1993 FORD MONDEO dimensions
[x] Cancel search: dimensionsPage 2 of 279

LIVING WITH YOUR FORD MONDEO
IntroductionPage 0•4
Safety First!Page 0•5
General dimensions and weights Page0•6
MOT Test Checks
Checks carried out from the driver’s seat Page0•7
Checks carried out with the vehicle on the ground Page0•8
Checks carried out with the vehicle raised Page0•9
Checks carried out on your vehicle’s exhaust emission system Page0•10
Roadside Repairs
Jacking, towing and wheel changing Page0•11
Booster battery (jump) starting Page0•12
Identifying leaksPage0•13
Conversion factorsPage0•14
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance and servicing Page1•1
Lubricants, fluids and capacities Page1•2
Maintenance schedule Page1•3
Weekly checks Page1•6
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months Page1•11
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years Page1•20
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years Page1•22
Every 60 000 miles Page1•26
Every 3 yearsPage1•26
Contents
procarmanuals.com
Page 6 of 279

0•6General Dimensions & Weights
Dimensions
Overall length:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4481 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4631 mm
Overall width - including mirrors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1925 mm
Overall height - at kerb weight:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1403 to 1435 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1416 to 1501 mm
Wheelbase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2704 mm
Front track - all models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1503 mm
Rear track:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1486 to 1487 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1504 mm
Turning circle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.9 m
Weights
Kerb weight:
1.6 Saloon, Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1215 to 1250 kg
1.6 Estate models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1265 to 1275 kg
1.8 Saloon, Hatchback models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1225 to 1260 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1260 to 1280 kg
1.8 Estate models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1275 to 1285 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1305 kg
2.0 Saloon, Hatchback models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1250 to 1310 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1285 to 1340 kg
2.0 Estate models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1295 to 1335 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1330 to 1415 kg
Maximum gross vehicle weight:
Saloon, Hatchback:
1.6 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1725 kg
1.8 Saloon models, automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1750 kg
2.0 models, automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1800 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1775 kg
Estate:
1.6 models, 2.0 models with manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . 1900 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1925 kg
Maximum roof rack load:
Estate models with integral roof rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 kg
