1993 FORD MONDEO cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 59 of 279

then an ordinary socket extension bar and an
angle gauge, to tighten the cylinder head
bolts in the stages given in the Specifications
Section of this Chapter (see illustrations).
Note:Once tightened correctly, following this
procedure, the cylinder head bolts do not
require check-tightening, and must notbe re-
torqued.
33Refit the hydraulic tappets (if removed),
the camshafts, their oil seals and pulleys (see
Sections 10, 11, 12 and 13, as appropriate).
Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley, and
rotate the crankshaft clockwise to return the
pulley notches to the position described in
paragraph 8 of Section 10.
34Refit the timing belt and covers, checking
the camshaft alignment (valve timing) and
setting the timing belt tension, as described in
Section 10.
35The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points:
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) When reassembling the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting,
renew the self-locking nuts, and do not
allow the mounting to twist as the middle
two of the bracket’s six nuts are
tightened.
(c) Refill the cooling system, and top-up the
engine oil.
(d) Check all disturbed joints for signs of oil
or coolant leakage, once the engine has
been restarted and warmed-up to normal
operating temperature.
Removal
Note:To carry out this task with the
engine/transmission installed in the vehicle
requires the assistance of at least one person,
plus the equipment necessary to raise and
support the front of the vehicle (high enough
that the sump can be withdrawn from
underneath), and to lift and support the
complete engine/transmission unit 2 to 3 inches from its mountings while the vehicle
is raised. Precise details of the procedure will
depend on the equipment available - the
following is typical.
The full procedure outlined below must be
followed, so that the mating surfaces can be
cleaned and prepared to achieve an oil-tight
joint on reassembly, and so that the sump
can be aligned correctly; depending on your
skill and experience, and the tools and
facilities available, it may be that this task can
be carried out only with the engine removed
from the vehicle.
Note that the sump gasket must be
renewed whenever it is disturbed.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Drain the engine oil, then clean and refit the
engine oil drain plug, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Although not
strictly necessary as part of the dismantling
procedure, owners are advised to remove
and discard the oil filter, so that it can be
renewed with the oil (see Chapter 1).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
4Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union and from the (heater)
coolant pipe. Unbolt the coolant pipe from
the sump; if they will prevent sump removal,
disconnect or release the coolant hoses from
the oil cooler unions (where fitted).
5Unscrew the two bolts securing the powersteering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
6Unplug the electrical connector(s) to
disconnect the oxygen sensor and, where
fitted, the oil level sensor wiring - unclip the
connectors to release the wiring where
necessary.
7Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, trace the fluid cooler lines from
the transmission to the radiator, and release
them from any clips etc, so that they have as
much movement as possible.
8Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1).
9Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then either unhook all the system’s
rubber mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle, or
remove only the downpipe/catalytic converter
(see Chapter 4 for details).
10Unscrew the sump-to-transmission bolts,
also any securing the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate.
11Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
12Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head; bolt on
15 Sump - removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•19
2A
14.32B . . . and to third stage using angle
gauge14.32C Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
Note:View from rear of vehicle15.12 Equipment must be available to raise
and support engine/transmission unit while
vehicle is raised, to allow sump removal
14.30 Refitting cylinder head - note
fabricated guide studs (arrowed)14.32A Tightening cylinder head bolts (to
first and second stages) using torque
wrench . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 60 of 279

additional lifting eyes where required (see
illustration). Remove completely the
engine/transmission front mounting, unscrew
the rear mounting’s centre bolt, and unbolt
the left-hand mounting from the body.
Unscrew the six nuts securing the right-hand
mounting bracket, and withdraw the bracket.
13Being careful to watch the wiring, coolant
hoses, fluid cooler pipes or gearchange
linkage and transmission support rods (where
appropriate), and the radiator electric cooling
fan, to ensure that nothing is trapped,
stretched or damaged, lift the
engine/transmission unit by 2 to 3 inches and
support it securely.
14Progressively unscrew the sump retaining
bolts. Break the joint by striking the sump
with the palm of the hand, then lower the
sump and withdraw it with the
engine/transmission lower adaptor plate; note
the presence of any shims between the sump
and transmission.
15Remove and discard the sump gasket;
this must be renewed as a matter of course
whenever it is disturbed.
16While the sump is removed, take the
opportunity to remove the oil pump pick-up/
strainer pipe and to clean it (see Section 16).
Refitting
17On reassembly, thoroughly clean and
degrease the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block/crankcase and sump, then use a cleanrag to wipe out the sump and the engine’s
interior. If the oil pump pick-up/strainer pipe
was removed, fit a new gasket and refit the
pipe, tightening its screws to the specified
torque wrench setting. Fit the new gasket to
the sump mating surface so that the gasket
fits into the sump groove (see illustration).
