1993 FORD MONDEO battery location
[x] Cancel search: battery locationPage 206 of 279
remade, prevent the onset of corrosion in the
future by applying a coat of petroleum jelly or
silicone-based grease, or by spraying on (at
regular intervals) a proprietary ignition sealer
such as Holts Damp Start, or a water-
dispersant lubricant such as Holts Wet Start.
Note:It is important to note that the ignition
switch and the appropriate electrical circuit
must always be switched off before any of the
fuses (or relays) are removed and renewed. In
the event of the fuse/relay unit having to be
removed, the battery earth lead must be
disconnected. When reconnecting the battery,
reference should be made to Chapter 5.
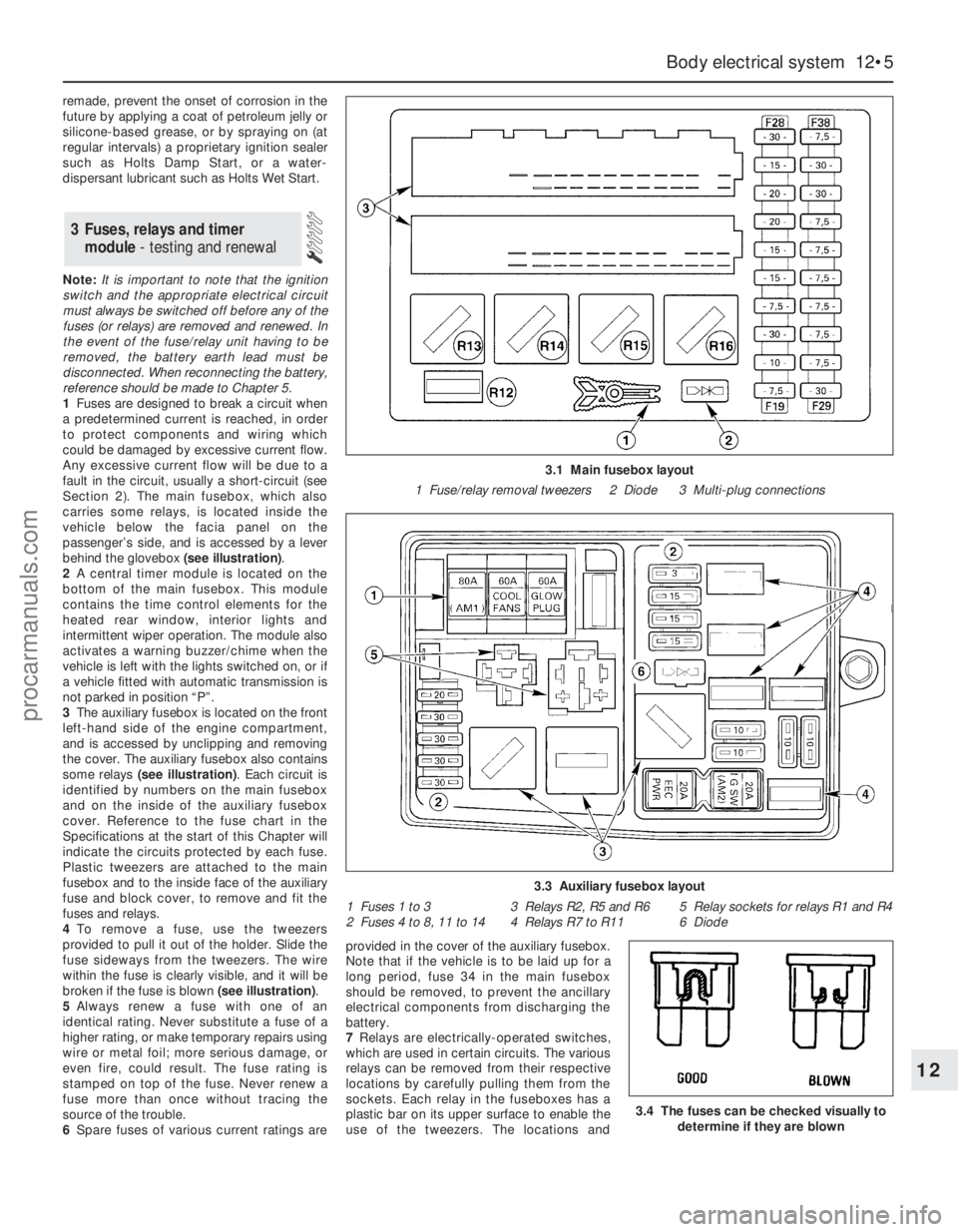
1Fuses are designed to break a circuit when
a predetermined current is reached, in order
to protect components and wiring which
could be damaged by excessive current flow.