Maximum towing weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500 kg
Trailer nose weight limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 kg
procarmanuals.com
Page 82 of 279
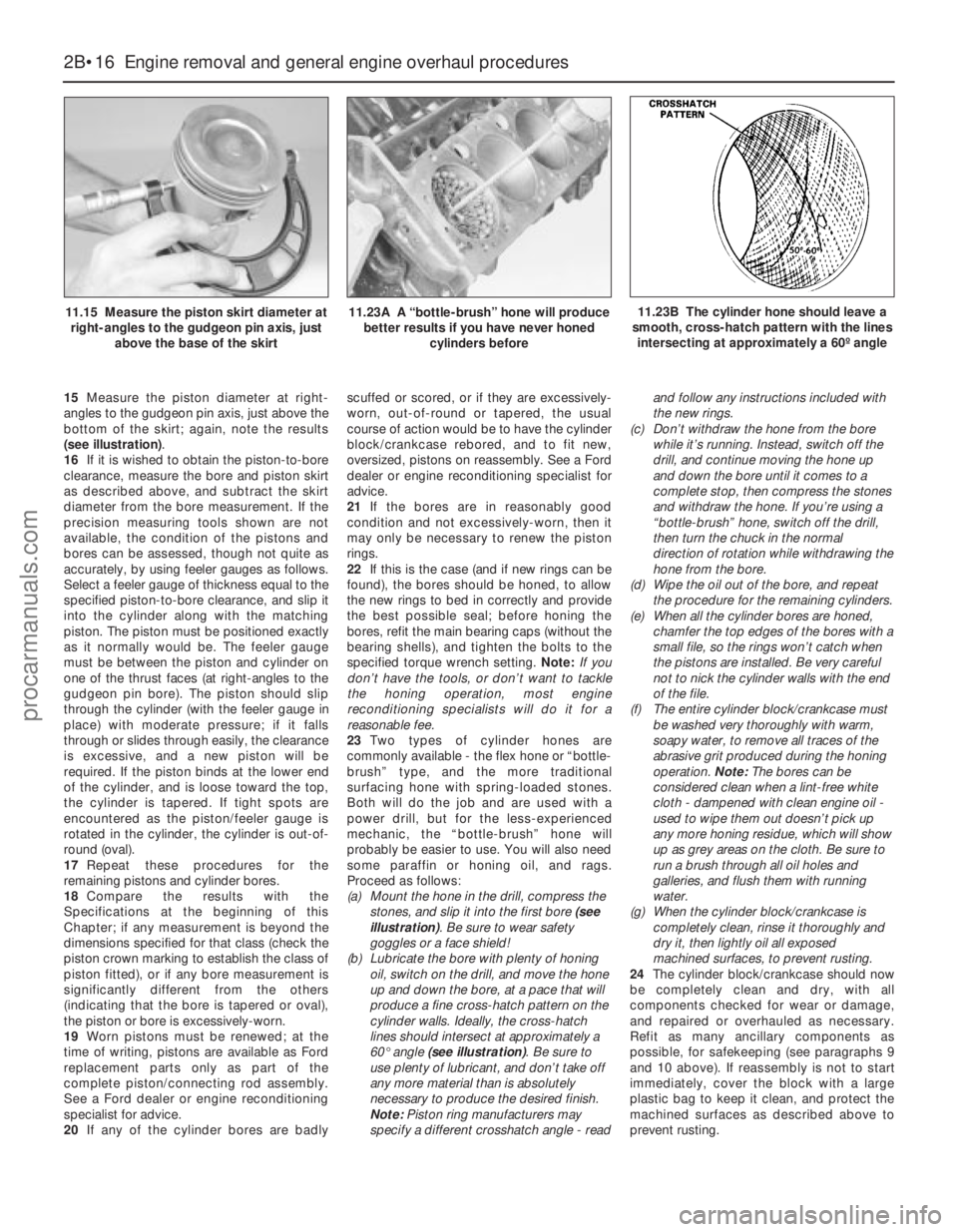
15Measure the piston diameter at right-
angles to the gudgeon pin axis, just above the
bottom of the skirt; again, note the results
(see illustration).
16If it is wished to obtain the piston-to-bore
clearance, measure the bore and piston skirt
as described above, and subtract the skirt
diameter from the bore measurement. If the
precision measuring tools shown are not
available, the condition of the pistons and
bores can be assessed, though not quite as
accurately, by using feeler gauges as follows.
Select a feeler gauge of thickness equal to the
specified piston-to-bore clearance, and slip it
into the cylinder along with the matching
piston. The piston must be positioned exactly
as it normally would be. The feeler gauge
must be between the piston and cylinder on
one of the thrust faces (at right-angles to the
gudgeon pin bore). The piston should slip
through the cylinder (with the feeler gauge in
place) with moderate pressure; if it falls
through or slides through easily, the clearance
is excessive, and a new piston will be
required. If the piston binds at the lower end
of the cylinder, and is loose toward the top,
the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is out-of-
round (oval).
17Repeat these procedures for the
remaining pistons and cylinder bores.
18Compare the results with the
Specifications at the beginning of this
Chapter; if any measurement is beyond the
dimensions specified for that class (check the
piston crown marking to establish the class of
piston fitted), or if any bore measurement is
significantly different from the others
(indicating that the bore is tapered or oval),
the piston or bore is excessively-worn.
19Worn pistons must be renewed; at the
time of writing, pistons are available as Ford
replacement parts only as part of the
complete piston/connecting rod assembly.
See a Ford dealer or engine reconditioning
specialist for advice.
20If any of the cylinder bores are badlyscuffed or scored, or if they are excessively-
worn, out-of-round or tapered, the usual
course of action would be to have the cylinder
block/crankcase rebored, and to fit new,
oversized, pistons on reassembly. See a Ford
dealer or engine reconditioning specialist for
advice.
21If the bores are in reasonably good
condition and not excessively-worn, then it
may only be necessary to renew the piston
rings.
22If this is the case (and if new rings can be
found), the bores should be honed, to allow
the new rings to bed in correctly and provide
the best possible seal; before honing the
bores, refit the main bearing caps (without the
bearing shells), and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting. Note:If you
don’t have the tools, or don’t want to tackle
the honing operation, most engine
reconditioning specialists will do it for a
reasonable fee.
23Two types of cylinder hones are
commonly available - the flex hone or “bottle-
brush” type, and the more traditional
surfacing hone with spring-loaded stones.
