1994 JEEP CHEROKEE Starter
[x] Cancel search: StarterPage 897 of 1784

(29) Disconnect the engine speed sensor wire con-
nection.
(30) Remove the exhaust pipe support.
(31) Remove the flywheel/converter housing access
cover.
(32)Vehicles with Automatic Transmission:
(a) Mark the converter and drive plate location.
(b) Remove the converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(33) Remove the upper flywheel/converter housing
bolts and loosen the bottom bolts.
(34) Remove the engine mount cushion-to-engine
compartment bracket bolts.
(35) Lower the vehicle.
(36) Attach a lifting device to the engine.
(37) Raise the engine off the front supports.
(38) Place a support or floor jack under the con-
verter (or flywheel) housing.
(39) Remove the remaining converter (or flywheel)
housing bolts.
(40) Lift the engine out of the engine compart-
ment.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: When installing the engine into a vehicle
equipped with an automatic transmission, be care-
ful not to damage the trigger wheel on the flywheel.
(1) Attach a lifting device to the engine and lower
the engine into the engine compartment. For easier
installation, it may be necessary to remove the en-
gine mount cushions from the engine mount bracket
as an aide in alignment of the engine to the trans-
mission.
(2)Vehicles with Manual Transmission:
(a) Insert the transmission shaft into the clutch
spline.
(b) Align the flywheel housing with the engine.
(c) Install and tighten the flywheel housing
lower bolts finger tight.(3)Vehicles with Automatic Transmission:
(a) Align the transmission torque converter
housing with the engine.
(b) Loosely install the converter housing lower
bolts and install the next higher bolt and nut on
each side.
(c) Tighten all 4 bolts finger tight.
(4) Install the engine mount cushions (if removed).
(5) Lower the engine and engine mount cushions
onto the engine compartment brackets. Install the
bolts and finger tighten the nuts.
(6) Remove the engine lifting device.
(7) Raise and support the vehicle.
(8) Install the remaining flywheel/converter hous-
ing bolts. Tighten all bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(9)Vehicles with Automatic Transmission:
(a) Install the converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(b) Ensure the installation reference marks are
aligned.
(10) Install the flywheel/converter housing access
cover.
(11) Install the exhaust pipe support and tighten
the screw.
(12) Tighten the engine mount-to-bracket bolts.
(13) Connect the engine speed sensor wire connec-
tions and tighten the screws.
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the manifold.
(15) Install the starter motor and connect the ca-
ble.
(16) Connect the wires to the starter motor sole-
noid.
(17) Lower the vehicle.
(18) Connect all the vacuum hoses and wire con-
nectors identified during engine removal.
(19) If equipped with power steering:
(a) Remove the protective caps
(b) Connect the hoses to the fittings at the steer-
ing gear. Tighten the nut to 52 Nzm (38 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(c) Fill the pump reservoir with fluid.
(20) Install the power brake vacuum check valve
to the booster, if equipped.
(21) Connect the fuel inlet and return hoses at the
fuel rail. Verify that the quick-connect fitting assem-
bly fits securely over the fuel lines by giving the fuel
lines a firm tug.
(22) Install the fuel line bracket to the intake
manifold.
(23) Connect the distributor electrical connector
and oil pressure switch connector.
(24) Connect the injection system wire harness
connector on the dash panel.
(25) Connect the line pressure cable (if equipped
with automatic transmission).
(26) Connect the speed control cable, if equipped.
(27) Connect the throttle cable linkages.
Fig. 16 Air Cleaner Assembly & Power Steering
Pump
9 - 56 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 898 of 1784

(28) Connect the heater hoses at the engine ther-
mostat housing and water pump.
(29) Install the fan assembly to the idler pulley.
(30) Install the radiator or radiator/condenser (if
equipped with A/C).
(31) Connect the service valves to the A/C com-
pressor ports, if equipped with A/C.
(32) Charge the air conditioner system.
(33) Connect radiator fan switch wire.
(34) Connect the radiator hoses and automatic
transmission fluid cooler pipes, if equipped.
(35) Install the fan shroud, electric cooling fan and
radiator/condenser (if equipped with A/C).
(36) Install upper radiator support.
(37) Connect the upper radiator hose and tighten
the clamp.
(38) Connect the lower radiator hose and tighten
the clamp.
(39) Fill the cooling system with reusable coolant
and/or new coolant.
(40) Align the hood to the scribe marks. Install the
hood.
(41) Connect the vacuum harness connector.
