1993 FORD MONDEO fuel type
[x] Cancel search: fuel typePage 44 of 279
end of the cylinder block, inboard of the
timing belt, and is driven with the power
steering pump and alternator by a flat
“polyvee”-type auxiliary drivebelt from the
crankshaft pulley.
When working on this engine, note that
Torx-type (both male and female heads) and
hexagon socket (Allen head) fasteners are
widely used; a good selection of bits, with the
necessary adaptors, will be required, so that
these can be unscrewed without damage
and, on reassembly, tightened to the torque
wrench settings specified.
General description - lubrication
system
Lubrication is by means of an eccentric-
rotor trochoidal pump, which is mounted on
the crankshaft right-hand end, and draws oil
through a strainer located in the sump. The
pump forces oil through an externally-
mounted full-flow cartridge-type filter - on
some versions of the engine, an oil cooler is
fitted to the oil filter mounting, so that clean
oil entering the engine’s galleries is cooled by
the main engine cooling system. From the
filter, the oil is pumped into a main gallery in
the cylinder block/crankcase, from where it is
distributed to the crankshaft (main bearings)
and cylinder head (see illustration).
The big-end bearings are supplied with oil
via internal drillings in the crankshaft. On
some versions of the engine, each piston
crown is cooled by a spray of oil directed at
its underside by a jet. These jets are fed by
passages off the crankshaft oil supply
galleries, with spring-loaded valves to ensure
that the jets open only when there is sufficient
pressure to guarantee a good oil supply to
the rest of the engine components; where the
jets are not fitted, separate blanking plugs are
provided, so that the passages are sealed,
but can be cleaned at overhaul (see
illustration).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
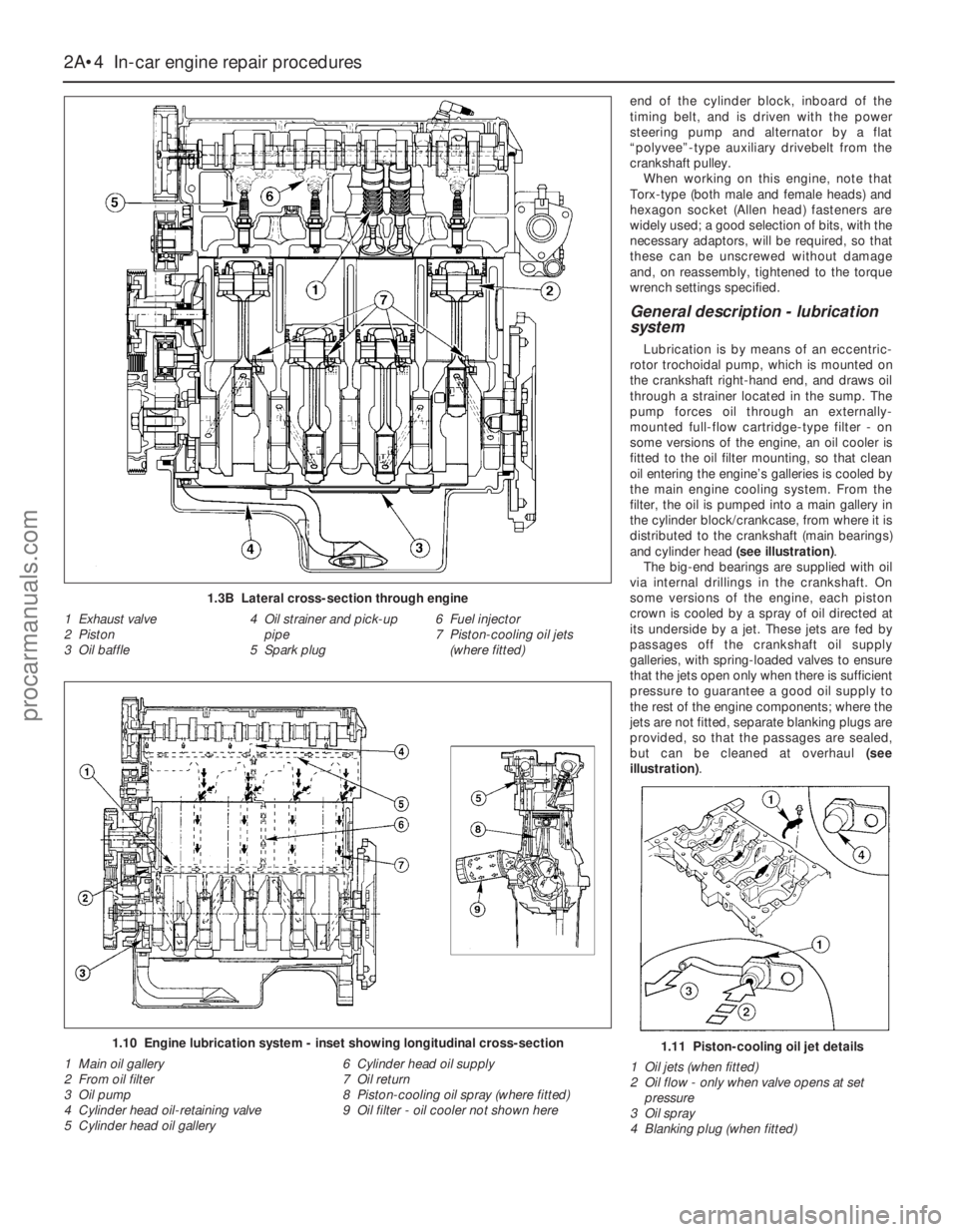
1.3B Lateral cross-section through engine
1 Exhaust valve
2 Piston
3 Oil baffle4 Oil strainer and pick-up
pipe
5 Spark plug6 Fuel injector
7 Piston-cooling oil jets
(where fitted)
1.10 Engine lubrication system - inset showing longitudinal cross-section
1 Main oil gallery
2 From oil filter
3 Oil pump
4 Cylinder head oil-retaining valve
5 Cylinder head oil gallery6 Cylinder head oil supply
7 Oil return
8 Piston-cooling oil spray (where fitted)
9 Oil filter - oil cooler not shown here1.11 Piston-cooling oil jet details
1 Oil jets (when fitted)
2 Oil flow - only when valve opens at set
pressure
3 Oil spray
4 Blanking plug (when fitted)
procarmanuals.com
Page 45 of 279

The cylinder head is provided with two oil
galleries, one on the inlet side and one on the
exhaust, to ensure constant oil supply to the
camshaft bearings and hydraulic tappets. A
retaining valve (inserted into the cylinder
head’s top surface, in the middle, on the inlet
side) prevents these galleries from being
drained when the engine is switched off. The
valve incorporates a ventilation hole in its
upper end, to allow air bubbles to escape
from the system when the engine is restarted.