Both will do the job and are used with a
power drill, but for the less-experienced
mechanic, the “bottle-brush” hone will
probably be easier to use. You will also need
some paraffin or honing oil, and rags.
Proceed as follows:
(a) Mount the hone in the drill, compress the
stones, and slip it into the first bore (see
illustration). Be sure to wear safety
goggles or a face shield!
(b) Lubricate the bore with plenty of honing
oil, switch on the drill, and move the hone
up and down the bore, at a pace that will
produce a fine cross-hatch pattern on the
cylinder walls. Ideally, the cross-hatch
lines should intersect at approximately a
60° angle (see illustration). Be sure to
use plenty of lubricant, and don’t take off
any more material than is absolutely
necessary to produce the desired finish.
Note:Piston ring manufacturers may
specify a different crosshatch angle - readand follow any instructions included with
the new rings.
(c) Don’t withdraw the hone from the bore
while it’s running. Instead, switch off the
drill, and continue moving the hone up
and down the bore until it comes to a
complete stop, then compress the stones
and withdraw the hone. If you’re using a
“bottle-brush” hone, switch off the drill,
then turn the chuck in the normal
direction of rotation while withdrawing the
hone from the bore.
(d) Wipe the oil out of the bore, and repeat
the procedure for the remaining cylinders.
(e) When all the cylinder bores are honed,
chamfer the top edges of the bores with a
small file, so the rings won’t catch when
the pistons are installed. Be very careful
not to nick the cylinder walls with the end
of the file.
(f) The entire cylinder block/crankcase must
be washed very thoroughly with warm,
soapy water, to remove all traces of the
abrasive grit produced during the honing
operation. Note:The bores can be
considered clean when a lint-free white
cloth - dampened with clean engine oil -
used to wipe them out doesn’t pick up
any more honing residue, which will show
up as grey areas on the cloth. Be sure to
run a brush through all oil holes and
galleries, and flush them with running
water.
(g) When the cylinder block/crankcase is
completely clean, rinse it thoroughly and
dry it, then lightly oil all exposed
machined surfaces, to prevent rusting.
24The cylinder block/crankcase should now
be completely clean and dry, with all
components checked for wear or damage,
and repaired or overhauled as necessary.
Refit as many ancillary components as
possible, for safekeeping (see paragraphs 9
and 10 above). If reassembly is not to start
immediately, cover the block with a large
plastic bag to keep it clean, and protect the
machined surfaces as described above to
prevent rusting.
2B•16 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
11.15 Measure the piston skirt diameter at
right-angles to the gudgeon pin axis, just
above the base of the skirt11.23A A “bottle-brush” hone will produce
better results if you have never honed
cylinders before11.23B The cylinder hone should leave a
smooth, cross-hatch pattern with the lines
intersecting at approximately a 60º angle
procarmanuals.com
Page 85 of 279

to the engine bearings, the acid attacks and
corrodes the bearing material.
7Incorrect shell refitting during engine
assembly will lead to bearing failure as well.
Tight-fitting shells leave insufficient bearing
running clearance, and will result in oil
starvation. Dirt or foreign particles trapped
behind a bearing shell result in high spots on
the bearing, which lead to failure. Do not
touch any shell’s bearing surface with your
fingers during reassembly; there is a risk of
scratching the delicate surface, or of
depositing particles of dirt on it.
1Before reassembly begins, ensure that all
new parts have been obtained, and that all
necessary tools are available. Read through
the entire procedure, to familiarise yourself
with the work involved, and to ensure that all
items necessary for reassembly of the engine
are at hand. In addition to all normal tools and
materials, suitable sealant will be required for
two of the joint faces (Ford recommend
Hylosil 102 for the cylinder block/crankcase-
to-sump/oil pump/oil seal carrier joints, and
Loctite 518 for the camshaft right-hand
bearing caps). In all other cases, provided the
relevant mating surfaces are clean and flat,
new gaskets will be sufficient to ensure joints
are oil-tight. Do notuse any kind of silicone-
based sealant on any part of the fuel system
or inlet manifold, and neveruse exhaust
sealants upstream of the catalytic converter.
2In order to save time and avoid problems,
engine reassembly can be carried out in the
following order:
(a) Crankshaft (Section 17).
(b) Piston/connecting rod assemblies
(Section 18).
(c) Oil pump (Part A of this Chapter, Section
16).
