1993 FORD MONDEO torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 5 of 279

Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle, always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on ramps.
Never venture
under a car
which is only
supported by
a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with
heart problems
or a pacemaker.
Don’t work on or
near the ignition
system with the
engine running or the
ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the
hands, face or any other part of
the body to injector spray; the
fuel can penetrate the skin with
potentially fatal results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
0•5Safety First!
procarmanuals.com
Page 14 of 279
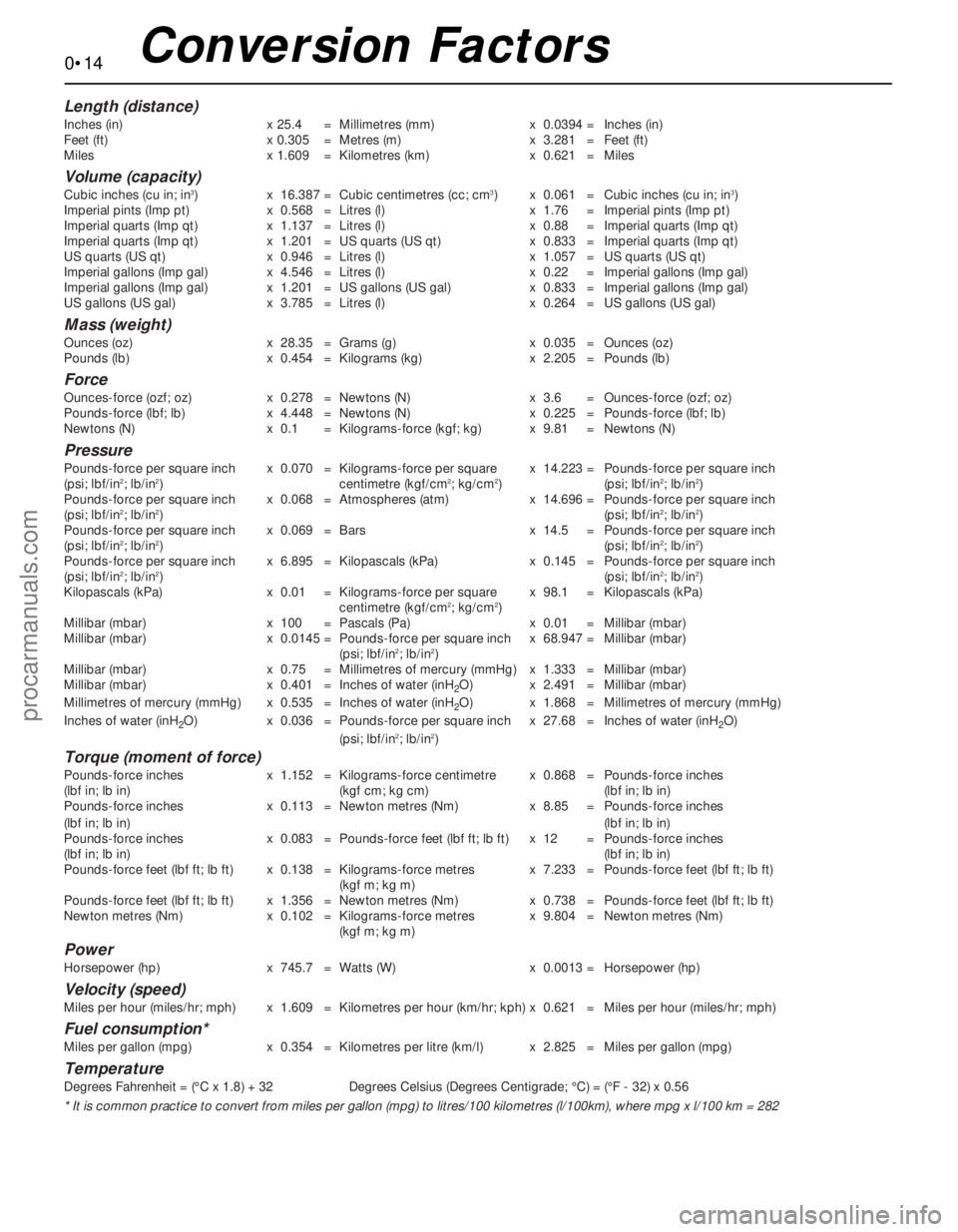
0•14Conversion Factors
Length (distance)
Inches (in) x 25.4 = Millimetres (mm) x 0.0394 = Inches (in)
Feet (ft) x 0.305 = Metres (m) x 3.281 = Feet (ft)
Miles x 1.609 = Kilometres (km) x 0.621 = Miles
Volume (capacity)
Cubic inches (cu in; in3) x 16.387 = Cubic centimetres (cc; cm3) x 0.061 = Cubic inches (cu in; in3)
Imperial pints (Imp pt) x 0.568 = Litres (l) x 1.76 = Imperial pints (Imp pt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.137 = Litres (l) x 0.88 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.201 = US quarts (US qt) x 0.833 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
US quarts (US qt) x 0.946 = Litres (l) x 1.057 = US quarts (US qt)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 4.546 = Litres (l) x 0.22 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 1.201 = US gallons (US gal) x 0.833 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
US gallons (US gal) x 3.785 = Litres (l) x 0.264 = US gallons (US gal)
Mass (weight)
Ounces (oz) x 28.35 = Grams (g) x 0.035 = Ounces (oz)
Pounds (lb) x 0.454 = Kilograms (kg) x 2.205 = Pounds (lb)
Force
Ounces-force (ozf; oz) x 0.278 = Newtons (N) x 3.6 = Ounces-force (ozf; oz)
Pounds-force (lbf; lb) x 4.448 = Newtons (N) x 0.225 = Pounds-force (lbf; lb)
Newtons (N) x 0.1 = Kilograms-force (kgf; kg) x 9.81 = Newtons (N)
Pressure
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.070 = Kilograms-force per square x 14.223 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2) centimetre (kgf/cm2; kg/cm2) (psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.068 = Atmospheres (atm) x 14.696 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.069 = Bars x 14.5 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 6.895 = Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.145 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.01 = Kilograms-force per square x 98.1 = Kilopascals (kPa)
centimetre (kgf/cm
2; kg/cm2)
Millibar (mbar) x 100 = Pascals (Pa) x 0.01 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.0145 = Pounds-force per square inch x 68.947 = Millibar (mbar)
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.75 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 1.333 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.401 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 2.491 = Millibar (mbar)
Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 0.535 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 1.868 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg)
Inches of water (inH
2O) x 0.036 = Pounds-force per square inch x 27.68 = Inches of water (inH2O)
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Torque (moment of force)
Pounds-force inches x 1.152 = Kilograms-force centimetre x 0.868 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in) (kgf cm; kg cm) (lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force inches x 0.113 = Newton metres (Nm) x 8.85 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in)(lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force inches x 0.083 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 12 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in)(lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 0.138 = Kilograms-force metres x 7.233 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
(kgf m; kg m)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 1.356 = Newton metres (Nm) x 0.738 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
Newton metres (Nm) x 0.102 = Kilograms-force metres x 9.804 = Newton metres (Nm)
(kgf m; kg m)
Power
Horsepower (hp) x 745.7 = Watts (W) x 0.0013 = Horsepower (hp)
Velocity (speed)
Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph) x 1.609 = Kilometres per hour (km/hr; kph) x 0.621 = Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph)
Fuel consumption*
Miles per gallon (mpg) x 0.354 = Kilometres per litre (km/l) x 2.825 = Miles per gallon (mpg)
Temperature
Degrees Fahrenheit = (°C x 1.8) + 32 Degrees Celsius (Degrees Centigrade; °C) = (°F - 32) x 0.56
* It is common practice to convert from miles per gallon (mpg) to litres/100 kilometres (l/100km), where mpg x l/100 km = 282
procarmanuals.com
Page 20 of 279

This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain the Ford Mondeo models
for peak performance, economy, safety and
long life.
On the following pages are Sections
dealing specifically with each item on the
maintenance schedule. Visual checks,
adjustments, component replacement and
other helpful items are included. Refer to the
accompanying illustrations of the engine
compartment and the underside of the vehicle
for the location of various components.
Servicing your Mondeo in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide it with a
planned maintenance programme, which
should result in a long and reliable service life.
This is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at the specified
service intervals will not produce the same
results.
As you service your Mondeo, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the nature of the particular procedure you’re
performing, or because of the close proximity
to one another of two otherwise-unrelated
components.
For example, if the vehicle is raised for anyreason, you should inspect the exhaust,
suspension, steering and fuel systems while
you’re under the vehicle. When you’re
checking the tyres, it makes good sense to
check the brakes and wheel bearings,
especially if the roadwheels have already
been removed.
