1994 JEEP CHEROKEE clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 1113 of 1784
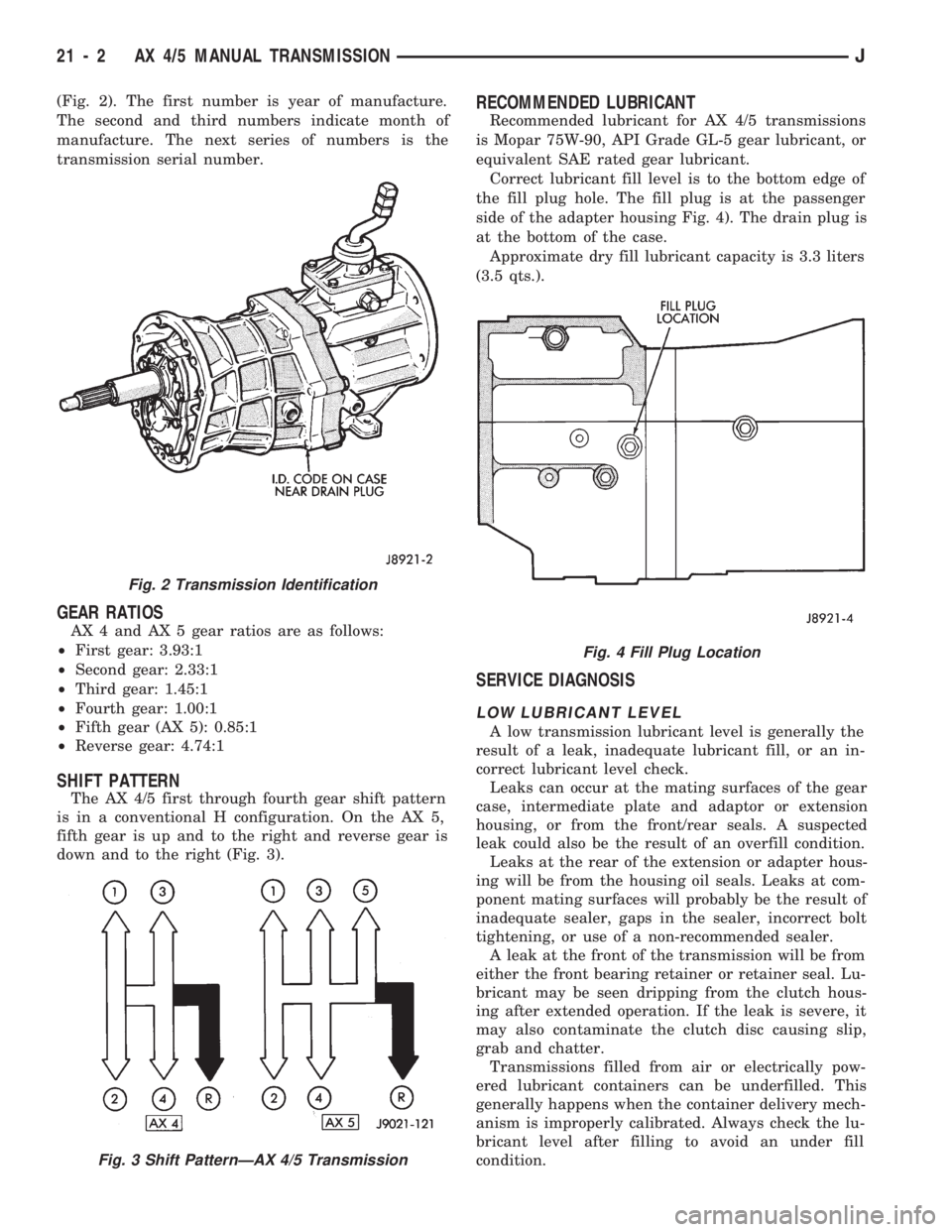
(Fig. 2). The first number is year of manufacture.
The second and third numbers indicate month of
manufacture. The next series of numbers is the
transmission serial number.
GEAR RATIOS
AX 4 and AX 5 gear ratios are as follows:
²First gear: 3.93:1
²Second gear: 2.33:1
²Third gear: 1.45:1
²Fourth gear: 1.00:1
²Fifth gear (AX 5): 0.85:1
²Reverse gear: 4.74:1
SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 4/5 first through fourth gear shift pattern
is in a conventional H configuration. On the AX 5,
fifth gear is up and to the right and reverse gear is
down and to the right (Fig. 3).
