1994 JEEP CHEROKEE stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 971 of 1784
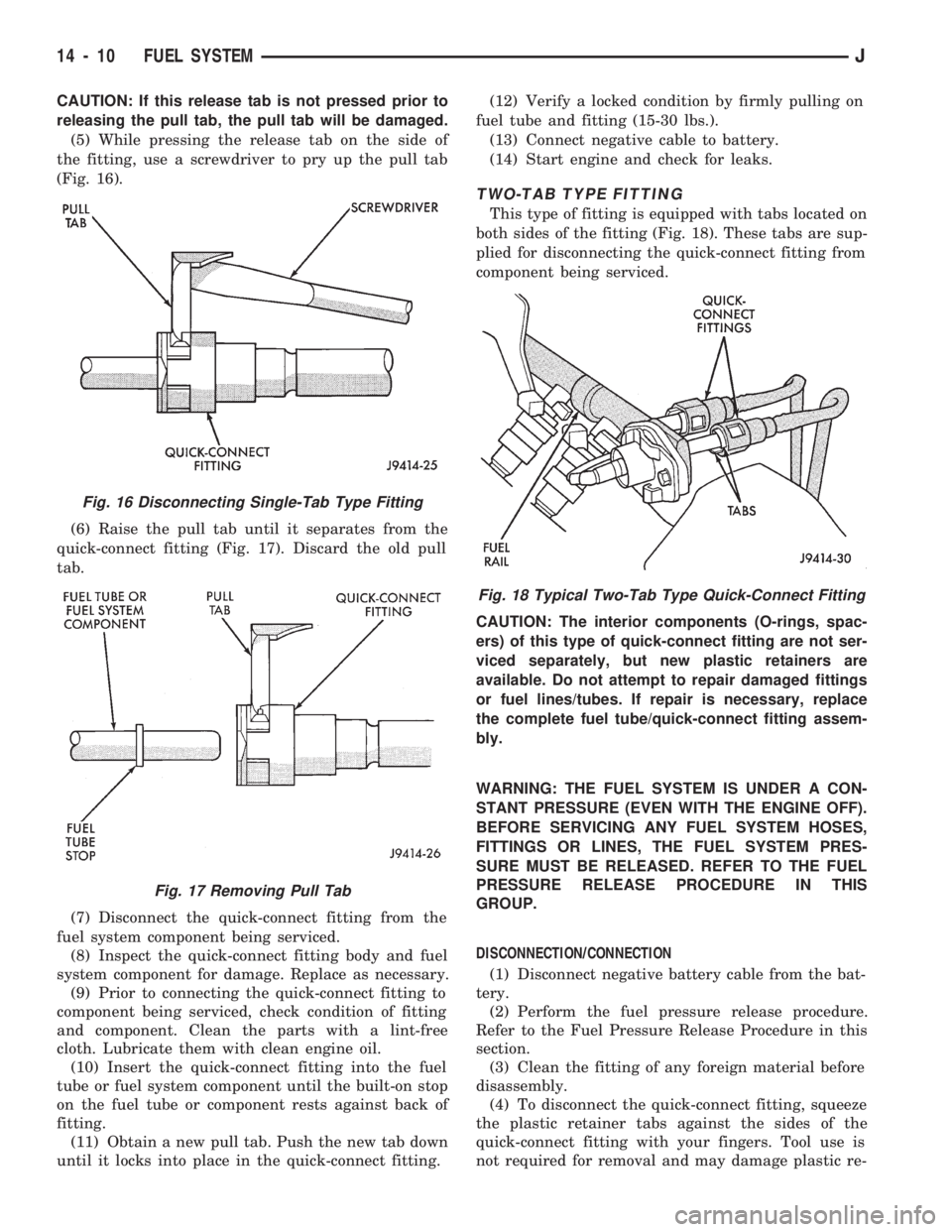
CAUTION: If this release tab is not pressed prior to
releasing the pull tab, the pull tab will be damaged.
(5) While pressing the release tab on the side of
the fitting, use a screwdriver to pry up the pull tab
(Fig. 16).
(6) Raise the pull tab until it separates from the
quick-connect fitting (Fig. 17). Discard the old pull
tab.
(7) Disconnect the quick-connect fitting from the
fuel system component being serviced.
(8) Inspect the quick-connect fitting body and fuel
system component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(9) Prior to connecting the quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean the parts with a lint-free
cloth. Lubricate them with clean engine oil.