(d) Sump (Part A of this Chapter, Section 15).
(e) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
(f) Cylinder head (Part A of this Chapter,
Section 14).(g) Timing belt inner cover, tensioner and
toothed pulleys, and timing belt (Part A of
this Chapter).
(h) Engine external components.
3At this stage, all engine components should
be absolutely clean and dry, with all faults
repaired; they should be laid out (or in
individual containers) on a completely-clean
work surface.
1Before installing new piston rings, check
the end gaps. Lay out each piston set with a
piston/connecting rod assembly, and keep
them together as a matched set from now on.
2Insert the top compression ring into the first
cylinder, and square it up with the cylinder
walls by pushing it in with the top of the piston
(see illustration). The ring should be near the
bottom of the cylinder, at the lower limit of
ring travel.
3To measure the end gap, slip feeler gauges
between the ends of the ring, until a gauge
equal to the gap width is found (see
illustration). The feeler gauge should slide
between the ring ends with a slight amount of
drag. Compare the measurement to the value
given in the Specifications Section of this
Chapter; if the gap is larger or smaller than
specified, double-check to make sure you
have the correct rings before proceeding. If
you are assessing the condition of used rings,
have the cylinder bores checked and
measured by a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist, so that you can be
sure of exactly which component is worn, and
seek advice as to the best course of action to
take.
4If the end gap is still too small, it must be
opened up by careful filing of the ring ends
using a fine file. If it is too large, this is not as
serious, unless the specified limit is exceeded,
in which case very careful checking is
required of the dimensions of all components,
as well as of the new parts.
5Repeat the procedure for each ring that will
be installed in the first cylinder, and for eachring in the remaining cylinders. Remember to
keep rings, pistons and cylinders matched up.
6Refit the piston rings as follows. Where the
original rings are being refitted, use the marks
or notes made on removal, to ensure that
each ring is refitted to its original groove and
the same way up. New rings generally have
their top surfaces identified by markings
(often an indication of size, such as “STD”, or
the word “TOP”) - the rings must be fitted with
such markings uppermost (see illustration).
Note:Always follow the instructions printed
on the ring package or box - different
manufacturers may require different
approaches. Do not mix up the top and
second compression rings, as they usually
have different cross-sections.
7The oil control ring (lowest one on the
piston) is usually installed first. It is composed
of three separate elements. Slip the
spacer/expander into the groove (see
illustration). If an anti-rotation tang is used,
make sure it is inserted into the drilled hole in
the ring groove. Next, install the lower side
rail. Don’t use a piston ring installation tool on
the oil ring side rails, as they may be
damaged. Instead, place one end of the side
rail into the groove between the
spacer/expander and the ring land, hold it
firmly in place, and slide a finger around the
piston while pushing the rail into the groove
16 Piston rings - refitting
15 Engine overhaul -
reassembly sequence
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•19
2B
16.7A Installing the spacer/expander in
the oil control ring groove
16.2 When checking piston ring end gap,
the ring must be square in the cylinder
bore (this is done by pushing the ring down
with the top of a piston, as shown)
16.3 With the ring square in the bore,
measure the end gap with a feeler
gauge16.6 Look for etched markings (“STD” -
indicating a standard-sized ring - shown
here) identifying piston ring top surface
procarmanuals.com
Page 113 of 279

5If you are renewing the battery, make sure
that you get one that’s identical, with the
same dimensions, amperage rating, cold
cranking rating, etc. Dispose of the old battery
in a responsible fashion. Most local authorities
have facilities for the collection and disposal
of such items - batteries contain sulphuric
acid and lead, and should not be simply
thrown out with the household rubbish!
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Note:See also the relevant Sections of
Chapter 1.
1Periodically inspect the entire length of
each battery lead for damage, cracked or
burned insulation, and corrosion. Poor battery
lead connections can cause starting problems
and decreased engine performance.
2Check the lead-to-terminal connections at
the ends of the leads for cracks, loose wire
strands and corrosion. The presence of white,
fluffy deposits under the insulation at the lead
terminal connection is a sign that the lead is
corroded and should be renewed. Check the
terminals for distortion, missing clamp bolts,
and corrosion.
3When removing the leads, always
disconnect the negative lead first, and
reconnect it last (see Section 1). Even if only
the positive lead is being renewed, be sure to
disconnect the negative lead from the battery
first (see Chapter 1 for further information
regarding battery lead removal).
