, damaged
or missing oil pick-up tube o-ring, clogged oil pick-up
tube screen, clogged oil filter and stuck open pres-
sure relief valve or other reasons for oil pressure
loss.
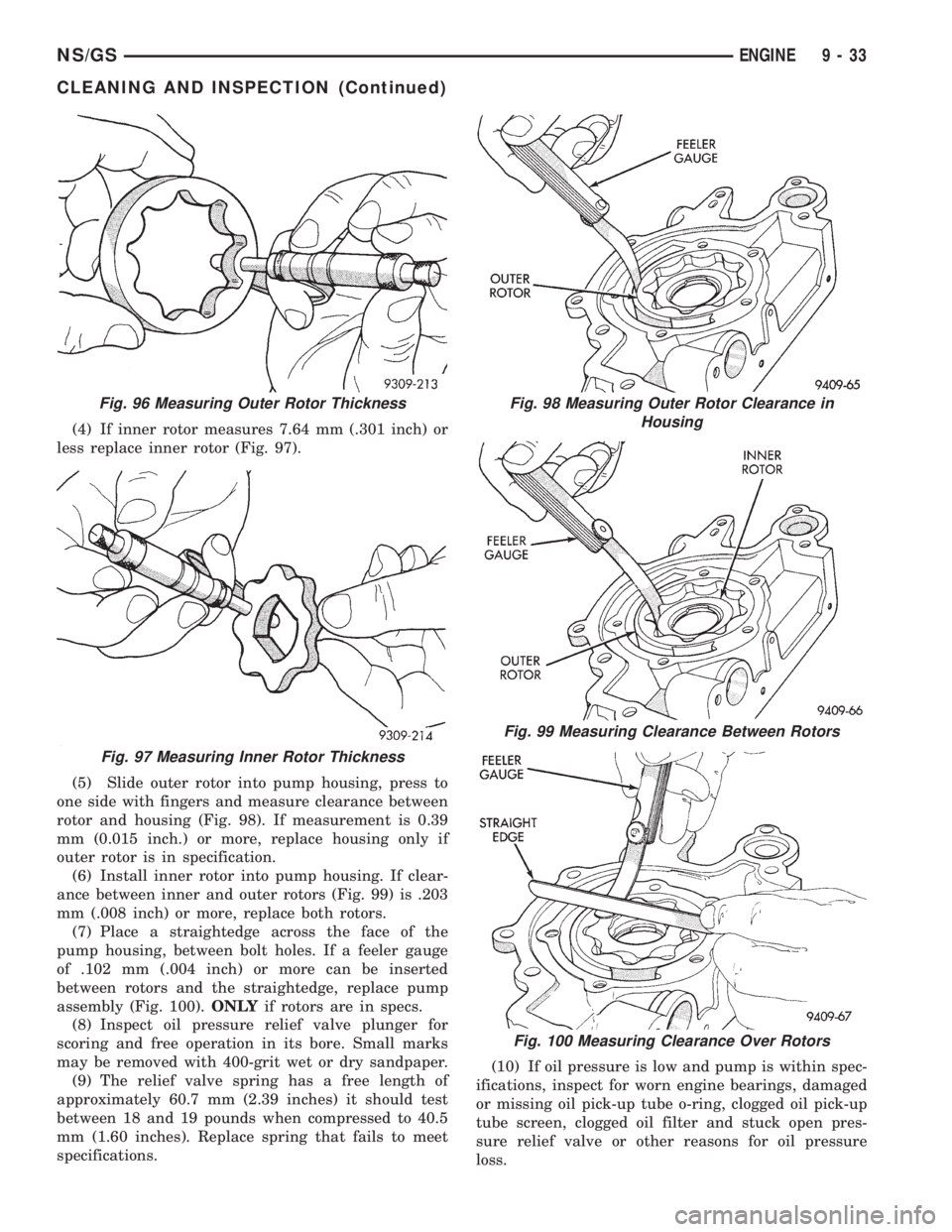
Fig. 96 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 97 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
Fig. 98 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance in
Housing
Fig. 99 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
Fig. 100 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 33
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)