18If the sump is being refitted with the
engine/transmission still connected and in the
vehicle, proceed as follows:
(a) Check that the mating surfaces of the
sump, the cylinder block/crankcase and
the transmission are absolutely clean and
flat. Any shims found on removal of the
sump must be refitted in their original
locations.
(b) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier. Without delay - the sump
bolts must be fully tightened within 10 to
20 minutes of applying the sealant - offer
up the sump and engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate, and refit the bolts,
tightening them lightly at first (see
illustration).
(c) Ensuring that the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate is correctly located,
firmly press the sump against the
transmission, and tighten the
transmission-to-sump (ie, engine) bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting.(d) Without disturbing the position of the
sump, and working in a diagonal
sequence from the centre outwards,
tighten the sump bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting.
(e) Proceed to paragraph 20.
19If the sump is being refitted with the
engine and transmission separated (in or out
of the vehicle), proceed as follows:
(a) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier (see illustration). Without
delay - the sump bolts must be fully
tightened within 10 to 20 minutes of
applying the sealant - offer up the sump
to the cylinder block/crankcase, and
insert the sump bolts, tightening them
lightly at first.
(b) Using a suitable straight edge to check
alignment across the flat-machined faces
of each, move the sump as necessary so
that its left-hand face - including any
shims found on removal - is flush with
that of the cylinder block/crankcase (see
illustration). Without disturbing the
position of the sump, and working in a
diagonal sequence from the centre
outwards, tighten the sump bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Check again that both faces are flush
before proceeding; if necessary, unbolt
the sump again, clean the mating
surfaces, and repeat the full procedure to
ensure that the sump is correctly aligned.
(d) If it is not possible to achieve exact
alignment by moving the sump, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.25 mm
(colour-coded yellow) or 0.50 mm (colour-
coded black) to eliminate the discrepancy
(see illustration).
20The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points.
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) Always renew any self-locking nuts
disturbed on removal.
(c) Lower the engine/transmission unit into
place, and reassemble the rear, left-hand
2A•20 In-car engine repair procedures
15.17 Ensure gasket is located correctly in
sump groove15.18 Engine/transmission lower adaptor
plate (arrowed) must be refitted with sump15.19A Apply sealant (arrowed) as
directed when refitting sump
15.19B Checking alignment of sump with
cylinder block/crankcase15.19C Sump-to-cylinder block/crankcase
alignment shims
1 Fitting points on sump 2 Shim
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 279
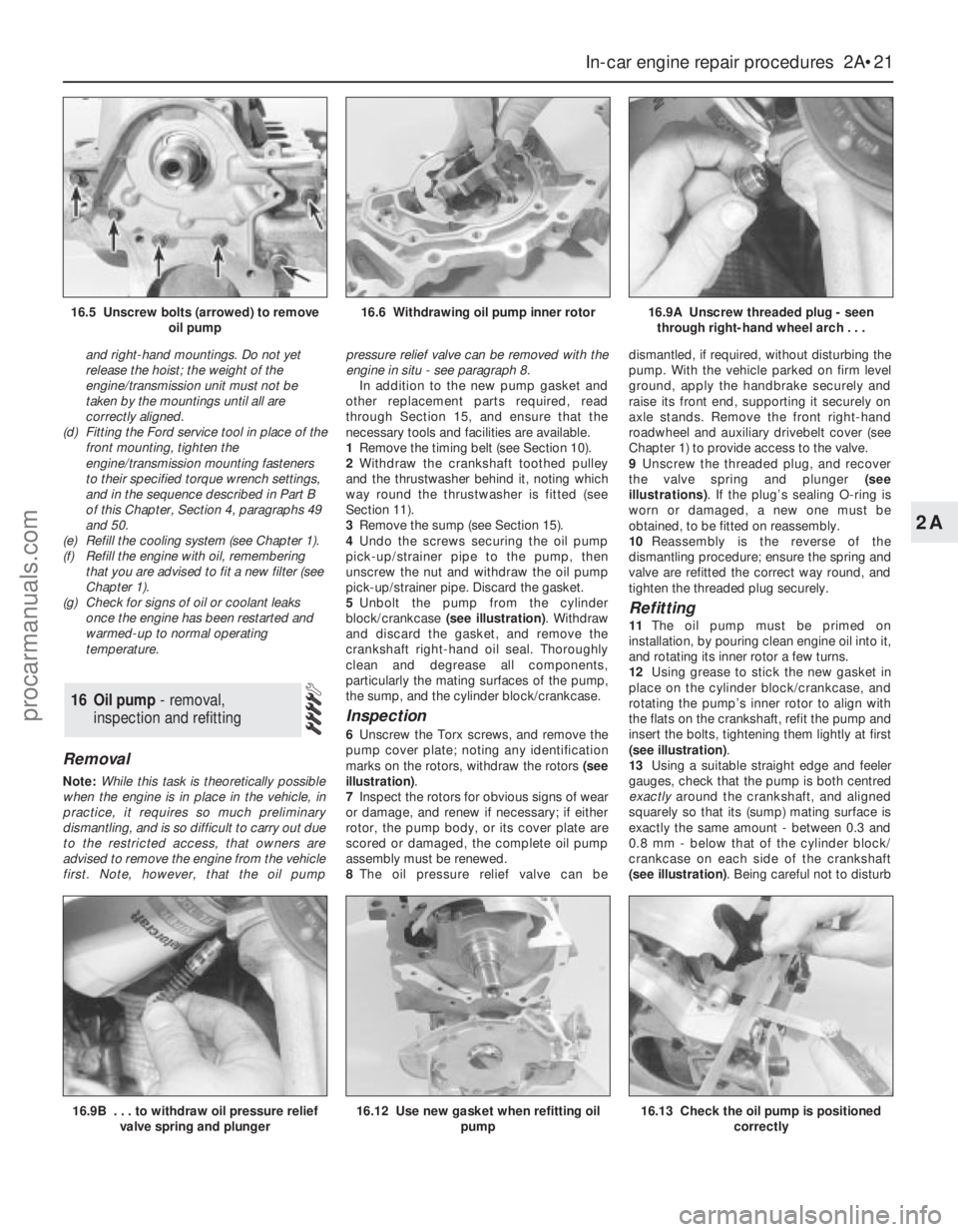
and right-hand mountings. Do not yet
release the hoist; the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be
taken by the mountings until all are