Any excessive current flow will be due to a
fault in the circuit, usually a short-circuit (see
Section 2). The main fusebox, which also
carries some relays, is located inside the
vehicle below the facia panel on the
passenger’s side, and is accessed by a lever
behind the glovebox (see illustration).
2A central timer module is located on the
bottom of the main fusebox. This module
contains the time control elements for the
heated rear window, interior lights and
intermittent wiper operation. The module also
activates a warning buzzer/chime when the
vehicle is left with the lights switched on, or if
a vehicle fitted with automatic transmission is
not parked in position “P”.
3The auxiliary fusebox is located on the front
left-hand side of the engine compartment,
and is accessed by unclipping and removing
the cover. The auxiliary fusebox also contains
some relays (see illustration). Each circuit is
identified by numbers on the main fusebox
and on the inside of the auxiliary fusebox
cover. Reference to the fuse chart in the
Specifications at the start of this Chapter will
indicate the circuits protected by each fuse.
Plastic tweezers are attached to the main
fusebox and to the inside face of the auxiliary
fuse and block cover, to remove and fit the
fuses and relays.
4To remove a fuse, use the tweezers
provided to pull it out of the holder. Slide the
fuse sideways from the tweezers. The wire
within the fuse is clearly visible, and it will be
broken if the fuse is blown (see illustration).
5Always renew a fuse with one of an
identical rating. Never substitute a fuse of a
higher rating, or make temporary repairs using
wire or metal foil; more serious damage, or
even fire, could result. The fuse rating is
stamped on top of the fuse. Never renew a
fuse more than once without tracing the
source of the trouble.
6Spare fuses of various current ratings areprovided in the cover of the auxiliary fusebox.
Note that if the vehicle is to be laid up for a
long period, fuse 34 in the main fusebox
should be removed, to prevent the ancillary
electrical components from discharging the
battery.
7Relays are electrically-operated switches,
which are used in certain circuits. The various
relays can be removed from their respective
locations by carefully pulling them from the
sockets. Each relay in the fuseboxes has a
plastic bar on its upper surface to enable the
use of the tweezers. The locations and
3 Fuses, relays and timer
module- testing and renewal
Body electrical system 12•5
12
3.4 The fuses can be checked visually to
determine if they are blown
3.1 Main fusebox layout
1 Fuse/relay removal tweezers 2 Diode 3 Multi-plug connections
3.3 Auxiliary fusebox layout
1 Fuses 1 to 3 3 Relays R2, R5 and R6 5 Relay sockets for relays R1 and R4
2 Fuses 4 to 8, 11 to 14 4 Relays R7 to R11 6 Diode
procarmanuals.com
Page 216 of 279

6Similarly remove the fuel gauge and
temperature gauge by unscrewing the single
screws.
7Remove all the pin contacts.
8Using a small punch, push in the multi-plug
securing pins, and remove the multi-plugs.
9Carefully lift the printed circuit from the
location dowels on the housing, taking care
not to damage it.
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Remove the windscreen wiper arms as
described in Section 15.
2With the bonnet closed, release the grille
panel upper edge from just in front of the
windscreen, by prising off the caps and
unscrewing the upper retaining screws.
3Open the bonnet, and support with the
stay.
4Pull off the sealing strip from the cross
panel at the rear of the engine compartment.
5Unscrew the lower screws, and remove the
grille panel halves from in front of thewindscreen, withdrawing first one side and
then the other.
6Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
7Reach in behind the bulkhead. Squeeze the
collar on the upper end of the speedometer
cable, where it is attached to the intermediate
cable from the rear of the speedometer head.
Disconnect the cable, and withdraw it from
the bulkhead inner panel, together with the
rubber grommet (see illustrations).
8Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
9Unscrew the nut and disconnect the
speedometer cable from the vehicle speed
sensor on the transmission, then withdraw the
cable from within the engine compartment.
Use two spanners to loosen the nut - one to
counterhold the sensor, and the other to
unscrew the cable nut (see illustrations).Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).2Using a small screwdriver, prise the clock
out of the facia (see illustration). To prevent
damage to the facia, place a cloth pad
beneath the screwdriver.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the rear of
the clock, and withdraw the clock (see
illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Reset the clock on completion.
Removal
1Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
2Unscrew the bolts, and release the clips
securing the radiator lower cover to the front
of the vehicle.
