1994 JEEP CHEROKEE battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 302 of 1784

CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim us-
ing a screwdriver as the synthetic fiber may be
damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
engine may overheat because the water pump will
be rotating in the wrong direction if the belt is in-
stalled incorrectly. Refer to the belt routing label in
engine compartment, or see Group 7 - Belt Sche-
matics.
(10) Place serpentine belt over pulley.
(11) Belt tension adjustment is made at power
steering pump (Fig. 6).
(12) Turn adjusting bolt until belt has correct ten-
sion. See Belt Tension in Specifications.
(13) Tighten rear mounting bolts, pivot bolt, and
lock nut to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Remove support and lower vehicle.
(15) Connect negative cable to battery.
GENERATOR REPLACEMENTÐRIGHT HAND DRIVE
The generator used on the right hand drive is the
same as used on left hand drive. However, the
mounting and accessory drive belt installation are
different.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DISCONNECT NEGATIVE
CABLE FROM BATTERY BEFORE DISCONNECTING
RED (OUTPUT) WIRE CONNECTOR FROM GENER-
ATOR CAN RESULT IN INJURY.
(1) Remove negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove 2 screws holding electric cooling fan
(Fig. 8).
(3) Unplug electric cooling fan connector.
(4) Pull fan up and out of vehicle.
(5) Remove generator drive belt. See Group 7 -
Cooling System, for instructions.
(6) Remove generator mounting bolts.
(7) Position generator to gain access to all of the
wire connectors.(8) Remove B+ terminal nut, 2 field terminal
nuts, ground and harness holddown nuts (Fig. 9). Re-
move wire connector assembly.
(9) Remove generator from vehicle.
(10) To install generator, reverse the removal pro-
cedures. Refer to Group 7 for belt installation.
(11) Tighten battery cable bolts to 10-20 Nzm (90-
178 in. lbs.).
Fig. 8 Electric Cooling Fan Removal/Installation
Fig. 9 Remove or Install Connector Assembly
JBATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE 8B - 9
Page 303 of 1784
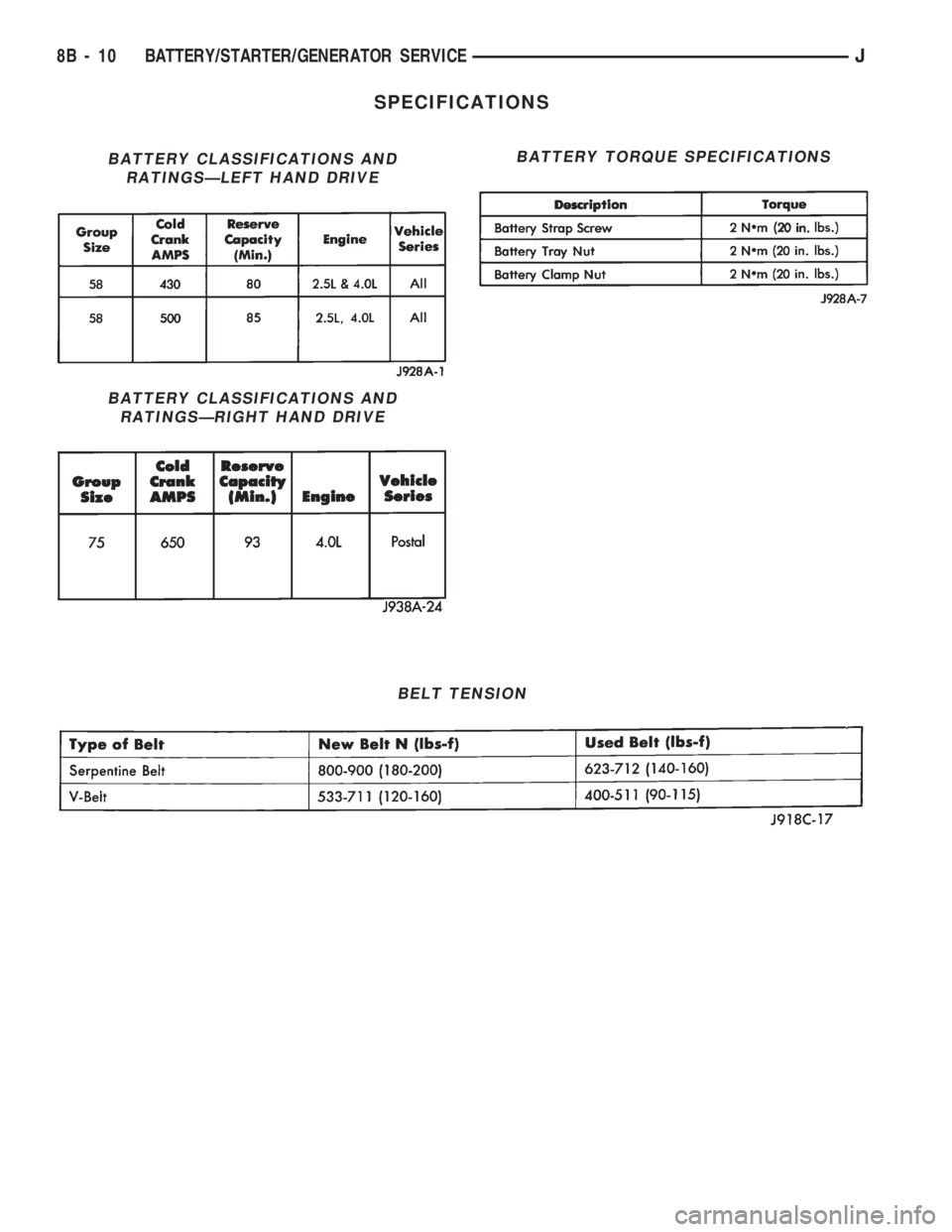
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS AND
RATINGSÐLEFT HAND DRIVE
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS AND