(a) Firmly push the connectors together ensuring
that the retaining tabs are engaged.
(b) Insert the vacuum connector assembly into
the retaining bracket on the intake manifold.
(42) Install the air cleaner assembly.
(43) Install the battery and connect the battery ca-
ble.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A DI-
RECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(44) Start the engine, inspect for leaks and correct
the fluid levels, as necessary.
ENGINE ASSEMBLYÐYJ VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Place a protective cloth over the windshield
frame. Raise the hood and rest it on the windshield
frame (Fig. 17).
(2) Disconnect the battery cables. Remove the bat-
tery.
WARNING: THE COOLANT IN A RECENTLY OPER-
ATED ENGINE IS HOT AND PRESSURIZED. USE
CARE TO PREVENT SCALDING BY HOT COOLANT.
CAREFULLY RELEASE THE PRESSURE BEFORE
REMOVING THE RADIATOR DRAIN COCK AND
CAP.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste reusablecoolant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant
into a clean container for reuse.
(4) Disconnect the wire connectors from the gener-
ator.
(5) Disconnect the ignition coil and distributor
wire connectors.
(6) Disconnect the oil pressure sender wire connec-
tor.
(7) Disconnect the wires at the starter motor sole-
noid and injection wire harness connector.
(8) Disconnect the quick-connect fuel lines at the
fuel rail and return line by squeezing the retaining
tabs against the fuel tube (Fig. 18). Pull the fuel
tube and retainer from the quick-connect fitting (re-
fer to Group 14, Fuel System for the proper proce-
dure).
(9) Remove the fuel line bracket from the intake
manifold.
(10) Disconnect the engine ground strap.
(11) Remove the air cleaner (Fig. 18).
(12) Disconnect the vacuum purge hose at the fuel
vapor canister tee.
(13) Disconnect the idle speed actuator wire con-
nector.
(14) Disconnect the throttle cable and remove it
from the bracket (Fig. 18).
(15) Disconnect the throttle rod at the bellcrank.
(16) Disconnect the speed control cable, if equipped
(Fig. 18).
(17) Disconnect the oxygen sensor wire connector.
(18) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose (Fig. 19).
(19) Disconnect lower radiator hoses at the radia-
tor.
Fig. 17 Hood on Windshield Frame
J4.0L ENGINE 9 - 57
Page 899 of 1784

(20) Disconnect the coolant hoses from the rear of
the intake manifold and thermostat housing.
(21) Remove the fan shroud screws.
(22) Remove the radiator attaching bolts.
(23) Remove the radiator and fan shroud (Fig. 19).
Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for the proper pro-
cedure.
(24) Remove the fan and spacer or Tempatrol fan
assembly.
(25) Install a 5/16 X 1/2-inch SAE capscrew
through fan pulley into water pump flange. This will
maintain the pulley and water pump in alignment
when crankshaft is rotated.
(26) Remove the power brake vacuum check valve
from the booster, if equipped.
(27) If equipped with power steering (Fig. 19):
(a) Disconnect the hoses from the fittings at the
steering gear.
(b) Drain the pump reservoir.
(c) Cap the fittings on the hoses and steering
gear to prevent foreign objects from entering the
system.
(28) Lift the vehicle and support it with support
stands.
(29) Remove the starter motor.
(30) Remove the flywheel housing access cover.
(31) Remove the engine support cushion-to-bracket
through bolts.
(32) Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the mani-
fold.
(33) Remove the upper flywheel housing bolts and
loosen the bottom bolts.
(34) Lower the vehicle.
(35) Attach a lifting device to the engine.
(36) Raise the engine off the front supports.
(37) Place a support stand under the flywheel
housing.
(38) Remove the remaining flywheel housing bolts.(39) Lift the engine out of the engine compartment
and install on an engine stand.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lift the engine off the stand and lower it into
the engine compartment. For easier installation, it
may be useful to remove the engine support cushions
from the engine support brackets as an aide for
alignment of the engine-to-transmission.
(2) Insert the transmission shaft into the clutch
spline.
(3) Align the flywheel housing with the engine.
(4) Install and finger tighten the flywheel housing
lower bolts.
(5) Install the engine support cushions (if re-
moved).
(6) Remove the support stand from beneath the fly-
wheel housing.
(7) Lower the engine and engine support cushions
onto the engine compartment brackets. Ensure that
the bolt holes are aligned. Install the bolts and
tighten the nuts.
(8) Remove the engine lifting device.