3Disconnect the wiring from the horn
terminal.
4Unscrew the mounting bolt, and withdraw
the horn with its mounting bracket from under
the vehicle (see illustration).
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
14 Horn - removal and refitting
13 Clock- removal and refitting
12 Speedometer drive cable -
removal and refitting
Body electrical system 12•15
12
12.9B . . . and disconnect the
speedometer cable from the vehicle speed
sensor13.2 Prising the clock out of the facia13.3 Disconnecting the multi-plug from
the rear of the clock
12.7A Squeeze the collar . . .12.7B . . . and disconnect the
speedometer main cable from the
intermediate cable12.9A Unscrew the cable nut . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 217 of 279
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1). If the windscreen
wiper arms are to be removed, close the bonnet.
2With the wiper(s) “parked” (ie in the normal
at-rest position), mark the positions of the
blade(s) on the screen, using a wax crayon or
strips of masking tape.
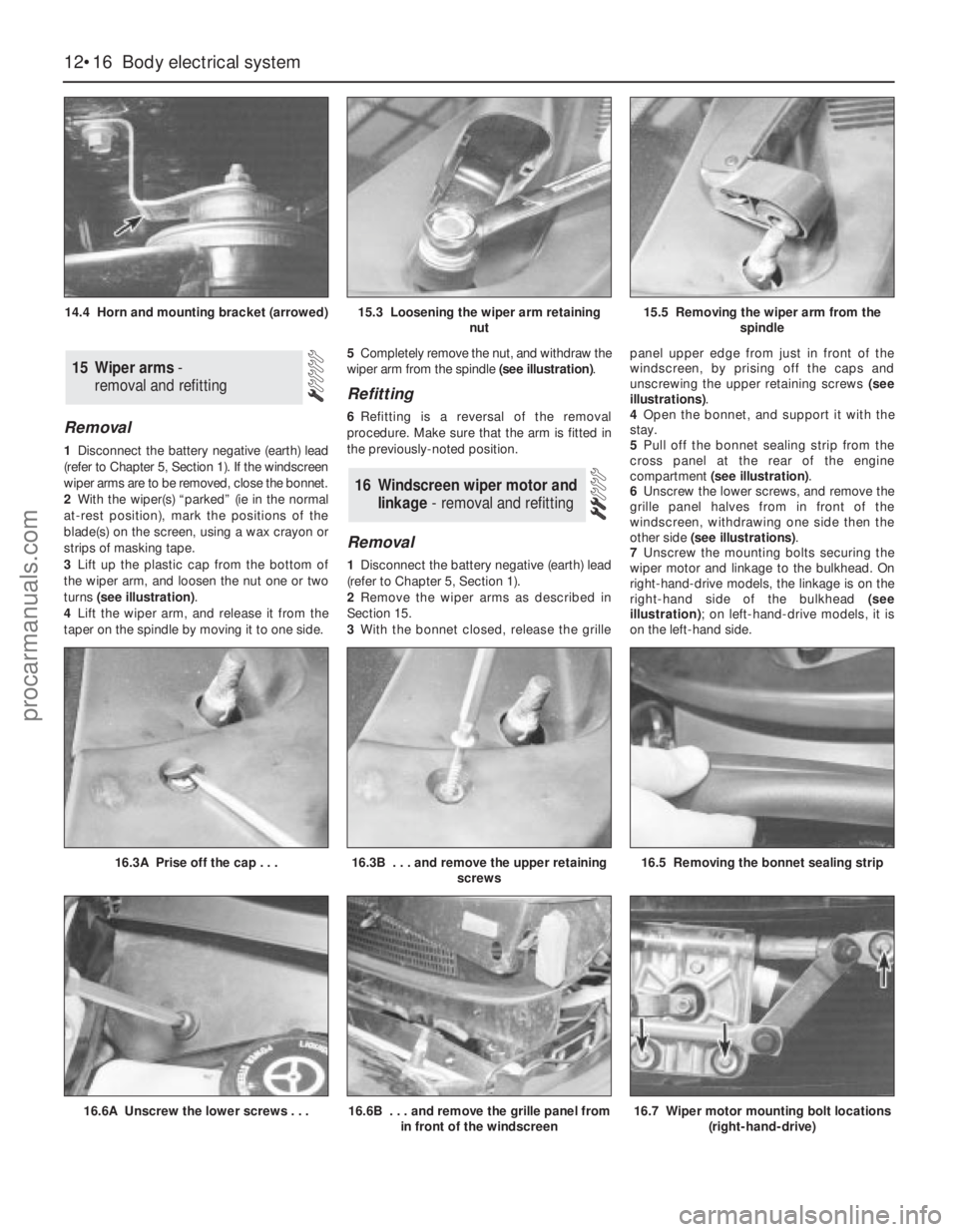
3Lift up the plastic cap from the bottom of
the wiper arm, and loosen the nut one or two
turns (see illustration).