While the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings and the hydraulic tappets receive a
pressurised supply, the camshaft lobes and
valves are lubricated by splash, as are all
other engine components.
Valve clearances - general
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced,
and the valves and their seats could be
severely damaged.
The engines covered in this manual,
however, employ hydraulic tappets which use
the lubricating system’s oil pressure
automatically to take up the clearance
between each camshaft lobe and its
respective valve stem. Therefore, there is no
need for regular checking and adjustment of
the valve clearances, but it is essential that
onlygood-quality oil of the recommended
viscosity and specification is used in the
engine, and that this oil is always changed at
the recommended intervals. If this advice is
not followed, the oilways and tappets may
become clogged with particles of dirt, or
deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil, so that
the system cannot work properly; ultimately,
one or more of the tappets may fail, and
expensive repairs may be required.
On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet.
After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the
oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care mustbe taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 seconds, or until the noise
ceases. Do not run the engine at more than
3000 rpm until the tappets are fully recharged
with oil and the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to
normal operating temperature, take the
vehicle to a Ford dealer for expert advice.
Depending on the mileage covered and the
usage to which each vehicle has been put,
some vehicles may be noisier than others;
only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell if the noise level is typical for
the vehicle’s mileage, or if a genuine fault
exists. If any tappet’s operation is faulty, it
must be renewed (Section 13).
The following major repair operations can
be accomplished without removing the
engine from the vehicle. However, owners
should note that any operation involving the
removal of the sump requires careful
forethought, depending on the level of skill
and the tools and facilities available; refer to
the relevant text for details.
(a) Compression pressure - testing.
(b) Cylinder head cover - removal and
refitting.
(c) Timing belt covers - removal and refitting.
(d) Timing belt - renewal.
(e) Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys
- removal and refitting.
(f) Camshaft oil seals - renewal.
(g) Camshafts and hydraulic tappets -
removal and refitting.
(h) Cylinder head - removal, overhaul and
refitting.
(i) Cylinder head and pistons -
decarbonising.
(j) Sump - removal and refitting.
(k) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
(l) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
(m) Piston/connecting rod assemblies -
removal and refitting (but see note below).
(n) Flywheel/driveplate - removal and
refitting.
(o) Engine/transmission mountings - removal
and refitting.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and will help to keep dirt
out of the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet, to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint; special covers are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for component/
gasket or seal replacement, the repairs can
generally be made with the engine in the
vehicle. The intake and exhaust manifold
gaskets, sump gasket, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place.
Exterior components such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
without lifting out the engine, camshaft and
valve component servicing can also be
accomplished with the engine in the vehicle,
as can renewal of the timing belt and toothed
pulleys.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine
in the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved, and because of the
amount of preliminary dismantling work
required - these operations are therefore
covered in Part B of this Chapter.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The aid of an assistant will be
required also.
3Disable the ignition system by unplugging
the ignition coil’s electrical connector, and
remove fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump.
4Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
5Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter
motor; after one or two revolutions, the
compression pressure should build up to a
maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record
the highest reading obtained.
6Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
7At the time of writing, no compression
3 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2 Repair operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 100 of 279

This Chapter is concerned with those
features of the engine management system
that supply clean fuel and air to the engine,
meter it in the required proportions, and
dispose of the results. Since the emission
control sub-systems modify the functions of
both the fuel and exhaust sub-systems, all of
which are integral parts of the whole engine
management system, there are many cross-
references to Chapters 5 and 6. Information
on the electronic control system, its fault
diagnosis, sensors and actuators, is given in
Chapter 6.
The air intake system consists of several
plastics components designed to eliminate
induction roar as much as possible. The air
intake tube (opening behind the direction
indicator/headlight assembly) is connected,
via small and large resonators located under
the front left-hand wing, to the air cleaner
assembly in the engine compartment. Once it
has passed through the filter element and the
air mass meter, the air enters the plenum
chamber mounted above the throttle housing
and inlet manifold; the resonator mounted in
the engine compartment further reduces noise
levels.
The fuel system consists of a plastic tank
(mounted under the body, beneath the rear
seats), combined metal and plastic fuel hoses,
an electric fuel pump mounted in the fuel tank,
and an electronic fuel injection system.
