1994 JEEP CHEROKEE sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 323 of 1784
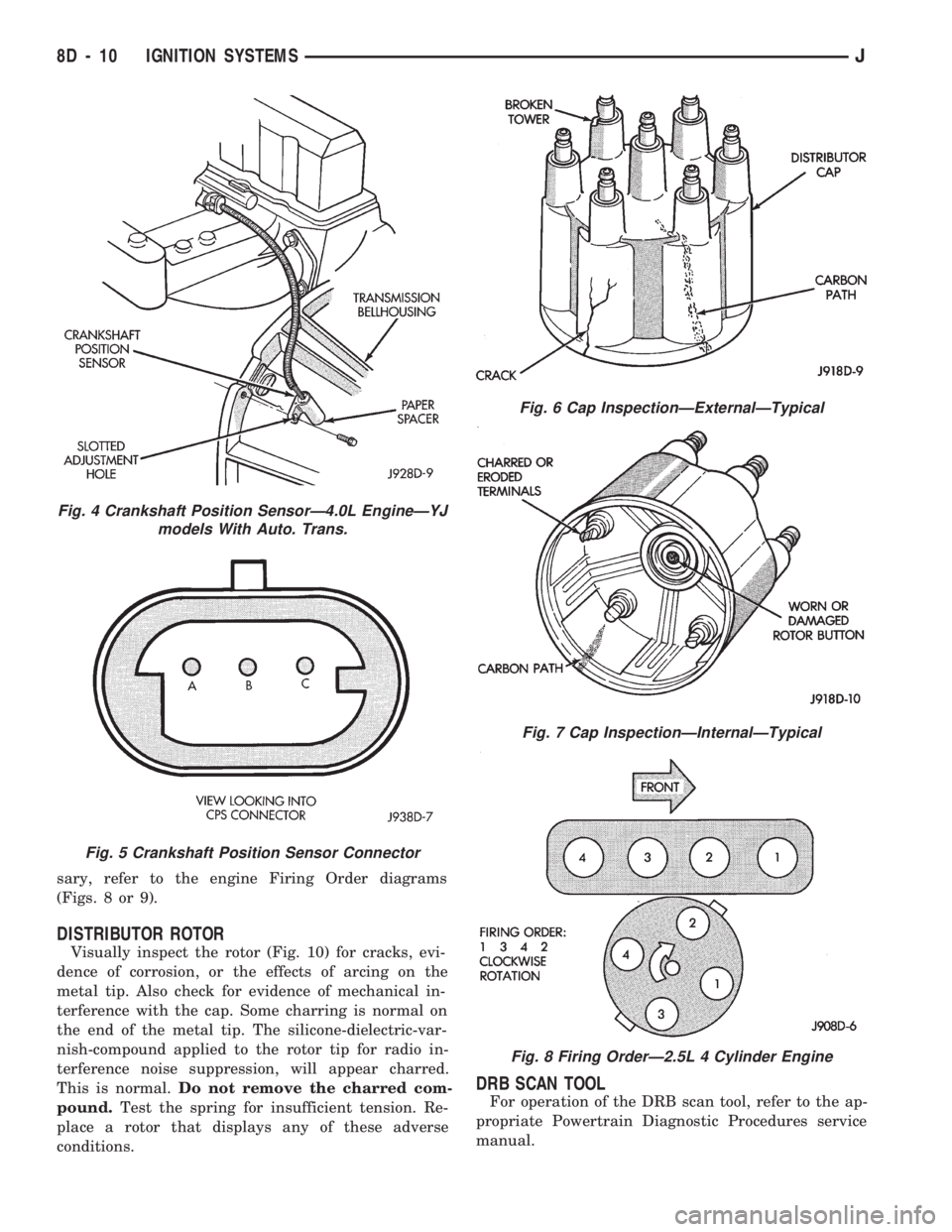
sary, refer to the engine Firing Order diagrams
(Figs. 8 or 9).
DISTRIBUTOR ROTOR
Visually inspect the rotor (Fig. 10) for cracks, evi-
dence of corrosion, or the effects of arcing on the
metal tip. Also check for evidence of mechanical in-
terference with the cap. Some charring is normal on
the end of the metal tip. The silicone-dielectric-var-
nish-compound applied to the rotor tip for radio in-
terference noise suppression, will appear charred.
This is normal.Do not remove the charred com-
pound.Test the spring for insufficient tension. Re-
place a rotor that displays any of these adverse
conditions.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L EngineÐYJ
models With Auto. Trans.
Fig. 5 Crankshaft Position Sensor Connector
Fig. 6 Cap InspectionÐExternalÐTypical
Fig. 7 Cap InspectionÐInternalÐTypical
Fig. 8 Firing OrderÐ2.5L 4 Cylinder Engine
8D - 10 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 325 of 1784

ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The sensor is installed in the thermostat housing
(Fig. 12).
(1) Disconnect wire harness connector from sensor
(Fig. 12).
(2) Test the resistance of the sensor with a high in-
put impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. The resis-
tance should be less than 1340 ohms at normal
engine operating idle temperature. For resistance
values, refer to the Sensor Resistance chart. Replace
the sensor if it is not within the range of resistance
specified in the chart.
(3) Test continuity of the wire harness. This is
done between Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
wire harness connector terminal-2 and the sensor
connector terminal. Also check continuity between
wire harness terminal-4 to the sensor connector ter-
minal. Repair the wire harness if an open circuit is
indicated.
IGNITION SECONDARY CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS
CHECKING FOR SPARK
CAUTION: When disconnecting a high voltage cable
from a spark plug or from the distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly (1/2 turn) to break it loose.
Grasp the boot (not the cable) and pull it off with a
steady, even force.
(1) Disconnect the ignition coil secondary cable
from center tower of the distributor cap. Hold the ca-
ble terminal approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from a
good engine ground (Fig. 13).WARNING: BE VERY CAREFUL WHEN THE ENGINE
IS CRANKING. DO NOT PUT YOUR HANDS NEAR
THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN. DO NOT
WEAR LOOSE FITTING CLOTHING.
(2) Rotate (crank) the engine with the starter mo-
tor and observe the cable terminal for a steady arc. If
steady arcing does not occur, inspect the secondary
coil cable. Refer to Spark Plug Cables in this group.
Also inspect the distributor cap and rotor for cracks
or burn marks. Repair as necessary. If steady arcing
occurs, connect ignition coil cable to the distributor
cap.
(3) Remove a cable from one spark plug.
Fig. 12 Coolant Temperature SensorÐTypical
SENSOR RESISTANCE (OHMS)
Fig. 13 Checking for SparkÐTypical
8D - 12 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 326 of 1784

(4) Using insulated pliers, hold the cable terminal
approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from the engine cylin-
der head or block while rotating the engine with the
starter motor. Observe the spark plug cable terminal
for an arc. If steady arcing occurs, it can be expected
that the ignition secondary system is operating cor-
rectly. If steady arcing occurs at the spark plug ca-
bles, but the engine will not start, connect the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual for DRB operation.
FAILURE TO START TEST
To prevent unnecessary diagnostic time and wrong
test results, the previous Checking For Spark test
should be performed prior to this test.
WARNING: SET PARKING BRAKE OR BLOCK THE
DRIVE WHEELS BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH THIS
TEST.
(1) Unplug the ignition coil harness connector at
the coil (Fig. 14).
(2) Connect a set of small jumper wires (18 gauge
or smaller) between the ignition coil and coil electri-
cal connector (Fig. 15).
(3) Determine that sufficient battery voltage (12.4
volts) is present for the starting and ignition sys-
tems.
(4) Crank the engine for 5 seconds while monitor-
ing the voltage at the coil positive terminal:
²If the voltage remains near zero during the entire
period of cranking, refer to On-Board Diagnostics in
Group 14, Fuel Systems. Check the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM) and auto shut down relay.
²If voltage is at near battery voltage and drops to
zero after 1-2 seconds of cranking, check the cam-
shaft position sensor-to-PCM circuit. Refer to On-
Board Diagnostics in Group 14, Fuel Systems.
²If voltage remains at near battery voltage during
the entire 5 seconds, turn the key off. Remove the60-way connector (Fig. 16) from the PCM. Check 60-
way connector for any spread terminals.
(5) Remove test lead from the coil positive termi-
nal. Connect an 18 gauge jumper wire between the
battery positive terminal and the coil positive termi-
nal.
(6) Make the special jumper shown in Figure 17.
Using the jumper,momentarilyground terminal-19
of the 60-way connector. A spark should be generated
at the coil cable when the ground is removed.
(7) If spark is generated, replace the powertrain
control module (PCM).
(8) If spark is not seen, use the special jumper to
ground the coil negative terminal directly.
(9) If spark is produced, repair wiring harness for
an open condition.
Fig. 14 Coil Harness ConnectorÐTypical
Fig. 15 Coil TerminalsÐTypical
Fig. 16 PCM 60-Way Connector
Fig. 17 Special Jumper Ground-to-Coil Negative
Terminal
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 13
Page 327 of 1784