correctly aligned.
(d) Fitting the Ford service tool in place of the
front mounting, tighten the
engine/transmission mounting fasteners
to their specified torque wrench settings,
and in the sequence described in Part B
of this Chapter, Section 4, paragraphs 49
and 50.
(e) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(f) Refill the engine with oil, remembering
that you are advised to fit a new filter (see
Chapter 1).
(g) Check for signs of oil or coolant leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating
temperature.
Removal
Note:While this task is theoretically possible
when the engine is in place in the vehicle, in
practice, it requires so much preliminary
dismantling, and is so difficult to carry out due
to the restricted access, that owners are
advised to remove the engine from the vehicle
first. Note, however, that the oil pumppressure relief valve can be removed with the
engine in situ - see paragraph 8.
In addition to the new pump gasket and
other replacement parts required, read
through Section 15, and ensure that the
necessary tools and facilities are available.
1Remove the timing belt (see Section 10).
2Withdraw the crankshaft toothed pulley
and the thrustwasher behind it, noting which
way round the thrustwasher is fitted (see
Section 11).
3Remove the sump (see Section 15).
4Undo the screws securing the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe to the pump, then
unscrew the nut and withdraw the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe. Discard the gasket.
5Unbolt the pump from the cylinder
block/crankcase (see illustration). Withdraw
and discard the gasket, and remove the
crankshaft right-hand oil seal. Thoroughly
clean and degrease all components,
particularly the mating surfaces of the pump,
the sump, and the cylinder block/crankcase.
Inspection
6Unscrew the Torx screws, and remove the
pump cover plate; noting any identification
marks on the rotors, withdraw the rotors (see
illustration).
7Inspect the rotors for obvious signs of wear
or damage, and renew if necessary; if either
rotor, the pump body, or its cover plate are
scored or damaged, the complete oil pump
assembly must be renewed.
8The oil pressure relief valve can bedismantled, if required, without disturbing the
pump. With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, apply the handbrake securely and
raise its front end, supporting it securely on
axle stands. Remove the front right-hand
roadwheel and auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1) to provide access to the valve.
9Unscrew the threaded plug, and recover
the valve spring and plunger (see
illustrations). If the plug’s sealing O-ring is
worn or damaged, a new one must be
obtained, to be fitted on reassembly.
10Reassembly is the reverse of the
dismantling procedure; ensure the spring and
valve are refitted the correct way round, and
tighten the threaded plug securely.
Refitting
11The oil pump must be primed on
installation, by pouring clean engine oil into it,
and rotating its inner rotor a few turns.
12Using grease to stick the new gasket in
place on the cylinder block/crankcase, and
rotating the pump’s inner rotor to align with
the flats on the crankshaft, refit the pump and
insert the bolts, tightening them lightly at first
(see illustration).