(9) Raise the vehicle.
(10) Attach the exhaust pipe to the manifold. In-
stall and tighten the nuts to 31 Nzm (23 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(11) Install the flywheel housing access cover.
(12) Install the remaining flywheel housing bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install the starter motor and connect the ca-
ble. Tighten the bolts to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Lower the vehicle.
(15) Connect the coolant hoses and tighten the
clamps.
(16) Remove the pulley-to-water pump flange
alignment capscrew and install the fan and spacer or
Tempatrol fan assembly.
Fig. 18 Fuel Line Quick-Connect Couplings, Air
Cleaner Assembly, Throttle & Speed Control CablesFig. 19 Upper Radiator Hose, Coolant Recovery
Hose, Fan Shroud & Power Steering Pump
9 - 58 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 913 of 1784

number of chain pins between the timing marks of
both sprockets. There must be 15 pins.
(6) Install the crankshaft oil slinger.
(7) Tighten the camshaft sprocket preload bolt to
108 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Check the valve timing.
(9) Lubricate the tension spring, the thrust pin
and the pin bore in the preload bolt with Mopar En-
gine Oil Supplement, or equivalent. Install the
spring and thrust pin in the preload bolt head.
(10) Coat both sides of the replacement timing case
cover gasket with gasket sealer. Applya3mm(1/8
inch) bead of Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant, or equivalent to the joint formed at the oil pan
and cylinder block.
(11) Position the timing case cover on the oil pan
gasket and the cylinder block.
(12) Place Timing Case Cover Alignment and Seal
Installation Tool 6139 in the crankshaft opening in
the cover (Fig. 13).
(13) Install the timing case cover-to-cylinder block
bolts. Install the oil pan-to-timing case cover bolts.
(14) Tighten the 1/4 inch cover-to-block bolts to 7
Nzm (60 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the 5/16 inch front
cover-to-block bolts to 22 Nzm (192 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten the oil pan-to-cover 1/4 inch bolts to 14 Nzm
(120 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the oil pan-to-cover 5/16
inch bolts to 18 Nzm (156 in. lbs.) torque.
(15) Remove the cover alignment tool and install a
replacement oil seal into the cover.
(16) Install the vibration damper on the crank-
shaft.(17) Lubricate and tighten the damper bolt to 108
Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) If equipped with air conditioning:
(a) Install the A/C compressor serpentine drive
belt idler pulley.
(b) Install the generator.
(c) Install the A/C condenser and receiver/drier
assembly.
(19) Install the serpentine drive belt on the pulleys
and tighten (refer to Group 7, Cooling System for the
specifications and procedures).
(20) Install the radiator. Connect the radiator
hoses and automatic transmission fluid cooler pipes,
if equipped. Fill the cooling system.
(21) Install the fan and shroud.
(22) Connect negative cable to battery.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove the oil pan drain plug and drain the
engine oil.
(4) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the exhaust
manifold.
(5) Disconnect the exhaust hanger at the catalytic
converter and lower the pipe.
(6) Remove the starter motor.
(7) Remove the engine flywheel/transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(8) If equipped with an oil level sensor, disconnect
the sensor.
(9) Position a jack stand directly under the engine
vibration damper.
(10) Place a piece of wood (2 x 2) between the jack
stand and the engine vibration damper.
(11) Remove the engine mount through bolts.
Fig. 12 Verify Crankshaft/Camshaft
InstallationÐTypical
Fig. 13 Timing Case Cover Alignment and Seal
Installation Tool 6139
9 - 72 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 914 of 1784
(12) Using the jack stand, raise the engine until
adequate clearance is obtained to remove the oil pan.
(13) Remove the oil pan bolts. Carefully slide the
oil pan and gasket to the rear. If equipped with an
oil level sensor, take care not to damage the sensor.
CLEANING
Clean the block and pan gasket surfaces.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fabricate 4 alignment dowels from 1 1/2 x 1/4
inch bolts. Cut the head off the bolts and cut a slot
into the top of the dowel. This will allow easier in-
stallation and removal with a screwdriver (Fig. 1).
(2) Install two dowels in the timing case cover. In-
stall the other two dowels in the cylinder block (Fig.
2).
(3) Slide the one-piece gasket over the dowels and
onto the block and timing case cover.
(4) Position the oil pan over the dowels and onto
the gasket. If equipped with an oil level sensor, take
care not to damage the sensor.