4Disconnect the old leads from the battery,
then trace each of them to their opposite
ends, and detach them from the starter
solenoid and earth terminals. Note the routing
of each lead, to ensure correct installation.
5If you are renewing either or both of the old
leads, take them with you when buying new
leads. It is vitally important that you replace
the leads with identical parts. Leads have
characteristics that make them easy to
identify: positive leads are usually red, larger
in cross-section, and have a larger-diameter
battery post clamp; earth leads are usually
black, smaller in cross-section and have a
slightly smaller-diameter clamp for the
negative post.
6Clean the threads of the solenoid or earth
connection with a wire brush to remove rust
and corrosion.
7Attach the lead to the solenoid or earth
connection, and tighten the mounting nut/bolt
securely.
8Before connecting a new lead to thebattery, make sure that it reaches the battery
post without having to be stretched.
9Connect the positive lead first, followed by
the negative lead.
General
The ignition system includes the ignition
switch, the battery, the crankshaft speed/
position sensor, the coil, the primary (low
tension/LT) and secondary (high tension/HT)
wiring circuits, and the spark plugs. On models
with automatic transmission, a separate
ignition module is also fitted, its functions
being incorporated in the ECU on models with
manual transmission. The ignition system is
controlled by the engine management
system’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU). Using
data provided by information sensors which
monitor various engine functions (such as
engine speed and piston position, intake air
mass and temperature, engine coolant
temperature, etc.), the ECU ensures a
perfectly-timed spark under all conditions (see
Chapter 6). Note:The ignition timing is under
the full control of the ECU, and cannot be
adjusted - see Section 8 for further details.
Precautions
When working on the ignition system, take
the following precautions:
(a) Do not keep the ignition switch on for more
than 10 seconds if the engine will not start.
(b) If a separate tachometer is ever required
for servicing work, consult a dealer
service department before buying a
tachometer for use with this vehicle -
some tachometers may be incompatible
with this ignition system - and always
connect it in accordance with the
equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
(c) Never connect the ignition coil terminals
to earth. This could result in damage to
the coil and/or the ECU or ignition module
(whichever is fitted).
(d) Do not disconnect the battery when the
engine is running.
(e) Make sure that the ignition module (where
fitted) is properly earthed.
(f) Refer to the warning at the beginning of
the next Section concerning HT voltage.
Warning: Because of the high
voltage generated by the ignition
system, extreme care should be
taken whenever an operation is performed
involving ignition components. This not
only includes the ignition module/ECU, coil
and spark plug (HT) leads, but related
components such as electrical connectors,
tachometer and other test equipment also.Note: This is an initial check of the “ignition
part” of the main engine management system,
to be carried out as part of the preliminary
checks of the complete engine management
system (see Chapter 6).
1If the engine turns over but won’t start,
disconnect the (HT) lead from any spark plug,
and attach it to a calibrated tester (available at
most automotive accessory shops). Connect
the clip on the tester to a good earth - a bolt
or metal bracket on the engine. If you’re
unable to obtain a calibrated ignition tester,
have the check carried out by a Ford dealer
service department or similar. Any other form
of testing (such as jumping a spark from the
end of an HT lead to earth) is not
recommended, because of the risk of
personal injury, or of damage to the
ECU/ignition module (see notes above and in
Section 4).
2Crank the engine and watch the end of the
tester to see if bright blue, well-defined sparks
occur.
3If sparks occur, sufficient voltage is
reaching the plug to fire it. Repeat the check
at the remaining plugs, to ensure that all leads
are sound and that the coil is serviceable.
However, the plugs themselves may be fouled
or faulty, so remove and check them as
described in Chapter 1.
4If no sparks or intermittent sparks occur,
the spark plug lead(s) may be defective -
check them as described in Chapter 1.
5If there’s still no spark, check the coil’s
electrical connector, to make sure it’s clean
and tight. Check for full battery voltage to the
coil at the connector’s centre terminal. The
coil is earthed through the ECU - do not
attempt to check this. Check the coil itself
(see Section 6). Make any necessary repairs,
then repeat the check again.
6The remainder of the system checks should
be left to a dealer service department or other
qualified repair facility, as there is a chance
that the ECU may be damaged if tests are not
performed properly.