13Using a suitable straight edge and feeler
gauges, check that the pump is both centred
exactlyaround the crankshaft, and aligned
squarely so that its (sump) mating surface is
exactly the same amount - between 0.3 and
0.8 mm - below that of the cylinder block/
crankcase on each side of the crankshaft
(see illustration). Being careful not to disturb
16 Oil pump - removal,
inspection and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•21
2A
16.9B . . . to withdraw oil pressure relief
valve spring and plunger16.12 Use new gasket when refitting oil
pump16.13 Check the oil pump is positioned
correctly
16.5 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
oil pump16.6 Withdrawing oil pump inner rotor16.9A Unscrew threaded plug - seen
through right-hand wheel arch . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 62 of 279

the gasket, move the pump into the correct
position, and tighten its bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting.
14Check that the pump is correctly located;
if necessary, unbolt it again, and repeat the
full procedure to ensure that the pump is
correctly aligned.
15Fit a new crankshaft right-hand oil seal
(see Section 20).
16Using grease to stick the gasket in place
on the pump, refit the pick-up/strainer pipe,
tightening its screws and nut to their specified
torque wrench settings (see illustration).
17The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, referring to
the relevant text for details where required.
1Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
Disconnect the coolant hoses from the oil
cooler.
2Unscrew the oil filter (see Chapter 1) -
catch any escaping oil in a drip tray.
3Unscrew the filter adaptor from the oil
pump, and withdraw the oil cooler; note how
its unions are aligned, and be prepared for oil
loss from the cooler.
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:(a) Renew all O-rings and seals disturbed on
removal.
(b) Align the cooler’s unions as noted on
removal, and tighten the adaptor to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(d) Refit the oil filter, then check the engine
oil level, and top-up as necessary (see
Chapter 1).
(e) Check for signs of oil or coolant leaks once
the engine has been restarted and warmed-
up to normal operating temperature.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands.
3Undo the two screws, and remove the
sensor’s cover from the front of the sump
(see illustration).
4Unplug the wiring from the sensor (see
illustration). Where necessary, unplug the
electrical connector to disconnect the sensor
wiring, and unclip the connector to release
the wiring from the vehicle.
5Unscrew the sensor, and quickly plug the
sump aperture to minimise oil loss; note the
sensor’s seal.6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; renew the sensor’s seal if it is
worn or damaged, and tighten the sensor to
the specified torque wrench setting. Check
the engine oil level, and top-up as necessary
(see Chapter 1) - check for signs of oil leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating temperature.
1The switch is screwed into the rear of the
cylinder block, above the right-hand
driveshaft’s support bearing (see
illustration).
2With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
3Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands.
4Unplug the wiring from the switch, and
unscrew it; be prepared for some oil loss.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; apply a thin smear of suitable
sealant to the switch threads, and tighten it to
the specified torque wrench setting. Check
the engine oil level, and top-up as necessary
(see Chapter 1). Check for signs of oil leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating temperature.
Note:Don’t try to prise these seals out
without removing the oil pump or seal carrier -
the seals are too soft, and the amount of
space available is too small, for this to be
possible without considerable risk of damage
to the seal housing and/or the crankshaft
journal. Follow exactly the procedure given
below.
Right-hand seal
1Remove the oil pump (see Section 16).
2Drive the oil seal out of the pump from
behind (see illustration).
