1993 DODGE TRUCK transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 28 of 1502
•
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
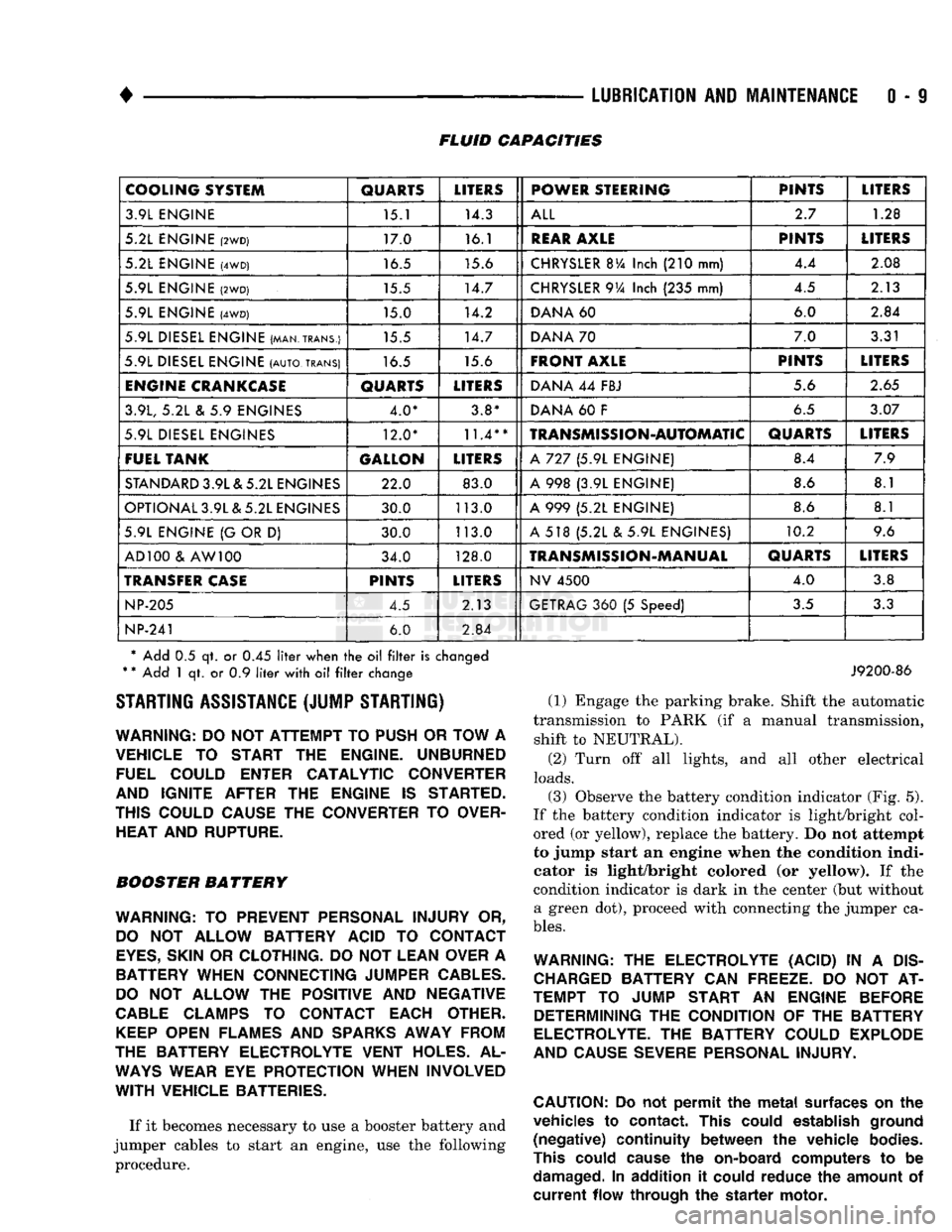
0 - 9 FLUID CAPACITIES
COOLING SYSTEM
QUARTS
LITERS
POWER STEERING PINTS
LITERS
3.9L ENGINE 15.1 14.3
ALL
2.7
1.28
5.2L ENGINE
(2WD)
17.0 16.1
REAR
AXLE
PINTS
LITERS
5.2L ENGINE
(4WD)
16.5 15.6
CHRYSLER
BVa
Inch
(210
mm) 4.4
2.08
5.9L ENGINE
(2WD)
15.5 14.7
CHRYSLER
9Va
Inch
(235
mm) 4.5
2.13
5.9L ENGINE
(4WD)
15.0 14.2
DANA
60 6.0
2.84
5.9L DIESEL ENGINE (MAN.TRANS.) 15.5 14.7
DANA
70 7.0
3.31
5.9L DIESEL ENGINE
(AUTO,
TRANS)
16.5 15.6
FRONT AXLE
PINTS
LITERS
ENGINE
CRANKCASE
QUARTS
LITERS
DANA
44
FBJ 5.6
2.65
3.9L,
5.2L & 5.9
ENGINES 4.0* 3.8*
DANA
60 F
6.5
3.07
5.9L DIESEL ENGINES 12.0*
11.4**
TRANSMISSION-AUTOMATIC
QUARTS
LITERS
FUEL TANK GALLON
LITERS
A
727 (5.9L
ENGINE) 8.4
7.9
STANDARD
3.9L & 5.2L ENGINES 22.0 83.0
A
998 (3.9L
ENGINE) 8.6
8.1
OPTIONAL 3.9L & 5.2L ENGINES 30.0 113.0
A
999 (5.2L
ENGINE) 8.6
8.1
5.9L ENGINE
{G
OR
D)
30.0 113.0
A
518 (5.2L & 5.9L
ENGINES) 10.2
9.6
AD 100
&
AW 100 34.0 128.0
TRANSMISSION-MANUAL
QUARTS
LITERS
TRANSFER
CASE
PINTS
LITERS
NV
4500
4.0
3.8
NP-205
4.5 2.13
GETRAG
360 (5
Speed)
3.5
3.3
NP-241
6.0
2.84
* Add
0.5 qt. or 0.45
liter
when
the oil filter
is
changed
*
*
Add
1 qt. or 0.9
liter
with
oil filter
change STARTING ASSISTANCE (JUMP STARTING)
WARNING:
DO NOT
ATTEMPT
TO
PUSH
OR
TOW
A
VEHICLE
TO
START
THE
ENGINE. UNBURNED FUEL COULD ENTER CATALYTIC CONVERTER
AND IGNITE AFTER
THE
ENGINE
IS
STARTED.
THIS COULD CAUSE
THE
CONVERTER
TO
OVER HEAT AND RUPTURE.
BOOSTER BATTERY
WARNING:
TO
PREVENT PERSONAL INJURY
OR,
DO
NOT
ALLOW BATTERY ACID
TO
CONTACT
EYES,
SKIN
OR
CLOTHING.
DO NOT
LEAN OVER
A
BATTERY WHEN CONNECTING JUMPER
CABLES.
DO
NOT
ALLOW
THE
POSITIVE
AND
NEGATIVE
CABLE
CLAMPS
TO
CONTACT EACH OTHER.
KEEP
OPEN FLAMES
AND
SPARKS
AWAY FROM
THE BATTERY ELECTROLYTE VENT HOLES.