(5) Install the 1/4 inch oil pan bolts. Tighten these
bolts to 14 Nzm (120 in. lbs.) torque. Install the 5/16
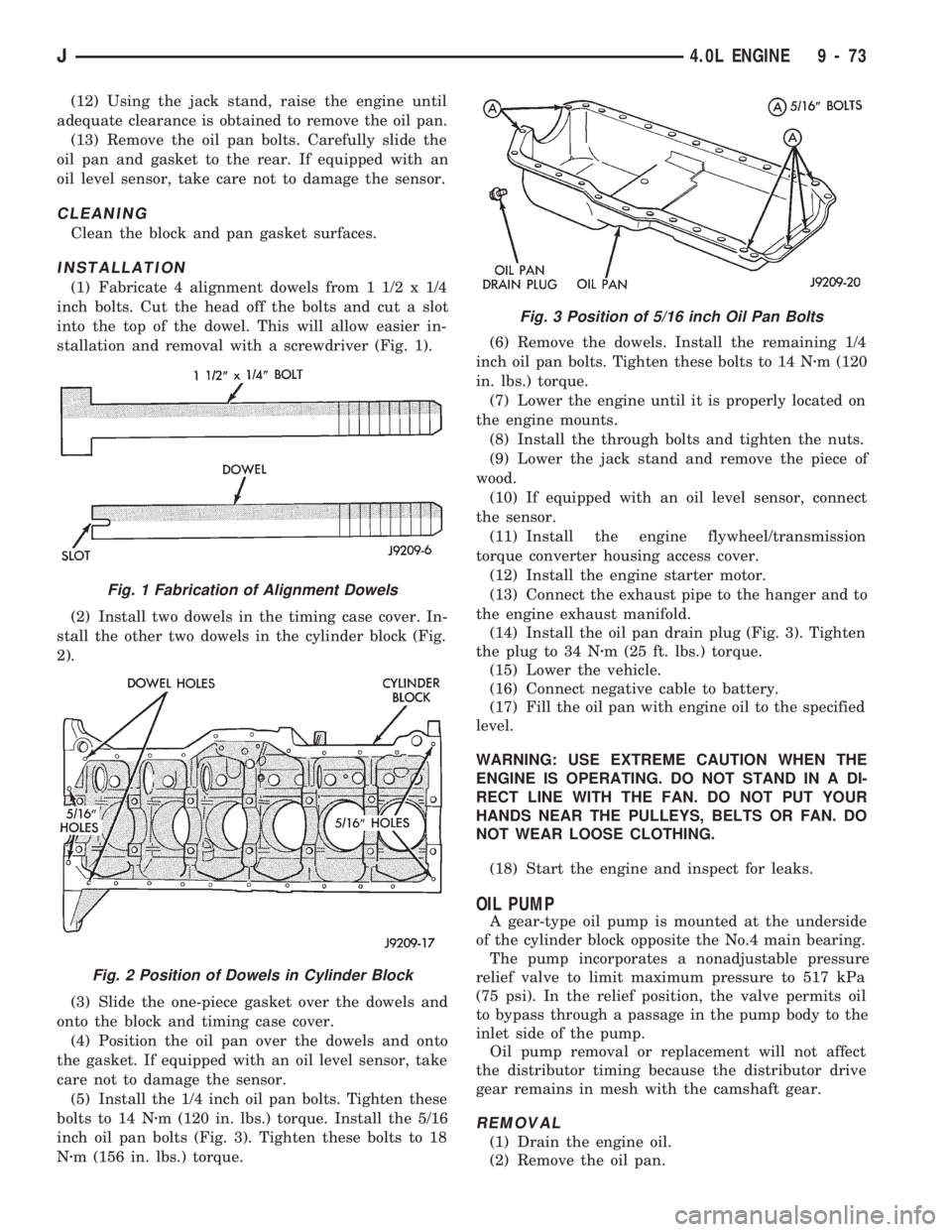
inch oil pan bolts (Fig. 3). Tighten these bolts to 18
Nzm (156 in. lbs.) torque.(6) Remove the dowels. Install the remaining 1/4
inch oil pan bolts. Tighten these bolts to 14 Nzm (120
in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Lower the engine until it is properly located on
the engine mounts.
(8) Install the through bolts and tighten the nuts.
(9) Lower the jack stand and remove the piece of
wood.
(10) If equipped with an oil level sensor, connect
the sensor.
(11) Install the engine flywheel/transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(12) Install the engine starter motor.
(13) Connect the exhaust pipe to the hanger and to
the engine exhaust manifold.