20 Crankshaft oil seals -
renewal
19 Oil pressure warning light
switch - removal and refitting
18 Oil level sensor-
removal and refitting
17 Oil cooler -
removal and refitting
2A•22 In-car engine repair procedures
16.16 Use new gasket when refitting oil
pick-up pipe to pump18.3 Remove screws (arrowed) to remove
oil level sensor cover . . .18.4 . . . disconnecting wiring from sensor
19.1 Oil pressure warning light switch
(arrowed) is screwed into rear of cylinder
block, above right-hand driveshaft support
bearing
20.2 Driving out crankshaft right-hand oil
seal
procarmanuals.com
Page 68 of 279

Pistons and piston rings
Piston diameter - 1.6 litre engine:
Class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75.975 to 75.985 mm
Class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75.985 to 75.995 mm
Class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75.995 to 76.005 mm
Piston diameter - 1.8 litre engine:
Class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.570 to 80.580 mm
Class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.580 to 80.590 mm
Class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.590 to 80.600 mm
Piston diameter - 2.0 litre engine:
Class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84.770 to 84.780 mm
Class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84.780 to 84.790 mm
Class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84.790 to 84.800 mm
Oversizes - all engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . None available
Piston-to-cylinder bore clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No information available at time of writing
Piston ring end gaps - installed:
Top compression ring - 1.6 and 1.8 litre engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.30 to 0.50 mm
Top compression ring - 2.0 litre engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.26 to 0.50 mm
Second compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.30 to 0.50 mm
Oil control ring - 1.6 litre engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.25 to 1.00 mm
Oil control ring - 1.8 litre engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.38 to 1.14 mm
Oil control ring - 2.0 litre engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 to 1.40 mm
Gudgeon pin
Diameter:
White colour code/piston crown marked “A” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.622 to 20.625 mm
Red colour code/piston crown marked “B” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.625 to 20.628 mm
Blue colour code/piston crown marked “C” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.628 to 20.631 mm
Clearance in piston . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.010 to 0.016 mm
Connecting rod small-end eye internal diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.589 to 20.609 mm
Interference fit in connecting rod . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.011 to 0.042 mm
Crankshaft and bearings
Main bearing shell standard inside diameter - installed . . . . . . . . . . . . 58.011 to 58.038 mm
Main bearing journal standard diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57.980 to 58.000 mm
Main bearing journal-to-shell running clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.011 to 0.058 mm
Main bearing shell undersizes available . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.02 mm, 0.25 mm
Big-end bearing shell standard inside diameter - installed . . . . . . . . . . . 46.926 to 46.960 mm
Crankpin (big-end) bearing journal standard diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46.890 to 46.910 mm
Crankpin (big-end) bearing journal-to-shell running clearance . . . . . . . . 0.016 to 0.070 mm
Big-end bearing shell undersizes available . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.02 mm, 0.25 mm
Crankshaft endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.090 to 0.310 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Main bearing cap bolts and nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80 59
Big-end bearing cap bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 13
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90°
Piston-cooling oil jet/blanking plug Torx screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Cylinder block and head oilway blanking plugs:
M6 x 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 11 6 to 8
M10 x 11.5 - in block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 17
1/4 PTF plug - in block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Power steering pump/air conditioning compressor mounting
bracket-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Exhaust manifold heat shield mounting bracket-to-cylinder
block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 24
Crankcase breather system:
Oil separator-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Pipe-to-cylinder head bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Water pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 3
Driveshaft support bearing bracket-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Transmission-to-engine bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Part A of this Chapter
Engine/transmission mounting fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Part A of this Chapter
Front suspension subframe bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130 96
Note:Refer to Part A of this Chapter for remaining torque wrench settings.
2B•2 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
procarmanuals.com
Page 69 of 279

How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to
engine/transmission removal and refitting, to
those repair procedures requiring the removal
of the engine/transmission from the vehicle,
and to the overhaul of engine components. It
includes only the Specifications relevant to
those procedures. Refer to Part A for
additional Specifications, if required.
General information
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts, to detailed
step-by-step procedures covering removal
and installation of internal engine components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and installation of
the external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Part A of this Chapter and
Section 5 of this Part.
When overhauling this engine, it is essential
to establish first exactly what replacement
parts are available. At the time of writing,
components such as the piston rings are not
available separately from the
piston/connecting rod assemblies; pistons,
gudgeon pins and valve guides are not
available separately, and very few under- or
oversized components are available for
engine reconditioning. In most cases, it would
appear that the easiest and most
economically-sensible course of action is to
replace a worn or damaged engine with an
exchange unit.
It’s not always easy to determine when, or
if, an engine should be completely
overhauled, as a number of factors must be
considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an
indication that an overhaul is needed, while
low mileage doesn’t preclude the need for an
overhaul. Frequency of servicing is probably
the most important consideration. An engine
that’s had regular and frequent oil and filter
changes, as well as other required
maintenance, will most likely give many
thousands of miles of reliable service.
Conversely, a neglected engine may require
an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make surethat oil leaks aren’t responsible before
deciding that the rings and/or guides are
worn. Perform a cylinder compression check
(Part A of this Chapter, Section 3) to
determine the extent of the work required.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption rates may
also point to the need for an overhaul,
especially if they’re all present at the same
time. If a full service doesn’t remedy the
situation, major mechanical work is the only
solution.
An engine overhaul involves restoring all
internal parts to the specification of a new
engine. Note:Always check first what
replacement parts are available before
planning any overhaul operation; refer to
Section 1 of this Part. Ford dealers, or a good
engine reconditioning specialist/automotive
parts supplier may be able to suggest
alternatives which will enable you to overcome
the lack of replacement parts.