RATINGSÐRIGHT HAND DRIVE
BATTERY TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
BELT TENSION
8B - 10 BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICEJ
Page 304 of 1784

4.0L ENGINES 2.5L ENGINES
4.0L STARTER MOTOR AND SOLENOID
TESTING SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM COLD CRANKING
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER MOTOR TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
2.5L STARTER MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM COLD CRANKING
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER MOTOR TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
JBATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE 8B - 11
Page 305 of 1784
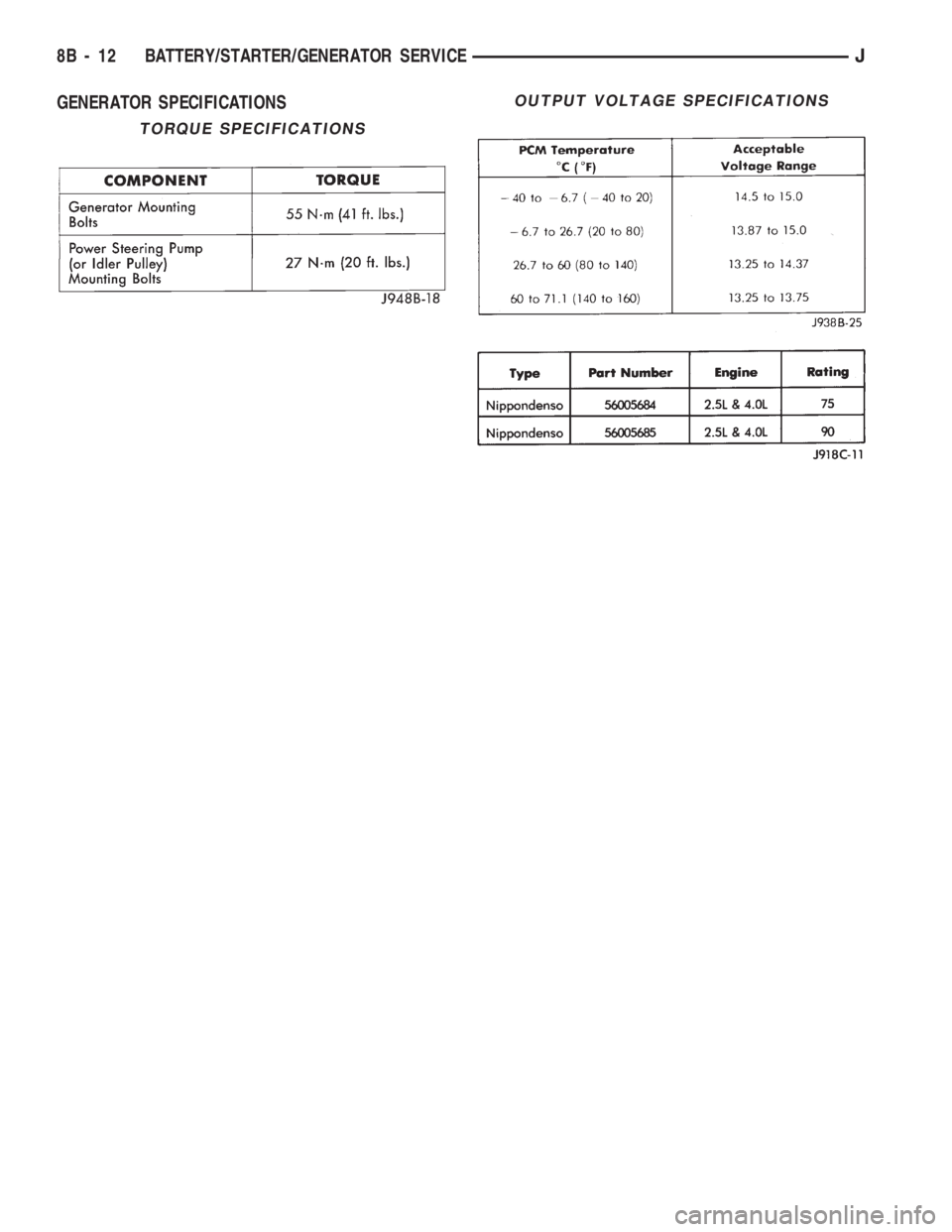
GENERATOR SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SPECIFICATIONS
8B - 12 BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICEJ
Page 314 of 1784

IGNITION SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM
OPERATION.......................... 1
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION..... 20DIAGNOSTICS/SERVICE PROCEDURES....... 8
IGNITION SWITCH...................... 30
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 33
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay............ 1
Camshaft Position Sensor................... 1
Crankshaft Position Sensor.................. 2
Distributors.............................. 3
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor........... 4
General Information........................ 1Ignition Coil.............................. 4
Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor........ 5
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor...... 5
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............. 6
Throttle Position Sensor.................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of alphabetical designa-
tions is included in the Introduction group at the be-
ginning of this manual.
This section of the group, Component Identifica-
tion/System Operation, will discuss ignition system
operation and will identify ignition system compo-
nents.
For diagnostic procedures and adjustments, refer to
the Diagnostics/Service Procedures section of this
group.
For removal and installation of ignition system