Finally, let’s suppose you have to borrow or
hire a torque wrench. Even if you only need to
tighten the spark plugs, you might as well
check the torque of as many critical fasteners
as time allows.
The first step of this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
Sections which are relevant to the procedures
you’re planning to carry out, then make a list
of, and gather together, all the parts and tools
you will need to do the job. If it looks as if you
might run into problems during a particular
segment of some procedure, seek advice
from your local parts man or dealer service
department.
Ford state that, where antifreeze to
specification ESD-M97B-49-A (the type with
which the vehicle’s cooling system would
have been filled on production at the factory)
is used, it will last the lifetime of the vehicle.This is subject to it being used in the
recommended concentration, unmixed with
any other type of antifreeze or additive, and
topped-up when necessary using only that
antifreeze mixed 50/50 with clean water. If any
other type of antifreeze is added, the lifetime
guarantee no longer applies; to restore the
lifetime protection, the system must be
drained and thoroughly reverse-flushed
before fresh coolant mixture is poured in.
If the vehicle’s history (and therefore the
quality of the antifreeze in it) is unknown,
owners who wish to follow Ford’s
recommendations are advised to drain and
thoroughly reverse-flush the system, as
outlined in Section 28, before refilling with
fresh coolant mixture. If the appropriate
quality of antifreeze is used, the coolant can
then be left for the life of the vehicle.
If any antifreeze other than Ford’s is to be
used, the coolant must be renewed at regular
intervals to provide an equivalent degree of
protection; the conventional recommendation
is to renew the coolant every two years.
The above assumes the use of a mixture (in
exactly the specified concentration) of clean,
soft water and of antifreeze to Ford’s
specification or equivalent. It is also assumed
that the cooling system is maintained in a
scrupulously-clean condition, by ensuring that
only clean coolant is added on topping-up,
and by thorough reverse-flushing whenever
the coolant is drained (Section 28).
2 Coolant renewal
1 Introduction
1•6Weekly checks
Weekly checks
General
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, braking and other
systems. Because these fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids and capacities”at the beginning of this
Chapter before adding fluid to any of the
following components. Note:The vehicle
must be on level ground before fluid levels can
be checked.
Engine oil
2The engine oil level is checked with a
dipstick located at the front of the engine; it
can be identified by its yellow/black plastic
grip (see illustration). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube, from which it protrudes
down into the sump at the bottom of the
engine.
3The oil level should be checked before the
vehicle is driven, or about 5 minutes after the
engine has been switched off.4Pull the dipstick from the tube, and wipe all
the oil from the end with a clean rag or paper
towel; note the dipstick’s maximum and
minimum levels, indicated by notches (seeillustration). Insert the clean dipstick all the way
back into its metal tube, and pull it out again.
Observe the oil on the end of the dipstick; its
level should be between these two notches.
5Do not allow the level to drop below the
minimum level notch, or oil starvation may
cause engine damage. Conversely, overfilling
the engine (adding oil above the maximum
level notch) may cause oil-fouled spark plugs,
oil leaks or oil seal failures.
6The yellow/black plastic oil filler cap is
screwed into the left-hand front end of the
3 Fluid level checks
3.2 The engine oil dipstick (arrowed) is
located at the front of the engine - note
yellow/black plastic grip
3.4 The oil level should be at or near the
maximum level notch (A) - if not, add
enough oil to correct the level. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise
the level from the minimum level notch (B)
to the maximum
If the level is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the engine upper
components, producing an inaccurate
dipstick reading.
procarmanuals.com
Page 27 of 279

amperage charger, but don’t use one rated
more than 1/10th the amp/hour rating of the
battery (ie no more than 5 amps, typically).
Rapid boost charges that claim to restore the
power of the battery in one to two hours are
hardest on the battery, and can damage
batteries not in good condition. This type of
charging should only be used in emergency
situations.
14The average time necessary to charge a
battery should be listed in the instructions that
come with the charger. As a general rule, a
trickle charger will charge a battery in 12 to
16 hours.
1Check the seat belts for satisfactory
operation and condition. Inspect the webbing
for fraying and cuts. Check that they retract
smoothly and without binding into their reels.
2Check that the seat belt mounting bolts are
tight, and if necessary tighten them to the
specified torque wrench setting.
