Page 2059 of 2543
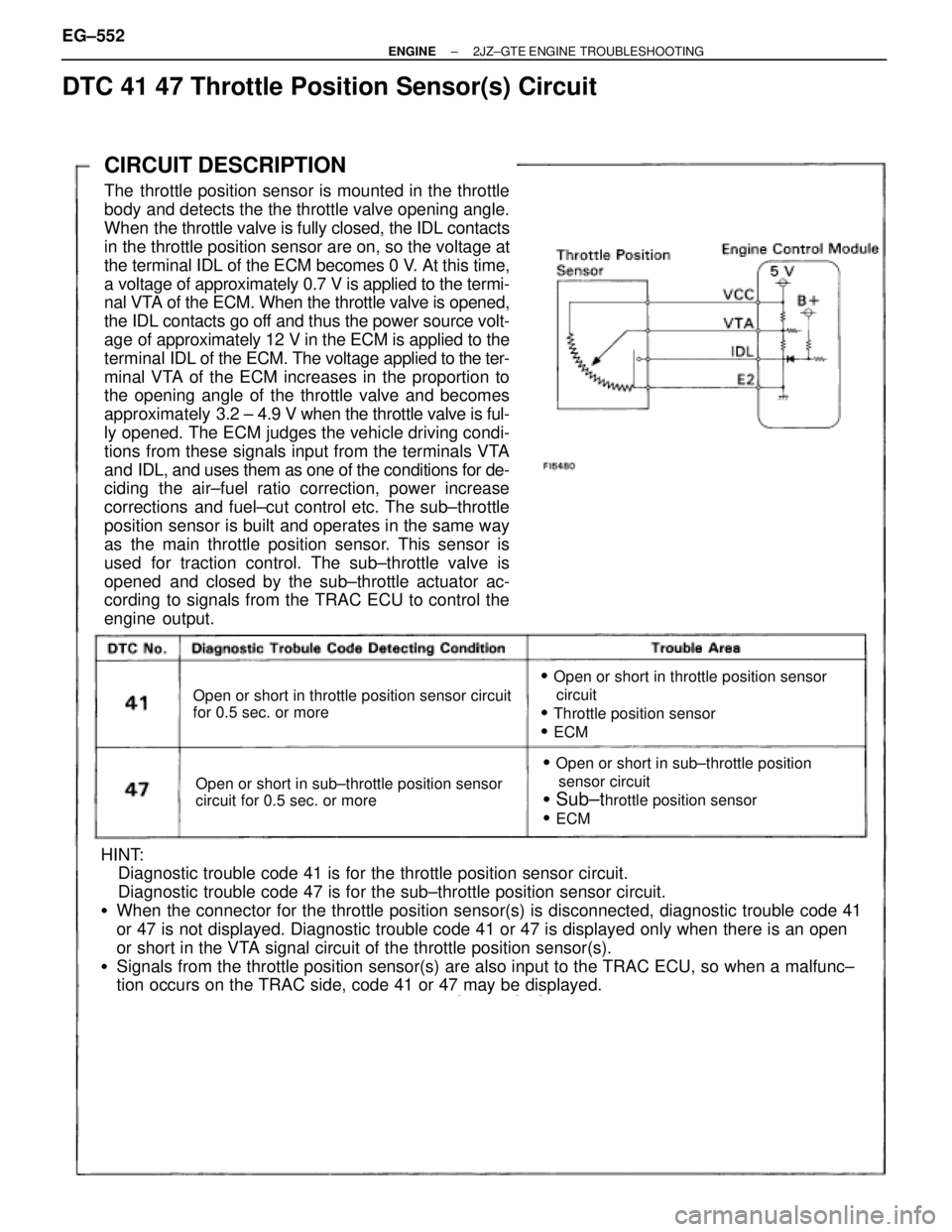
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The throttle position sensor is mounted in the throttle
body and detects the the throttle valve opening angle.
When the throttle valve is fully closed, the IDL contacts
in the throttle position sensor are on, so the voltage at
the terminal IDL of the ECM becomes 0 V. At this time,
a voltage of approximately 0.7 V is applied to the termi-
nal VTA of the ECM. When the throttle valve is opened,
the IDL contacts go off and thus the power source volt-
age of approximately 12 V in the ECM is applied to the
terminal IDL of the ECM. The voltage applied to the ter-
minal VTA of the ECM increases in the proportion to
the opening angle of the throttle valve and becomes
approximately 3.2 ± 4.9 V when the throttle valve is ful-
ly opened. The ECM judges the vehicle driving condi-
tions from these signals input from the terminals VTA
and IDL, and uses them as one of the conditions for de-
ciding the air±fuel ratio correction, power increase
corrections and fuel±cut control etc. The sub±throttle
position sensor is built and operates in the same way
as the main throttle position sensor. This sensor is
used for traction control. The sub±throttle valve is
opened and closed by the sub±throttle actuator ac-
cording to signals from the TRAC ECU to control the
engine output.
Open or short in throttle position sensor circuit
for 0.5 sec. or more
Open or short in sub±throttle position sensor
circuit for 0.5 sec. or more
�Open or short in throttle position sensor
circuit
�Throttle position sensor
�ECM
�Open or short in sub±throttle position
sensor circuit
�Sub±throttle position sensor
�ECM
HINT:
Diagnostic trouble code 41 is for the throttle position sensor circuit.
Diagnostic trouble code 47 is for the sub±throttle position sensor circuit.