AL
WAYS
WEAR
EYE
PROTECTION WHEN INVOLVED
WITH
VEHICLE BATTERIES.
If it becomes necessary to use a booster battery and
jumper cables to start an engine, use the following procedure.
J9200-86
(1) Engage the parking brake. Shift the automatic
transmission to PARK (if a manual transmission, shift to NEUTRAL).
(2) Turn off all lights, and all other electrical
loads.
(3)
Observe the battery condition indicator (Fig. 5).
If the battery condition indicator is light/bright col
ored (or yellow), replace the battery. Do not attempt
to jump start an engine when the condition indi
cator is light/bright colored (or yellow). If the
condition indicator is dark in the center (but without a green dot), proceed with connecting the jumper ca
bles.
WARNING:
THE
ELECTROLYTE (ACID)
IN A
DIS
CHARGED
BATTERY
CAN
FREEZE.
DO NOT AT
TEMPT
TO
JUMP START
AN
ENGINE BEFORE DETERMINING
THE
CONDITION
OF THE
BATTERY
ELECTROLYTE.
THE
BATTERY COULD EXPLODE
AND CAUSE SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION:
Do not
permit
the
metal
surfaces
on the
vehicles
to
contact.
This
could
establish
ground
(negative)
continuity
between
the
vehicle
bodies.
This
could
cause
the
on-board
computers
to be
damaged.
In
addition
it
could
reduce
the
amount
of
current
flow
through
the
starter
motor.
Page 30 of 1502

LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0-11
J
DRIVE-ON
HOIST
I
FRAME
CONTACT
HOIST
TWIN
POST
CHASSIS
HOIST
FLOOR
JACK
RROOD30
Fig.
8 Correct Vehicle Lifting
Locations
An axle tube
A body side sill
A steering linkage component
A drive shaft
The engine or transmission oil pan
The fuel tank
• A front suspension arm Use the correct frame rail lifting locations only
(Fig. 8).
HOIST A vehicle can be lifted with:
• A single-post, frame-contact hoist
• A twin-post, chassis hoist
• A ramp-type, drive-on hoist
When a frame-contact type hoist is used, verify
that the lifting pads are positioned properly (Fig. 8).