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 4/5 transmissions
is Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent SAE rated gear lubricant.
Correct lubricant fill level is to the bottom edge of
the fill plug hole. The fill plug is at the passenger
side of the adapter housing Fig. 4). The drain plug is
at the bottom of the case.
Approximate dry fill lubricant capacity is 3.3 liters
(3.5 qts.).
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an in-
correct lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adaptor or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch hous-
ing after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it
may also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip,
grab and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically pow-
ered lubricant containers can be underfilled. This
generally happens when the container delivery mech-
anism is improperly calibrated. Always check the lu-
bricant level after filling to avoid an under fill
condition.
Fig. 2 Transmission Identification
Fig. 3 Shift PatternÐAX 4/5 Transmission
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
21 - 2 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1114 of 1784

A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damaged
pressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear
clash when shifting into any forward gear. In some
new or rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings maytend to stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In
most cases, this condition will decline as the rings
wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears can generate a
mild whine that may only be audible at extreme
speeds.
Severe, obviously audible transmission noise is
generally the result of a lubricant problem. Insuffi-
cient, improper, or contaminated lubricant can pro-
mote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks
and bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear. Then
raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support engine with adjustable jack stand. Be
sure to position wood block between jack and oil pan.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system compo-
nents.
(4) Disconnect rear cushion and bracket from
transmission (Fig. 5). Then remove skid plate, or
rear crossmember.
(5) Disconnect transfer case shift linkage, vehicle
speed sensor wires, and vent hose.
Fig. 5 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 3
Page 1115 of 1784

(6) Remove slave cylinder from clutch housing.
(7) Disconnect transmission shift lever as follows:
(a) Lower transmission-transfer case assembly ap-
proximately 7-8 cm (3 in.) for access to shift lever.
(b) Reach up and around transmission case and
unseat shift lever dust boot from transmission shift
tower (Fig. 6). Move boot upward on shift lever for
access to retainer that secures lever in shift tower.
(c) Reach up and around transmission case and
press shift lever retainer downward with your fin-
gers. Turn retainer counterclockwise to release it.
(d) Lift lever and retainer out of shift tower (Fig.
6).Do not remove the shift lever from the
floorpan boots. Leave the lever in place for
later transmission installation.
(8) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for instal-
lation alignment (Fig. 7). Then remove shafts.
(9) Remove crankshaft position position sensor (Fig.
8).
(10) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor wires.
(11) Disconnect transmission and transfer case
vent hoses.(12) Disconnect clutch master cylinder hydraulic
line from concentric bearing inlet line (Fig. 8).
(13) Support transmission-transfer case assembly
with a transmission jack. Secure assembly to jack
with safety chains.
(14) Remove clutch housing brace rod on 4-cylinder
models.
(15) Remove clutch housing-to-engine bolts and re-
move transmission-transfer case assembly.
(16) Remove bolts attaching transmission to trans-
fer case and separate components.
(17) Remove release bearing, fork and retainer clip.
(18) Remove clutch housing.
TRANSMISSION INSTALLATION
(1) Install clutch housing on transmission. Tighten
housing bolts to 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Lubricate contact surfaces of release fork pivot
ball stud and release fork with high temp grease.
Then install release bearing, fork and retainer clip.
(3) Mount transmission on transmission jack.
(4) Lightly lubricate pilot bearing and transmis-
sion input shaft splines with Mopar high tempera-
ture grease.
(5) Align transmission input shaft and clutch disc
splines and install transmission.
(6) Install and tighten clutch housing-to-engine
bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque.Be sure the
housing is properly seated on engine block be-
fore tightening bolts.
(7) Lower transmission approximately 7-8 cm (3
in.) for access to shift tower. Be sure transmission is
in first or third gear.
(8) Reach up and around transmission and insert
shift lever in shift tower. Press lever retainer down-
ward and turn it clockwise to lock it in place. Then
install lever dust boot on shift tower.
(9) Install slave cylinder in clutch housing.
(10) Connect engine timing sensor wires.
