Page 32 of 2248
G2M0198
4) Manually push valve rocker (at lash adjuster location) to
check that there is no air in it.
NOTE:
When air is in lash adjuster, valve rocker moves when
pushed with fingers.
G2M0199
5) If air is in lash adjuster, remove valve rocker assembly
from engine and bleed air completely.
B2M0382A
B: AIR BLEEDING
1) Remove valve rocker assembly.
(1) Remove bolts�
1through�4in numerical
sequence.
CAUTION:
Leave two or three threads of bolt�
1engaged to retain
valve rocker assembly.
(2) Equally loosen bolts�
5through�8all the way,
being careful that knock pin is not gouged.
2) Manually remove lash adjusters where air is trapped.
CAUTION:
If lash adjuster is difficult to remove manually, use pli-
ers. Be careful not to scratch lash adjuster.
12
2-3SERVICE PROCEDURE
2. Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Page 33 of 2248

G2M0131
3) Bleed air from hydraulic lash adjuster as described
below:
(1) While dipping hydraulic lash adjuster in engine oil,
as shown in Figure, push check ball in usinga2mm
(0.08 in) diameter round bar.
(2) With check ball pushed in, manually move plunger
up and down at one second intervals until air bubbles
disappear.
(3) After air bubbles disappear, remove round bar and
quickly push plunger in to ensure it is locked. If plunger
does not lock properly, replace hydraulic lash adjuster.
CAUTION:
Leave hydraulic lash adjuster (after air is bled) in
engine oil until it is ready for installation.
G2M0200
4) Using ST;
(1) Insert lash adjuster into ST, and fill ST with engine
oil. Usinga2mm(0.08 in) diameter rod, push check
ball in.
ST 499597000 OIL SEAL GUIDE
(2) With check ball pushed in, push plunger at an inter-
val of one second.
(3) Move plunger up and down until air bubbles are no
longer emitted from lash adjuster.
NOTE:
Hold hydraulic lash adjusters vertically during air bleeding.
5) Remove the rod. Push plunger to ensure that air is
completely bled out.
CAUTION:
If plunger does not properly lock (when pushed),
replace lash adjuster with a new one.
13
2-3SERVICE PROCEDURE
2. Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Page 49 of 2248
G2M0131
C: INSPECTION
1. HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER
1) Bleed air from hydraulic lash adjuster as described
below:
(1) While dipping hydraulic lash adjuster in engine oil,
as shown in Figure, push check ball in usinga2mm
(0.08 in) diameter round bar.
(2) With check ball pushed in, manually move plunger
up and down at one second intervals until air bubbles
disappear.
(3) After air bubbles disappear, remove round bar and
quickly push plunger in to ensure it is locked. If plunger
does not lock properly, replace hydraulic lash adjuster.
CAUTION:
Leave hydraulic lash adjuster (after air is bled) in
engine oil until it is ready for installation.
2) Replace hydraulic lash adjuster with a new one if valve
contact surface is scratched.
29
2-3SERVICE PROCEDURE
4. Valve Rocker Assembly
Page 64 of 2248
B2M0077A
(6) Check the valve guide protrusion.
Valve guide protrusion: L
17.5—18.0 mm (0.689—0.709 in)
B2M0078
(7) Ream the inside of valve guide with ST. Gently
rotate the reamer clockwise while pressing it lightly into
valve guide, and return it also rotating clockwise. After
reaming, clean valve guide to remove chips.
ST 499767400 VALVE GUIDE REAMER
CAUTION:
�Apply engine oil to the reamer when reaming.
�If the inner surface of the valve guide is torn, the
edge of the reamer should be slightly ground with an
oil stone.
�If the inner surface of the valve guide becomes lus-
trous and the reamer does not chips, use a new reamer
or remedy the reamer.
(8) Recheck the contact condition between valve and
valve seat after replacing valve guide.
43
2-3SERVICE PROCEDURE
6. Cylinder Head
Page 99 of 2248

2. Engine Noise
Valve lash adjusters may make clicking noise once engine
starts. It is normal if clicking noise ceases after a few min-
utes.
If clicking noise continues after a few minutes, check
engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
Then, do as follows to cease clicking noise.
1) Warm-up engine for five minutes.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF.
3) Connect test mode connector.