�When the connector for the throttle position sensor(s) is disconnected, diagnostic trouble code 41
or 47 is not displayed. Diagnostic trouble code 41 or 47 is displayed only when there is an open
or short in the VTA signal circuit of the throttle position sensor(s).
�Signals from the throttle position sensor(s) are also input to the TRAC ECU, so when a malfunc±
tion occurs on the TRAC side, code 41 or 47 may be displayed.
DTC 41 47 Throttle Position Sensor(s) Circuit
EG±552± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 2066 of 2543
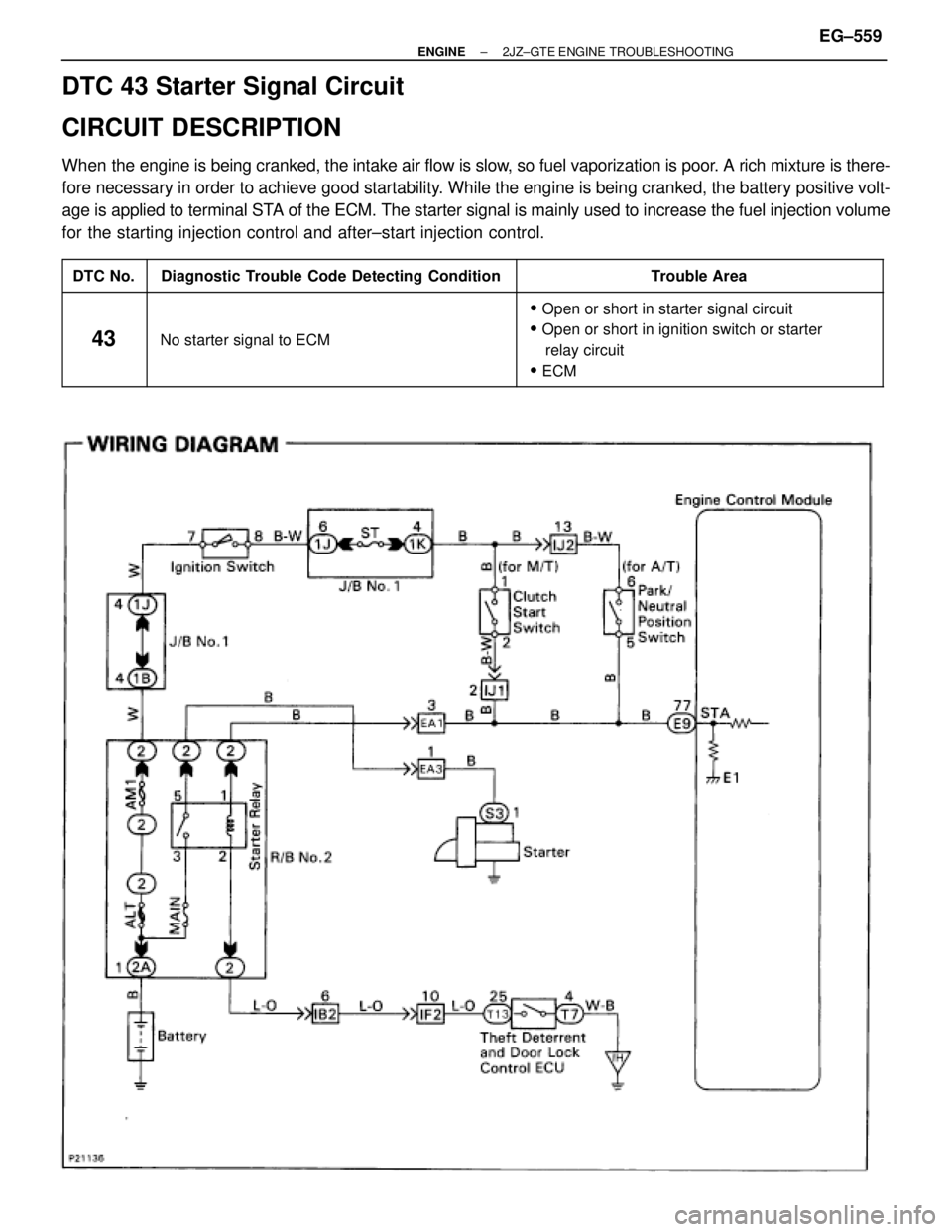
DTC 43 Starter Signal Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the engine is being cranked, the intake air flow is slow, so fuel vaporization is poor. A rich mixture is there-
fore necessary in order to achieve good startability. While the engine is being cranked, the battery positive volt-
age is applied to terminal STA of the ECM. The starter signal is mainly used to increase the fuel injection volume
for the starting injection control and after±start injection control.
����� �
���� �����DTC No.
���������������� �
��������������� ����������������Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
���������������� �
��������������� ����������������Trouble Area
����� �
���� �
���� �
���� �����
43
���������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� ����������������
No starter signal to ECM
���������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� ����������������
�Open or short in starter signal circuit
�Open or short in ignition switch or starter
relay circuit
�ECM
± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTINGEG±559
Page 2071 of 2543
See page EG±503.
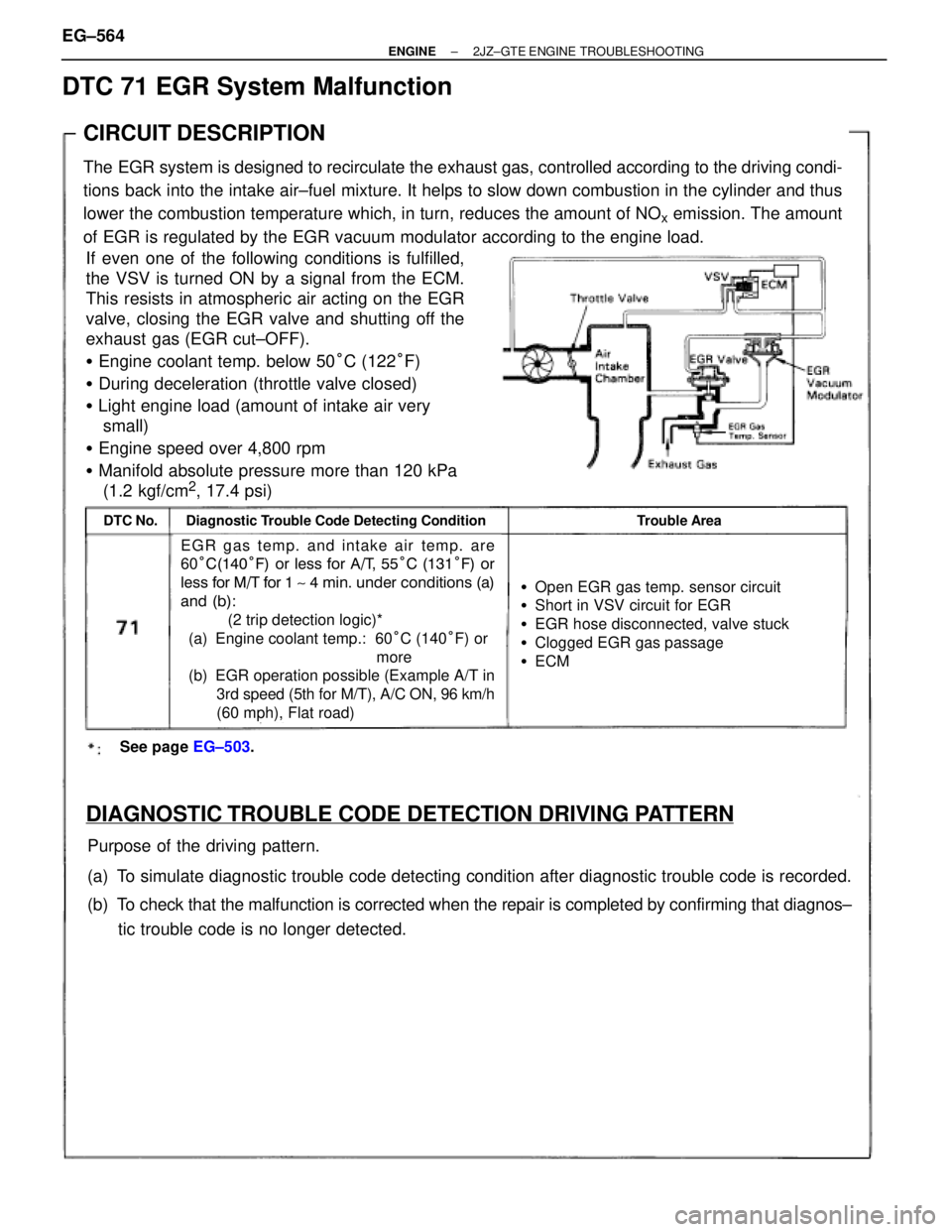
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The EGR system is designed to recirculate the exhaust gas, controlled according to the driving condi-
tions back into the intake air±fuel mixture. It helps to slow down combustion in the cylinder and thus
lower the combustion temperature which, in turn, reduces the amount of NO
x emission. The amount
of EGR is regulated by the EGR vacuum modulator according to the engine load.
If even one of the following conditions is fulfilled,
the VSV is turned ON by a signal from the ECM.
This resists in atmospheric air acting on the EGR
valve, closing the EGR valve and shutting off the
exhaust gas (EGR cut±OFF).
� Engine coolant temp. below 50°C (122°F)
� During deceleration (throttle valve closed)
� Light engine load (amount of intake air very
small)
� Engine speed over 4,800 rpm
� Manifold absolute pressure more than 120 kPa
(1.2 kgf/cm
2, 17.4 psi)
DTC No.Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
No No.1 knock sensor signal to ECM for 4
crank revolutions with engine speed between
2,050 rpm and 5,950 rpm
�Open EGR gas temp. sensor circuit
�Short in VSV circuit for EGR
�EGR hose disconnected, valve stuck
�Clogged EGR gas passage
�ECM
EGR gas temp. and intake air temp. are
60°C(140°F) or less for A/T, 55°C (131°F) or
less for M/T for 1 ~ 4 min. under conditions (a)
and (b):
(2 trip detection logic)*
(a) Engine coolant temp.: 60°C (140°F) or
more
(b) EGR operation possible (Example A/T in
3rd speed (5th for M/T), A/C ON, 96 km/h
(60 mph), Flat road)
Purpose of the driving pattern.
(a) To simulate diagnostic trouble code detecting condition after diagnostic trouble code is recorded.