Warning: Because of the high
voltage generated by the ignition
system, extreme care should be
taken whenever an operation is performed
involving ignition components. This not
only includes the ignition module/ECU, coil
and spark plug (HT) leads, but related
components such as electrical connectors,
tachometer and other test equipment also.
Check
1Having checked that full battery voltage is
available at the centre terminal of the coil’s
electrical connector (see Section 5),
disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead -
see Section 1.
2Unplug the coil’s electrical connector, if not
already disconnected.
6 Ignition coil -
removal and refitting
5 Ignition system - testing
4 Ignition system - general
information and precautions
3 Battery leads -
check and renewal
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
Apply a light coat of battery
terminal corrosion inhibitor,
or petroleum jelly, to the
threads, to prevent future
corrosion.
procarmanuals.com
Page 272 of 279
REF•13Glossary of Technical Terms
A
ABS (Anti-lock brake system)A system,
usually electronically controlled, that senses
incipient wheel lockup during braking and
relieves hydraulic pressure at wheels that are
about to skid.
Air bag An inflatable bag hidden in the
steering wheel (driver’s side) or the dash or
glovebox (passenger side). In a head-on
collision, the bags inflate, preventing the
driver and front passenger from being thrown
forward into the steering wheel or windscreen.
Air cleanerA metal or plastic housing,
containing a filter element, which removes
dust and dirt from the air being drawn into the
engine.
Air filter elementThe actual filter in an air
cleaner system, usually manufactured from
pleated paper and requiring renewal at regular
intervals.
Allen keyA hexagonal wrench which fits into
a recessed hexagonal hole.
Alligator clipA long-nosed spring-loaded
metal clip with meshing teeth. Used to make
temporary electrical connections.
AlternatorA component in the electrical
system which converts mechanical energy
from a drivebelt into electrical energy to
charge the battery and to operate the starting
system, ignition system and electrical
accessories.
Ampere (amp)A unit of measurement for the
flow of electric current. One amp is the
amount of current produced by one volt
acting through a resistance of one ohm.
Anaerobic sealerA substance used to
prevent bolts and screws from loosening.
Anaerobic means that it does not require
oxygen for activation. The Loctite brand is
widely used.
AntifreezeA substance (usually ethylene
glycol) mixed with water, and added to a
vehicle’s cooling system, to prevent freezing
of the coolant in winter. Antifreeze also
contains chemicals to inhibit corrosion and
the formation of rust and other deposits that
would tend to clog the radiator and coolant
passages and reduce cooling efficiency.
Anti-seize compoundA coating that
reduces the risk of seizing on fasteners that
are subjected to high temperatures, such as
exhaust manifold bolts and nuts.
AsbestosA natural fibrous mineral with great
heat resistance, commonly used in the
composition of brake friction materials.Asbestos is a health hazard and the dust
created by brake systems should never be
inhaled or ingested.
AxleA shaft on which a wheel revolves, or
which revolves with a wheel. Also, a solid
beam that connects the two wheels at one
end of the vehicle. An axle which also
transmits power to the wheels is known as a
live axle.
AxleshaftA single rotating shaft, on either
side of the differential, which delivers power
from the final drive assembly to the drive
wheels. Also called a driveshaft or a halfshaft.
BBall bearingAn anti-friction bearing
consisting of a hardened inner and outer race
with hardened steel balls between two races.
BearingThe curved surface on a shaft or in a
bore, or the part assembled into either, that
permits relative motion between them with
minimum wear and friction.
Big-end bearingThe bearing in the end of
the connecting rod that’s attached to the
crankshaft.
Bleed nippleA valve on a brake wheel
cylinder, caliper or other hydraulic component
that is opened to purge the hydraulic system
of air. Also called a bleed screw.
Brake bleedingProcedure for removing air
from lines of a hydraulic brake system.
Brake discThe component of a disc brake
that rotates with the wheels.Brake drumThe component of a drum brake
that rotates with the wheels.
Brake liningsThe friction material which
contacts the brake disc or drum to retard the
vehicle’s speed. The linings are bonded or
riveted to the brake pads or shoes.
Brake padsThe replaceable friction pads
that pinch the brake disc when the brakes are
applied. Brake pads consist of a friction
material bonded or riveted to a rigid backing
plate.
Brake shoeThe crescent-shaped carrier to
which the brake linings are mounted and
which forces the lining against the rotating
drum during braking.