4) Start the engine and run it at approximately 2,000 rpm
for twenty minutes.
5) Turn ignition switch OFF.
6) Disconnect test mode connector.
7) Start the engine and check that clicking noise is ceased.
If noise still exists, conduct troubleshooting procedures in
accordance with the following table.
CAUTION:
Do not disconnect spark plug cord while engine is run-
ning.
Type of sound Condition Possible cause
Regular clicking soundSound increases as engine
speed increases.Valve mechanism is defective.
�Broken lash adjuster
�Worn valve rocker
�Worn camshaft
�Broken valve spring
�Worn valve lifter hole
Heavy and dull clankOil pressure is low.�Worn crankshaft main bearing
�Worn connecting rod bearing (big end)
Oil pressure is normal.�Loose flywheel mounting bolts
�Damaged engine mounting
High-pitched clank
(Spark knock)Sound is noticeable when
accelerating with an overload.�Ignition timing advanced
�Accumulation of carbon inside combustion chamber
�Wrong spark plug
�Improper gasoline
Clank when engine speed is
medium (1,000 to 2,000 rpm).Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy
cylinder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)�Worn crankshaft main bearing
�Worn bearing at crankshaft end of connecting rod
Knocking sound when engine
is operating under idling speed
and engine is warm.Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy
cylinder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)�Worn cylinder liner and piston ring
�Broken or stuck piston ring
�Worn piston pin and hole at piston end of connecting rod
Sound is not reduced if each
fuel injector connector is
disconnected in turn. (NOTE*)�Unusually worn valve lifter
�Worn cam gear
�Worn camshaft journal bore in crankcase
Squeaky sound—�Insufficient generator lubrication
Rubbing sound—�Defective generator brush and rotor contact
Gear scream when starting
engine—�Defective ignition starter switch
�Worn gear and starter pinion
Sound like polishing glass with
a dry cloth—�Loose drive belt
�Defective engine coolant pump shaft
78
2-3DIAGNOSTICS
2. Engine Noise
Page 100 of 2248
Type of sound Condition Possible cause
Hissing sound—�Loss of compression
�Air leakage in air intake system, hoses, connections or
manifolds
Timing belt noise—�Loose timing belt
�Belt contacting case/adjacent part
NOTE*:
When disconnecting fuel injector connector, Malfunction Indicator Light (CHECK ENGINE light) illuminates and trouble code is stored in
ECM memory.
Therefore, carry out the CLEAR MEMORY MODE and INSPECTION MODE after connecting fuel injector connector. (Ref. to 2-7 On-Board
Diagnostics II System.)
79
2-3DIAGNOSTICS
2. Engine Noise
Page 109 of 2248
G2M0376
15) Remove oil strainer.
G2M0377
16) Remove baffle plate and oil strainer stay.
B: INSPECTION
By visual check make sure oil pan, oil strainer, oil strainer
stay and baffle plate are not damaged.
G2M0377
C: INSTALLATION
CAUTION:
Before installing oil pan, clean sealant from oil and
engine block.
1) Install baffle plate and oil strainer stay.
Tightening torque:
5N⋅m (0.5 kg-m, 3.6 ft-lb)
G2M0376
2) Install oil strainer onto baffle plate.
CAUTION:
Replace O-ring with a new one.