General
1The auxiliary drivebelt is of the flat, multi-
ribbed (or “polyvee”) type, and is located on
the right-hand end of the engine. It drives the
alternator, water pump, power steering pump
and (when fitted) the air conditioning
compressor from the engine’s crankshaft
pulley.
2The good condition and proper tension of
the auxiliary drivebelt is critical to the
operation of the engine. Because of their
composition and the high stresses to which
they are subjected, drivebelts stretch anddeteriorate as they get older. They must,
therefore, be regularly inspected.
Check
3With the engine switched off, open and
support the bonnet, then locate the auxiliary
drivebelt on the right-hand end of the engine,
under the engine right-hand mounting
bracket. (Be very careful, and wear protective
gloves to minimise the risk of burning your
hands on hot components, if the engine has
recently been running.) For improved access,
jack up the front right-hand side of the
vehicle, support it securely on an axle stand,
remove the roadwheel, then remove the
auxiliary drivebelt cover (two fasteners) from
inside the wheel arch (see illustration).
4Using an inspection light or a small electric
torch, and rotating the engine when necessary
with a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, check the whole length of the
drivebelt for cracks, separation of the rubber,
and torn or worn ribs (see illustration). Also
check for fraying and glazing, which gives the
drivebelt a shiny appearance. Both sides of
the drivebelt should be inspected, which
means you will have to twist the drivebelt to
check the underside. Use your fingers to feel
the drivebelt where you can’t see it. If you are
in any doubt as to the condition of the
drivebelt, renew it (go to paragraph 7).
Drivebelt tension
5The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by an
automatic tensioner; regular checks are not
required, and manual “adjustment” is not
possible.
6If you suspect that the drivebelt is slipping
and/or running slack, or that the tensioner is
otherwise faulty, it must be renewed. To do
this, remove the drivebelt as described below,
then unbolt the tensioner (two Torx-type
screws accessible from underneath, via the
wheel arch) from the alternator mounting
bracket (see illustration). On fitting the new
tensioner, ensure it is aligned correctly on its
mountings, and tighten the screws to the
specified torque wrench setting.
Renewal
7Open the bonnet. Jack up the front right-
hand side of the vehicle and support it
securely on an axle stand, remove the
roadwheel, then remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (two fasteners) from inside the wheel
arch.
8If the existing drivebelt is to be refitted,
mark it, or note the maker’s markings on its
flat surface, so that it can be installed the
same way round.
9Reaching up between the body and the
engine (above and to the rear of the
crankshaft pulley), apply a spanner to the
hexagon in the centre of the automatic
tensioner’s pulley. Rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise to release its pressure on the
drivebelt, then slip the drivebelt off the
crankshaft pulley, and release the tensioner
again (see illustration). Working from the
wheel arch or engine compartment as
necessary, and noting its routing, slip the
drivebelt off the remaining pulleys and
withdraw it.
10Check all the pulleys, ensuring that their
grooves are clean, and removing all traces of
oil and grease. Check that the tensioner
works properly, with strong spring pressure
11 Auxiliary drivebelt check and
renewal
10 Seat belt check
1•13
1
11.9 Rotate the tensioner pulley clockwise
to release its pressure on the drivebelt,
then slip the drivebelt off the crankshaft
pulley
11.3 Removing the auxiliary drivebelt
cover - it is secured by a fastener at each
end (arrowed) - from inside the right-hand
front wheel arch
11.4 Check the auxiliary drivebelt for signs
of wear like these. Very small cracks across
the drivebelt ribs are acceptable. If the
cracks are deep, or if the drivebelt looks
worn or damaged in any other way, renew it
11.6 The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by
an automatic tensioner; Torx screws
(arrowed) secure it to alternator mounting
bracket
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 31 of 279
Warning: To avoid personal
injury, never get beneath the
vehicle when it is supported by
only by a jack. The jack provided
with your vehicle is designed solely for
raising the vehicle to remove and refit the
roadwheels. Always use axle stands to
support the vehicle when it becomes
necessary to place your body underneath
the vehicle.