Braking systemsFor more information on
braking systems, consult the Haynes
Automotive Brake Manual.
Breaker barA long socket wrench handle
providing greater leverage.
BulkheadThe insulated partition between
the engine and the passenger compartment.
CCaliperThe non-rotating part of a disc-brake
assembly that straddles the disc and carries
the brake pads. The caliper also contains the
hydraulic components that cause the pads to
pinch the disc when the brakes are applied. A
caliper is also a measuring tool that can be set
to measure inside or outside dimensions of an
object.
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.
Canister
Brake bleeding
Bearing
Air filter
procarmanuals.com
Page 275 of 279

REF•16Glossary of Technical Terms
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
automatic transmission, a switch that
prevents starting if the vehicle is not in Neutral
or Park.
StrutSee MacPherson strut.
TTappetA cylindrical component which
transmits motion from the cam to the valve
stem, either directly or via a pushrod and
rocker arm. Also called a cam follower.
ThermostatA heat-controlled valve that
regulates the flow of coolant between the
cylinder block and the radiator, so maintaining
optimum engine operating temperature. A
thermostat is also used in some air cleaners in
which the temperature is regulated.
Thrust bearingThe bearing in the clutch
assembly that is moved in to the release
levers by clutch pedal action to disengage the
clutch. Also referred to as a release bearing.
Timing beltA toothed belt which drives the
camshaft. Serious engine damage may result
if it breaks in service.
Timing chainA chain which drives the
camshaft.
Toe-inThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the front than at the rear. On
rear wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-in is usually specified to keep the front
wheels running parallel on the road by
offsetting other forces that tend to spread the
wheels apart.
Toe-outThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the rear than at the front. On
front wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-out is usually specified.
ToolsFor full information on choosing and
using tools, refer to the Haynes Automotive
Tools Manual.
TracerA stripe of a second colour applied to
a wire insulator to distinguish that wire from
another one with the same colour insulator.
Tune-upA process of accurate and careful
adjustments and parts replacement to obtain
the best possible engine performance.TurbochargerA centrifugal device, driven by
exhaust gases, that pressurises the intake air.
Normally used to increase the power output
from a given engine displacement, but can
also be used primarily to reduce exhaust
emissions (as on VW’s “Umwelt” Diesel
engine).
UUniversal joint or U-jointA double-pivoted
connection for transmitting power from a
driving to a driven shaft through an angle. A
U-joint consists of two Y-shaped yokes and a
cross-shaped member called the spider.
VValveA device through which the flow of
liquid, gas, vacuum, or loose material in bulk
may be started, stopped, or regulated by a
movable part that opens, shuts, or partially
obstructs one or more ports or passageways.
A valve is also the movable part of such a
device.
Valve clearanceThe clearance between the
valve tip (the end of the valve stem) and the
rocker arm or tappet. The valve clearance is
measured when the valve is closed.
Vernier caliperA precision measuring
instrument that measures inside and outside
dimensions. Not quite as accurate as a
micrometer, but more convenient.
ViscosityThe thickness of a liquid or its
resistance to flow.
VoltA unit for expressing electrical
“pressure” in a circuit. One volt that will
produce a current of one ampere through a
resistance of one ohm.
WWeldingVarious processes used to join metal
items by heating the areas to be joined to a
molten state and fusing them together. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Welding Manual.
Wiring diagramA drawing portraying the
components and wires in a vehicle’s electrical
system, using standardised symbols. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Electrical and Electronic Systems
Manual.