The exhaust system consists of an exhaust
manifold, the front downpipe and catalytic
converter and, on production-fit systems, a
rear section incorporating two or three
silencers and the tailpipe assembly. The
service replacement exhaust system consists
of three or four sections: the front
downpipe/catalytic converter, the
intermediate pipe and front silencer, and the
tailpipe and rear silencer. On some versions,
the tailpipe is in two pieces, with two rear
silencers. The system is suspended
throughout its entire length by rubber
mountings.
Extreme caution should be exercised when
dealing with either the fuel or exhaust
systems. Fuel is a primary element for
combustion. Be very careful! The exhaust
system is an area for exercising caution, as it
operates at very high temperatures. Serious
burns can result from even momentary
contact with any part of the exhaust system,
and the fire risk is ever-present. The catalytic
converter in particular runs at very high
temperatures - refer to the information in
Chapter 6.
Warning: Many of the procedures
in this Chapter require the
removal of fuel lines and
connections, which may result in
some fuel spillage. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautionswhen you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand. Before carrying out any operation
on the fuel system, refer also to the
precautions given in “Safety first!” at the
beginning of this manual, and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly-dangerous and
volatile liquid, and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed.
Warning: The fuel system will
remain pressurised for long
periods of time after the engine is
switched off - this pressure must
be released before any part of the system
is disturbed. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautions
when you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
1The fuel system referred to in this Chapter
is defined as the fuel tank and tank-mounted
fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit, the fuel
filter, the fuel injectors and the pressure
regulator in the injector rail, and the metal
pipes and flexible hoses of the fuel lines
between these components. All these contain
fuel, which will be under pressure while the
engine is running and/or while the ignition is
switched on.
2The pressure will remain for some time after
the ignition has been switched off, and must
be relieved before any of these components is
disturbed for servicing work.
3The simplest method is simply to
disconnect the fuel pump’s electrical supply
while the engine is running - either by
removing the fuel pump fuse (number 14), or
by lifting the red button on the fuel cut-off
switch (see Section 13) - and to allow the
engine to idle until it dies through lack of fuel
pressure. Turn the engine over once or twice
on the starter to ensure that all pressure is
released, then switch off the ignition; do not
forget to refit the fuse (or depress the redbutton, as appropriate) when work is
complete.
4The Ford method of depressurisation is to
use service tool 29-033 fitted to the fuel rail
pressure test/release fitting - a Schrader-type
valve with a blue plastic cap, located on the
union of the fuel feed line and the fuel rail - to
release the pressure, using a suitable
container and wads of rag to catch the spilt
fuel. Do notsimply depress the valve core to
release fuel pressure - droplets of fuel will
spray out, with a consequent risk of fire, and
of personal injury through fuel getting into
your eyes.
Warning: Either procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run. Remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
5Note that, once the fuel system has been
depressurised and drained (even partially), it
will take significantly longer to restart the
engine - perhaps several seconds of cranking
- before the system is refilled and pressure
restored.
Warning: The fuel system
pressure must be released before
any part of the system is
disturbed - see Section 2. Petrol
is extremely flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on any part of
the fuel system. Don’t smoke, or allow
open flames or bare light bulbs, near the
work area. Don’t work in a garage where a
natural gas-type appliance (such as a
water heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot
light is present. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
Disconnecting and connecting
quick-release couplings
1Quick-release couplings are employed at all
unions in the fuel feed and return lines.
2Before disconnecting any fuel system
component, relieve the residual pressure in
the system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
3 Fuel lines and fittings-
general information
2 Fuel system - depressurisation
1 General information and
precautions
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 103 of 279

which pulley, disconnect the first cable end
nipple from the throttle actuator’s upper
pulley, then slide the cable outer upwards out
of the actuator housing. Disconnect the
second cable in the same way from the
actuator’s lower pulley.
6Working in the passenger compartment,
reach up to the top of the accelerator pedal.
Pull the end fitting and collar out of the pedal,
then release the cable inner wire through the
slot in the pedal. Tie a length of string to the
end of the cable.
7Returning to the engine compartment, pull
the cable through the bulkhead until the string
can be untied and the pedal-to-actuator cable
removed.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Use the string to draw the pedal-
to-actuator cable through the bulkhead.
Ensure that each cable end is connected to
the correct actuator pulley.
9Adjust both cables as described below.
Adjustment
Note:Both sections of the cable must be
adjusted together, even if only one has been
disturbed.
10Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
11Remove the metal clip from the adjuster
of each cable section (see illustration), and
lubricate the adjusters’ grommets with soapy
water.
12Remove any slack by pulling both cable
outers as far as possible out of their
respective adjusters.
13Unplug the TCS throttle actuator’s
electrical connector, and prise off its cover.
Lock both pulleys together by pushing a
locking pin (a pin punch or a similar tool of
suitable size) into their alignment holes.
Disconnect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable’s end nipple from the throttle linkage.
14Have an assistant depress the accelerator
pedal fully. The pedal-to-actuator cable outer
will move back into the adjuster; hold it there,
and refit the clip.
15Connect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable end nipple to the throttle linkage, andcheck that the cable outer’s grommet is
correctly secured in the housing bracket.
16Again have the assistant depress the
accelerator pedal fully. The actuator-to-
throttle housing cable outer will move back
into the adjuster; hold it there, and refit the
clip.
17Remove the locking pin from the pulleys.
Check that the throttle valve moves smoothly
and easily from the fully-closed to the fully-
open position and back again, as the
assistant depresses and releases the
accelerator pedal. Re-adjust the cable(s) if
required.
18When the setting is correct, refit the TCS
throttle actuator’s cover and electrical
connector, then refit the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
1Disconnect the cable inner wire from the
pedal - see Section 5 or 6, as appropriate.