(11) Remove jack from under transmission and
mount transfer case on jack.Fig. 6 Removing/Installing Shift Lever
Fig. 7 Marking Propeller Shaft And Axle Yokes
Fig. 8 Hydraulic Line And Timing Sensor Location
21 - 4 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1116 of 1784
(12) Align transfer case and transmission shafts
and install transfer case. Tighten transfer case-to-
transmission nuts/bolts to 35 Nzm (26 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Remove jack stand from under engine and re-
position jack under transmission. Then remove trans-
mission jack.
(14) Connect transfer case vent hose and shift link-
age. Check and adjust linkage if necessary.
(15) Connect transmission and transfer case vent
hoses.
(16) Connect backup light switch wires.
(17) Connect vehicle speed sensor wires.
(18) Install and connect crankshaft position sensor
if equipped.
(19) Install rear crossmember, or skid plate (Fig. 5).
On XJ, tighten crossmember-to-frame bolts to 41 Nzm
(31 ft. lbs.) torque. Then tighten transmission-to-rear
support bolts/nuts to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque. On YJ,
tighten bolts/nuts to indicated torque (Fig. 5).
(20) Align and install front/rear propeller shafts.
Tighten shaft U-joint clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (170 in.
lbs.) torque.
(21) On XJ, install skid plate, if removed. Tighten
bolts to 42 Nzm (31 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten stud nuts