components, refer to the Component Removal/Instal-
lation section of this group.
For other useful information, refer to On-Board Di-
agnostics in the General Diagnosis sections of Group
14, Fuel System in this manual.
For operation of the DRB Scan Tool, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
An Ignition specifications section is included at the
end of this group. A general Maintenance Schedule
(mileage intervals) for ignition related items can be
found in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. This
schedule can also be found in the Owners Manual.
IGNITION SYSTEMS
A multi-port, fuel injected engine is used on all
models. The ignition system is controlled by the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) on all engines. The
PCM was formerly referred to as the SBEC or engine
controller.
The ignition system consists of:
²Spark Plugs
²Ignition Coil
²Secondary Ignition Cables
²Ignition distributor (contains rotor and camshaft
position sensor)
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY
The automatic shut down (ASD) relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC) near the bat-
tery (Fig. 1 or 2). As one of its functions, it will sup-
ply battery voltage to the ignition coil. The ground
circuit for the ASD relay is controlled by the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). The PCM regulates
ASD relay operation by switching the ground circuit
on-and-off.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor is located in the igni-
tion distributor (Figs. 3 or 4) on all engines.
The camshaft position sensor contains a hall effect
device called a sync signal generator to generate a
fuel sync signal. This sync signal generator detects a
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 1
Page 317 of 1784
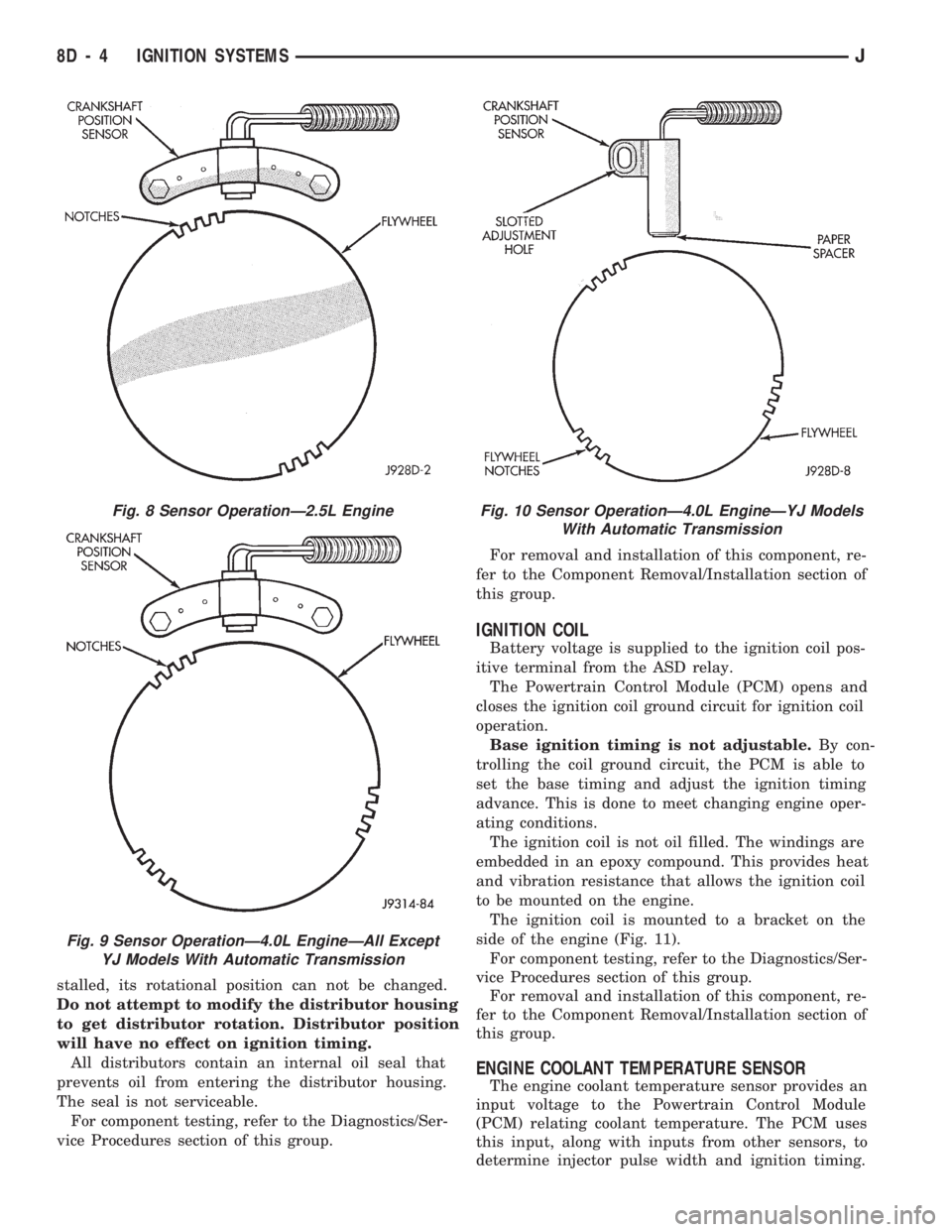
stalled, its rotational position can not be changed.
Do not attempt to modify the distributor housing
to get distributor rotation. Distributor position
will have no effect on ignition timing.
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
IGNITION COIL
Battery voltage is supplied to the ignition coil pos-
itive terminal from the ASD relay.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) opens and
closes the ignition coil ground circuit for ignition coil