Serpentine drivebelt
procarmanuals.com
Page 276 of 279

REF•17Index
A
A pillar trim - 11•20
ABS - 9•14
Accelerator cable - 4•4
Accelerator pedal - 4•5
Accumulator - 3•9
Acknowledgements - 0•4
Adaptive damping switch - 12•8
Aerial - 12•22
Air bag - 0•5, 1•22, 12•22
Air cleaner - 4•3, 6•19
Air conditioning - 1•15, 3•2, 3•8, 3•9, 6•11
Air distribution control - 3•8
Air induction system - 4•9
Air intake components - 4•3
Air mass meter - 4•3, 6•10, 6•11, 6•12
Air temperature warning sender unit -
12•18
Alarm - 11•17, 12•18
Alternator - 5•5, 5•6
Amplifier - 12•21
Anti-lock Braking System - 9•14
Anti-roll bar - 10•8, 10•12, 10•15
Anti-theft alarm system - 12•18
Antifreeze - 1•2, 1•22, 3•2
Asbestos - 0•5
ATF - 1•2
Automatic transmission- 1•11, 1•17,
2A•24, 2B•3, 2B•4, 6•11, 7B•1et seq,
12•11
Automatic transmission fault finding -
REF•10
Automatic transmission fluid - 1•2
Auxiliary drivebelt - 1•13
Auxiliary warning system - 12•17
B
B pillar trim - 11•20
Backfire - REF•8
Backrest - 11•18
Battery - 0•5, 1•8, 1•11, 5•2, 5•3
Battery fault - REF•12
Big-end bearings - 2B•18, 2B•21
Bleeding brakes - 9•12
Bleeding power steering - 10•21
Blower/air conditioning control - 3•8Body corrosion - 0•10
Body electrical system- 12•1et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 11•1et seq
Bonnet - 1•20, 11•5, 11•6
Booster battery (jump) starting - 0•12
Boot - 11•14, 11•15
Brake check - 1•19
Brake fluid - 1•2, 1•8, 1•26
Brake line check - 1•19
Braking system- 0•7, 0•8, 0•9, 1•20, 9•1et
seq
Braking system fault finding - REF•10
Brush renewal - 5•8
Bulb failure module - 12•18
Bulbs - 12•8, 12•11, 12•18
Bumpers - 11•4, 11•5
Burning - 0•5
C
C pillar trim - 11•20, 11•21
Cables - 4•4, 7B•2, 8•2, 9•16, 11•6, 12•15
Calipers - 9•4, 9•9
Camshaft - 2A•13, 2A•14, 6•11, 6•12
Cassette player - 12•21
Catalytic converter - 6•19
CD player - 12•22
Central locking system - 11•17
Central locking system fault - REF•12
Centre console - 11•21
Charcoal canister - 6•14
Charging - 1•12, 5•5
Check strap - 11•13
Clock - 12•11, 12•15
Clutch and driveshafts- 1•17, 1•20, 8•1et
seq
Clutch fault finding - REF•9
CO emissions (mixture) - 0•10
Coil spring - 10•15
Compact disc player - 12•22
Compression test - 2A•5
Compressor - 3•9
Condenser - 3•9
Connecting rods - 2B•12, 2B•17, 2B•21,
2B•22
Console - 11•21, 11•22
Contents - 0•2
Conversion factors - 0•14Coolant - 1•2, 1•6, 1•7, 1•21
Coolant leakage - REF•9
Coolant low level switch - 3•5
Coolant temperature gauge sender - 3•4
Coolant temperature sensor - 3•5, 6•11,
6•13
Coolant warning switch - 12•18
Cooling, heating, and air conditioning
systems- 1•22, 3•1et seq
Cooling, heating, and air conditioning
systems fault finding - REF•8
Corrosion - REF•9
Courtesy light - 12•8
Crankcase - 2B•13
Crankshaft - 2A•9, 2A•13, 2A•22, 2B•13,
2B•18, 2B•20, 5•4, 6•10, 6•11, 6•12
Crossmember - 10•13, 10•17
Cruise control system - 12•19
Crushing - 0•5
Cushion - 11•18
CV joints - 1•18, 8•7, 8•9
Cylinder block - 2B•13
Cylinder head - 2A•6, 2A•17, 2B•9, 2B•10,
2B•11, 6•19
D
D pillar trim - 11•21
Damping switch - 12•8
Dehydrator - 3•9
Dents in bodywork - 11•3
Depressurisation - 4•2
Diagnosis system - 6•4
Differential - 7A•2, 7B•3
Dimensions - 0•6
Dipped beam switch - 12•7
Direction indicators - 12•7, 12•9, 12•12
Discs - 1•19, 9•5, 9•10
Display warning bulb - 12•18
Doors - 0•8, 1•20, 11•6, 11•7, 11•8, 11•9,
11•10, 11•11, 11•13, 12•7, 12•8, 12•11,
12•18
Drivebelts - 1•13
Driveplate - 2A•24
Driveshafts - 0•9, 1•18, 8•5, 8•6, 8•7, 8•9,
8•10
Driveshafts fault finding - REF•10
Drivetrain - 1•20
Drums - 1•19, 9•6 Note: References throughout this index relate to Chapter•page number
procarmanuals.com