to 17 Nzm (150 in. lbs.) torque.
(22) Top off transmission and transfer case lubri-
cant levels.
(23) Lower vehicle.
TRANSMISSION DISASSEMBLY AND OVERHAUL
ADAPTER HOUSING AND FRONT BEARING
RETAINER REMOVAL
(1) Drain transmission lubricant.
(2) Remove concentric bearing.
(3) Remove clutch housing bolts and remove housing.
(4) On 2-wheel drive models, remove vehicle speed
sensor, speedometer adapter and speedometer driven
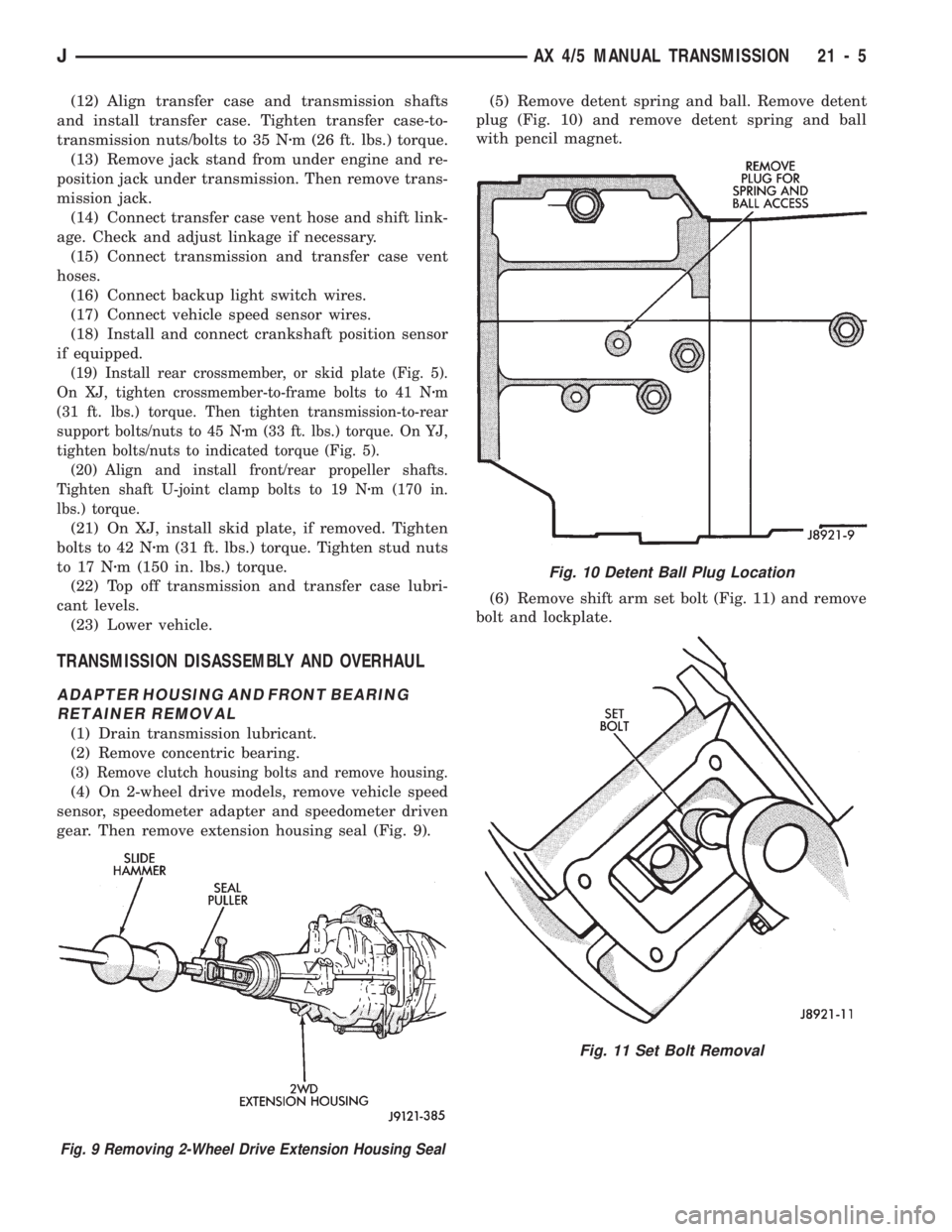
gear. Then remove extension housing seal (Fig. 9).(5) Remove detent spring and ball. Remove detent
plug (Fig. 10) and remove detent spring and ball
with pencil magnet.
(6) Remove shift arm set bolt (Fig. 11) and remove
bolt and lockplate.
Fig. 10 Detent Ball Plug Location
Fig. 11 Set Bolt Removal
Fig. 9 Removing 2-Wheel Drive Extension Housing Seal
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 5
Page 1117 of 1784
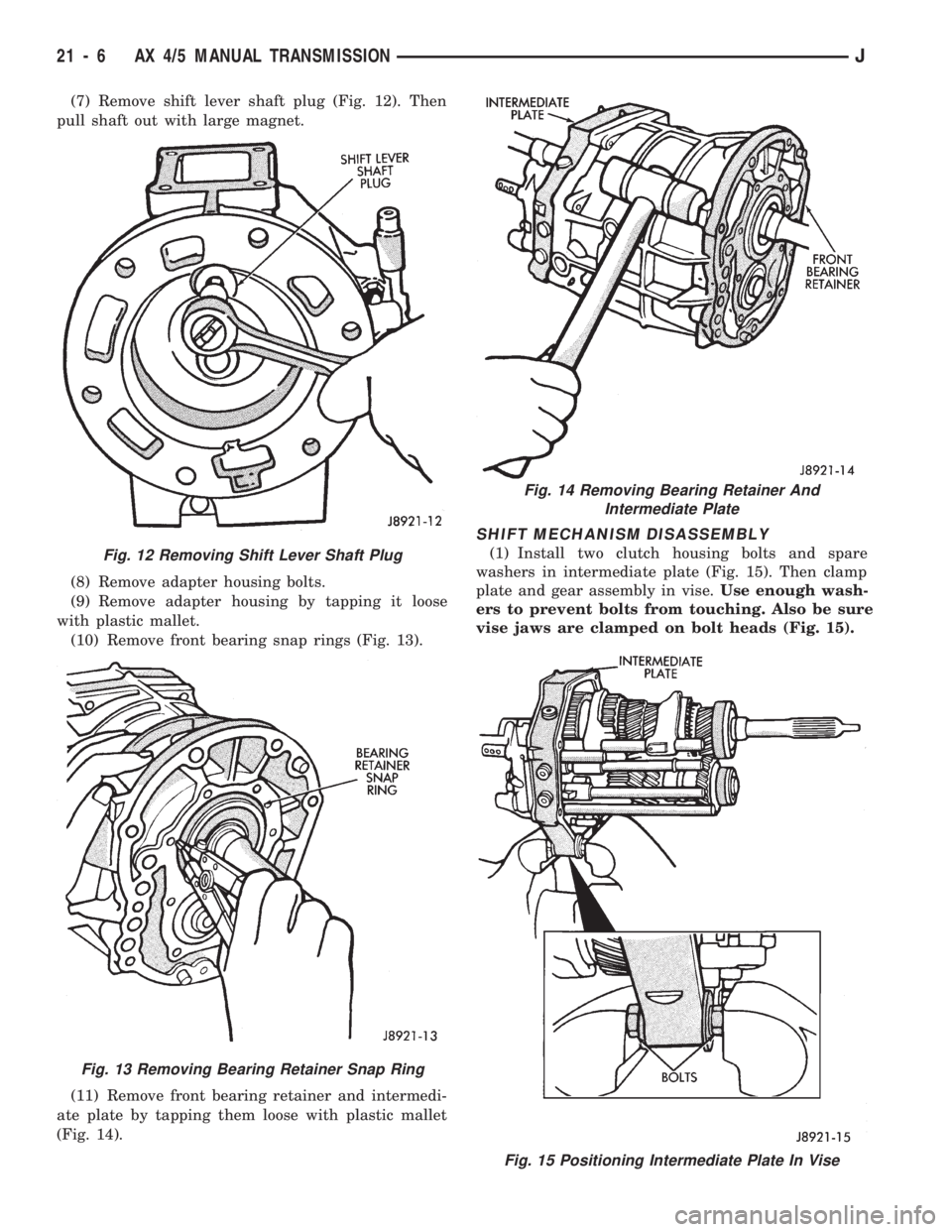
(7) Remove shift lever shaft plug (Fig. 12). Then
pull shaft out with large magnet.
(8) Remove adapter housing bolts.
(9) Remove adapter housing by tapping it loose
with plastic mallet.
(10) Remove front bearing snap rings (Fig. 13).
(11) Remove front bearing retainer and intermedi-
ate plate by tapping them loose with plastic mallet
(Fig. 14).
SHIFT MECHANISM DISASSEMBLY
(1) Install two clutch housing bolts and spare
washers in intermediate plate (Fig. 15). Then clamp