operation.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable.By con-
trolling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to
set the base timing and adjust the ignition timing
advance. This is done to meet changing engine oper-
ating conditions.
The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are
embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat
and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil
to be mounted on the engine.
The ignition coil is mounted to a bracket on the
side of the engine (Fig. 11).
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The engine coolant temperature sensor provides an
input voltage to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) relating coolant temperature. The PCM uses
this input, along with inputs from other sensors, to
determine injector pulse width and ignition timing.
Fig. 8 Sensor OperationÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 9 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L EngineÐAll Except
YJ Models With Automatic Transmission
Fig. 10 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L EngineÐYJ Models
With Automatic Transmission
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 326 of 1784

(4) Using insulated pliers, hold the cable terminal
approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from the engine cylin-
der head or block while rotating the engine with the
starter motor. Observe the spark plug cable terminal
for an arc. If steady arcing occurs, it can be expected
that the ignition secondary system is operating cor-
rectly. If steady arcing occurs at the spark plug ca-
bles, but the engine will not start, connect the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual for DRB operation.
FAILURE TO START TEST
To prevent unnecessary diagnostic time and wrong
test results, the previous Checking For Spark test
should be performed prior to this test.
WARNING: SET PARKING BRAKE OR BLOCK THE
DRIVE WHEELS BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH THIS
TEST.
(1) Unplug the ignition coil harness connector at
the coil (Fig. 14).
(2) Connect a set of small jumper wires (18 gauge
or smaller) between the ignition coil and coil electri-
cal connector (Fig. 15).
(3) Determine that sufficient battery voltage (12.4
volts) is present for the starting and ignition sys-
tems.