4Lift the wiper arm, and release it from the
taper on the spindle by moving it to one side.5Completely remove the nut, and withdraw the
wiper arm from the spindle (see illustration).
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Make sure that the arm is fitted in
the previously-noted position.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Remove the wiper arms as described in
Section 15.
3With the bonnet closed, release the grillepanel upper edge from just in front of the
windscreen, by prising off the caps and
unscrewing the upper retaining screws (see
illustrations).
4Open the bonnet, and support it with the
stay.
5Pull off the bonnet sealing strip from the
cross panel at the rear of the engine
compartment (see illustration).
6Unscrew the lower screws, and remove the
grille panel halves from in front of the
windscreen, withdrawing one side then the
other side (see illustrations).
7Unscrew the mounting bolts securing the
wiper motor and linkage to the bulkhead. On
right-hand-drive models, the linkage is on the
right-hand side of the bulkhead (see
illustration); on left-hand-drive models, it is
on the left-hand side.
16 Windscreen wiper motor and
linkage - removal and refitting
15 Wiper arms-
removal and refitting
12•16 Body electrical system
14.4 Horn and mounting bracket (arrowed)15.3 Loosening the wiper arm retaining
nut15.5 Removing the wiper arm from the
spindle
16.6A Unscrew the lower screws . . .16.6B . . . and remove the grille panel from
in front of the windscreen16.7 Wiper motor mounting bolt locations
(right-hand-drive)
16.3A Prise off the cap . . .16.3B . . . and remove the upper retaining
screws16.5 Removing the bonnet sealing strip
procarmanuals.com
Page 274 of 279

REF•15Glossary of Technical Terms
GGapThe distance the spark must travel in
jumping from the centre electrode to the side
electrode in a spark plug. Also refers to the
spacing between the points in a contact
breaker assembly in a conventional points-
type ignition, or to the distance between the
reluctor or rotor and the pickup coil in an
electronic ignition.
GasketAny thin, soft material - usually cork,
cardboard, asbestos or soft metal - installed
between two metal surfaces to ensure a good
seal. For instance, the cylinder head gasket
seals the joint between the block and the
cylinder head.
GaugeAn instrument panel display used to
monitor engine conditions. A gauge with a
movable pointer on a dial or a fixed scale is an
analogue gauge. A gauge with a numerical
readout is called a digital gauge.
HHalfshaftA rotating shaft that transmits
power from the final drive unit to a drive
wheel, usually when referring to a live rear
axle.
Harmonic balancerA device designed to
reduce torsion or twisting vibration in the
crankshaft. May be incorporated in the
crankshaft pulley. Also known as a vibration
damper.
HoneAn abrasive tool for correcting small
irregularities or differences in diameter in an
engine cylinder, brake cylinder, etc.
Hydraulic tappetA tappet that utilises
hydraulic pressure from the engine’s
lubrication system to maintain zero clearance
(constant contact with both camshaft and
valve stem). Automatically adjusts to variation
in valve stem length. Hydraulic tappets also
reduce valve noise.
IIgnition timingThe moment at which the
spark plug fires, usually expressed in the
number of crankshaft degrees before the
piston reaches the top of its stroke.
Inlet manifoldA tube or housing with
passages through which flows the air-fuel
mixture (carburettor vehicles and vehicles with
throttle body injection) or air only (port fuel-
injected vehicles) to the port openings in the
cylinder head.
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
LocknutA nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
LockwasherA form of washer designed to
prevent an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strutA type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
creates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location.
MultimeterAn electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOxOxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhmThe unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
produce a current of one amp.
OhmmeterAn instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ringA type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action.
Overhead cam (ohc) engineAn engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).Overhead valve (ohv) engineAn engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensorA device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screwA type of screw head having a
cross instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
PlastigageA thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring
clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts are
assembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
journal and bearing.
Propeller shaftThe long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential
on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Proportioning valveA hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steeringA steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
rods to the steering arms at the wheels.
RadiatorA liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
RefrigerantAny substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful to
the ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker armA lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
Adjusting spark plug gap
Plastigage
Gasket
procarmanuals.com