(14) Install the oil pan drain plug (Fig. 3). Tighten
the plug to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Connect negative cable to battery.
(17) Fill the oil pan with engine oil to the specified
level.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A DI-
RECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(18) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
OIL PUMP
A gear-type oil pump is mounted at the underside
of the cylinder block opposite the No.4 main bearing.
The pump incorporates a nonadjustable pressure
relief valve to limit maximum pressure to 517 kPa
(75 psi). In the relief position, the valve permits oil
to bypass through a passage in the pump body to the
inlet side of the pump.
Oil pump removal or replacement will not affect
the distributor timing because the distributor drive
gear remains in mesh with the camshaft gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain the engine oil.
(2) Remove the oil pan.
Fig. 1 Fabrication of Alignment Dowels
Fig. 2 Position of Dowels in Cylinder Block
Fig. 3 Position of 5/16 inch Oil Pan Bolts
J4.0L ENGINE 9 - 73
Page 978 of 1784

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM
OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.24
Air Conditioning (A/C) ControlsÐPCM Input.... 19
Auto Shut Down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output.... 24
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) SenseÐPCM Input . 19
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input................ 19
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input.................. 20
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input........ 20
Crankshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input....... 20
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Input............ 20
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output........... 24
EMR LampÐPCM Output.................. 24
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input . 21
Extended Idle SwitchÐPCM Input............ 21
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output................ 25
Fuel Pressure Regulator................... 30
Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output............. 25
Fuel Rail............................... 30
General Information....................... 17
Generator FieldÐPCM Output............... 25
Generator LampÐPCM Output.............. 25
Idle Air Control (IAC) MotorÐPCM Output...... 25
Ignition Circuit SenseÐPCM Input............ 21
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output.................. 26Intake Air Temperature SensorÐPCM Input.... 20
Malfunction Indicator LampÐPCM Output...... 26
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐ
PCM Input............................ 21
Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes of Operation . . . 27
Overdrive/Override Switch.................. 22
Oxygen (O2S) SensorÐPCM Input........... 22
Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input............. 22
Power Ground........................... 22
Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐPCM Input . . . 22
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............ 18
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output............ 26
SCI ReceiveÐPCM Input.................. 22
SCI TransmitÐPCM Output................. 26
Sensor ReturnÐPCM Input................. 23
Shift IndicatorÐPCM Output................ 26
Speed ControlÐPCM Input................. 23
Speed ControlÐPCM Output................ 27
TachometerÐPCM Output.................. 27
Throttle Body............................ 29
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input..... 23
Torque Converter Clutch RelayÐPCM Output . . . 27
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input........... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
All 2.5L 4 cylinder and 4.0L 6 cylinder engines are
equipped with sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection
(MFI). The MFI system provides precise air/fuel ra-
tios for all driving conditions.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the fuel system. The PCM was formerly referred to
as the SBEC or engine controller. The PCM is a pre-
programmed, dual microprocessor digital computer.
It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission
control devices, charging system, speed control, air
conditioning compressor clutch engagement and idle
speed. The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputsrep-
resent the instantaneous engine operating conditions.
Air-fuel mixture and ignition timing calibrations for
various driving and atmospheric conditions are pre-
programmed into the PCM. The PCM monitors and
analyzes various inputs. It then computes engine fuel
and ignition timing requirements based on these in-
puts. Fuel delivery control and ignition timing will
then be adjusted accordingly.
Other inputs to the PCM are provided by the brake
light switch, air conditioning select switch and the
speed control switches. All inputs to the PCM are
converted into signals.
Electrically operated fuel injectors spray fuel in
precise metered amounts into the intake port directlyabove the intake valve. The injectors are fired in a
specific sequence by the PCM. The PCM maintains
an air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1 by constantly adjusting
injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time that the injector opens and sprays fuel
into the chamber. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width by opening and closing the ground path to the
injector.
Manifold absolute pressure (air density) and engine
rpm (speed) are the primary inputs that determine
fuel injector pulse width. The PCM also monitors
other inputs when adjusting air-fuel ratio.
Inputs That Effect Fuel Injector Pulse Width
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
²Engine speed
²Throttle position
²Battery voltage
²Air conditioning selection
²Transmission gear selection (automatic transmis-
sions only)
²Speed control
The powertrain control module (PCM) adjusts igni-
tion timing by controlling ignition coil operation. The
ignition coil receives battery voltage when the igni-
tion key is in the run or starter position. The PCM
provides a ground for the ignition coil. The coil dis-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 17
Page 989 of 1784

²Intake manifold air temperature sensor input is
monitored
²Throttle position sensor (TPS) is monitored
²The auto shut down (ASD) relay is energized by
the PCM for approximately three seconds.