(4) Crank the engine for 5 seconds while monitor-
ing the voltage at the coil positive terminal:
²If the voltage remains near zero during the entire
period of cranking, refer to On-Board Diagnostics in
Group 14, Fuel Systems. Check the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM) and auto shut down relay.
²If voltage is at near battery voltage and drops to
zero after 1-2 seconds of cranking, check the cam-
shaft position sensor-to-PCM circuit. Refer to On-
Board Diagnostics in Group 14, Fuel Systems.
²If voltage remains at near battery voltage during
the entire 5 seconds, turn the key off. Remove the60-way connector (Fig. 16) from the PCM. Check 60-
way connector for any spread terminals.
(5) Remove test lead from the coil positive termi-
nal. Connect an 18 gauge jumper wire between the
battery positive terminal and the coil positive termi-
nal.
(6) Make the special jumper shown in Figure 17.
Using the jumper,momentarilyground terminal-19
of the 60-way connector. A spark should be generated
at the coil cable when the ground is removed.
(7) If spark is generated, replace the powertrain
control module (PCM).
(8) If spark is not seen, use the special jumper to
ground the coil negative terminal directly.
(9) If spark is produced, repair wiring harness for
an open condition.
Fig. 14 Coil Harness ConnectorÐTypical
Fig. 15 Coil TerminalsÐTypical
Fig. 16 PCM 60-Way Connector
Fig. 17 Special Jumper Ground-to-Coil Negative
Terminal
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 13
Page 336 of 1784

INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant temperature sensor into the
thermostat housing. Tighten to 28 Nzm (21 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Connect the wire connector.
(3) Fill the cooling system. Refer to group 7, Cool-
ing System.
DISTRIBUTOR
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
The camshaft position sensor is located in the dis-
tributor on all engines (Fig. 9).
Refer to Fig. 9 for an exploded view of the distrib-
utor.
REMOVALÐ2.5L ENGINE
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable at the
battery.
(2) Disconnect coil secondary cable at coil.
(3) Remove distributor cap from distributor (2
screws). Do not remove cables from cap.
(4) Disconnect the distributor wiring harness from
the main engine harness.
(5) Scribe a mark on the distributor housing in
line with the tip of the rotor. Note the position of the
rotor and distributor housing. This is in relation tothe surrounding engine components as reference
points for installing the distributor.
(6) Remove the distributor holddown bolt and
clamp.
(7) Remove the distributor from engine by lifting
straight up. Remove and discard old distributor-to-
engine block gasket. Note that the rotor will rotate
slightly in a counterclockwise direction while lifting
up the distributor. Note this position after removal.
INSTALLATIONÐ2.5L ENGINE
ENGINE NOT ROTATED AFTER REMOVAL
This procedure assumes that the engine was not ro-
tated with distributor out of engine.
(1) Clean the distributor mounting hole area of the
engine block.
(2) Install a new distributor-to-engine block gas-
ket.
There is a fork on the distributor housing where
the housing seats against the engine block. The slot
in the fork aligns with the distributor holddown bolt
hole in the engine block. The distributor is correctly
installed when the rotor is correctly positioned. This
is with the slot in the fork aligned with the hold-
down bolt hole in the cylinder block. Because of the
fork on the distributor housing, initial ignition tim-
ing is not adjustable (the distributor cannot be rotat-
ed).
(3) Position the distributor shaft in the cylinder
block. If the engine was not rotated while the distrib-
utor was removed, perform the following:
²Align the rotor tip with the scribe mark on the
distributor housing during removal. Turn the rotor
approximately 1/8-turn counterclockwise past the
scribe mark.
CAUTION: Be sure that the distributor shaft fully
engages into the oil pump drive gear shaft. It may
be necessary to slightly rotate (bump) the engine.
This is done while applying downward hand force
on the distributor body. It should fully engage the
distributor shaft with the oil pump drive gear shaft.
²Slide the distributor shaft down into the engine.
It may be necessary to move the rotor and shaft
(slightly) to engage the distributor shaft with the slot
in the oil pump shaft. The same may have to be done
to engage the distributor gear with the camshaft
gear. However, the rotor should align with the scribe
mark when the distributor shaft is down in place.
²Install the distributor holddown clamp and bolt.
Tighten the bolt to 23 Nzm (17 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install the distributor cap (with the ignition ca-
bles) on the distributor housing (Fig. 10). Tighten
distributor cap holddown screws to 3 Nzm (26 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Connect the distributor wiring harness to the
main engine harness.
Fig. 9 DistributorÐ2.5L/4.0L EnginesÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 23