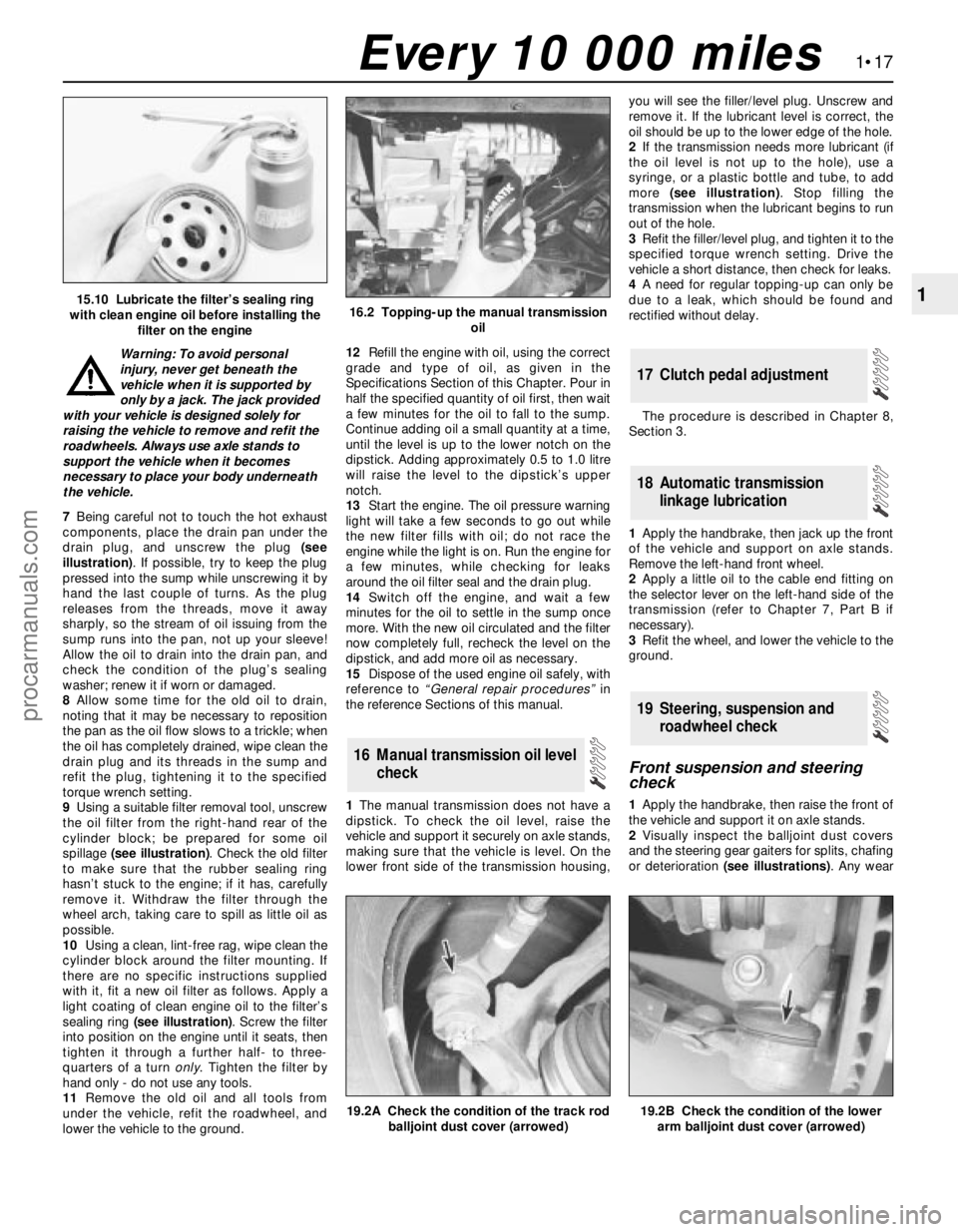
7Being careful not to touch the hot exhaust
components, place the drain pan under the
drain plug, and unscrew the plug (see
illustration). If possible, try to keep the plug
pressed into the sump while unscrewing it by
hand the last couple of turns. As the plug
releases from the threads, move it away
sharply, so the stream of oil issuing from the
sump runs into the pan, not up your sleeve!
Allow the oil to drain into the drain pan, and
check the condition of the plug’s sealing
washer; renew it if worn or damaged.
8Allow some time for the old oil to drain,
noting that it may be necessary to reposition
the pan as the oil flow slows to a trickle; when
the oil has completely drained, wipe clean the
drain plug and its threads in the sump and
refit the plug, tightening it to the specified
torque wrench setting.