(10) If spark is not produced, replace the ignition
coil.
IGNITION TIMING
Base (initial) ignition timing is NOT adjustable
on any of the 2.5L 4 cylinder or 4.0L 6 cylinder
engines. Do not attempt to adjust ignition timing
by rotating the distributor.
Do not attempt to modify the distributor hous-
ing to get distributor rotation. Distributor posi-
tion will have no effect on ignition timing.
All ignition timing functions are controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM). Refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in the Multi-Port Fuel InjectionÐGen-
eral Diagnosis section of Group 14, Fuel Systems for
more information. Also refer to the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedures service manual for
operation of the DRB Scan Tool.
INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
(1) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
sensor (Figs. 18 or 19).
(2) Test the resistance of the sensor with a input
impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. Do not remove
the sensor from the engine for testing. For resistance
values, refer to the Sensor Resistance chart. Replace
the sensor if it is not within the range of resistance
specified in the chart.
(3) Test the resistance of the wire harness. This is
done between the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
wire harness connector terminal-21 and the sensor
connector terminal. Also check continuity between
terminal-4 to the sensor connector terminal. Repair
the wire harness as necessary if the resistance is
greater than 1 ohm.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The MAP sensor is located on the cowl panel near
the rear of the engine cylinder head (valve) cover
(Fig. 20).
(1) Inspect the sensor vacuum hose connections at
the throttle body and sensor (Fig. 20). Repair as nec-
essary.
CAUTION: When testing the sensor, be sure that
the harness wires are not damaged by the test
meter probes.Fig. 18 Air Temperature SensorÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 19 Air Temperature SensorÐ4.0L Engine
SENSOR RESISTANCE (OHMS)
8D - 14 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 328 of 1784

(2) Test the sensor output voltage at the sensor
connector between terminals A and B as marked on
the sensor body (Fig. 21). This is done with the igni-
tion switch ON and the engine OFF. Output voltage
should be 4-to-5 volts.The voltage should drop to
1.5-to-2.1 volts with a hot, neutral idle speed con-
dition.
(3) Test Powertrain Control Module (PCM) termi-
nal-1 for the same voltage described above to verify
the wire harness condition. Repair as necessary.
(4) Test sensor supply voltage at sensor connector
between terminals A and C with the ignition ON.
The voltage should be approximately 5 volts (60.5V).
Five volts (60.5V) should also be at terminal-6 of the
corresponding Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
wire harness connector. Repair or replace the wire
harness as necessary.(5) Test the sensor ground circuit at sensor connec-
tor terminal-A and PCM connector terminal-4. Re-
pair the wire harness if necessary.
(6) Test the sensor ground circuit at the PCM con-
nector between terminal-4 and terminal-11 with an
ohmmeter. If the ohmmeter indicates an open circuit,
inspect for a defective sensor ground connection. Re-
fer to Group 8W, Wiring for location of ground con-
nection. If the ground connection is good, replace the
PCM. If terminal-4 has a short circuit to 12 volts,
correct this condition before replacing the PCM.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The PCM (formerly called the SBEC or engine con-
troller) is located in the engine compartment behind
the windshield washer fluid tank on YJ models (Fig.
22). It is located in the engine compartment next to
the air cleaner on XJ models (Fig. 23).
The ignition system is controlled by the PCM.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
Fig. 20 MAP SensorÐTypical
Fig. 21 MAP Sensor TestÐTypical
Fig. 22 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
Fig. 23 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 15
Page 331 of 1784

Check the high-tension cable connections for good
contact at the ignition coil, distributor cap towers
and spark plugs. Terminals should be fully seated.
The terminals and spark plug covers should be in
good condition. Terminals should fit tightly to the ig-
nition coil, distributor cap and spark plugs. The
spark plug cover (boot) of the cable should fit tight
around the spark plug insulator. Loose cable connec-
tions can cause corrosion and increase resistance, re-
sulting in shorter cable service life.
Clean the high tension cables with a cloth moist-
ened with a nonflammable solvent and wipe dry.
Check for brittle or cracked insulation.
When testing secondary cables for damage with an
oscilloscope, follow the instructions of the equipment
manufacturer.
If an oscilloscope is not available, spark plug cables
may be tested as follows:
CAUTION: Do not leave any one spark plug cable
disconnected for longer than necessary during test-
ing. This may cause possible heat damage to the
catalytic converter. Total test time must not exceed
ten minutes.
With the engine not running, connect one end of a
test probe to a good ground. Start the engine and run
the other end of the test probe along the entire
length of all spark plug cables. If cables are cracked
or punctured, there will be a noticeable spark jump
from the damaged area to the test probe. The cable
running from the ignition coil to the distributor cap
can be checked in the same manner. Cracked, dam-
aged or faulty cables should be replaced with resis-
tance type cable. This can be identified by the words
ELECTRONIC SUPPRESSION printed on the cable
jacket.
Use an ohmmeter to test for open circuits, exces-
sive resistance or loose terminals. Remove the dis-
tributor cap from the distributor.Do not remove
cables from cap.Remove cable from spark plug.
Connect ohmmeter to spark plug terminal end of ca-
ble and to corresponding electrode in distributor cap.
Resistance should be 250 to 1000 Ohms per inch of
cable. If not, remove cable from distributor cap tower
and connect ohmmeter to the terminal ends of cable.
If resistance is not within specifications as found in
the Spark Plug Cable Resistance chart, replace the
cable. Test all spark plug cables in this manner.To test ignition coil-to-distributor cap cable, do not
remove the cable from the cap. Connect ohmmeter to
rotor button (center contact) of distributor cap and
terminal at ignition coil end of cable. If resistance is
not within specifications as found in the Spark Plug
Cable Resistance chart, remove the cable from the
distributor cap. Connect the ohmmeter to the termi-
nal ends of the cable. If resistance is not within spec-
ifications as found in the Spark Plug Cable
Resistance chart, replace the cable. Inspect the igni-
tion coil tower for cracks, burns or corrosion.
For removal and installation of spark plug cables,
refer to Spark Plug Secondary Cables in the Compo-
nent Removal/Installation section.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The throttle position sensor can be tested with a
digital voltmeter. The center terminal of the sensor
connector is the output terminal (Figs. 30 or 31).
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
Fig. 30 SensorÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 31 SensorÐ4.0L Engine
8D - 18 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 332 of 1784