During an overhaul, it is usual to renew the
piston rings, and to rebore and/or hone the
cylinder bores; where the rebore is done by an
automotive machine shop, new oversize
pistons and rings will also be installed - all
these operations, of course, assume the
availability of suitable replacement parts. The
main and big-end bearings are generally
renewed and, if necessary, the crankshaft
may be reground to restore the journals.
Generally, the valves are serviced as well,
since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the starter and alternator, can be renewed as
well, or rebuilt, if the necessary parts can be
found. The end result should be an as-new
engine that will give many trouble-free miles.
Note:Critical cooling system components
such as the hoses, drivebelt, thermostat and
water pump MUST be replaced with new
parts when an engine is overhauled. The
radiator should be checked carefully, to
ensure that it isn’t clogged or leaking (see
Chapter 3). Also, as a general rule, the oil
pump should be renewed when an engine is
rebuilt.
Before beginning the engine overhaul, read
through the entire procedure to familiarise
yourself with the scope and requirements of
the job. Overhauling an engine isn’t difficult,
but it is time-consuming. Plan on the vehicle
being off the road for a minimum of two
weeks, especially if parts must be taken to an
automotive machine shop for repair or
reconditioning. Check on availability of parts,
and make sure that any necessary special
tools and equipment are obtained in advance.
Most work can be done with typical hand
tools, although a number of precision
measuring tools are required, for inspecting
parts to determine if they must be replaced.
Often, an automotive machine shop will
handle the inspection of parts, and will offer
advice concerning reconditioning andreplacement. Note:Always wait until the
engine has been completely dismantled, and
all components, especially the cylinder
block/crankcase, have been inspected, before
deciding what service and repair operations
must be performed by an automotive machine
shop. Since the block’s condition will be the
major factor to consider when determining
whether to overhaul the original engine or buy
a rebuilt one, never purchase parts or have
machine work done on other components
until the cylinder block/crankcase has been
thoroughly inspected.As a general rule, time
is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it
doesn’t pay to install worn or sub-standard
parts.
As a final note, to ensure maximum life and
minimum trouble from a rebuilt engine,
everything must be assembled with care, in a
spotlessly-clean environment.
If you’ve decided that an engine must be
removed for overhaul or major repair work,
several preliminary steps should be taken.
Locating a suitable place to work is
extremely important. Adequate work space,
along with storage space for the vehicle, will
be needed. If a workshop or garage isn’t
available, at the very least, a flat, level, clean
work surface made of concrete or asphalt is
required.
Cleaning the engine compartment and
engine/transmission before beginning the
removal procedure will help keep tools clean
and organized.
The engine can only be withdrawn by
removing it complete with the transmission;
the vehicle’s body must be raised and
supported securely, sufficiently high that the
engine/transmission can be unbolted as a
single unit and lowered to the ground; the
engine/transmission unit can then be
withdrawn from under the vehicle and
separated. An engine hoist or A-frame will
therefore be necessary. Make sure the
equipment is rated in excess of the combined
weight of the engine and transmission. Safety
is of primary importance, considering the
potential hazards involved in removing the
engine/transmission from the vehicle.
If this is the first time you have removed an
engine, a helper should ideally be available.
Advice and aid from someone more
experienced would also be helpful. There are
many instances when one person cannot
simultaneously perform all of the operations
required when removing the engine/
transmission from the vehicle.
Plan the operation ahead of time. Arrange for,
or obtain, all of the tools and equipment you’ll
need prior to beginning the job. Some of the
equipment necessary to perform
engine/transmission removal and installation
3 Engine/transmission removal -
methods and precautions
2 Engine overhaul -
general information
1 General information
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•3
2B
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 279

inner wing panel, release the engine
wiring loom and refit the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(g) Secure the engine wiring loom neatly to
the engine/transmission so that it cannot
be damaged as the unit is removed from
the vehicle.
14Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow
the upper part to be withdrawn.
15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the power steering pump (see
Chapter 10); secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
17Raise the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands, then remove the front
roadwheels. Drain the cooling system and (if
the engine is to be dismantled) drain the
engine oil and remove the oil filter (see
Chapter 1). Also drain the transmission as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 7.
18Withdraw the lower part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield.
19Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then unhook all the system’s rubber
mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle (see
Chapter 4 for details).
20Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, mark their positions, then
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
transmission support rods from the rear of the
transmission. Unscrew the retaining nuts, and
withdraw the gear linkage heat shield from the
underbody. Unbolt the rear end of the linkage
from the underbody, swivel the linkage around
to the rear, and tie it to the underbody (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
21Disconnect both anti-roll bar links from
their respective suspension strut - note the
flexible brake hose bracket attached to each
link stud - and both track rod ends from their
steering knuckles. Unfasten the clamp bolt
securing each front suspension lower arm
balljoint to its steering knuckle (see Chap-
ter 10 for details). Check that both balljoints
can be released from the knuckle assemblies
when required, but leave them in place for thetime being, secured by the clamp bolts if
necessary.
22Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unbolt the accumulator/
dehydrator from the subframe; secure it as far
as possible (without disconnecting the
system’s hoses) clear of the engine/
transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
23Unbolt the steering gear from the
subframe; if the bolts are not accessible from
above, a Ford service tool will be required to
reach them from underneath the vehicle (see
Chapter 10 for details).
24Unscrew the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
25Hold the radiator in its raised position, by
inserting split pins through the holes in the
rear of the engine compartment front
crossmember and into the radiator’s upper
mounting extensions. Unbolt the radiator
mounting brackets from the subframe; note
that they are handed, and are marked to
ensure correct refitting (see illustrations).
Collect and store the bottom mounting
rubbers for safekeeping, noting which way up
they are fitted.
26Unbolt the engine/transmission rear
mounting from the subframe - where the
vehicle is fitted with automatic transmission, a
separate damper may be fitted beneath the
subframe, which must be unbolted to reach
the mounting’s fasteners. Where the vehicle is
fitted with manual transmission, also unscrew
the mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting bracket from the transmission.
27Unscrew the engine/transmission front
mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting from the subframe, noting the
location of the wiring connector bracket.
28Use white paint or similar (do not use a
sharp-pointed scriber, which might break the
underbody protective coating and cause
rusting) to mark the exact relationship of the
subframe to the underbody. Unscrew the four
mounting bolts from the subframe (note their
different-sized washers - see also illus-tration 4.47A) and allow the subframe to hang
down on the suspension lower arm balljoints.
Disconnect the balljoints one at a time from
the steering knuckle assemblies (see Chap-
ter 10) and lower the subframe to the ground;
withdraw the subframe from under the
vehicle.
29Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above) and catching as much as possible of
the escaping coolant in the drain tray,
disconnect the cooling system hoses and
pipes as follows - refer to Chapter 3 for further
details, if required:
(a) Remove the radiator top hose.
(b) Remove the (heater) hose running from
the thermostat to the engine
compartment bulkhead union.
(c) Disconnect from the thermostat the hose
running to the expansion tank - secure the
hose clear of the working area.
(d) Disconnect from the thermostat the
coolant hose/pipe which runs to the
radiator bottom hose.
(e) Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union, from the (sump) heater
coolant pipe and from the water pump
union - secure the hose clear of the
working area.
(f) Unbolt the (heater) coolant pipe from the
sump, trace the pipe/hose round to the
engine compartment bulkhead union,
disconnecting (where fitted) the oil cooler
hoses from the cooler unions, then
remove it.
(g) Unless the vehicle has air conditioning
fitted, secure the radiator as far forwards
as possible while it is in its raised position;
if air conditioning is fitted, remove the
radiator completely (see Chapter 3).
30Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unplug the compressor’s
electrical connector, and unbolt the
compressor from the engine (see
illustration). Secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
2B•6 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.25A Use split pins as shown to secure
radiator in its raised position . . .
4.25B . . . while you unbolt the bottom
mountings (arrowed) - note that the
mountings are handed, and do not lose the
mounting rubbers
4.30 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to release
air conditioning compressor from engine
procarmanuals.com
Page 73 of 279

31Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, disconnect the driveshafts from
the transmission as follows, referring to
Chapter 8 for further details when required:
(a) Unscrew the nuts securing the right-hand
driveshaft support bearing, and withdraw
the heat shield.
(b) Pull the right-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission; be prepared to catch any
spilt oil.
(c) Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission - remember that the
unit is to be lowered out of the vehicle -
and ensure that the inner joint is not
turned through more than 18°.
(d) Prise the left-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission - again, be prepared for oil
spillage. Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission, and ensure that its
inner joint is not turned through more than
18°.
32Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, proceed as follows, referring to
Chapter 7, Part B and to Chapter 8 for further
details when required:
(a) Unscrew its centre bolt, then unbolt the
engine/transmission rear mounting
bracket from the transmission.
(b) Disconnect the fluid cooler pipe from the
rear of the transmission, and secure it
clear of the unit.
(c) Prise the left-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission; be prepared to catch any
spilt oil.
(d) Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission - remember that the
unit is to be lowered out of the vehicle -
and ensure that the inner joint is not
turned through more than 18°.
(e) Unscrew the nuts securing the right-hand
driveshaft support bearing, and withdraw
the heat shield.