9Using a suitable filter removal tool, unscrew
the oil filter from the right-hand rear of the
cylinder block; be prepared for some oil
spillage (see illustration). Check the old filter
to make sure that the rubber sealing ring
hasn’t stuck to the engine; if it has, carefully
remove it. Withdraw the filter through the
wheel arch, taking care to spill as little oil as
possible.
10Using a clean, lint-free rag, wipe clean the
cylinder block around the filter mounting. If
there are no specific instructions supplied
with it, fit a new oil filter as follows. Apply a
light coating of clean engine oil to the filter’s
sealing ring (see illustration). Screw the filter
into position on the engine until it seats, then
tighten it through a further half- to three-
quarters of a turn only. Tighten the filter by
hand only - do not use any tools.
11Remove the old oil and all tools from
under the vehicle, refit the roadwheel, and
lower the vehicle to the ground.12Refill the engine with oil, using the correct
grade and type of oil, as given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter. Pour in
half the specified quantity of oil first, then wait
a few minutes for the oil to fall to the sump.
Continue adding oil a small quantity at a time,
until the level is up to the lower notch on the
dipstick. Adding approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre
will raise the level to the dipstick’s upper
notch.
13Start the engine. The oil pressure warning
light will take a few seconds to go out while
the new filter fills with oil; do not race the
engine while the light is on. Run the engine for
a few minutes, while checking for leaks
around the oil filter seal and the drain plug.
14Switch off the engine, and wait a few
minutes for the oil to settle in the sump once
more. With the new oil circulated and the filter
now completely full, recheck the level on the
dipstick, and add more oil as necessary.
15Dispose of the used engine oil safely, with
reference to “General repair procedures”in
the reference Sections of this manual.
1The manual transmission does not have a
dipstick. To check the oil level, raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands,
making sure that the vehicle is level. On the
lower front side of the transmission housing,you will see the filler/level plug. Unscrew and
remove it. If the lubricant level is correct, the
oil should be up to the lower edge of the hole.
2If the transmission needs more lubricant (if
the oil level is not up to the hole), use a
syringe, or a plastic bottle and tube, to add
more (see illustration). Stop filling the
transmission when the lubricant begins to run
out of the hole.
3Refit the filler/level plug, and tighten it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Drive the
vehicle a short distance, then check for leaks.
4A need for regular topping-up can only be
due to a leak, which should be found and
rectified without delay.
The procedure is described in Chapter 8,
Section 3.
1Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support on axle stands.
Remove the left-hand front wheel.
2Apply a little oil to the cable end fitting on
the selector lever on the left-hand side of the
transmission (refer to Chapter 7, Part B if
necessary).
3Refit the wheel, and lower the vehicle to the
ground.
Front suspension and steering
check
1Apply the handbrake, then raise the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
2Visually inspect the balljoint dust covers
and the steering gear gaiters for splits, chafing
or deterioration (see illustrations). Any wear
19 Steering, suspension and
roadwheel check
18 Automatic transmission
linkage lubrication
17 Clutch pedal adjustment
16 Manual transmission oil level
check
1•17
1
19.2B Check the condition of the lower
arm balljoint dust cover (arrowed)
15.10 Lubricate the filter’s sealing ring
with clean engine oil before installing the
filter on the engine16.2 Topping-up the manual transmission
oil
19.2A Check the condition of the track rod
balljoint dust cover (arrowed)
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 34 of 279

brake shoes is not less than the
recommendation given in the Specifications.
14If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the brake shoe linings, or if you
are at all concerned about the condition of the
shoes, then remove the rear drums for a more
comprehensive inspection (refer to Chapter 9)
(see illustration).
15With the drum removed, check the shoe
return and hold-down springs for correct
installation, and check the wheel cylinders for
leakage of brake fluid. Check the friction
surface of the brake drums for scoring and
discoloration. If excessive, the drum should
be resurfaced or renewed.
16Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). On
completion, apply the handbrake and check
that the rear wheels are locked. The
handbrake is self-adjusting, and no manual
adjustment is possible.
1Check that the doors, bonnet and
tailgate/boot lid close securely. Check that
the bonnet safety catch operates correctly.
Check the operation of the door check straps.
2Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.1Apply the handbrake.
2Remove the wheel covers, using the flat
end of the wheelbrace supplied in the tool kit
(on models with the RS trim kit, it will be
necessary to unscrew the retaining bolts with
the special key).
3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4Refit the wheel covers.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking.
3Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4With the engine switched off, test the
operation of the brake servo unit as follows.
Depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then start the engine. As
the engine starts, there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake
pedal is now depressed again, it should be
possible to detect a hiss from the servo as the
pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
harder.
Steering and suspension
5Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, andcheck for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13On automatic transmission models, make
sure that all gearchanges occur smoothly
without snatching, and without an increase in
engine speed between changes. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the gearbox end and inside the
car, for signs of wear and fraying.
17Check the pedal stroke as described in
Chapter 8, Section 3, and adjust if necessary.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
18Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
19Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
26 Road test
25 Roadwheel nut tightness
check
24 Door and bonnet check and
lubrication
1•20
23.14 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here; if the lining is riveted to the
shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
Every 20 000 miles
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years
1The air entering the vehicle’s ventilation
system is passed through a very fine pleated-
paper air filter element, which removes
particles of pollen, dust and other airborne
foreign matter. To ensure its continued
effectiveness, this filter’s element must be
renewed at regular intervals.2Remove the left-hand side windscreen
wiper arm (Chapter 12).
3Prise off their trim caps, then unscrew the two
screws securing the windscreen edge of the cowl
grille panel; open the bonnet and remove the
remaining three retaining screws (see illustration).
4Peel back the rubber seal and withdraw the
cowl grille panel.
5Releasing the clip at each end, lift out the
pollen filter housing, and withdraw the
element (see illustrations).6Wipe out the ventilation system intake and
the filter housing, removing any leaves, dead
insects etc.
7If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition. If you are checking the element for
any other reason, inspect its front surface; if it
is very dirty, renew the element. If it is only
moderately dusty, it can be re-used by
blowing it clean from the rear to the front
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
27 Ventilation system pollen
filter renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 37 of 279

5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Ensure that the element and cover
are securely seated, so that unfiltered air
cannot enter the engine.
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system components are located at the front of
the engine, underneath the exhaust manifold
and air intake resonator. Refer to Chapter 6
for further information.
2Check that all components of the system
are securely fastened, correctly routed (with
no kinks or sharp bends to restrict flow) and in
sound condition; renew any worn or damaged
components.
3If oil leakage is noted, disconnect the
various hoses and pipes, and check that all
are clear and unblocked. Remove the air
cleaner assembly cover, air mass meter and
resonator, then check that the hose from the
cylinder head cover to the air cleaner housing
is clear and undamaged. Disconnect the
rubber T-piece both from the union on the
inlet manifold left-hand end, and from the
metal crankcase breather pipe under the
ignition coil. Connect a spare, clean, length of
hose to the breather pipe. Suck on the end of
the hose, then blow through it - little or norestriction to airflow should be felt in either
direction. A similar test can be applied to
check that the inlet manifold passages are
clear - air should be heard hissing out of the
plenum chamber mouth as you blow.
4The PCV valve is designed to allow gases
to flow out of the crankcase only, so that a
depression is created in the crankcase under
most operating conditions, particularly at idle.
Therefore, if either the oil separator or the PCV
valve are thought to be blocked, they must be
renewed (see Chapter 6). In such a case,
however, there is nothing to be lost by
attempting to flush out the blockage using a
suitable solvent. The PCV valve should rattle
when shaken.
5While the air filter element is removed (see
Section 29), wipe out the housing, and
withdraw the small foam filter from its location
in the rear right-hand corner of the housing
(see illustration). If the foam is badly clogged
with dirt or oil, it must be cleaned by soaking it
in a suitable solvent, and allowed to dry
before being refitted.
Spark plug check and renewal
1It is vital for the correct running, full
performance and proper economy of the
engine that the spark plugs perform with
maximum efficiency. The most important
factor in ensuring this is that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine. The suitable
type is given in the Specifications Section at
the beginning of this Chapter, on the Vehicle
Emissions Control Information (VECI) label
located on the underside of the bonnet (only
on models sold in some areas) or in the
vehicle’s Owner’s Handbook. If these sources
specify different plugs, purchase the spark
plug type specified on the VECI label (where
appropriate), as that information is provided
specifically for your engine. If this type is used
and the engine is in good condition, the spark
plugs should not need attention between
scheduled renewal intervals. Spark plug
cleaning is rarely necessary, and should notbe attempted unless specialised equipment is
available, as damage can easily be caused to
the firing ends.
2Spark plug removal and refitting requires a
spark plug socket, with an extension which
can be turned by a ratchet handle or similar.
This socket is lined with a rubber sleeve, to
protect the porcelain insulator of the spark
plug, and to hold the plug while you insert it
into the spark plug hole. You will also need a
wire-type feeler gauge, to check and adjust
the spark plug electrode gap, and a torque
wrench to tighten the new plugs to the
specified torque (see illustration).
3To remove the spark plugs, first open the
bonnet; the plugs are easily reached at the
top of the engine. Note how the spark plug
(HT) leads are routed and secured by clips
along the channel in the cylinder head cover.
31 Spark plug renewal
30 Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) system
check and filter cleaning
1•23
1
30.5 The Positive Crankcase Ventilation
(PCV) system filter in the air cleaner
assembly must be cleaned whenever the
air filter element is renewed
31.2 Tools required for changing spark
plugs
1Spark plug socket- This will have special
padding inside, to protect the spark plug
porcelain insulator
2Torque wrench- Although not essential,
use of this tool is the best way to ensure that
the plugs are tightened properly
3Ratchet- Standard hand tool to fit the
plug socket
4Extension- Depending on the other tools
available, you may need an extension to reach
the plugs
5Spark plug gap gauge- This gauge for
checking the gap comes in a variety of styles.
Make sure the gap for your engine is included
29.1A Release the wire clips to detach the
cover from the air cleaner assembly . . .29.1B . . . noting the long clip normally
hidden by the battery . . .29.2 . . . lift the element out of the housing,
and wipe out its interior before fitting the
new element
Every 30 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 38 of 279

To prevent the possibility of mixing up spark
plug (HT) leads, it is a good idea to try to work
on one spark plug at a time.
4If the marks on the original-equipment
spark plug (HT) leads cannot be seen, mark
the leads 1 to 4, to correspond to the cylinder
the lead serves (No 1 cylinder is at the timing
belt end of the engine). Pull the leads from the
plugs by gripping the rubber boot sealing thecylinder head cover opening, not the lead,
otherwise the lead connection may be
fractured.
5It is advisable to soak up any water in the
spark plug recesses with a rag, and to remove
any dirt from them using a clean brush,
vacuum cleaner or compressed air before
removing the plugs, to prevent any dirt or
water from dropping into the cylinders. Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
6Unscrew the spark plugs, ensuring that the
socket is kept in alignment with each plug - if
the socket is forcibly moved to either side, the
porcelain top of the plug may be broken off. If
any undue difficulty is encountered when
unscrewing any of the spark plugs, carefully
1•24Every 30 000 miles
Specifications
Engine
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Oil filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C148
Cooling system
Coolant protection at 40% antifreeze/water mixture ratio:
Slush point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -25°C (-13°F)
Solidifying point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -30°C (-22°F)
Coolant specific gravity at 40% antifreeze/water mixture ratio and
15°C/59°F - with no other additives in coolant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.061
Fuel system
Idle speed - nominal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830 ± 50 rpm*
Air filter element . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U618
Fuel filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion L218
* Note: Given for reference only - not adjustable.
Ignition system
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end of engine)
Spark plugs:*
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion RE7YCC
Electrode gap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Spark plug (HT) leads:
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 000 ohms
* Information on spark plug types and electrode gaps is as recommended by Champion Spark Plug. Where alternative types are used, refer to
their manufacturer’s recommendations
Braking system
Note: No minimum lining thicknesses are given by Ford - the following is given as a general recommendation. If the pad wear warning light
comes on before the front brake pad linings reach the minimum thickness, the pads should nevertheless be renewed immediately.
Minimum front or rear brake pad lining thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm
Minimum rear brake shoe lining thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Suspension and steering
Tyre pressures (cold):Front Rear
Normally laden* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 bars (31 psi) 2.1 bars (31 psi)
Fully laden* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.4 bars (35 psi) 2.8 bars (41 psi)
Note: Normally laden means up to 3 persons. For sustained high speeds above 100 mph (160 km/h), increased pressures are necessary.
Consult the driver’s handbook supplied with the vehicle.
Wiper blades
Windscreen:
Driver’s side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X 5303 (and SP 01 spoiler)
Passenger’s side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X 5103
Tailgate:
Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X 5103
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Auxiliary drivebelt cover fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 10 4 to 7
Auxiliary drivebelt automatic tensioner Torx screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Engine oil drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Manual transmission filler/level plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 26
Radiator undershield screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 11
procarmanuals.com