WARNING:
WHEN
A
SERVICE
PROCEDURE
RE
QUIRES
THE
REMOVAL
OF
THE
REAR
AXLE,
FUEL
TANK,
OR
SPARE
TIRE,
EITHER:
• PLACE ADDITIONAL WEIGHT ON THE REAR
END OF THE VEHICLE
« ATTACH THE VEHICLE TO THE HOIST
« PLACE JACK STANDS UNDER THE VEHICLE
FOR SUPPORT TO PREVENT TIPPING WHEN
THE CENTER OF BALANCE CHANGES
4WD VEHICLES A standard hoist can be used to lift a 4WD vehicle.
The hoist should be inspected for adequate clearance. The lift arms, pads or ramps should be adjusted to
ensure that there is adequate clearance (Fig. 9).
ADJUSTMENT
PAD
ii 7
MAINTAIN
CLEARANCE
HOIST
ARM
RK44
Fig.
9 Lifting 4WD Vehicle
With
Single-Post
Hoist—
Typical
When a twin-post hoist is used, a 4 x 4 x 12-inch
wood spacer also could be required. Place the wood spacer under the front axle (opposite the differential
housing). This will maintain balance and level lift ing.
CAUTION:
The
block
that
is
used must
be
secured in
a
safe manner. This
will
ensure
that
it
will
not un
balance
the
vehicle.
VEHICLE
TOWING
RECOMMENDATIONS
When it is necessary to tow a Ram Truck, the rec
ommended method is either:
• the sling-type, rear-end raised towing method; or
• the wheel-lift towing method with a tow dolly lo
cated under the front wheels. A vehicle with flat-bed hauling equipment can also
be used to transport a disabled vehicle.
SLING-TYPE
FLAT
BED
RR0OD29
Fig.
10 Tow Vehicles
With
Approved
Equipment
Page 31 of 1502

0 - 12
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• A vehicle equipped with SAE approved sling-type
towing equipment can be used (Fig. 10). However,
many vehicles are equipped with air dams, spoilers, and/or ground effect panels. In this case a wheel-lift
towing vehicle or a flat-bed hauling vehicle is recom mended (Fig. 10). If a flat bed device is used, the ap
proach angle should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE The lifted wheels of the disabled vehicle should be
a minimum of 10 cm (4 in.) off the ground. Make
sure there is enough clearance at the opposite end.
This is critical when towing over rough terrain. If necessary, the rear ground clearance can be increased by removing the wheels from the lifted end
and then towing with the lifted end closer to the
ground. If the rear wheels are removed, secure the
brake drums. A 20 cm (8 in.) ground clearance must
be maintained between brake drums or rotors and the ground.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS The following safety precautions must be consid
ered when preparing for and during a vehicle towing operation:
• Remove exhaust pipe tips that interfere with the
tow sling and crossbar • Padding should be placed between the tow sling/
crossbar and any painted surfaces
• If the vehicle is damaged, secure the loose and pro
truding parts
• Always use a safety chain system that is indepen dent of the lifting and towing equipment
• When placing tow hooks on the rear axle, position them so they do not damage the brake tubing or
hoses
• Do not allow any of the towing equipment to con
tact the fuel tank
• Do not tow the vehicle by connecting to the front
or rear shock absorbers
• The operator should not go under a vehicle while
it is lifted by the towing equipment. The vehicle
should first be supported by safety stands
• Do not allow passengers in a vehicle being towed
• Observe all state and local laws involving warning signals, night illumination, speed, etc.
• Do not exceed a towing speed of 48 km/h (30 mph)
• Avoid towing distances of more than 24 km (15
miles) whenever possible • Do not attach tow chains or a tow sling to a
bumper, the steering linkage, the universal joints, or a drive shaft
REAR-END RAISED TOWING It is recommended that the rear-end raised towing
method be used. Vehicles can be towed with the front
wheels on the ground for extended distances at speeds not exceeding 48 km/h (30 mph) (Fig. 11). (1) Attach the J-hooks around the axle shaft tubes
outboard of the rear springs. (2) Position and center the sling under and for
ward of the rear bumper. (3) Attach safety chains (with pads) at each end of
the rear bumper.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position to
unlock the steering wheel. (5) Clamp the steering wheel with the front wheels
in the straight ahead position.
CAUTION:
Do not use the steering
column
lock
to
secure
front
wheel
in the straight-ahead
position.
(6) Shift the transmission to NEUTRAL.
POSITION CENTER BAR FORWARD
OF
BUMPER
-
/
J-HOOKS OUTBOARD
OF
SPRINGS
RN967A
Fig. 11 Rear-End
Raised
Towing
FRONT'END RAISED TOWING If a vehicle cannot be towed from the rear, the
front-end raised towing method normally can be
used (Fig. 12). (1) Center the sling with the bumper and position
it at the frame front crossmember.
CAUTION:
Use tow
chains
with
J-hooks
for
con
necting
to the
disabled
vehicle's
lower
suspension
arms.
Never use
T-hooks.
(2) Route the J-hooks and tow chains over the
steering linkage outboard of the coil spring.
(3) Attach the J-hooks to the outer end of the
lower suspension arms.
(4) Raise the vehicle.
(5.) Attach the safety chains to the disabled vehicle
at the frame rails.
Vehicles equipped with a MANUAL TRANSMIS
SION can be towed with the rear wheels on the
Page 37 of 1502

0-18
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
A crankcase ventilation system must be clean to
provide good operation and durability. Periodic main
tenance is necessary. Replace the PCV valve. Re
move residual combustion deposits from the hoses and throttle body/intake manifold passages.
The PCV valve should be replaced and the system
should be serviced at the interval specified in main
tenance schedule. If a vehicle is routinely used for short trips, the crankcase ventilation system could
possibly require more maintenance.
CRANKCASE AIR INLET FILTER
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE Replace or clean, the air inlet filter at the interval
specified in maintenance schedule.
More frequent PCV system maintenance could be
required for:
• Vehicles routinely used for short trips
• Vehicles routinely involved in stop and go traffic
operation
• Vehicles routinely involved in extended periods of
engine idle
MAINTENANCE Clean and lubricate the crankcase air inlet filter
according to the following procedure. (1) Disconnect the fresh air hose from the port on
the crankcase air inlet filter housing (Fig. 8).
(2) Remove the air filter housing from the cylinder
head cover (Fig. 8). Clean the filter in kerosene or a similar solvent.
(3) Lubricate the filter by inverting the housing
and filling it with SAE 30 viscosity engine oil.
(4) Insert the air filter housing nipple in the cylin
der head cover grommet. Connect the fresh air hose
to the upper port (Fig. 8).
J9000-52
Fig.
8
Crankcase
Air Inlet
Filter
THROTTLE CONTROL LINKAGE
Transmission linkage pivot pin areas (Fig. 9),
should be serviced. The areas lubricated every second
oil change with a multi-purpose lubricant (NLGI GC-
LB).
PIVOT
AREAS
Fig.
9
Transmission
Linkage
Pivot Areas
FUEL
SYSTEM
INSPECTION The fuel system filler cap, nozzle, tubes, hoses, and
connections should be inspected periodically.
FUEL FILTER The fuel filter requires service only when a fuel
contamination problem is suspected. For proper diag
nosis and service procedures refer to Group 14, Fuel
System.
GASOLINE ENGINE FUEL REQUIREMENTS All gasoline engines require fuel that has a mini
mum octane rating of 87 determined by the (R +
M)/2 calculation method.
The use of a brand of unleaded gasoline that con
tains additives is recommended. Gasoline with addi
tives will improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
ALCOHOL/GASOLINE
BLENDS
Many brands of blended unleaded gasoline am now
available. Unleaded gasoline is blended with oxygenated-type
fuels to produce a clean air gasoline in many areas.
The use of this type of blended fuel is recommended.
ETH ANOL—Unleaded gasoline and ethanol
blended fuels are a mixture of 10 percent ethanol and 90 percent unleaded gasoline. This is an accept
able blend of fuel.
MTBE— MTBE blended fuels are a mixture of un
leaded gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE (Methyl
Tertiary Butyl Ether). Unleaded gasoline blended
with MTBE is acceptable.
Page 42 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 23 GEAR SHIFTER BOOTS
Inspect the shifter boots periodically for stone and
heat damage. Replace, if necessary.
SEVERE DRIVING CONDITIONS The interval between the transmission drain and
refill maintenance should be decreased to:
• NV4500 manual transmission—every 29 000 km (18,000 miles)
• Automatic transmission—every 19 000 km (12,000
miles)
A severe driving condition includes:
• Extended operation with heavy cargo loads
• Driving in deep mud or snow
• Off-road operation (4WD)
• Trailer towing
• Operation as a commercial vehicle
• Snow plowing
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
INSPECTION/LUBE
OIL
LEVEL
The transmission should be checked for leaks when
other service is necessary under the vehicle. To check
the lube oil level, remove the fill hole plug (Fig. 2 ). If the level is below the bottom of the fill hole, raise
the level to the bottom of the fill hole with:
• Castrol Syntorq for NV4500 transmissions
• SAE 5W-30 engine oil (API Service SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE) for Getrag 360 transmissions.
Fig.
2 NV4500 Manual
Transmission
DRAIN
AND
FILL
The NV4500 transmission fluid should be changed
according to the intervals listed in the Manual
Transmission—Drain & Refill Intervals chart below.
Also,
refer to the Fluid Capacities chart.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
FLUID
LEWEL
It is recommended that the fluid (ATF) level in au
tomatic transmissions be checked while involved
with other underhood maintenance.
Vehicle operation with an incorrect ATF level
will greatly reduce the life of the transmission.
Fig.
3 Getrag 360 Manual
Transmission
MANUAL TRANSMISSION-DRAIN & REFILL INTERVALS
Normal
Service
Light
Duty
Cycle
60 000
km
37,500
miles
Heavy
Duty
Cycle
58 000
km
36,000
miles
Severe
Service
29 000
km
18,000
miles
J9000-43
The condition of the ATF also should be deter
mined. If the ATF is dark in color and has a strong odor, the fluid should be changed. Also the filter should be replaced and the bands adjusted.
The following procedure must be used to check the
automatic transmission fluid (ATF) level.
(1) Position the vehicle on level ground.
(2) Operate the engine at idle speed.
(3) Apply the parking brake.
(4) Place the gear selector in N (neutral).
(5) Remove the dipstick from the tube. Wipe it
clean and determine if the ATF is hot or warm.
Hot ATF has a temperature of approximately
82°C (180°F). Warm ATF is when its temperature
is between 29-52°C (85-125°F). (6) Wipe the dipstick clean and completely insert it
into the tube. Remove the dipstick from the tube and
observe the ATF level.
(7) If the ATF is hot, the level should be in the
crosshatched area that is marked OK.
(8) If the ATF is warm, the level should be be
tween the two dimples.
Page 43 of 1502
0
- 24
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
•
CAUTION:
Do not
overfill
the
transmission.
(9) Adjust
the
level
of the ATF
accordingly.
It
is
important
to use the
correct fluid
in an
automatic transmission. MOPAR®ATF PLUS
(ATF Type
7176)
should
be
used. Dexron®
II
ATF
can be
used
if the
recommended fluid
is not
available,
(10) Insert
the
dipstick into
the
tube.
DRAIN, FILTER CHANGE, BAND ADJUSTMENT AND REFILL
The chart below lists
the
intervals
at
which
the
transmission should
be
serviced. Also, refer
to the
Fluid Capacities chart
for
fill capacity.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SERVICE
IN-
TERVALS
Normal
Usage
Light
Duty
Cycle
60 000
km
37,500
miles
Heavy
Duty
Cycle
38
000 km 24,000
miles
Severe
Usage
19 000 km 12,000
miles
J9100-19
It
is
very important
to use the
correct fluid
in
an automatic transmission. MOPAR®ATF PLUS
(ATF Type
7176)
should
be
used.
An
equivalent
Dexron®
II ATF
could
be
used only
if the
recom
mended fluid
is not
available.
The torque converter does
not
have
a
drain plug.
No attempt should
be
made
to
drain
the
converter.
Refer
to
Group
21
—Transmissions
for
transmission
drain
and
refill procedures.
TRANSFER
CASE
(4WD
VEHICLES)
INSPECTION The NP205
and
NP241 transfer cases fluid level
should
be
checked whenever maintenance
is
neces
sary under
the
vehicle.
FLUID
LEVEL
The vehicle must
be
level when
the
fluid level
is checked.
The transfer case drain fill hole plugs
are
located
at
the
rear
of the
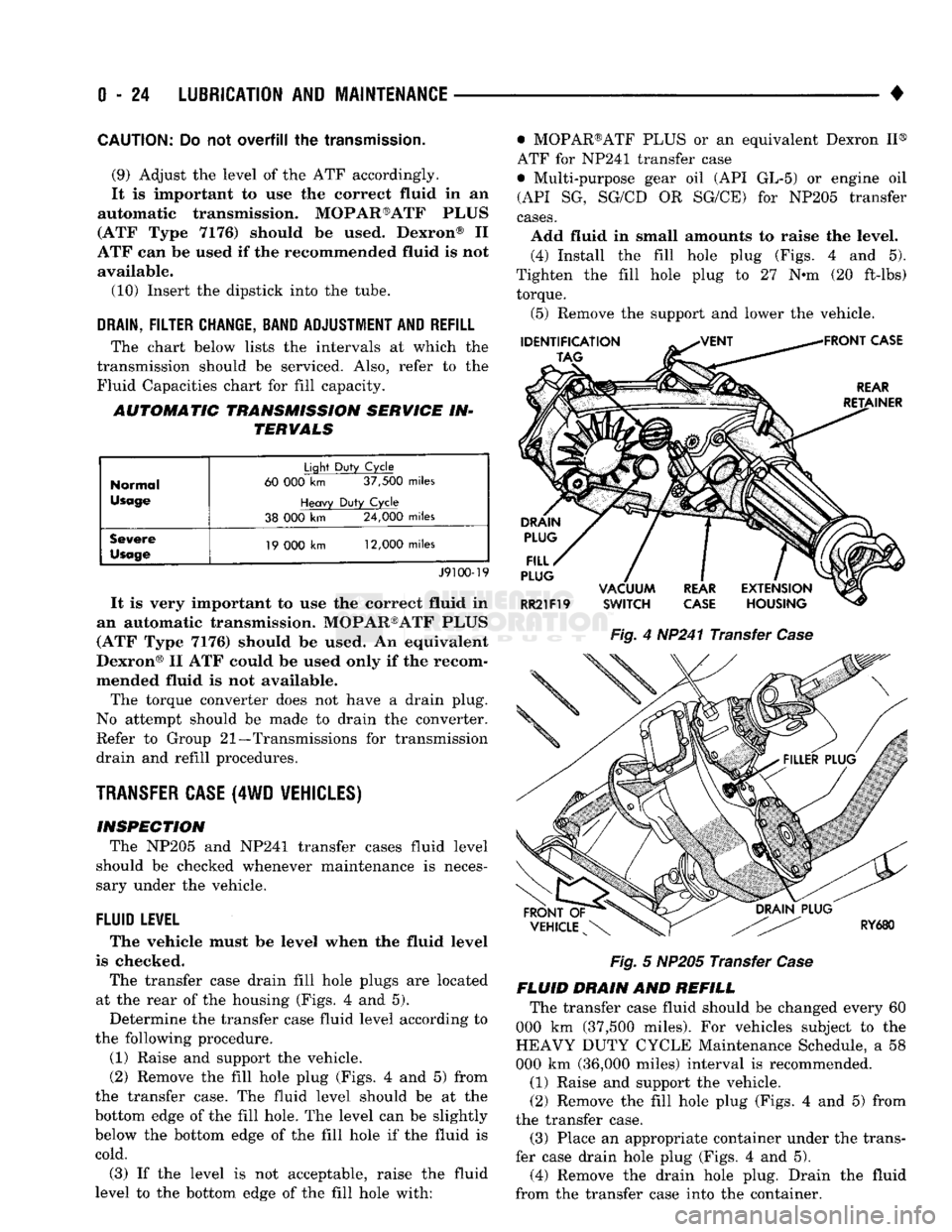
housing (Figs.
4 and 5).
Determine
the
transfer case fluid level according
to
the following procedure.
(1) Raise
and
support
the
vehicle.
(2) Remove
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5)
from
the transfer case.
The
fluid level should
be at the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole.
The
level
can be
slightly
below
the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole
if the
fluid
is
cold.
(3)
If the
level
is not
acceptable, raise
the
fluid
level
to the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole with: • MOPAR®ATF PLUS
or an
equivalent Dexron
II®
ATF
for
NP241 transfer case
• Multi-purpose gear
oil (API GL-5) or
engine
oil
(API
SG,
SG/CD
OR
SG/CE)
for
NP205 transfer
cases.
Add fluid
in
small amounts
to
raise
the
level. (4) Install
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5).
Tighten
the
fill hole plug
to 27 N-m (20
ft-lbs) torque.
(5) Remove
the
support
and
lower
the
vehicle.
Fig.
4
HP241 Transfer
Case
Fig.
5
NP205 Transfer
Case
FLUID DRAIN
AND
REFILL The transfer case fluid should
be
changed every
60
000
km
(37,500 miles).
For
vehicles subject
to the
HEAVY DUTY CYCLE Maintenance Schedule,
a 58
000
km
(36,000 miles) interval
is
recommended.
(1) Raise
and
support
the
vehicle.
(2) Remove
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5)
from
the transfer case. (3) Place
an
appropriate container under
the
trans
fer case drain hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5).
(4) Remove
the
drain hole plug. Drain
the
fluid
from
the
transfer case into
the
container.
Page 44 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 25
CAUTION:
Do not
over-tighten
the
drain
and fill
hole
plugs.
Over-tightening
can strip the
hole
threads
and/or crack
the
aluminum housing.
(5) Install the drain hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in
the transfer case. Tighten the drain hole plug to 27 N*m (20 ft-lbs) torque. (6) Fill the transfer case to the bottom edge of the
fill hole (Figs. 4 and 5) with: • MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases
• Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases. (7) Install the fill hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in the
transfer case. Tighten the plug to 27 N«m (20 ft-lbs) torque.
(8) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
• MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases • Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases
NP20I
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL/ENGINE
OIL
SELECTION
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL-if the anticipated
minimum temperature will: • Be above 32°C (90°F)-use SAE 140, API GL-5;
• Decrease to as low as -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 90,
API GL-5; and • Be below -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 80, API GL-5. ENGINE OIL—if the anticipated minimum tem
perature will be: ® Above 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 50, API SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE;
• Below 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 30, API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE.
SHIFT MECHANISM-NP241 AND NP205 The transfer case shift mechanism should be
cleaned and lubricated as necessary.
Lubricate the pivot, the sliding contact areas and
the shift linkage pivot ends with light-weight engine oil (Figs. 6 and 7).
AXLES
INSPECTION/LUBRICANT LEVEL For normal vehicle operation, periodic axle lubri
cant level checks are not necessary. The exterior of
the axle housing should be inspected for leakage. Check the lubricant level to confirm the leakage.
LUBRICANT LEVEL
(1) Raise the vehicle with an axle or wheel type
hoist. Support the vehicle.
(2) The rear axle differential housings have a rub
ber, PRESS-IN type fill plug (Fig. 8). Pry the fill
TRANSMISSION
ASSEMBLY
GEARSHIFT
MECHANISM TRANSFER CASE
SCREWS
(2)
50
FT. LBS.
(68 N*m)
CLAMP
SHIFT
ROD
SCREW
80 IN.
LBS.
(9 N*m)
RP1091
Fig.
6 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP241 Transfer
Case
Fig.
RY682
7 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP205 Transfer
Case
plug from the differential housing. The front axle (4WD vehicles)*differential housings have a thread
ed-type fill plug (Fig. 9). Un-thread the fill plug from
the differential housing.
(3) The lubricant level should be within 12 mm
(1/2 in) of the fill hole for the 8.25 and 9.25 rear ax
les.
The lubricant level should be between 12mm (1/2
in) and 24mm (1 in.) of the fill hole for the Dana ax
les.
(4) If necessary, add lubricant to raise the level to
the acceptable position.
(5) Install the fill hole plug in the differential
housing (Figs. 8 and 9).
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
Periodic axle lubricant change for normal vehicle
operation is not necessary. Refer to the chart below-
Page 155 of 1502
3
- 28
REAR
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
•
SURE-GRIP
DIFFERENTIAL
SERVICE
GENERAL
INFORMATION
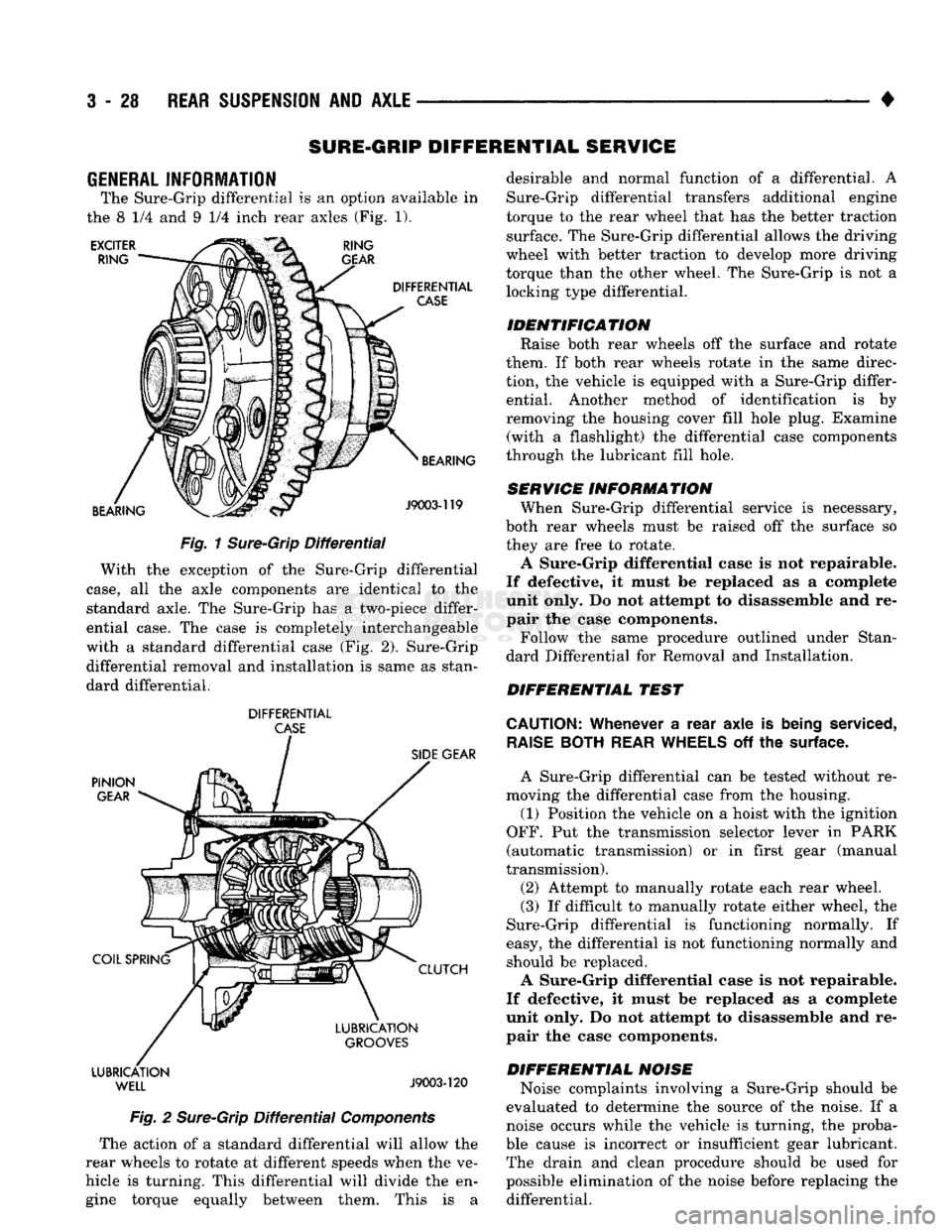
The Sure-Grip differential
is an
option available
in
the
8 1/4 and 9 1/4
inch rear axles
(Fig. 1).
EXCITER
RING RING
GEAR
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
BEARING BEARING
J9003-119
Fig.
1
Sure-Grip
Differential
With
the
exception
of the
Sure-Grip differential
case,
all the
axle components
are
identical
to the
standard axle.
The
Sure-Grip
has a
two-piece differ
ential case.
The
case
is
completely interchangeable
with
a
standard differential case
(Fig. 2).
Sure-Grip differential removal
and
installation
is
same
as
stan
dard differential.
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
PINION
GEAR
COIL SPRING LUBRICATION
WELL
SIDE
GEAR
CLUTCH
LUBRICATION
GROOVES
J9003-120
Fig.
2
Sure-Grip
Differential
Components
The action
of a
standard differential will allow
the
rear wheels
to
rotate
at
different speeds when
the ve
hicle
is
turning. This differential will divide
the en
gine torque equally between them. This
is a
desirable
and
normal function
of a
differential.
A
Sure-Grip differential transfers additional engine
torque
to the
rear wheel that
has the
better traction surface.
The
Sure-Grip differential allows
the
driving
wheel with better traction
to
develop more driving
torque than
the
other wheel.
The
Sure-Grip
is not a
locking type differential.
IDENTIFICATION Raise both rear wheels
off the
surface
and
rotate
them.
If
both rear wheels rotate
in the
same direc
tion,
the
vehicle
is
equipped with
a
Sure-Grip differ ential. Another method
of
identification
is by
removing
the
housing cover fill hole plug. Examine (with
a
flashlight)
the
differential case components
through
the
lubricant fill hole.
SERVICE INFORMATION When Sure-Grip differential service
is
necessary,
both rear wheels must
be
raised
off the
surface
so
they
are
free
to
rotate.
A Sure-Grip differential case
is not
repairable.
If defective,
it
must
be
replaced
as a
complete
unit only.
Do not
attempt
to
disassemble
and re
pair
the
case components.
Follow
the
same procedure outlined under Stan
dard Differential
for
Removal
and
Installation.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
CAUTION:
Whenever
a
rear axle
is
being
serviced,
RAISE
BOTH
REAR
WHEELS
off the
surface.
A Sure-Grip differential
can be
tested without
re
moving
the
differential case from
the
housing.
(1) Position
the
vehicle
on a
hoist with
the
ignition
OFF.
Put the
transmission selector lever
in
PARK
(automatic transmission)
or in
first gear (manual
transmission).
(2) Attempt
to
manually rotate each rear wheel.
(3)
If
difficult
to
manually rotate either wheel,
the
Sure-Grip differential
is
functioning normally.
If
easy,
the
differential
is not
functioning normally
and
should
be
replaced.
A Sure-Grip differential case
is not
repairable.
If defective,
it
must
be
replaced
as a
complete
unit only.
Do not
attempt
to
disassemble
and re
pair
the
case components.
DIFFERENTIAL NOISE Noise complaints involving
a
Sure-Grip should
be
evaluated
to
determine
the
source
of the
noise.
If a
noise occurs while
the
vehicle
is
turning,
the
proba
ble cause
is
incorrect
or
insufficient gear lubricant. The drain
and
clean procedure should
be
used
for
possible elimination
of the
noise before replacing
the
differential.