2Undo the retaining nuts and bolt, then
withdraw the pedal assembly (see
illustration).
3Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Adjust the cable(s) as described in
the relevant Section of this Chapter.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
Fuel pump operation check
1Switch on the ignition and listen for the fuel
pump (the sound of an electric motor running,
audible from beneath the rear seats). Assuming
there is sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump
should start and run for approximately one or
two seconds, then stop, each time the ignition
is switched on. Note:If the pump runs
continuously all the time the ignition is switched
on, the electronic control system is running in
the backup (or “limp-home”) mode referred to
by Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
ECU itself, and the vehicle should therefore be
taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the
complete system, using the correct diagnostic
equipment; do not waste time trying to test the
system without such facilities.
2Listen for fuel return noises from the fuel
pressure regulator. It should be possible to
feel the fuel pulsing in the regulator and in the
feed hose from the fuel filter.
3If the pump does not run at all, check the
fuse, relay and wiring (see Chapter 6).
Fuel pressure check
3A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with an
adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve on the
fuel rail pressure test/release fitting
(identifiable by its blue plastic cap, and
located on the union of the fuel feed line and
the fuel rail) is required for the following
procedure. If the Ford special tool 29-033 is
available (see Section 2), the tool can be
attached to the valve, and a conventional-type
pressure gauge attached to the tool.
4If using the service tool, ensure that its tap
is turned fully anti-clockwise, then attach it to
the valve. Connect the pressure gauge to the
service tool. If using a fuel pressure gauge
with its own adaptor, connect it in accordance
with its maker’s instructions (see illustration).
5Start the engine and allow it to idle. Note
the gauge reading as soon as the pressure
stabilises, and compare it with the pressure
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
(a) If the pressure is high, check for a
restricted fuel return line. If the line is
clear, renew the pressure regulator.
8 Fuel pump/fuel pressure -
check
7 Accelerator pedal -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4
6.11 Location of TCS throttle actuator-to-
throttle housing cable adjuster (arrowed)7.2 Removing the accelerator pedal
assembly8.4 A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with
an adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve
on the fuel rail pressure test/release fitting,
is needed to check fuel pressure
procarmanuals.com
Page 104 of 279
(b) If the pressure is low, pinch the fuel return
line. If the pressure now goes up, renew
the fuel pressure regulator. If the pressure
does not increase, check the fuel feed
line, the fuel pump and the fuel filter.
6Detach the vacuum hose from the fuel
pressure regulator; the pressure shown on the
gauge should increase. Note the increase in
pressure, and compare it with that listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications. If the pressure
increase is not as specified, check the
vacuum hose and pressure regulator.
7Reconnect the regulator vacuum hose, and
switch off the engine. Verify that the fuel
pressure stays at the specified level for five
minutes after the engine is turned off.
8Carefully disconnect the fuel pressure
gauge. Be sure to cover the fitting with a rag
before slackening it. Mop up any spilt petrol.
9Run the engine, and check that there are no
fuel leaks.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t smoke,
or allow open flames or bare light bulbs,
near the work area. Don’t work in a garage
where a natural gas-type appliance (such
as a water heater or clothes dryer) with a
pilot light is present. If you spill any fuel on
your skin, rinse it off immediately with
soap and water. When you perform any
kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
Note: Ford specify the use of their service tool
23-038 (a large box spanner with projecting teeth
to engage the fuel pump/sender unit retaining
ring’s slots) for this task. While alternatives are
possible, as shown below, in view of the difficulty
experienced in removing and refitting the
pump/sender unit, owners are strongly advised
to obtain this tool before starting work. The help
of an assistant will be required.
1Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap. Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
2Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
3Unbolt or fold forwards (as appropriate) the
rear seat base cushion (see Chapter 11).
Withdraw from the vehicle’s floor the grommet
covering the fuel pump/sender unit. Wash off
any dirt from the tank’s top surface, and dry it;
use a vacuum cleaner to clean the immediate
surroundings of the vehicle’s interior, to
reduce the risk of introducing water, dirt and
dust into the tank while it is open.
4Unplug the fuel pump/sender unit’s
electrical connector (see illustration).
5To disconnect the fuel feed and return
pipes from the unit, release each pipe’s
coupling, by squeezing together the
protruding locking lugs on each union and
carefully pulling the coupling apart. Use rag to
soak up any spilt fuel. Where the couplings
are difficult to separate, use a pair of pliers
and a block of wood as shown, to lever the
pipe out of the union. Considerable force maybe required, but be as careful as possible to
avoid damaging any of the components (see
illustration).
6Release the fuel pump/sender unit’s
retaining ring by turning it anti-clockwise. As
noted above, Ford recommend the use of
service tool 23-038. For those without access
to such equipment, a hammer and drift, or a
pair of slip-jointed pliers, will serve as an
adequate substitute - at least for removal (see
illustration).
7Withdraw the fuel pump/fuel gauge sender
unit, taking care not to bend the float arm. The
float arm is mounted on a spring-loaded
extension, to hold it closely against the
bottom of the tank. Note the sealing ring; this
must be renewed whenever it is disturbed
(see illustrations).
8On refitting, use a new sealing ring, and
ensure that the gauze filter over the base of
the pump pick-up is clean.
9Align the pump/sender unit with the tank
opening, and refit it, ensuring that the float
arm is not bent. Insert the unit so that the float
arm slides correctly up the extension, until the
unit’s top mounting plate can be aligned with
the tank opening and pressed onto the sealing
ring. This may require a considerable amount
of pressure; if so, be careful to avoid
damaging any of the components. The Ford
service tool provides the best way of holding
9 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender
unit- removal and refitting
4•6 Fuel and exhaust systems
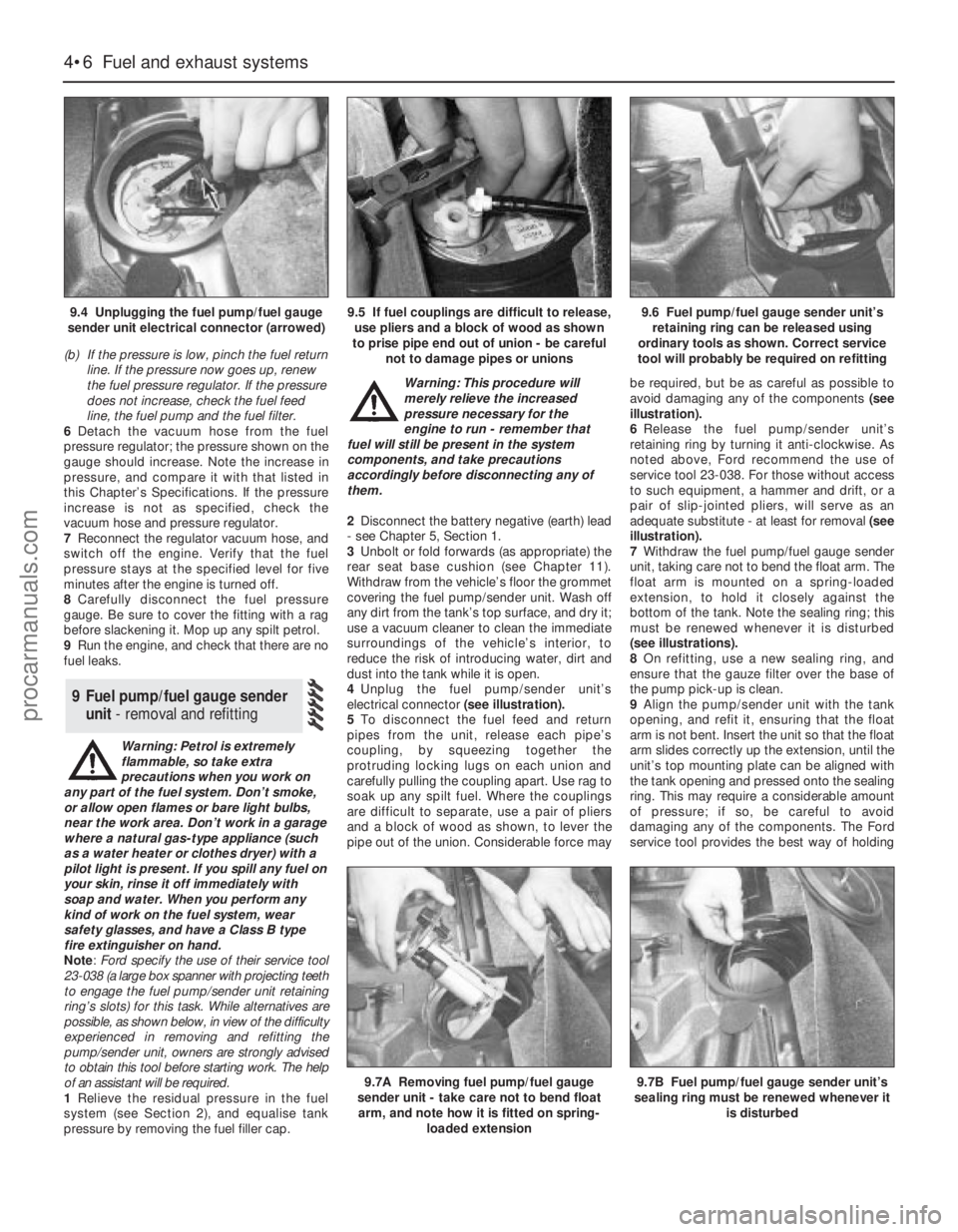
9.4 Unplugging the fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit electrical connector (arrowed)9.5 If fuel couplings are difficult to release,
use pliers and a block of wood as shown
to prise pipe end out of union - be careful
not to damage pipes or unions9.6 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit’s
retaining ring can be released using
ordinary tools as shown. Correct service
tool will probably be required on refitting
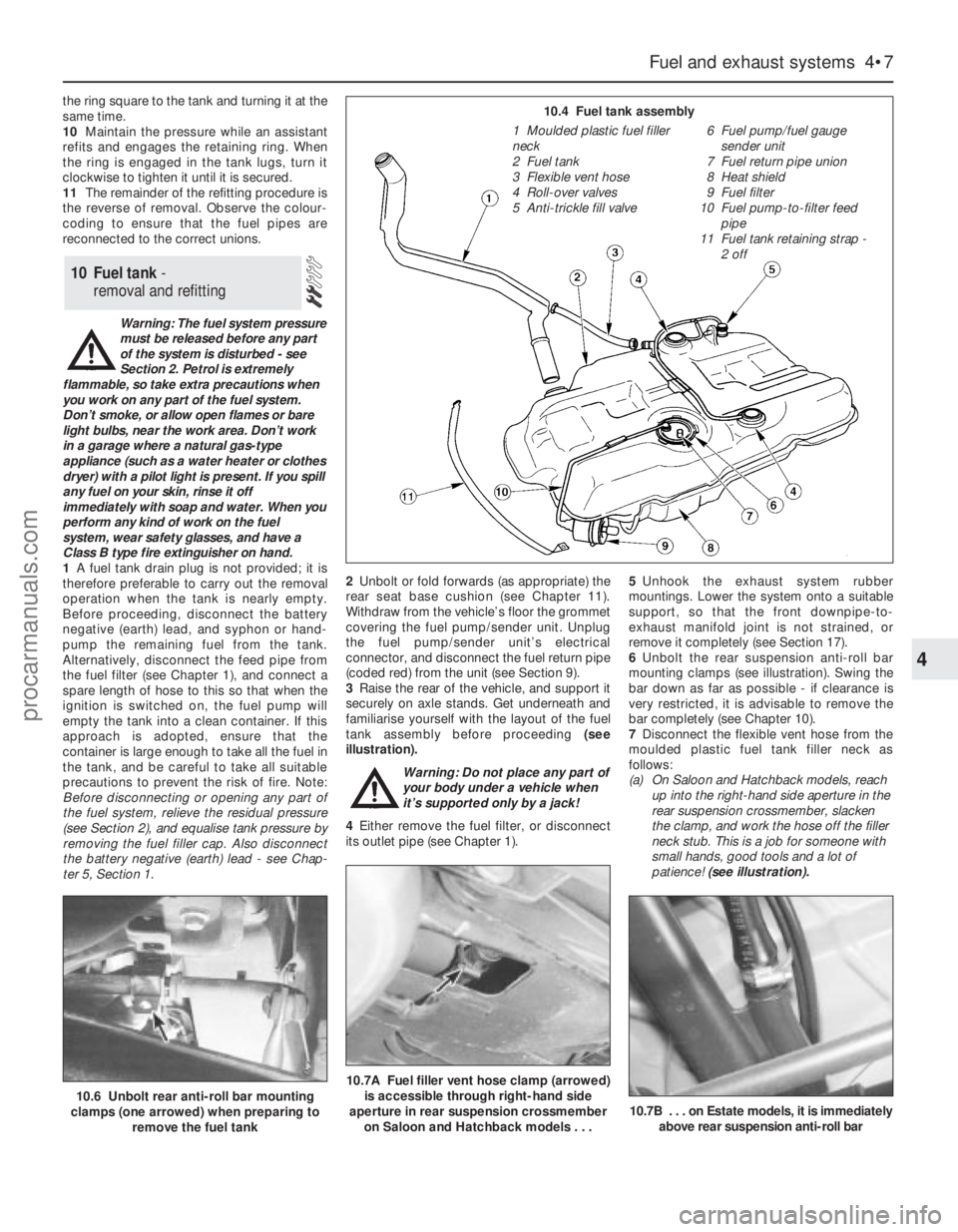
9.7A Removing fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit - take care not to bend float
arm, and note how it is fitted on spring-
loaded extension9.7B Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit’s
sealing ring must be renewed whenever it
is disturbed
procarmanuals.com
Page 105 of 279
the ring square to the tank and turning it at the
same time.
10Maintain the pressure while an assistant
refits and engages the retaining ring. When
the ring is engaged in the tank lugs, turn it
clockwise to tighten it until it is secured.
11The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal. Observe the colour-
coding to ensure that the fuel pipes are
reconnected to the correct unions.
Warning: The fuel system pressure
must be released before any part
of the system is disturbed - see
Section 2. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautions when
you work on any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or clothes
dryer) with a pilot light is present. If you spill
any fuel on your skin, rinse it off
immediately with soap and water. When you
perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses, and have a
Class B type fire extinguisher on hand.