(b) To check that the malfunction is corrected when the repair is completed by confirming that diagnos±
tic trouble code is no longer detected.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DETECTION DRIVING PATTERN
DTC 71 EGR System Malfunction
EG±564± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 2075 of 2543
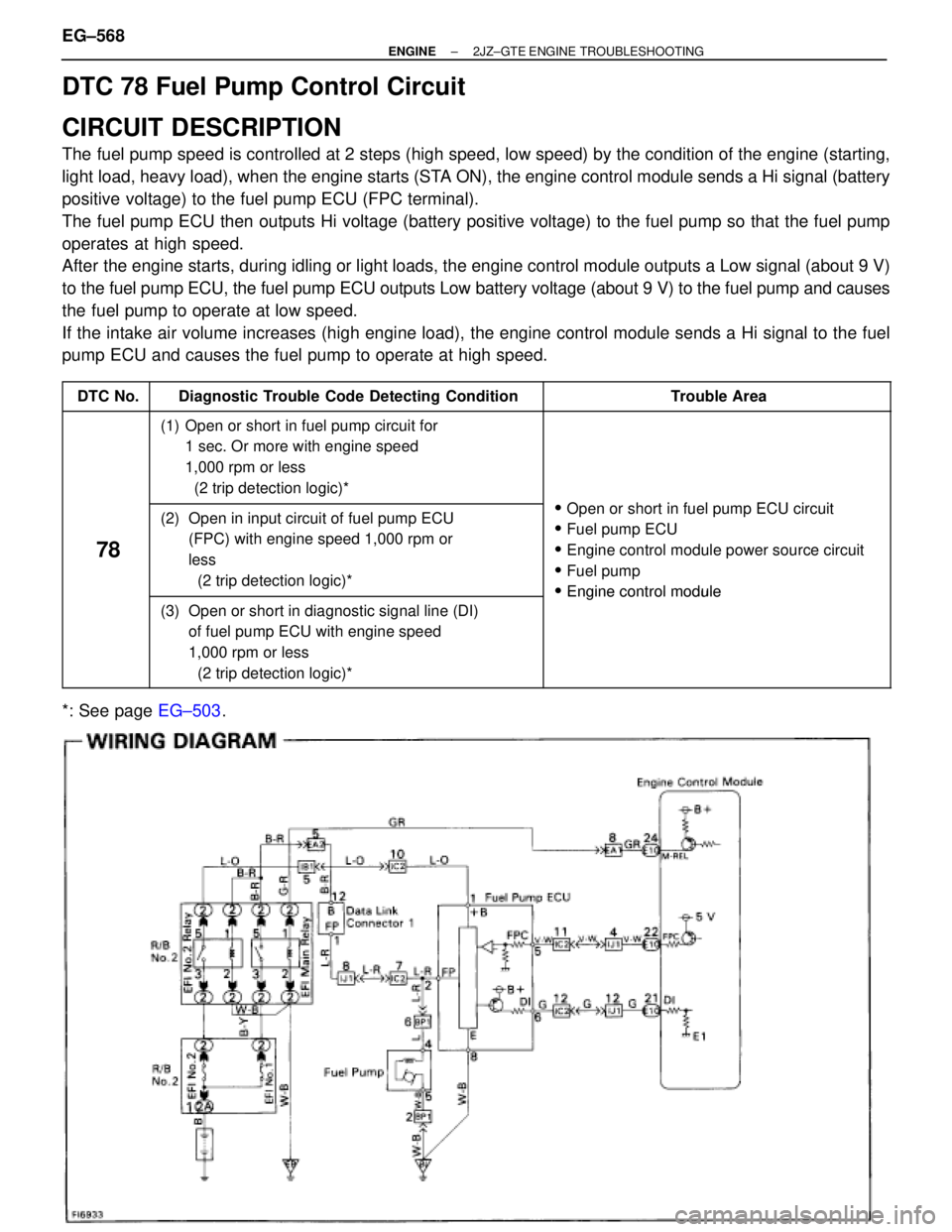
DTC 78 Fuel Pump Control Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump speed is controlled at 2 steps (high speed, low speed) by the condition of the engine (starting,
light load, heavy load), when the engine starts (STA ON), the engine control module sends a Hi signal (battery
positive voltage) to the fuel pump ECU (FPC terminal).
The fuel pump ECU then outputs Hi voltage (battery positive voltage) to the fuel pump so that the fuel pump
operates at high speed.
After the engine starts, during idling or light loads, the engine control module outputs a Low signal (about 9 V)
to the fuel pump ECU, the fuel pump ECU outputs Low battery voltage (about 9 V) to the fuel pump and causes
the fuel pump to operate at low speed.
If the intake air volume increases (high engine load), the engine control module sends a Hi signal to the fuel
pump ECU and causes the fuel pump to operate at high speed.
����� �
���� �����DTC No.
����������������� �
���������������� �����������������Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
���������������� �
��������������� ����������������Trouble Area
����� �
���� �
���� �
���� �����
����������������� �
���������������� �
���������������� �
���������������� �����������������
(1) Open or short in fuel pump circuit for
1 sec. Or more with engine speed
1,000 rpm or less
(2 trip detection logic)*���������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� ����������������O h t i f l ECU i it����� �
���� �
���� �����
78
����������������� �
���������������� �
���������������� �����������������
(2) Open in input circuit of fuel pump ECU
(FPC) with engine speed 1,000 rpm or
less
(2 trip detection logic)*���������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� ����������������
�Open or short in fuel pump ECU circuit
�Fuel pump ECU
�Engine control module power source circuit
�Fuel pump
�Engine control module����� �
���� �
���� �
���� �����
����������������� �
���������������� �
���������������� �
���������������� �����������������
(3) Open or short in diagnostic signal line (DI)
of fuel pump ECU with engine speed
1,000 rpm or less
(2 trip detection logic)*
���������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� �
��������������� ����������������
�Engine control module
*: See page EG±503. EG±568
± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 2076 of 2543
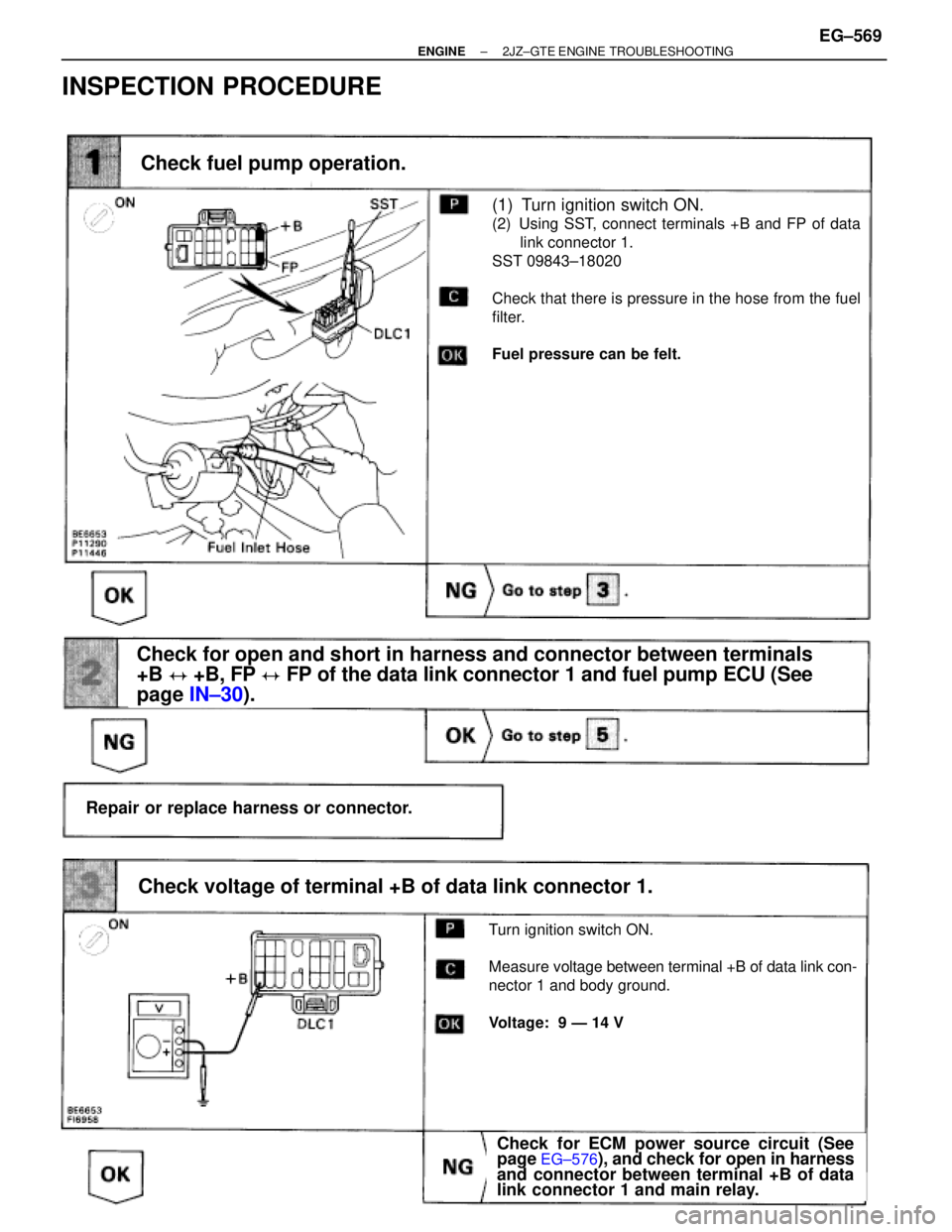
(See page IN±30).
Check for ECM power source circuit (See page
EG±576), and check for open in harness and
connector between terminal +B of data link
connector 1 and main relay.
(1) Turn ignition switch ON.
(2) Using SST, connect terminals +B and FP of data
link connector 1.
SST 09843±18020
Check that there is pressure in the hose from the fuel
filter.
Fuel pressure can be felt.
Check fuel pump operation.
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Check for open and short in harness and connector between terminals
+B � +B, FP � FP of the data link connector 1 and fuel pump ECU (See
page IN±30).
Turn ignition switch ON.
Measure voltage between terminal +B of data link con-
nector 1 and body ground.
Voltage: 9 Ð 14 V
Check voltage of terminal +B of data link connector 1.
Check for ECM power source circuit (See
page EG±576), and check for open in harness
and connector between terminal +B of data
link connector 1 and main relay.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTINGEG±569
Page 2077 of 2543
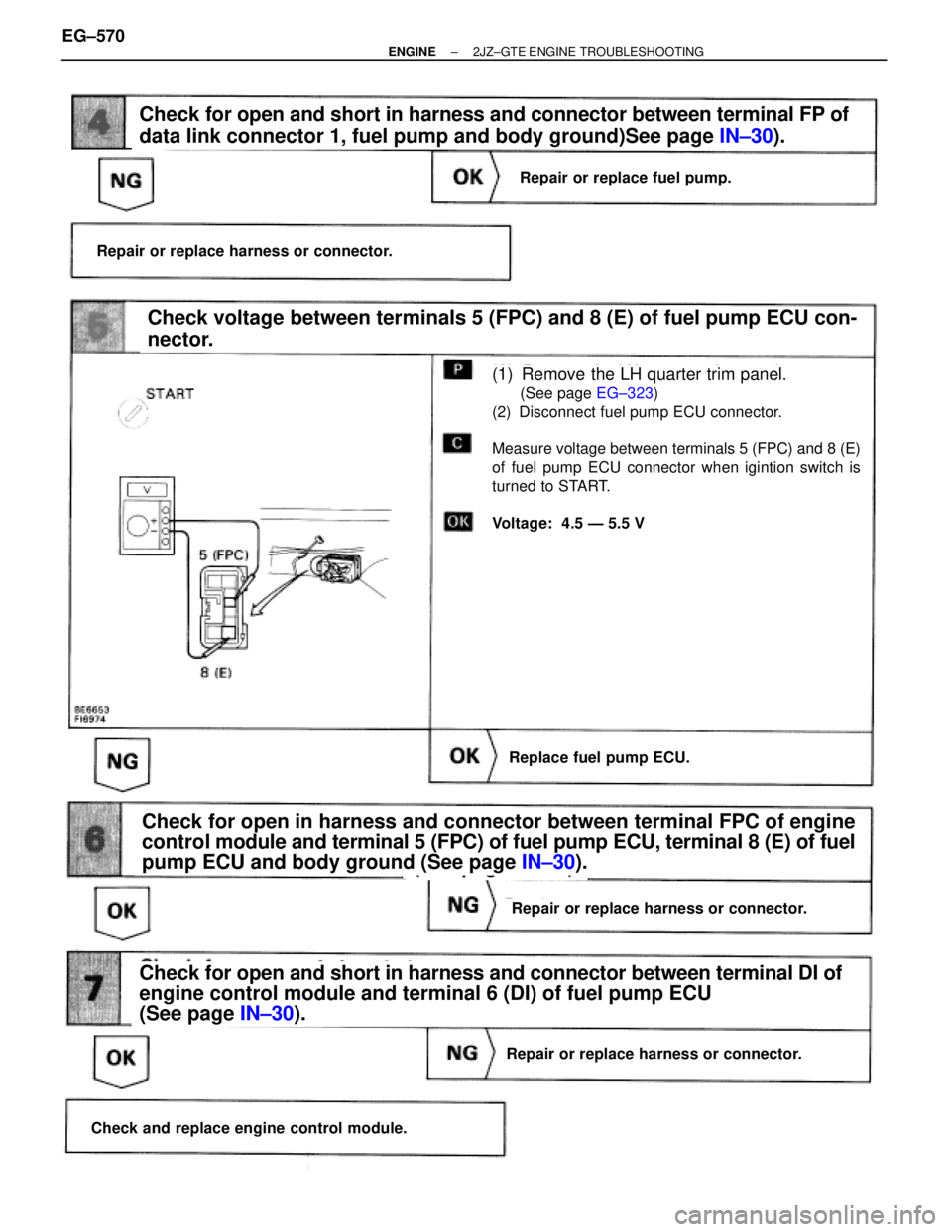
(See page IN±30).
(See page IN±30).(See page IN±30).
(See page EG±323)
(See page IN±30).
(1) Remove the LH quarter trim panel.
(See page EG±323)
(2) Disconnect fuel pump ECU connector.
Measure voltage between terminals 5 (FPC) and 8 (E)
of fuel pump ECU connector when igintion switch is
turned to START.
Voltage: 4.5 Ð 5.5 V
Check voltage between terminals 5 (FPC) and 8 (E) of fuel pump ECU con-
nector.
Check for open and short in harness and connector between terminal DI of
engine control module and terminal 6 (DI) of fuel pump ECU
(See page IN±30).
Check for open and short in harness and connector between terminal FP of
data link connector 1, fuel pump and body ground)See page IN±30).
Repair or replace fuel pump.
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Replace fuel pump ECU.
Check for open in harness and connector between terminal FPC of engine
control module and terminal 5 (FPC) of fuel pump ECU, terminal 8 (E) of fuel
pump ECU and body ground (See page IN±30).
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Check and replace engine control module.
EG±570± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 2081 of 2543
Park Neutral Position Switch Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The park/neutral position switch goes on when the shift lever is in the N or P shift position. When it goes on the
terminal NSW of the ECM is grounded to body ground via the starter relay and theft deterrent ECU, thus the
terminal NSW voltage becomes 0 V. When the shift lever is in the D, 2, L or R position, the park/neutral position
switch goes off, so the voltage of ECM terminal NSW becomes positive battery voltage, the voltage of the ECM
internal power source.
If the shift lever is moved from the N position to the D position, this signal is used for air±fuel ratio correction
and for idle speed control (estimated control), etc.
When the park/neutral position switch is off, code º51º is output in the test mode diagnosis. (This is not abnor-
mal.)
EG±574± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 2088 of 2543
Back Up Power Source Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Battery positive voltage is supplied to terminal BATT of the ECM even when the ignition switch is off for use by
the diagnostic trouble code memory and air±fuel ratio adaptive control value memory, etc.
± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTINGEG±581