plate and gear assembly in vise.Use enough wash-
ers to prevent bolts from touching. Also be sure
vise jaws are clamped on bolt heads (Fig. 15).
Fig. 15 Positioning Intermediate Plate In Vise
Fig. 12 Removing Shift Lever Shaft Plug
Fig. 13 Removing Bearing Retainer Snap Ring
Fig. 14 Removing Bearing Retainer And
Intermediate Plate
21 - 6 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1142 of 1784
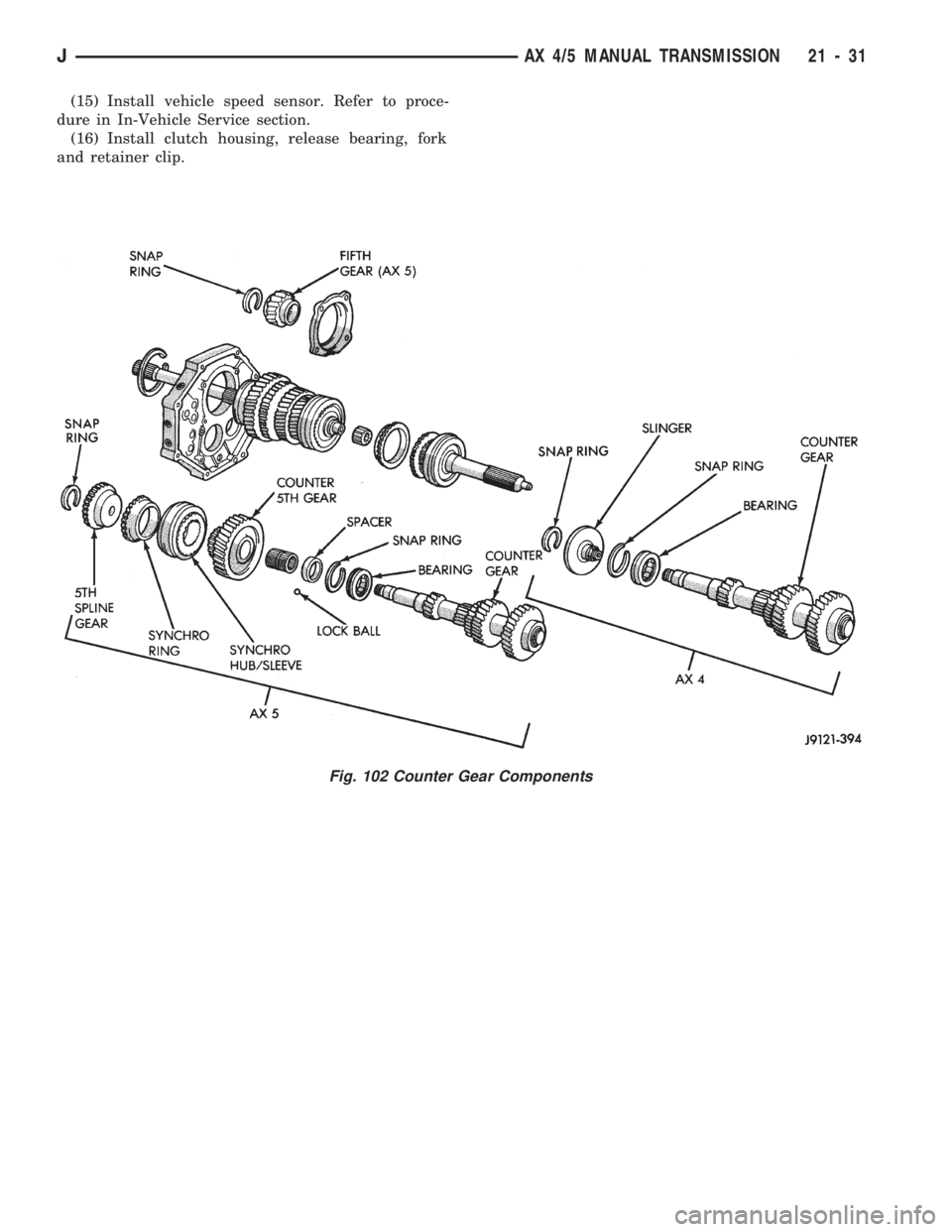
(15) Install vehicle speed sensor. Refer to proce-
dure in In-Vehicle Service section.
(16) Install clutch housing, release bearing, fork
and retainer clip.
Fig. 102 Counter Gear Components
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 31
Page 1144 of 1784
TRANSMISSION SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 15 shift pattern is shown in Figure 3. First
and second and third and fourth gear ranges are in
line for improved shifting. Fifth and reverse gear
ranges are also in line at the extreme right of the
pattern (Fig. 3).
The AX 15 is equipped with a reverse lockout
mechanism. The shift lever must be moved through
the Neutral detent before making a shift to reverse.
TRANSMISSION LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 15 transmissions is
Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent.
Correct lubricant refill or top-off level is to the bot-
tom edge of the fill plug hole.
Lubricant capacity is:
²3.10 liters (3.27 qts.) in 4-wheel drive models.
²3.15 liters (3.32 qts.) in 2-wheel drive models.
TRANSMISSION SWITCH AND PLUG LOCATIONS
The fill plug is at the driver side of the gear case
(Fig. 4).
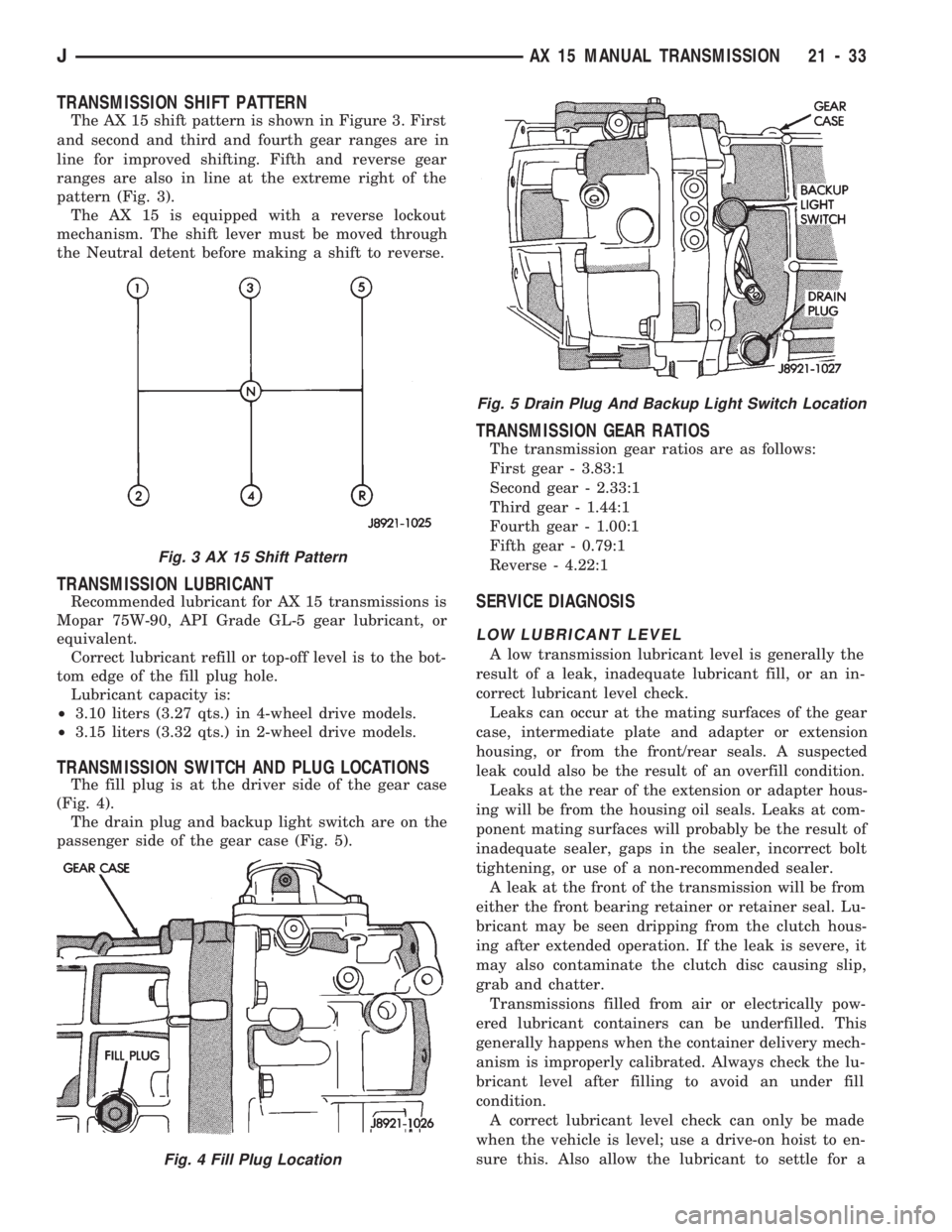
The drain plug and backup light switch are on the
passenger side of the gear case (Fig. 5).
TRANSMISSION GEAR RATIOS
The transmission gear ratios are as follows:
First gear - 3.83:1
Second gear - 2.33:1
Third gear - 1.44:1
Fourth gear - 1.00:1
Fifth gear - 0.79:1
Reverse - 4.22:1
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an in-
correct lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adapter or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch hous-
ing after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it
may also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip,
grab and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically pow-
ered lubricant containers can be underfilled. This
generally happens when the container delivery mech-
anism is improperly calibrated. Always check the lu-
bricant level after filling to avoid an under fill
condition.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
Fig. 3 AX 15 Shift Pattern
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
Fig. 5 Drain Plug And Backup Light Switch Location
JAX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 33
Page 1145 of 1784

minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damaged
pressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear
clash when shifting into any forward gear. In some
new or rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may
tend to stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In
most cases, this condition will decline as the rings
wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears can generate a
mild whine that may only be audible at extreme
speeds.
Severe, obviously audible transmission noise is
generally the result of a lubricant problem. Insuffi-
cient, improper, or contaminated lubricant can pro-
mote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks
and bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVALÐAX 15
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear.
(2) Raise vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system compo-
nents.
(4) Support transmission with adjustable jack
stand.
(5) Disconnect rear cushion and mounting bracket
from transmission, or transfer case (Fig. 1).
(6) On XJ, remove rear crossmember. On YJ, re-
move skid plate (Fig. 1).
(7) Disconnect transmission shift linkage, speed-
ometer cable, transfer case vacuum lines and clutch
hydraulic lines.
(8) Lower transmission-transfer case assembly no
more than 7.6 cm (3 in.) for access to shift lever.
Fig. 1 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
21 - 34 AX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