1A fuel tank drain plug is not provided; it is
therefore preferable to carry out the removal
operation when the tank is nearly empty.
Before proceeding, disconnect the battery
negative (earth) lead, and syphon or hand-
pump the remaining fuel from the tank.
Alternatively, disconnect the feed pipe from
the fuel filter (see Chapter 1), and connect a
spare length of hose to this so that when the
ignition is switched on, the fuel pump will
empty the tank into a clean container. If this
approach is adopted, ensure that the
container is large enough to take all the fuel in
the tank, and be careful to take all suitable
precautions to prevent the risk of fire. Note:
Before disconnecting or opening any part of
the fuel system, relieve the residual pressure
(see Section 2), and equalise tank pressure by
removing the fuel filler cap. Also disconnect
the battery negative (earth) lead - see Chap-
ter 5, Section 1.2Unbolt or fold forwards (as appropriate) the
rear seat base cushion (see Chapter 11).
Withdraw from the vehicle’s floor the grommet
covering the fuel pump/sender unit. Unplug
the fuel pump/sender unit’s electrical
connector, and disconnect the fuel return pipe
(coded red) from the unit (see Section 9).
3Raise the rear of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands. Get underneath and
familiarise yourself with the layout of the fuel
tank assembly before proceeding (see
illustration).
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
4Either remove the fuel filter, or disconnect
its outlet pipe (see Chapter 1).5Unhook the exhaust system rubber
mountings. Lower the system onto a suitable
support, so that the front downpipe-to-
exhaust manifold joint is not strained, or
remove it completely (see Section 17).
6Unbolt the rear suspension anti-roll bar
mounting clamps (see illustration). Swing the
bar down as far as possible - if clearance is
very restricted, it is advisable to remove the
bar completely (see Chapter 10).
7Disconnect the flexible vent hose from the
moulded plastic fuel tank filler neck as
follows:
(a) On Saloon and Hatchback models, reach
up into the right-hand side aperture in the
rear suspension crossmember, slacken
the clamp, and work the hose off the filler
neck stub. This is a job for someone with
small hands, good tools and a lot of
patience! (see illustration).
10 Fuel tank -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•7
4
10.6 Unbolt rear anti-roll bar mounting
clamps (one arrowed) when preparing to
remove the fuel tank10.7A Fuel filler vent hose clamp (arrowed)
is accessible through right-hand side
aperture in rear suspension crossmember
on Saloon and Hatchback models . . .
10.7B . . . on Estate models, it is immediately
above rear suspension anti-roll bar
10.4 Fuel tank assembly
1 Moulded plastic fuel filler
neck
2 Fuel tank
3 Flexible vent hose
4 Roll-over valves
5 Anti-trickle fill valve6 Fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit
7 Fuel return pipe union
8 Heat shield
9 Fuel filter
10 Fuel pump-to-filter feed
pipe
11 Fuel tank retaining strap -
2 off
procarmanuals.com
Page 106 of 279

(b) On Estate models, slacken the clamp
immediately above the rear anti-roll bar,
and work the hose off the filler neck stub
(see illustration).
8Unscrew the six retaining nuts, and
withdraw the exhaust system’s rear heat
shield from the underbody (see illustration).
9Support the tank with a trolley jack or
similar. Place a sturdy plank between the
support and the tank, to protect the tank.
10Unscrew the bolt at the front of each
retaining strap, and pivot them down until
they are hanging out of the way. Note the
earth lead under the left-hand strap’s bolt -
clean the mating surfaces before the tank is
refitted, so that clean, metal-to-metal contact
is ensured.
11Lower the tank enough to unclip the fuel
return pipe (coded red) from its top surface,
then disconnect the charcoal canister’s
vapour hose from the union at the top rear of
the tank (see illustration). If you have any
doubts, clearly label the fuel lines and hoses,
and their respective unions. Plug the hoses, to
prevent leakage and contamination of the fuel
system.
12Remove the tank from the vehicle,
releasing it from the filler neck stub. While the
tank is removed, unhook the retaining straps
(twist them through 90° to do so), and check
that they and their locations in the underbody
are in good condition.
13With the fuel tank removed, the filler neck
can be withdrawn. It is secured by a single
screw in the filler opening, and by two bolts to
the underbody.
14Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
1Any repairs to the fuel tank or filler neck
should be carried out by a professional who
has experience in this critical and potentially-
dangerous work. Even after cleaning and
flushing of the fuel system, explosive fumes
can remain and ignite during repair of the
tank.
2If the fuel tank is removed from the vehicle,
it should not be placed in an area where
sparks or open flames could ignite the fumes
coming out of the tank. Be especially careful
inside garages where a natural gas-type
appliance is located, because the pilot light
could cause an explosion.
Warning: The fuel system
pressure must be released before
any part of the system is
disturbed - see Section 2. Petrol
is extremely flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on any part of
the fuel system. Don’t smoke, or allow
open flames or bare light bulbs, near the
work area. Don’t work in a garage where a
natural gas-type appliance (such as a
water heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot
light is present. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
Note: Refer to illustrations 10.4 and 10.11 for
details.
1Remove the fuel tank (see Section 10).
2Prise the two valves out of the tank, and
remove the anti-trickle fill valve from its
mounting. Take care not to damage the valves
or the tank. Prise out the rubber seals fromthe tank openings, and renew then if they are
worn, distorted, or if either has been leaking.
3If either valve is thought to be faulty, seek
the advice of a Ford dealer as to whether they
can be renewed individually. If not, the
complete valve and pipe assembly must be
renewed.
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Ensure that both roll-over valves
are pressed securely into their seals, so that
there can be no fuel leaks.
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
2Remove the trim panel from the left-hand
footwell.
3Peel back the sound-insulating material
from the switch, and undo its two retaining
screws (see illustration).
4Unplug the switch electrical connector, and
withdraw the switch.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Ensure that the switch is reset by
depressing its red button.
These models are equipped with a
Sequential Electronically-controlled Fuel
Injection (SEFI) system. The system is
composed of three basic sub-systems: fuel
system, air induction system and electronic
control system. Note:Refer to illustrations
2.1A and 2.1B of Chapter 6 for further
information on the components of the system.
Fuel system
An electric fuel pump located inside the fuel
tank supplies fuel under pressure to the fuel
rail, which distributes fuel evenly to all
injectors. A filter between the fuel pump and
the fuel rail protects the components of the
system. A pressure regulator controls the
system pressure in relation to inlet tract
depression. From the fuel rail, fuel is injected
14 Fuel injection system/engine
management system - general
information
13 Fuel cut-off switch -
removal and refitting
12 Roll-over valves -
removal and refitting
11 Fuel tank cleaning and repair -
general information
4•8 Fuel and exhaust systems
10.8 Exhaust system must be lowered and
heat shield removed to enable fuel tank
removal - arrows show location of
retaining strap front bolts10.11 Lower fuel tank - do not distort filler
neck stub (A) - and unclip (red-coded) fuel
return pipe (B), then disconnect charcoal
canister’s vapour hose (C)13.3 Fuel cut-off switch retaining screws
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 107 of 279

into the inlet ports, just above the inlet valves,
by four fuel injectors. The system also
includes features such as the flushing of fresh
(ie, cold) fuel around each injector on start-up,
thus improving hot starts.
The amount of fuel supplied by the injectors
is precisely controlled by an Electronic
Control Unit (ECU). The ECU uses the signals
derived from the engine speed/crankshaft
position sensor and the camshaft position
sensor, to trigger each injector separately in
cylinder firing order (sequential injection), with
benefits in terms of better fuel economy and
lower exhaust emissions.
Air induction system
The air system consists of an air filter
housing, an air mass meter, an intake
resonator and plenum chamber, and a throttle
housing. The air mass meter is an information-
gathering device for the ECU; it uses a “hot-
wire” system to send the ECU a constantly-
varying (analogue) voltage signal
corresponding to the volume of air passing
into the engine. Another sensor in the air mass
meter measures intake air temperature. The
ECU uses these signals to calculate the mass
of air entering the engine.
The throttle valve inside the throttle housing
is controlled by the driver, through the
accelerator pedal. As the valve opens, the
amount of air that can pass through the
system increases. The throttle potentiometer
opens further, the air mass meter’s signal
alters, and the ECU opens each injector for a
longer duration, to increase the amount of fuel
delivered to the inlet ports.
Electronic control system
The ECU controls the fuel injection system,
as well as the other sub-systems which make
up the entire engine management system. It
receives signals from a number of information
sensors, which monitor such variables as
intake air mass and temperature, coolant
temperature, engine speed and position,
acceleration/deceleration, and exhaust gas
oxygen content. These signals help the ECU
determine the injection duration necessary for
the optimum air/fuel ratio. These sensors and
associated ECU-controlled relays are located
throughout the engine compartment. For
further information regarding the ECU and its
control of the engine management system,
see Chapter 6.
Idle speed and mixture
adjustment - general
Both the idle speed and mixture are under
the control of the ECU, and cannot be
adjusted. Not only can they not be adjusted,
they cannot even be checked, except with the
use of special diagnostic equipment (see
Chapter 6) - this makes it a task for a Ford
dealer service department. Do notattempt to
“adjust” these settings in any way without
such equipment.
If the idle speed and mixture are thought tobe incorrect, take the vehicle to a Ford dealer
for the complete system to be tested.
On models equipped with a heated
windscreen, an idle-increase solenoid valve is
fitted, which raises the idle speed to
compensate for the increased load on the
engine when the heated windscreen is
switched on. When the valve is open, air from
the plenum chamber bypasses the throttle
housing and idle speed control valve, passing
directly into the inlet manifold through the
union on its left-hand end. The system is
active only for the four minutes that the
heated windscreen circuit is live, and is
supplementary to the main (ECU-controlled)
idle speed regulation.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so extra precautions
must be taken when working on
any part of the fuel system. Do
not smoke, or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work
in a garage if a natural gas-type appliance
with a pilot light is present. While
performing any work on the fuel system,
wear safety glasses, and have a dry
chemical (Class B) fire extinguisher on
hand. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water.
Note: This is an initial check of the fuel delivery
and air induction sub-systems of the engine
management system, to be carried out in
conjunction with the operational check of the
fuel pump (see Section 8), and as part of the
preliminary checks of the complete engine
management system (see Section 3 of
Chapter 6).
1Check the earth wire connections for
tightness. Check all wiring and electrical
connectors that are related to the system.
Loose electrical connectors and poor earths
can cause many problems that resemble
more serious malfunctions.
2Check to see that the battery is fully-
charged. The ECU and sensors depend on an
accurate supply voltage to properly meter the
fuel.
3Check the air filter element - a dirty or
partially-blocked filter will severely impede
performance and economy (see Chapter 1).
4If a blown fuse is found, renew it and see if
it blows again. If it does, search for a short-
circuited wire in the harness related to the
system (see Chapter 6).
5Check the air intake duct from the intake to
the inlet manifold for leaks, which will result in
an excessively-lean mixture. Also check the
condition of the vacuum hoses connected to
the inlet manifold.
6Remove the plenum chamber from the
throttle housing. Check the throttle valve for
dirt, carbon or other residue build-up. If it’sdirty, seek the advice of a Ford dealer - since
the electronic control system is designed to
compensate for factors such as the build-up
of dirt in the throttle housing, it may well be
best to leave it dirty, unless the deposits are
extensive. Note: A warning label on the
housing states specifically that the housing
bore and the throttle valve have a special
coating, and must not be cleaned using
carburettor cleaner, as this may damage it.
7With the engine running, place a
screwdriver or a stethoscope against each
injector, one at a time. Listen through the
screwdriver handle or stethoscope for a
clicking sound, indicating operation.
8If an injector isn’t operating (or sounds
different from the others), turn off the engine,
and unplug the electrical connector from the
injector. Check the resistance across the
terminals of the injector, and compare your
reading with the resistance value listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If the resistance
isn’t as specified, renew the injector.
9A rough idle, diminished performance
and/or increased fuel consumption could also
be caused by clogged or fouled fuel injectors.
Fuel additives that can sometimes clean
fouled injectors are available at car accessory
shops.
10The remainder of the system checks
should be left to a dealer service department
or other qualified repair specialist, as there is
a chance that the ECU may be damaged if
tests are not performed properly.
Warning: The fuel system
pressure must be released before
any part of the system is
disturbed - see Section 2. Petrol
is extremely flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on any part of
the fuel system. Don’t smoke, or allow
open flames or bare light bulbs, near the
work area. Don’t work in a garage where a
natural gas-type appliance (such as a
water heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot
light is present. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
Throttle housing
Check
1Remove the plenum chamber (see Sec-
tion 4), and verify that the throttle linkage
operates smoothly.
2If the housing bore and valve are dirty
enough for you to think that this might be the
cause of a fault, seek the advice of a Ford
dealer. Do notclean the housing (see the
notes in the checking procedure given in
Section 15).
16 Fuel system components-
check and renewal
15 Fuel injection system/engine
management system - check
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•9
4
procarmanuals.com