(f) Pull the right-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission - again, be prepared for oil
spillage. Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission, and ensure that its
inner joint is not turned through more than
18°.
(g) Disconnect the fluid cooler pipe from the
front of the transmission, and secure it
clear of the unit.
33The engine/transmission unit should now
be hanging on the right- and left-hand
mountings only, with all components which
connect it to the rest of the vehicle
disconnected or removed and secured well
clear of the unit. Make a final check that this is
the case, then ensure that the body is
securely supported, high enough to permit the
withdrawal of the engine/transmission unit
from underneath; allow for the height of the
engine dolly, if used.
34Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit, using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head. Unscrew the
six nuts securing the right-hand mounting
bracket, then the three nuts securing the left-
hand bracket. Warning: Do not put any part of
your body under the vehicle, or
under the engine/transmission
unit, when they are supported only by a
hoist or other lifting equipment.
35Lower the engine/transmission to the
ground, and withdraw it from under the
vehicle (see illustration).
36Referring to the relevant part of Chapter 7,
separate the transmission from the engine.
37While the engine/transmission is removed,
check the mountings; renew them if they are
worn or damaged. Similarly, check the
condition of all coolant and vacuum hoses
and pipes (see Chapter 1); components that
are normally hidden can now be checked
properly, and should be renewed if there is
any doubt at all about their condition. Where
the vehicle is fitted with manual transmission,
take the opportunity to overhaul the clutch
components (see Chapter 8). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components (such as the transmission oil
seals) disturbed on removal, and renew any
that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
38Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points.
Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings given; where settings are not quoted
in the Specifications Sections of the two Parts
of this Chapter, refer to the Specifications
Section of the relevant Chapter of this manual.
39In addition to the points noted in
paragraph 37 above, always renew any
circlips and self-locking nuts disturbed on
removal.
40Where wiring, etc, was secured by cable
ties which had to be cut on removal, ensure
that it is secured with new ties on refitting.
41With all overhaul operations completed,
refit the transmission to the engine as
described in Chapter 7.
42Manoeuvre the engine/transmission unit
under the vehicle, attach the hoist, and lift the
unit into position until the right- and left-hand
mountings can be reassembled; tighten the
(new) nuts only lightly at this stage. Do not yet
release the hoist; the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be taken by
the mountings until all are correctly aligned.
43Using new circlips, and ensuring that the
inner joints are not twisted through too great
an angle (see Chapter 8), refit the driveshafts.
Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, the procedure is the reverse of
that outlined in paragraph 31 above. Where
the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, proceed as follows, referring to
Chapter 7, Part B and to Chapter 8 for further
details when required:
(a) Refit the left-hand driveshaft.
(b) Using the clips provided to ensure that
they are correctly routed, and tighteningthe couplings to the specified torque
wrench setting where possible, reconnect
the fluid cooler pipes, first to the rear,
then to the front, of the transmission.
(c) Refit the right-hand driveshaft to the
transmission, refit the heat shield, and
tighten the support bearing nuts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(d) Refit the engine/transmission rear
mounting bracket to the transmission,
tightening the bolts to the torque wrench
setting specified, then refit the mounting,
tightening the centre bolt only lightly at
this stage.
44Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, do not forget to refit the
compressor; tighten the bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting, and plug in its
electrical connector.
45Using the marks and notes made on
removal, refit the cooling system hoses.
Where they are left disconnected or unclipped
for the time being, do not forget to secure
them at the appropriate moment during the
reassembly procedure. Refit the radiator (if
removed), using split pins to secure it in the
raised position.
46Offer up the subframe one side at a time,
and hold it by securing the suspension lower
arm balljoints to the steering knuckle
assemblies. Refit the subframe bolts, ensuring
that the washers are refitted correctly, and
tightening the bolts only lightly at this stage.
47The subframe must now be aligned on the
underbody. Ford specify the use of service
tool 15-097, which is a pair of tapered guides,
with attachments to hold them in the
subframe as it is refitted. However, since the
working diameter of these tools is 20.4 mm,
and since the corresponding aligning holes in
the subframe and underbody are respectively
21 mm and 22 mm in diameter, there is a
significant in-built tolerance possible in the
subframe’s alignment, even if the correct tools
are used. If these tools are not available, you
can align the subframe by eye, centring the
subframe aligning holes on those of the
underbody, and using the marks made on
removal for assistance. Alternatively, you can
align the subframe using a tapered drift (such
as a clutch-aligning tool), or even a deep
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•7
2B
4.35 Lowering the engine/transmission
unit out of the vehicle
procarmanuals.com