Tightening torque:
9.8 N⋅m (1.0 kg-m, 7 ft-lb)
10
2-4SERVICE PROCEDURE
2. Oil Pan and Oil Strainer
Page 116 of 2248
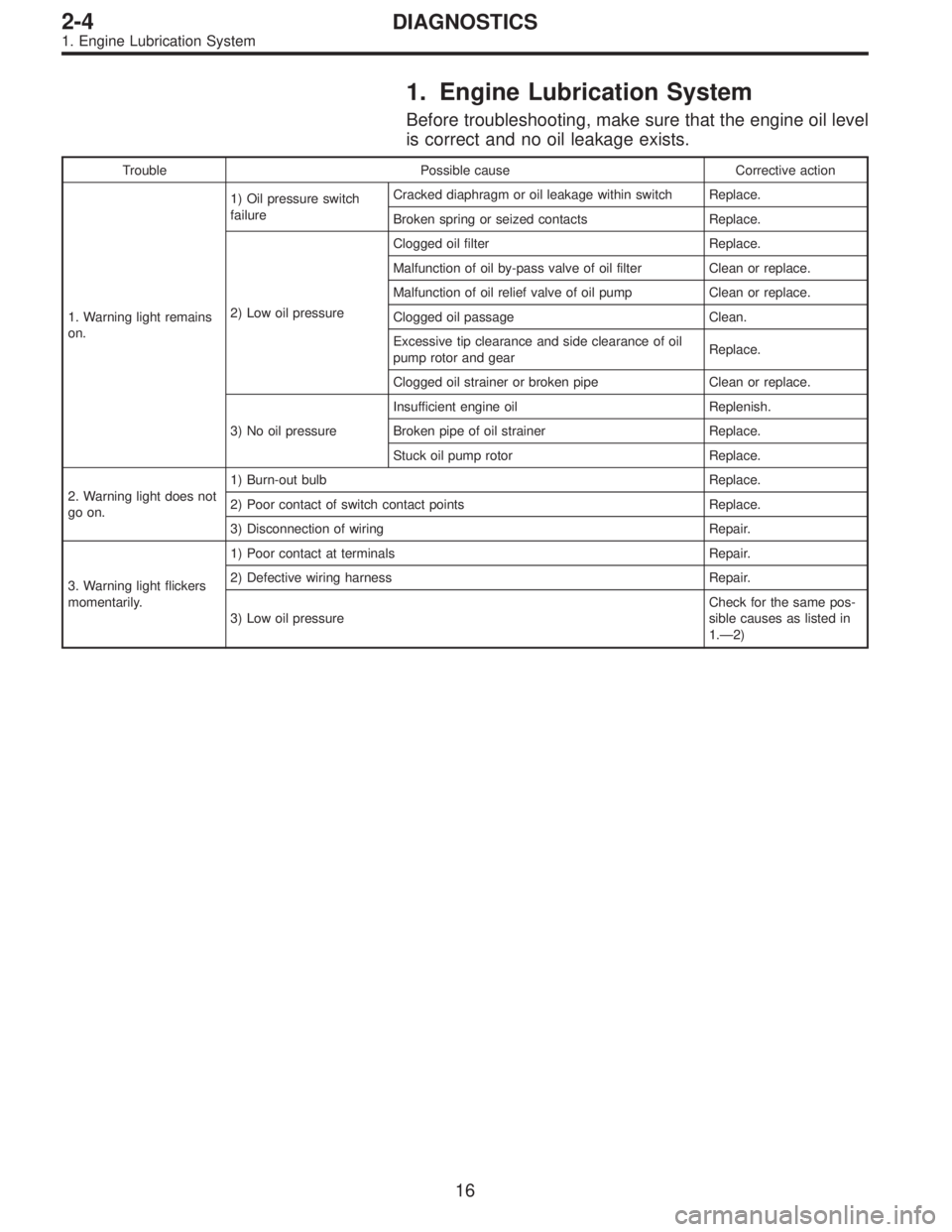
1. Engine Lubrication System
Before troubleshooting, make sure that the engine oil level
is correct and no oil leakage exists.
Trouble Possible cause Corrective action
1. Warning light remains
on.1) Oil pressure switch
failureCracked diaphragm or oil leakage within switch Replace.
Broken spring or seized contacts Replace.
2) Low oil pressureClogged oil filter Replace.
Malfunction of oil by-pass valve of oil filter Clean or replace.
Malfunction of oil relief valve of oil pump Clean or replace.
Clogged oil passage Clean.
Excessive tip clearance and side clearance of oil
pump rotor and gearReplace.
Clogged oil strainer or broken pipe Clean or replace.
3) No oil pressureInsufficient engine oil Replenish.
Broken pipe of oil strainer Replace.
Stuck oil pump rotor Replace.
2. Warning light does not
go on.1) Burn-out bulb Replace.
2) Poor contact of switch contact points Replace.
3) Disconnection of wiring Repair.
3. Warning light flickers
momentarily.1) Poor contact at terminals Repair.
2) Defective wiring harness Repair.
3) Low oil pressureCheck for the same pos-
sible causes as listed in
1.—2)
16
2-4DIAGNOSTICS
1. Engine Lubrication System