(10) Insert the quick-connect fitting into the fuel
tube or fuel system component until the built-on stop
on the fuel tube or component rests against back of
fitting.
(11) Obtain a new pull tab. Push the new tab down
until it locks into place in the quick-connect fitting.(12) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(13) Connect negative cable to battery.
(14) Start engine and check for leaks.
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 18). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assem-
bly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Clean the fitting of any foreign material before
disassembly.
(4) To disconnect the quick-connect fitting, squeeze
the plastic retainer tabs against the sides of the
quick-connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is
not required for removal and may damage plastic re-
Fig. 16 Disconnecting Single-Tab Type Fitting
Fig. 17 Removing Pull Tab
Fig. 18 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 987 of 1784

ing the IAC motor pintle in and out of the air control
passage. The IAC motor is positioned when the igni-
tion key is turned to the On position.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
System voltage is supplied to the ignition coil pos-
itive terminal. The powertrain control module (PCM)
operates the ignition coil.Base (initial) ignition
timing is not adjustable.The PCM adjusts ignition
timing to meet changing engine operating conditions.
The ignition coil is located near the ignition distrib-
utor (Fig. 22).
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System for additional
information.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (formerly referred
to as the Check Engine Lamp) illuminates on the in-
strument panel each time the ignition key is turned
on. It will stay on for three seconds as a bulb test.
If the powertrain control module (PCM) receives an
incorrect signal, or no signal from certain sensors or
emission related systems, the lamp is turned on. This
is a warning that the PCM has recorded a system or
sensor malfunction. In some cases, when a problem is
declared, the PCM will go into a limp-in mode. This
is an attempt to keep the system operating. It signals
an immediate need for service.
The lamp can also be used to display a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch On-
Off-On-Off-On within three seconds and any codes
stored in the PCM memory will be displayed. This is
done in a series of flashes representing digits. Refer
to On-Board Diagnostics in the General Diagnosis
section of this group for more information.
RADIATOR FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
XJ MODELS ONLY
The electric radiator cooling fan used in XJ models
(equipped with 4.0L engine, heavy duty cooling
and/or air conditioning) is controlled by the power-
train control module (PCM) through radiator fan re-
lay. The relay is energized when coolant temperature
is above 103ÉC (217ÉF). It will then de-energize when
coolant temperature drops to 98ÉC (208ÉF). Refer to
Group 7, Cooling Systems for more information.
The relay is located in the power distribution cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 23).
The electric radiator cooling fan is not used on YJ
models.
SCI TRANSMITÐPCM OUTPUT
SCI Transmit is the serial data communication
transmit circuit for the DRB scan tool. The power-
train control module (PCM) transmits data to the
DRB through the SCI Transmit circuit.
SHIFT INDICATORÐPCM OUTPUT
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an Up-Shift indicator lamp. The lamp is controlled
by the powertrain control module (PCM). The lamp
illuminates on the instrument panel to indicate when
the driver should shift to the next highest gear for
best fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp OFF
after 3 to 5 seconds if the shift of gears is not per-
formed. The up-shift light will remain off until vehi-
cle stops accelerating and is brought back to range of
up-shift light operation. This will also happen if ve-
hicle is shifted into fifth gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned on and it is turned off
when the engine is started up. With the engine run-
ning, the lamp is turned on/off depending upon en-
gine speed and load.
Fig. 23 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 22 Ignition CoilÐTypical
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1026 of 1784

SERVICE DIAGNOSIS/PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Runout................................. 4
Unbalance............................... 3Universal Joint Angle Measurement............ 4
Vibration................................ 3
VIBRATION
Tires that are out-of-round or wheels that are un-
balanced will cause a low frequency vibration. Refer
to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for additional infor-
mation.
Brake drums that are unbalanced will cause a
harsh, low frequency vibration. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for additional information.
Driveline vibration can also result from loose or
damaged engine mounts. Refer to Group 21, Trans-
missions for additional information.
Propeller shaft vibration will increase as the vehi-
cle speed is increased. A vibration that occurs within
a specific speed range is not caused by propeller
shaft unbalance. Defective universal joints or an in-
correct propeller shaft angle are usually the cause.
UNBALANCE
If propeller shaft unbalance is suspected, it can be
verified with the following procedure.
Removing and re-indexing the propeller shaft
180É may eliminate some vibrations.
²Clean all the foreign material from the propeller
shaft and the universal joints.²Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds, and bent areas.If the pro-
peller shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
²Ensure the universal joints are not worn, are prop-
erly installed, and are correctly aligned with the
shaft.
²Check the universal joint clamp screws torque
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tires assembly. Install
the wheel lug nuts to retain the brake drums.
(3) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.
(4) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration oc-
curred. Stop the engine.
(5) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 1).
(6) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(7) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the vibration may not be propshaft
unbalance.
DRIVELINE VIBRATION
JPROPELLER SHAFTS 16 - 3
Page 1040 of 1784

POWER STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
PUMP PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check belt tension and adjust as necessary.
(2) Disconnect high pressure hose at gear or pump.
Use a container for dripping fluid.
(3) Connect Gauge 7617 (J21567) to both hoses us-
ing adapter fitting (Fig. 1). Connect spare pressure
hose to gear or pump.
(4) Open the test valve completely.
(5) Start engine and let idle.
(6) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary.
(7) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the
range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than 5 seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
(8) Close valve fully three times and record highest
pressure indicated each time.All three readings
must be above specifications and within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other.
²Pressures above specifications but not within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace pump.
²Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other
but below specifications, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 2 to 4 seconds at a time.
Pump damage will result.
(9) Open the test valve, turn steering wheel ex-
treme left and right positions against the stops.
Record the highest indicated pressure at each posi-
tion. Compare readings to specifications. If highest
output pressures are not the same against either
stop, the gear is leaking internally and must be re-
paired.
Fig. 1 Pressure Test Gauge
PUMP OPERATING SPECIFICATIONS
JSTEERING 19 - 3
Page 1050 of 1784

(2) Remove fitting from pump housing (Fig. 10).
Prevent flow control valve and spring from
sliding out of housing bore.
(3) Remove and discard O-ring seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) If necessary, clean and install flow control valve
and spring in pump housing bore.Be sure the hex
nut end of the valve is facing in toward pump.
(2) Install O-ring seal onto fitting (Fig. 10).(3) Install flow control valve in pump housing and
tighten to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install pressure hose to valve.
POWER STEERING PUMPÐINITIAL OPERATION
CAUTION: The fluid level should be checked with
engine off to prevent injury from moving compo-
nents. Use only Mopar Power Steering Fluid. Do not
use automatic transmission fluid. Do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicate FULL COLD when the
fluid is at normal temperature 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to
80ÉF).
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds.
Then turn the engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Start the engine. Slowly turn the steering
wheel right and left, lightly contacting the wheel
stops.
(6) Add power steering fluid if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle and turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock to lock.
(8) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and refill
as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stand a few minutes and repeat the above pro-
cedure.
Fig. 10 Flow Control Valve Fitting
JSTEERING 19 - 13
Page 1058 of 1784
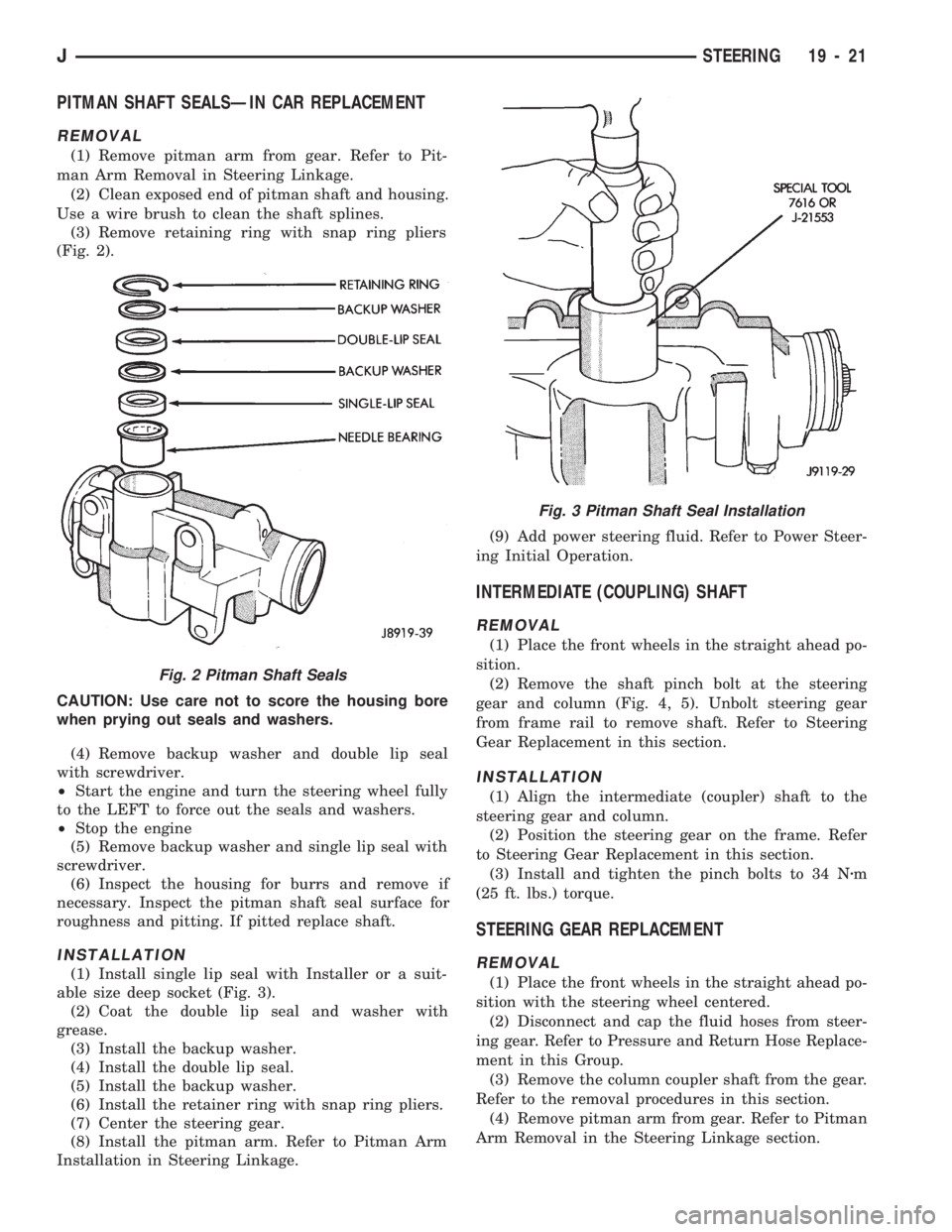
PITMAN SHAFT SEALSÐIN CAR REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove pitman arm from gear. Refer to Pit-
man Arm Removal in Steering Linkage.
(2) Clean exposed end of pitman shaft and housing.
Use a wire brush to clean the shaft splines.
(3) Remove retaining ring with snap ring pliers
(Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Use care not to score the housing bore
when prying out seals and washers.
(4) Remove backup washer and double lip seal
with screwdriver.
²Start the engine and turn the steering wheel fully
to the LEFT to force out the seals and washers.
²Stop the engine
(5) Remove backup washer and single lip seal with
screwdriver.
(6) Inspect the housing for burrs and remove if
necessary. Inspect the pitman shaft seal surface for
roughness and pitting. If pitted replace shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install single lip seal with Installer or a suit-
able size deep socket (Fig. 3).
(2) Coat the double lip seal and washer with
grease.
(3) Install the backup washer.
(4) Install the double lip seal.
(5) Install the backup washer.
(6) Install the retainer ring with snap ring pliers.
(7) Center the steering gear.
(8) Install the pitman arm. Refer to Pitman Arm
Installation in Steering Linkage.(9) Add power steering fluid. Refer to Power Steer-
ing Initial Operation.
INTERMEDIATE (COUPLING) SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight ahead po-
sition.
(2) Remove the shaft pinch bolt at the steering
gear and column (Fig. 4, 5). Unbolt steering gear
from frame rail to remove shaft. Refer to Steering
Gear Replacement in this section.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the intermediate (coupler) shaft to the
steering gear and column.
(2) Position the steering gear on the frame. Refer
to Steering Gear Replacement in this section.
(3) Install and tighten the pinch bolts to 34 Nzm
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
STEERING GEAR REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight ahead po-
sition with the steering wheel centered.
(2) Disconnect and cap the fluid hoses from steer-
ing gear. Refer to Pressure and Return Hose Replace-
ment in this Group.
(3) Remove the column coupler shaft from the gear.
Refer to the removal procedures in this section.
(4) Remove pitman arm from gear. Refer to Pitman
Arm Removal in the Steering Linkage section.
Fig. 2 Pitman Shaft Seals
Fig. 3 Pitman Shaft Seal Installation
JSTEERING 19 - 21
Page 1061 of 1784

(2) Starting at either stop turn the stub shaft back
1/2 the total number of turns. This is the center of
the gear travel (Fig. 12).
(3) Turn the pitman shaft adjuster screw back
(COUNTERCLOCKWISE) until extended, then turn
back in (CLOCKWISE) one full turn.
(4) Place the torque wrench in the vertical position
on the stub shaft. Rotate the wrench 45 degrees each
side of the center and record the highest rotational
torque on center (Fig. 13).
(5) Turn the adjuster in until torque to turn stub
shaft is 0.6 to 1.2 Nzm (6.0 to 10.0 in. lbs.) more than
reading in Step 4.
(6) Prevent the adjuster screw from turning while
tightening adjuster lock nut. Tighten the adjuster
lock nut to 49 Nzm (36 ft. lbs.).
GEAR DISASSEMBLY INFORMATION
CAUTION: Cleanliness is extremely important when
repairing a power steering gear. Keep the bench,
tools and components clean at all times. Thor-
oughly clean the exterior of the gear with cleaning
solvent before disassembly. Drain as much of the
fluid as possible. Use protective vise jaws at all
times when clamping components. During assem-bly, lubricate all components with power steering
fluid except where noted (Fig. 14).
Fig. 13 Checking Over-center Rotation Torque
Fig. 12 Steering Gear Centered
19 - 24 STEERINGJ
Page 1180 of 1784

30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Air Pressure Test........................ 73
Analyzing the Road Test................... 70
Converter Housing Leak Diagnosis........... 73
Converter Stall Test...................... 72
Diagnosis Guides and Charts............... 76
Fluid Level and Condition.................. 69Gearshift Linkage........................ 70
General Information....................... 69
Hydraulic Pressure Test................... 71
Preliminary Diagnosis..................... 69
Road Test.............................. 70
Transmission Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment . . 70
GENERAL INFORMATION
Automatic transmission problems are generally the
result of:
²poor engine performance
²incorrect fluid level
²incorrect cable/linkage adjustment
²incorrect band adjustment
²incorrect hydraulic control pressure adjustments
²hydraulic component malfunctions
²mechanical component malfunctions.
Begin diagnosis by checking the easily accessible
items such as fluid level, fluid condition and control
linkage adjustment. A road test will determine if fur-
ther diagnosis is necessary.
Procedures outlined in this section should be per-
formed in the following sequence to realize the most
accurate results:
²Preliminary diagnosis
²Check fluid Level and condition
²Check control linkage Adjustment
²Road test
²Stall test
²Hydraulic pressure test
²Air pressure tests
²Leak Tests
²Analyze test results and consult diagnosis charts
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are driveable and an alternate pro-
cedure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or
move forward).
Vehicle Is Driveable
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Adjust throttle cable and gearshift linkage if
complaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh
shifts.
(3) Road test vehicle and note transmission operat-
ing characteristics.
(4) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish, low speed acceleration or abnormal throttle
opening needed to maintain normal speeds with
properly tuned engine.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure tests.(6) Perform air pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
Vehicle Is Disabled
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken, disconnected throttle link-
age.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or
loose, missing pressure port plugs.
(4) Raise vehicle, start engine, shift transmission
into gear and note following:
(a) If propeller shafts turn but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic pressure test to
determine if problem is a hydraulic or mechanical.
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
(1) Position vehicle on level surface. This is impor-
tant in obtaining an accurate fluid level check.
(2) To avoid false readings, which could produce
under or over fill condition, do not check level until
fluid is at normal operating temperature.
(3) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Operate engine at curb idle speed.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING UNDERHOOD OP-
ERATIONS WITH THE ENGINE RUNNING, KEEP
YOUR HANDS WELL AWAY FROM HOT OR ROTAT-
ING ENGINE COMPONENTS. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE ARTICLES OF CLOTHING WHICH COULD
BECOME ENTANGLED IN ENGINE COMPONENTS
OR ACCESSORIES.
(6) Clean dipstick filler cap and tube before remov-
ing dipstick.
(7) Remove dipstick and inspect fluid level.
²Correct level is to FULL mark
²Acceptable level is between ADD and FULL marks
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 69