With the ignition key in the ON position and en-
gine not running, check the sensor output voltage at
the center terminal wire of the connector. Check this
at idle (throttle plate closed) and at wide open throt-
tle (WOT). At idle, sensor output voltage should be
greater than 200 millivolts. At wide open throttle,
sensor output voltage must be less than 4.8 volts.
The output voltage should increase gradually as the
throttle plate is slowly opened from idle to WOT.
OXYGEN SENSOR TESTS
For diagnosis, removal or installation, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems in this manual.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
FOR IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain ignition system cir-
cuits:
EXAMPLE:
If a reference signal is not being detected during
engine cranking from the crankshaft position sensor,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 11 can be
observed at the Check Engine Lamp.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit of-
ten enough to indicate an actual problem, a DTC is
stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory
for eventual display to the service technician. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be en-
tered into PCM memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine rpm, engine temperature and/or
input voltage to the PCM.
A DTC indicates that the PCM has recognized an
abnormal signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC
may indicate the result of a failure, but never iden-
tify the failed component directly.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) in Group 14, Fuel Systems for additional in-
formation.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp. This lamp was formerly referred to
as the Check Engine Lamp. The lamp is located on
the instrument panel.
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
connects to the data link connector in the enginecompartment (Figs. 32 or 33). For operation of the
DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 1
more time, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
number 11 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 3 times, pauses and flashes 5
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 35 is indicated.
After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored
information.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, the DRB scan
tool must be used to erase a DTC. Refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
Fig. 32 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 33 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 19
Page 333 of 1784

COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay........... 20
Camshaft Position Sensor.................. 20
Crankshaft Position Sensor................. 21
Distributor.............................. 23
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.......... 22
General Information....................... 20
Ignition Coil............................. 26Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor....... 27
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor..... 27
Oxygen (O2S) Sensor..................... 28
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............ 28
Spark Plug Secondary Cables............... 29
Spark Plugs............................ 28
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS).............. 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section of the group, Component Removal/In-
stallation, will discuss the removal and installation
of ignition system components.
For basic ignition system diagnostics and service
adjustments, refer to the Diagnostics/Service Proce-
dures section of this group.
For system operation and component identification,
refer to the Component Identification/System Opera-
tion section of this group.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY
The ASD relay is installed in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) (Fig. 1). Relay location is printed
on the PDC cover.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the PDC cover.
(2) Remove the relay by lifting straight up.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check the condition of relay wire terminals at
PDC before installing relay. Repair as necessary.
(2) Push the relay into the connector.
(3) Install the relay cover.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor is located in the dis-
tributor.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the distributor. Refer to Distributor
Removal.
(2) Remove the distributor rotor.
CAUTION: Do not position the distributor in a vise
when removing or installing the drive gear roll pin.
Support the distributor with wooden blocks.
(3) Mark the position of the gear and the shaft in
line with the roll pin. The gearMUSTbe installed
back to its original position on the distributor shaft.
(4) Using a small pin punch and hammer, remove
the distributor gear roll (spring) pin (Fig. 3).
(5) Lightly tap the end of the distributor shaft un-
til distributor gear and thrust washer are removed.
(6) Slide the distributor shaft out of the distributor
housing.
(7) Remove the camshaft position sensor mounting
screw and positioning arm (Fig. 4).
(8) Slide the wire harness grommet out of the dis-
tributor housing. Remove the camshaft position sen-
sor.
Fig. 1 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 2 PDCÐYJ Models
8D - 20 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