²The fuel pump is energized through the fuel pump
relay by the PCM. The fuel pump will operate for ap-
proximately one second unless the engine is operat-
ing or the starter motor is engaged
²The O2S sensor heater element is energized
through the fuel pump relay. The O2S sensor input
is not used by the PCM to calibrate air-fuel ratio
during this mode of operation.
²The up-shift indicator light is illuminated (manual
transmission only).
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged.
The powertrain control module (PCM) receives in-
puts from:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Starter motor relay
²Camshaft position sensor signal
The PCM monitors the crankshaft position sensor.
If the PCM does not receive a crankshaft position
sensor signal within 3 seconds of cranking the en-
gine, it will shut down the fuel injection system.
The fuel pump is activated by the PCM through
the fuel pump relay.
Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
PCM. The PCM will then control the injection se-
quence and injector pulse width by turning the
ground circuit to each individual injector on and off.
The PCM determines the proper ignition timing ac-
cording to input received from the crankshaft posi-
tion sensor.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During engine warm-
up, the powertrain control module (PCM) receives in-
puts from:
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal (in the distributor)
²Park/Neutral Switch (Gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)Based on these inputs the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM will
then control the injection sequence and injector pulse
width by turning the ground circuit to each individ-
ual injector on and off.
²The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control (IAC) motor and adjusts ignition tim-
ing.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the clutch relay. This is done if A/C has
been selected by the vehicle operator and requested
by the A/C thermostat.
²If the vehicle has a manual transmission, the up-
shift light is operated by the PCM.
²When engine has reached operating temperature,
the PCM will begin monitoring O2S sensor input.
The system will then leave the warm-up mode and
go into closed loop operation.
IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is a Closed Loop mode. At idle speed, the powertrain
control module (PCM) receives inputs from:
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal (in the distributor)
²Battery voltage
²Park/Neutral Switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Oxygen sensor
Based on these inputs, the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM will
then control injection sequence and injector pulse
width by turning the ground circuit to each individ-
ual injector on and off.
²The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and ad-
justs air-fuel ratio by varying injector pulse width. It
also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by increasing
and decreasing spark advance.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the clutch relay. This happens if A/C has
been selected by the vehicle operator and requested
by the A/C thermostat.
The optional Extended Idle Switch is used to raise
the engine idle speed to approximately 1000 rpm.
This is when the shifter is in either the Park or Neu-
tral position. A rocker-type 2-wire switch (extended
idle switch) is mounted to the instrument panel. This
14 - 28 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 993 of 1784

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐGENERAL DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay Testing...... 43
Camshaft Position Sensor Test.............. 43
Crankshaft Position Sensor Test............. 44
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).............. 51
DRB Scan Tool.......................... 51
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Test...... 43
Extended Idle Switch Test.................. 45
Fuel Pump Relay Testing.................. 44
Fuel System Pressure Test................. 48
General Information....................... 32
Idle Air Control Motor Test................. 46
Injector Test............................ 48
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Test.......... 43Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Test . 44
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)................ 48
Oxygen Sensor (O2S) Heating Element Test.... 45
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 60-Way
Connector............................ 38
RelaysÐOperation/Testing.................. 47
Starter Motor Relay Test................... 48
System Schematics....................... 38
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Test.......... 45
Torque Converter Clutch Relay Test.......... 45
Vehicle Speed Sensor Test................. 45
Visual Inspection......................... 32
GENERAL INFORMATION
All 2.5L 4 cylinder and 4.0L 6 cylinder engines are
equipped with sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection
(MFI). The MFI system provides precise air/fuel ra-
tios for all driving conditions.
VISUAL INSPECTION
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will in-
clude the following checks:
(1) Verify that the 60-way connector is fully inserted
into the connector of the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) (Figs. 1 or 2). Verify that the connector mount-
ing bolt is tightened to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning com-
pressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect ASD relay andradiator fan relay (if equipped) connections. Inspect starter
motor relay connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical
damage and corrosion. The relays are installed in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Figs. 3 or 4).
Fig. 1 PCMÐYJ Models
Fig. 2 PCMÐXJ Models
Fig. 3 PDCÐYJ Models
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMJ